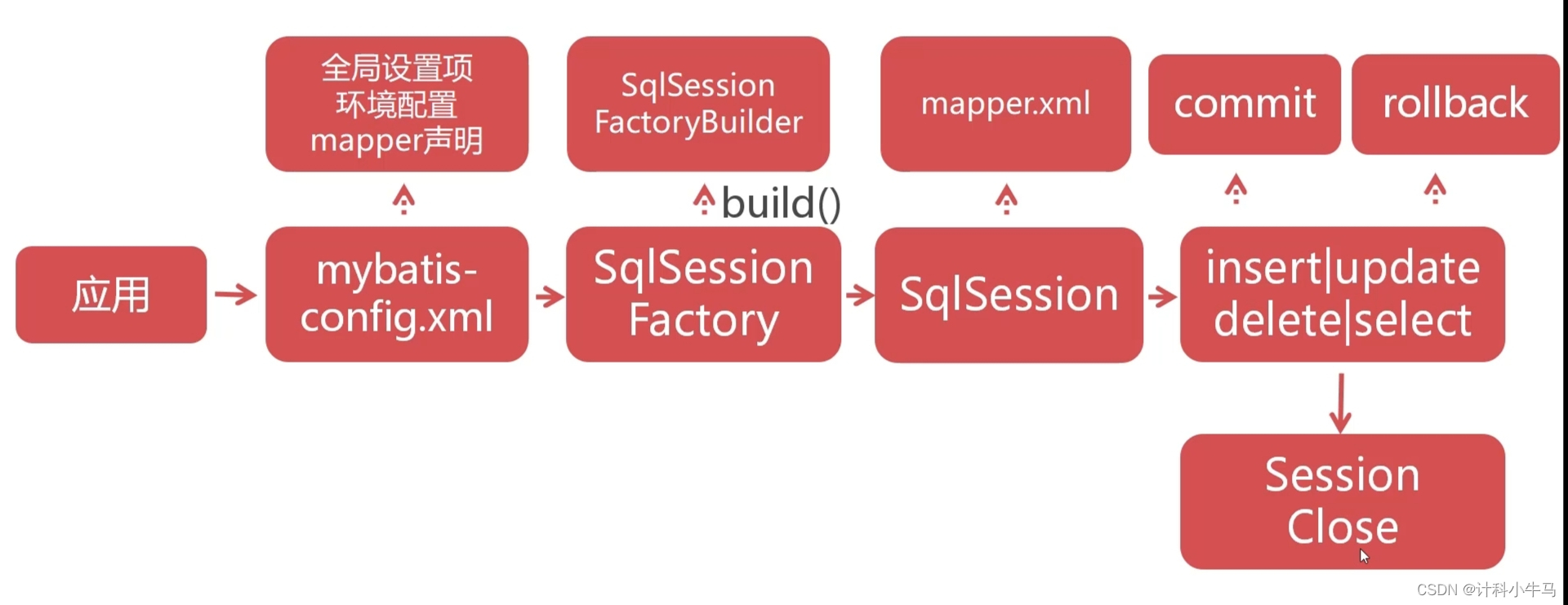
一、SSM框架介绍
1.框架
(1)什么是框架
框架是可被应用开发者定制的应用骨架
框架是一种规则,保证开发者遵循相同的方式开发程序
框架提倡"不要重复造轮子",对基础功能进行封装
(2)框架的优点
极大提高了开发效率
统一的编码规则,利于团队管理
灵活配置的应用,拥有更好的维护性
2.SSM
(1)Spring
Spring是一个对象容器框架,作用是对系统中的各个对象进行管理。
是一种框架的框架,也就是其他的框架,要基于Spring这个容器框架进行开发。
(2)SpringMVC
SpringMVC是一种架构模式,帮助我们对Web应用程序进行分层,进行有效的解耦,是一种Spring的分支产品,让我们更有效的进行Web开发。
(3)Mybatis
数据交互的框架,封装和扩展JDBC的操作,简化开发。
(4)三者相互作用
Spring提供了底层的对象管理,SpringMVC提供了Web层面的交互,Mybatis则提供了数据库的从删改查的便捷操作。
二、Mybatis介绍
1.什么是Mybatis
MyBatis是优秀的持久层框架
MyBatis使用XML将SQL与程序解耦,便于维护
MyBatis学习简单,执行高效,是JDBC的延伸
2.Mybatis开发流程 6步
引入MyBatis依赖
创建核心配置文件
创建实体(Entity)类
创建Mapper映射文件
初始化SessionFactory
利用SgISession对象操作数据
三、Mybatis基本使用
1.Mybatis环境配置
环境配置就是要配置Mysql的驱动,连接,用户名,密码等信息,这些信息一帮配置在Mybatis的
mybatis-config.xml文件里面
MyBatis采用XML格式配置数据库环境信息
MyBaits环境配置标签<environment>
environment包含数据库驱动、URL、用户名与密码
2.SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory是MyBatis的核心对象
用于初始化MyBatis(加载配置文件),创建SgISession对象
保证SglSessionFactory在应用中全局唯一
3.SqlSession
SqlSession是MyBatis操作数据库的核心对象
SqISession使用JDBC方式与数据库交互
SqISession对象提供了数据表CRUD对应方法
创建SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession示例代码
java
//利用Reader加载classpath下的mybatis-config.xml核心配置文件
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
//初始化SqlSessionFactory对象,同时解析mybatis-config.xml文件 构造者模式
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
//创建SqlSession对象,SqlSession是JDBc的扩展类,用于与数据库交互
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建数据库连接(测试用)实际上mybatis自动创建连接
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = sqlSession.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//如果type="POOLED",代表使用连接池,close则是将连接回收到连接池中
//如果type=""UNPOOLED",代表直连,close则会调用Connection.close()方法关闭连接
conn.close();
}4.初始化工具类MybatisUtils
每次使用Mybatis时,要先创建SqlSessionFactory对象,要不断的cv代码,而且还要保证SglSessionFactory在应用中全局唯一,于是我们提取出公共的部分作为工具类使用。并提供获得SqlSession方法和关闭SqlSession的方法
java
/**
* MyBatisUtils工具类,创建全局唯一的SqlSessionFactory对象
*/
public class MybatisUtils {
//利用static(静态)属于类不属于对象,且全局唯一
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
//利用静态块在初始化类时实例化sqlSessionFactory
static {
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
//初始化错误时,通过抛出异常ExceptionInInitializerError通知调用者
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
public static void closeSqlSession(SqlSession sqlSession){
if (sqlSession != null){
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}5.MyBatis数据查询
(1)步骤
创建实体类(Entity)
创建Mapper XML
编写<select>SQL标签
开启驼峰命名映射
新增<mapper>
SqlSession执行select语句
(2)示例
创建实体类
javapublic class Goods { private Integer goodsId; private String title; private String subTitle; private Float originalCost; private Float currentPrice; private Float discount; private Integer isFreeDelivery; private Integer categoryId; //还有对应的getter,setter方法 }
创建Mapper XML
编写<select>SQL标签
XML<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="goods"> <select id="selectAll" resultType="com.pzh.entity.Goods"> select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10 </select> </mapper>
在Mybatis配置文件开启驼峰命名映射
XML<settings> <!-- goods_id==>goodsId驼峰命名转换--> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings>在Mybatis配置文件新增<mapper>坐标,指明哪个mapper文件加入mybatis中
XML<mappers> <mapper resource="mappers/goods.xml"/> </mappers>最后的mybatis-config.xml
XML<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <settings> <!-- goods_id==>goodsId驼峰命名转换--> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings> <environments default="dev"> <environment id="dev"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/babytun"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="12345678"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="mappers/goods.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
测试SqlSession执行select语句
java@Test public void testSelectAll(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //参数是命名空间.id List<Goods> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectAll"); for(Goods goods : list){ System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId()); } MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession); }
四、SQL传参
查询-<select>为例
1.单参数传递
parameterType表示传入参数的类型,resultType表示sql查询结果的返回类型
需求:按照goodsId查询商品信息
配置mapper文件
XML<select id="selectById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.pzh.entity.Goods"> select * from t_goods where goods_id = #{value} </select>测试方法
java@Test public void testSelectById(){ SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //参数1 指明执行哪个SQL //参数2 指定SQL的参数 Goods goods = sqlSession.selectOne("goods.selectById", 765); System.out.println(goods); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession); } }
2.多参数传递
在单参传递的基础上,将parameterType的值改为Map集合,即java.util.Map
需求:
按照价格范围查询商品,并指定前几条数据
配置mapper文件
XML<select id="selectByPriceRange" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.pzh.entity.Goods"> select * from t_goods where current_price between #{min} and #{max} order by current_price desc limit #{limit} </select>测试方法
java@Test public void testSelectByPriceRange(){ SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("min", 100); map.put("max", 500); map.put("limit",10); List<Goods> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectByPriceRange", map); list.stream().forEach(System.out::println); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession); } }
五、多表关联查询
1.分装复杂查询结果为dto类
多表关联查询的结果一般涉及多个不同表的列,我们的实体类是相对于单表的所有列的,不够用了,所以我们可以创建一个dto包,下面存放可以存放多表关联查询结果的dto类
javaselect g.*, c.category_name, '1' as test from t_goods g , t_category c where g.category_id = c.category_id对上面的多表查询可以封装为
javapublic class GoodsDTO { private Goods goods = new Goods(); private String categoryName; private String test; //对应的getter,setter方法 }
2.ResultMap结果映射
ResultMap可以将查询结果映射为复杂类型的Java对象
ResultMap适用于Java对象保存多表关联结果
ResultMap支持对象关联查询等高级特性
3.一对一查询
首先写多表关联查询的sql语句,分析出查询的结果的结构
创建接收查询结果的dto
javapublic class GoodsDTO { private Goods goods = new Goods(); private String categoryName; private String test; //对应的getter,setter方法 }
mapper配置文件
XML<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="goods"> <!--结果映射--> <resultMap id="oneToOne" type="com.pzh.dto.GoodsDTO"> <!--设置主键与属性映射--> <id property="goods.goodsId" column="goods_id"></id> <!--设置非主键字段与属性映射--> <result property="goods.title" column="title"></result> <result property="goods.currentPrice" column="current_price"></result> <result property="goods.originalCost" column="original_cost"></result> <result property="goods.subTitle" column="sub_title"></result> <result property="goods.discount" column="discount"></result> <result property="goods.isFreeDelivery" column="is_free_delivery"></result> <result property="goods.categoryId" column="category_id"></result> <result property="categoryName" column="category_name"></result> <result property="test" column="test"></result> </resultMap> <select id="selectGoods" resultMap="oneToOne"> select g.*, c.category_name, '1' as test from t_goods g , t_category c where g.category_id = c.category_id </select> </mapper>
测试方法
java@Test public void testSelectGoodsDTO(){ SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); List<GoodsDTO> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectGoods"); list.stream().forEach(System.out::println); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession); } }
4.一对多查询
商品表t_goods的一行对应商品订单表t_goods_cover的多个行
首先写多表关联查询的sql语句,分析出查询的结果的结构
这里用内连接一样的
sqlselect g.goods_id,f.* from t_goods g,t_goods_cover f where g.goods_id=f.goods_id order by g.goods_id desc定义接收结果结构类dto
javapublic class GoodsCoverDTO { private Integer goodsId; private List<GoodsCover> goodsCoverList; //对应的getter,setter。。 }mapper文件添加配置
XML<resultMap id="oneToMore" type="com.pzh.dto.GoodsCoverDTO"> <id property="goodsId" column="goods_id"></id> <collection property="goodsCoverList" ofType="com.pzh.entity.GoodsCover"> <id property="gcId" column="gc_id"></id> <result property="goodsId" column="goods_id"></result> <result property="gcPicUrl" column="gc_pic_url"></result> <result property="gcThumbUrl" column="gc_thumb_url"></result> <result property="gcOrder" column="gc_order"></result> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="selectGoodsCover" resultMap="oneToMore"> select g.goods_id,f.* from t_goods g,t_goods_cover f where g.goods_id=f.goods_id order by g.goods_id desc </select>测试方法
java@Test public void testSelectGoodsCoverDTO(){ SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); List<GoodsCoverDTO> list = sqlSession.selectList("goods.selectGoodsCover"); list.stream().forEach(System.out::println); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession); } }
5.多对多查询
多对多的查询需要使用中间表,具体参考
两个dto类定义和1对多一样。
五、数据插入
1.Mybatis事务

2.mapper配置文件

用selectKey将最新的主键值返回
3.测试方法
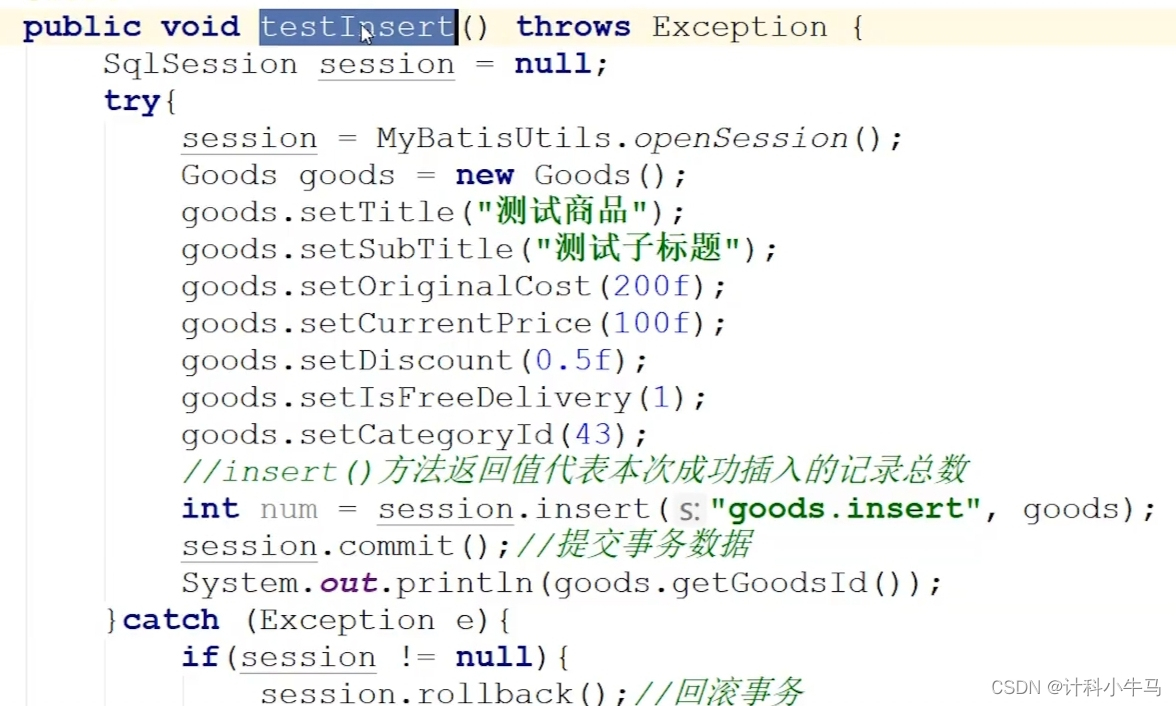
4.selectKey和useGeneratedKeys的区别
selectKey和useGeneratedKeys都是将最新的主键值返回,但他们有区别
selectKey必须写在insert标签里面

useGeneratedKeys则是insert标签的一个属性

其他区别



Oracle不支持useGeneratedKeys
总结

六、数据更新和删除
1.mapper文件


2.测试方法


七、预防SQL注入攻击
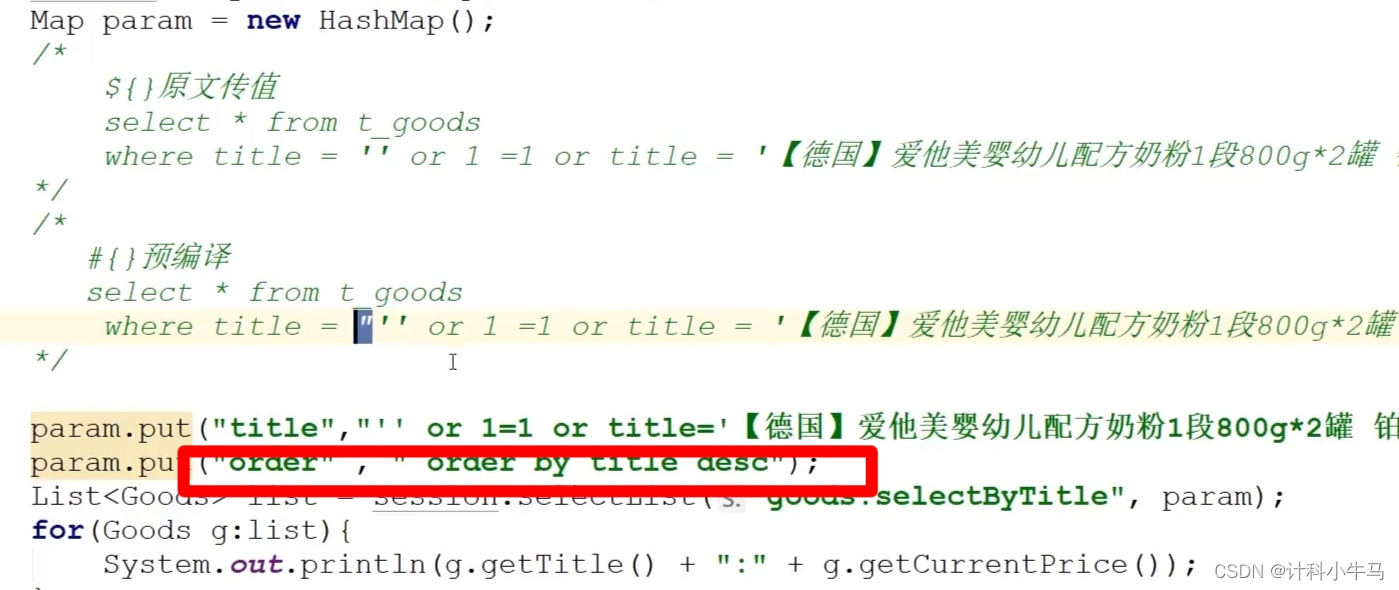
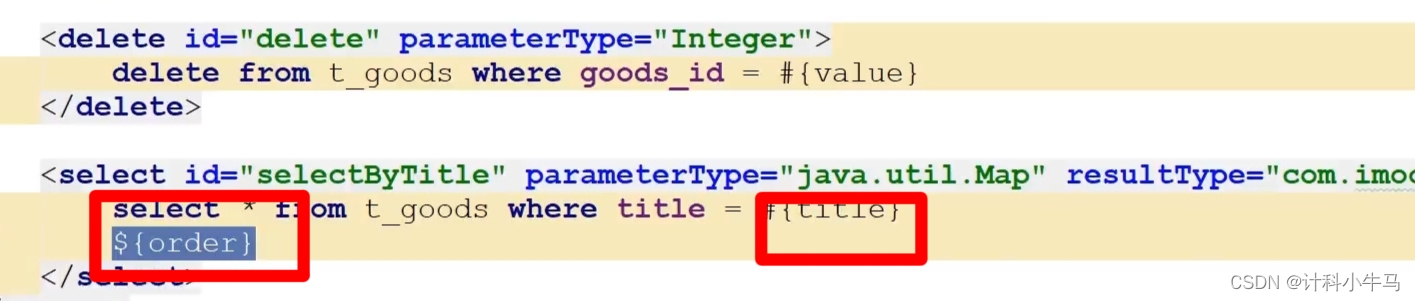
1.SQL注入

2.Mybatis两种传值方式

${} 应用于非用户输入的传值,一般用于SQL子句的拼接。
#{}应用于用户的输入,不能用于SQL子句的拼接 ,一般用于用户输入传值。
八、总结Mybatis工作流程