工作区和暂存区是 Git 中一个非常重要的概念,弄明白了他们,就弄明白了 Git 的很多操作到底干了什么。
工作区(Working Directory)
工作区,就是一个目录,比如我的 LearnGit 文件夹就是一个工作区:

我们平时更新版本什么的,都是在这里完成的,可以理解成是在这里工作的。
版本库(Repository)
工作区有一个隐藏目录 .git,这个不算工作区,而是 Git 的版本库。
Git 的版本库里存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是称为 stage(或者叫 index)的暂存区,还有 Git 为我们自动创建的第一个分支 master,以及指向 master的一个指针叫 HEAD。(分支的概念我们后续介绍)
前面讲了我们把文件往 Git 版本库里添加的时候,是分两步执行的:
- 第一步是用
git add把文件添加进去,实际上就是把文件修改添加到暂存区。 - 第二步是用
git commit提交更改,实际上就是把暂存区的所有内容提交到当前分支,这里是 master 分支。在我们创建 Git 版本库时,Git 会自动为我们创建master分支。
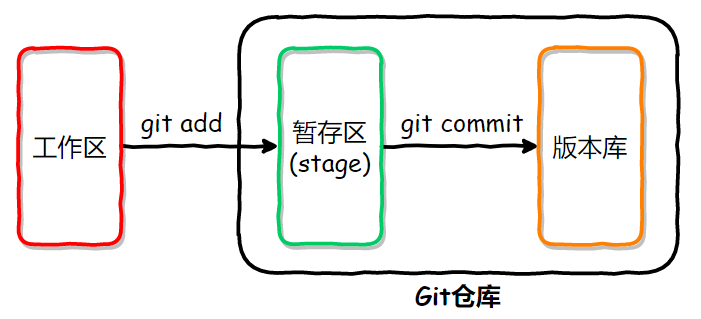
你可以简单理解为,需要提交的文件修改通通放到暂存区,然后,一次性提交暂存区的所有修改。
在.git 文件夹里面有一个 index 文件,就是暂存区。
通过 「git status」 查看 「git」 状态时, 「红色」 的文件表示在 「工作区」 ; 「绿色」 的文件表示在 「暂存区」。
实践是检验标准的唯一真理
我们来逐步说明下,一个文件是怎么提交的。首先我们吸怪下 readme.txt,加上一行:
bash
$ echo "Git has a mutable index called stage." >> readme.txt
$ cat .\readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
并且,新添加一个文件,叫做 LICENSE:
bash
$ echo "something" > LICENSE
$ cat LICENSE
something
然后我们查看下仓库状态:
bash
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: readme.txt
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
LICENSEGit 非常清楚地告诉我们,readme.txt 被修改了,而 LICENSE 还从来没有被添加过,所以它的状态是 Untracked。
现在,使用两次命令 git add,把 readme.txt 和 LICENSE 都添加后,用 git status 再查看一下:
shell
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: LICENSE
modified: readme.txt现在,暂存区的状态就变成这样了:
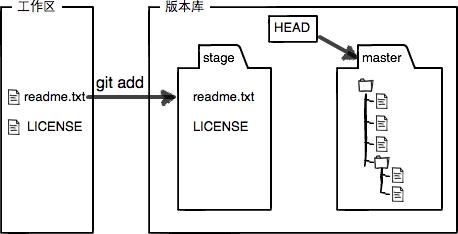
所以,git add 命令实际上就是把要提交的所有修改放到暂存区(Stage)。
接下来,我们提交:
shell
$ git commit -m "understand how stage works"
[master 8f5bb58] understand how stage works
2 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 2-versionControl/LICENSE
此时,工作区就是干净的了:
shell
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
现在版本库变成了这样,暂存区就没有任何内容了:
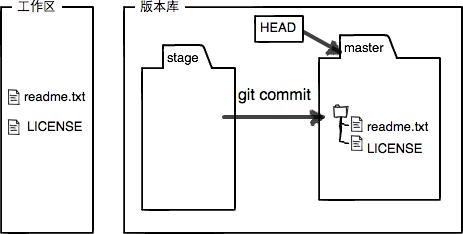
管理修改
为什么 Git 比其他版本控制系统设计得优秀,因为 Git 跟踪并管理的是修改,而非文件。
举个例子,假设目前 readme.txt 有 114514 行,然后你在最后一行添加了一句话;
在使用版本控制工具之前,我们的备份方式可能就是直接复制一份 readme.txt,然后再后面再追加一行。此时我们就有了两个文件:
bash
readme.txt //新版本的
readme.txt.backup //旧版本的并且,这两个文件是相差无几的!很多内容都是一样的(除了最后一行),这会造成存储空间的浪费。
而 Git,管理的是修改。比如,你增加了一行内容后,Git 会记录这个修改:增加了一行,内容为"xxxx",这样,如果想要回退到上一个版本,只需将上次修改的内容撤销就可以了!相比重复存储一个文件的方式,大大节省了存储空间的浪费,还可以直接查看修改,而不是将前后两个版本的文件用 diff 比较后才能得到差异。
在 Git 中,添加一个文件,修改文件里的内容,删除一个文件,都算一个修改。
暂存区里的修改
在 Git 中,我们每次修改得先放到暂存区,只有暂存区里的修改才会被 commit,我们修改下 readme.txt:
bash
$ echo "Git tracks changes." >> readme.txt
$ cat readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes.
此时我们查看下仓库状态,可以看到已经添加到暂存区了,可以被提交了:
bash
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: readme.txt
我们再次修改 readme.txt:
bash
$ cat readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system.
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes of files.
然后提交:
bash
$ git commit -m "git tracks changes"
[master aeb06f4] git tracks changes
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
然后再次查看仓库状态:
bash
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: readme.txt可以看到第二次的修改,并没有被提交!只有 git add 后,才会把修改提交到暂存区,git commit 只负责把暂存区的修改提交了。
撤销修改
当你在工作区里写代码的时候,突然发现写错文件了,这些代码应该是写到另一个文件的,怎么办呢?
你可以打开文件,然后手工删除自己加上去的代码,但这样不仅费时费力,还可能删错或者删漏代码。
其实,在修改文件后,如果查看仓库状态,Git 会很贴心的告诉你怎么丢弃工作区的修改。我们来测试下:
bash
$ echo "AAA" >> readme.txt //假设这是错误的代码
$ cat readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system.
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes of files.
AAA
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: readme.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
Git 告诉我们,使用 "git restore <file>..." 可以丢弃(discard )工作区里的修改,我们来测试下:
bash
$ git restore readme.txt
$ cat readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes.可以看到我们的修改确实被丢弃了,如果想要撤销工作区的所有修改:git resotre .
撤销工作区的所有修改
如果你不仅在工作区里修改了,还添加到了暂存区怎么办?同样的,我们查看仓库状态的时候,Git 也会贴心的告诉我们怎么丢弃暂存区里的修改:
bash
$ echo "AAA" >> readme.txt
$ cat readme.txt
Git is a distributed version control system
Git is free software distributed under the GPL.
Git has a mutable index called stage.
Git tracks changes.
AAA
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: readme.txt
Git 告诉我们,使用 "git restore --staged <file>..." 可以丢弃暂存区里的修改(unstage)。我们来试试:
bash
$ git restore --staged readme.txt
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: readme.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")可以看到目前暂存区里是空的,没有需要提交的,如果要提交着用 git add。
还有其他类似的命令可以撤销修改,例如在廖雪峰老师的博客里撤销修改,这样写到:
场景 1:当你改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,想直接丢弃工作区的修改时,用命令
git checkout -- file场景 2:当你不但改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,还添加到了暂存区时,想丢弃修改,分两步,第一步用命令
git reset HEAD <file>,就回到了场景 1,第二步按场景 1 操作。
Git 是一直在更新的,有些新版本提供了新的命令,个人认为 restore 更加好记一点。
删除文件
在 Git 中,删除也是一个修改操作,我们实战一下,先添加一个新文件 test.txt 到 Git 并且提交:
bash
$ git add test.txt
$ git commit -m "add test.txt"
[master 8889d50] add test.txt
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 test.txt
一般情况下,我们可以在文件管理器中把没用的文件删了,或者用 rm 命令删了:
bash
$ rm test.txt
目前工作区和版本库的版本就不一致了,使用 git status 可以看到哪些文件被删除了:
bash
$ git status
On branch master
Your branch is ahead of 'gitee/master' by 3 commits.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: test.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
我们可以使用提交这次修改:
bash
$ git add test.txt
$ git commit -m "delete test.txt"
[master b391595] delete test.txt
1 file changed, 1 deletion(-)
delete mode 100644 test.txt
使用 git rm:一步到位
注意我们刚刚是先删除,然后再 add 和 commit 的,我们可以简化为一条命令:git rm。
首先我们准备下文件
bash
$ echo "test" > test.txt
$ git add test.txt
$ git commit -m "add test.txt"
[master 42c477d] add test.txt
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 test.txt
然后使用 git rm,并查看仓库状态
bash
$ git rm test.txt
rm 'test.txt'
$ git st
On branch master
Your branch is ahead of 'gitee/master' by 5 commits.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: test.txt
可以看到文件被删除了,并且本次删除已经被提交到了暂存区,可以 commit 了,我们再次提交,结束。
bash
$ git commit -m "delete test.txt"
以下两种情况,不能正常使用 git rm
- 工作区是 clean 的,然后修改了工作区的文件;
- 工作区是 clean 的,然后修改了工作区的文件,并提交到暂存区
我们可以加上-f 参数,git rm -f,表明强制删除。
git rm -f
先准备文件:
bash
$ echo "test" > test.txt
$ git add test.txt
$ git commit -m "add test.txt"
修改文件后使用 git rm:会提示不能删除
bash
$ echo "test" >> test.txt
$ git rm test.txt
error: the following file has local modifications:
test.txt
(use --cached to keep the file, or -f to force removal)
我们可以使用 git rm -f 文件名来强制删除
bash
$ git rm -f test.txt
rm 'test.txt'
$ git st
On branch master
Your branch is ahead of 'gitee/master' by 7 commits.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: test.txt
如果我们误删了怎么办呢?还是和之前一样,使用 git restore --staged <file> 来将修改从暂存区里拿出来,然后再使用 git restore <file> 来恢复数据:
bash
$ git restore --staged test.txt
$ git restore test.txt
$ ll
total 7
drwxr-xr-x 1 peterjxl 197121 0 1月 11 07:37 1-diffAndPath/
drwxr-xr-x 1 peterjxl 197121 0 1月 14 07:19 2-versionControl/
-rw-r--r-- 1 peterjxl 197121 6 1月 14 11:58 test.txt注意:
- 从来没有被添加到版本库就被删除的文件,是无法恢复的!
- 如果想删除文件夹,使用-r 参数,例如
git rm -r 文件夹
git rm --cached
使用 git rm --cached,可以使一个文件脱离版本控制 演示:
首选准备数据
bash
$ echo "test" > test.txt
$ git add test.txt
$ git commit -m "add test.txt"
然后使用 git rm --cached test.txt
bash
$ git rm --cached test.txt
rm 'test.txt'
查看仓库状态,可以看到删除文件这个修改已经添加到暂存区了,并且 test.txt 目前是 Untracked
bash
$ git st
On branch master
Your branch is ahead of 'gitee/master' by 7 commits.
(use "git push" to publish your local commits)
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: test.txt
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
test.txt
但是工作区里的文件还在:
bash
$ ll
drwxr-xr-x 1 peterjxl 197121 0 1月 11 07:37 1-diffAndPath/
drwxr-xr-x 1 peterjxl 197121 0 1月 14 07:19 2-versionControl/
-rw-r--r-- 1 peterjxl 197121 6 1月 14 11:58 test.txt
我们提交下,结束演示
bash
$ git commit -m "delete test.txt by git rm --chched"
小结
小结:本文我们主要介绍了如下内容:
- 版本库,工作区和暂存区的概念,这对理解 Git 非常重要。
- Git 是管理修改的,添加文件、修改文件内容和删除文件都是一种修改
- 撤销修改
git restore <file>...,git restore --staged <file>...