常用的二维绘图
常用绘图包括下面的种类:
- 线图,
plot - 柱图,
bar - 梯步图,
stairstep - 误差棒图,
errorbar - 极坐标图,
polarplot - 跟图,
stem - 散点图,
scatter
这些命令都可以通过help xxx来查看基本的帮助,并通过doc xxx来查看详细的帮助,帮助中通常还有海量的例子来学习如何调用,并且在高版本的Matlab里面,还能打开相应的LiveScript,修改参数查看绘图结果。
详细介绍每个函数感觉必要性不大,还不如看一些通用的概念,能够更好应对实际应用中可能出现的状况。
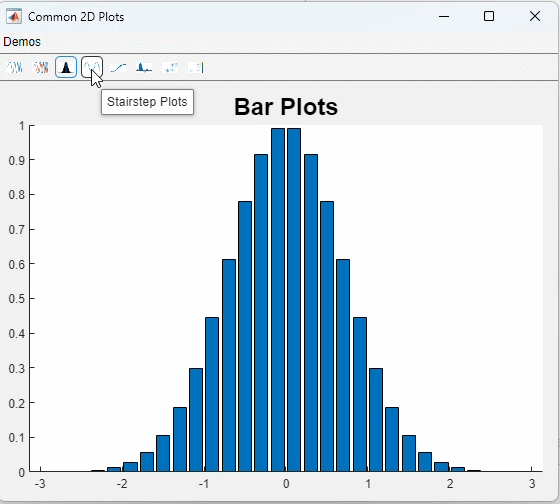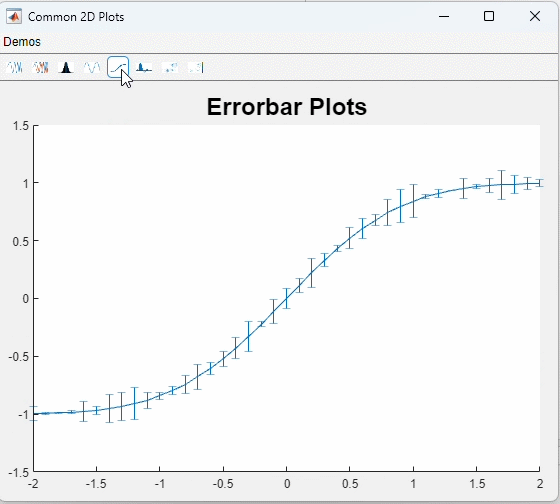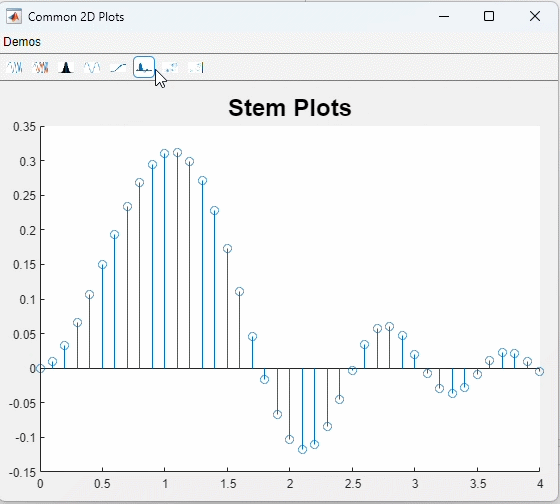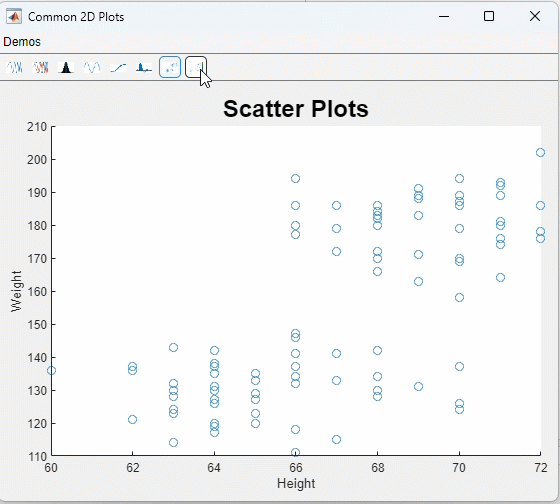
这是一个很无聊的例子......
matlab
function f = common2DPlots
f = uifigure(Name='Common 2D Plots', Visible='off', WindowState='minimized');
movegui(f, 'center');
g = uigridlayout(f, [1, 1]);
ax = uiaxes(g, Visible='off');
ax.Layout.Row = 1;
ax.Layout.Column = 1;
menu = uimenu(f, Text="Demos");
tb = uitoolbar(f);
texts = {...
"Line Plots", ...
"Multiple Lines Plots", ...
"Bar Plots", ...
"Stairstep Plots", ...
"Errorbar Plots", ...
"Stem Plots", ...
"Scatter Plots", ...
"Scatter Colorbar Plots", ...
};
fcns = {...
@linePlotFcn, ...
@multipleLinePlotFcn, ...
@barPlot,...
@stairStepPlot, ...
@errorBarPlot, ...
@stemPlot, ...
@scatterPlot, ...
@scatterColorPlot, ...
};
n = numel(texts);
for idx = 1:n
fn = matlab.lang.makeValidName(texts{idx}) + ".png";
if ~exist(fn, 'file')
feval(fcns{idx}, ax);
exportgraphics(ax, fn, Resolution=10);
end
cb = makeCallback(fcns{idx}, ax, texts{idx});
uimenu(menu, Text=texts{idx}, ...
MenuSelectedFcn=cb);
uipushtool(tb, Tooltip=texts{idx}, ...
Icon=fn, ...
ClickedCallback=cb)
end
uimenu(menu, Text="Quit", ...
Accelerator="Q", ...
Separator='on', ...
MenuSelectedFcn=@(~, ~)close(f));
clearAll(ax);
f.WindowState = "normal";
f.Visible = 'on';
end
function fh = makeCallback(func, ax_handle, textLabel)
function retCb(~, ~)
clearAll(ax_handle);
feval(func, ax_handle);
ax_handle.Title.String = textLabel;
ax_handle.Title.FontWeight = 'bold';
ax_handle.Title.FontSize = 24;
ax_handle.Visible = 'on';
end
fh = @retCb;
end
function clearAll(ax_handle)
colorbar(ax_handle, 'off');
cla(ax_handle);
end
function scatterPlot(ax_handle)
load patients Height Weight Systolic
scatter(ax_handle, Height,Weight)
xlabel(ax_handle,'Height')
ylabel(ax_handle,'Weight')
end
function scatterColorPlot(ax_handle)
load patients Height Weight Systolic
scatter(ax_handle, Height,Weight, 20,Systolic)
xlabel(ax_handle,'Height')
ylabel(ax_handle,'Weight')
colorbar(ax_handle);
end
function stemPlot(ax_handle)
x = 0:0.1:4;
y = sin(x.^2) .* exp(-x);
stem(ax_handle, x, y);
end
function polarPlot(ax_handle)
clearAll(ax_handle);
theta = 0:0.01:2*pi;
rho = abs(sin(2*theta) .* cos(2*theta));
polarplot(ax_handle, theta, rho);
end
function errorBarPlot(ax_handle)
x = -2:0.1:2;
y = erf(x);
eb = rand(size(x)) / 7;
errorbar(ax_handle, x, y, eb);
end
function stairStepPlot(ax_handle)
x = 0:0.25:10;
y = sin(x);
stairs(ax_handle, x, y);
end
function barPlot(ax_handle)
x = -2.9:0.2:2.9;
y = exp(-x .* x);
bar(ax_handle, x, y);
end
function linePlotFcn(ax_handle)
x = 0:0.05:5;
y = sin(x.^2);
plot(ax_handle, x, y);
end
function multipleLinePlotFcn(ax_handle)
x = 0:0.05:5;
y1 = sin(x.^2);
y2 = cos(x.^2);
plot(ax_handle, x, y1, x, y2);
end图形窗口和坐标系
首先对于一个图形,最基本的两个概念就是:
- 图形窗口
- 坐标系
这两个前者是实体的画布,后者是概念的画布。实际的图线,都要画在图形窗口的像素上;而图线对应点的坐标数据,则映射在坐标系中。
在实际的对象层次结构中,Matlab中图形窗口对象Figre有一个属性Childeren ,是一个数组,中间有若干坐标系;而代表坐标系的Axes ,也有一个属性Children ,也是一个数组,里面放着若干图形对象。
Children Children Children groot Figure Axes Line
对下面这个例子可以看到相应的关系。
matlab
x = 0:0.1:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
%
f = gcf; % 如果当前没有活动的窗口句柄则自动调用`gcf`创建一个图形窗口
a = gca;
% l = plot(x, y); 自动调用`gca`获得默认的笛卡尔坐标系
l = plot(a, x, y);
a1 = sprintf('图线对象是否在坐标系的Children中: %d\n', ismember(l, a.Children));
a2 = sprintf('坐标系对象是否在图形窗口的Children中:%d\n', ismember(a, f.Children));
title([a1 a2])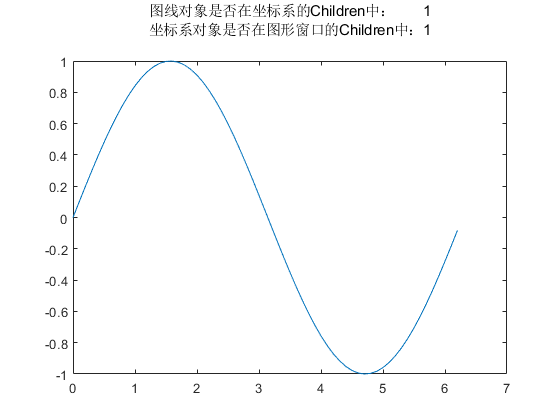
这里,我们用gcf来得到一个图窗对象,用gca来得到一个默认的笛卡尔坐标系。实际上,我们调用上述绘图函数的时候,可以把第一个参数设置为一个坐标系对象,如果省略这个参数,Matlab会自动调用gca来作为坐标系对象,并把绘图函数返回的图形对象加入(append)到对应坐标系的Children属性中。
gcf和gca两个函数都是称为lazy的函数,如果最近有一个句柄可见(Figure和Axes对象的HandleVisibility属性)的对象,就返回,如果没有,那就新建一个。这个过程是逐级向上的。例如,我们在没有图形窗口的情况下调用gca,就会触发如下的流程。
- 通过
groot的Children逐步找下来,看是否有一个句柄可见的Axes对象 - 没有的话需要新建一个
Axes
3.gcf一个y图窗Figure对象
4. 试图从groot的Children逐步找下来,没有找到一个句柄可见的Figure对象
5. 新建一个Figure对象,添加到groot的Children中
6. 把新建的坐标系添加到图窗的Children中 - 返回坐标系对象
我们可以自己在groot开始,翻找Children构成的树结构,也可以调用函数findobj来看看组合条件查看对象,当然直接调用不带任何参数返回所有的图形对象。
matlab
help findobj findobj - 查找具有特定属性的图形对象
此 MATLAB 函数 返回图形根对象及其所有后代。
语法
h = findobj
h = findobj(prop,value)
h = findobj('-not',prop,value)
h = findobj(prop1,value1,oper,prop2,value2)
h = findobj('-regexp',prop,expr)
h = findobj('-property',prop)
h = findobj(prop1,value1,...,propN,valueN)
h = findobj(objhandles,___)
h = findobj(objhandles,'-depth',d,___)
h = findobj(objhandles,'flat',___)
输入参数
prop - 属性名称
字符向量 | 字符串标量
value - 属性值
标量 | 数组
oper - 逻辑运算符
'-and' (默认值) | '-or' | '-xor'
expr - 正则表达式
字符串数组 | 字符向量 | 字符向量元胞数组
objhandles - 要从中搜索的对象
图形对象数组
d - 搜索深度
非负整数
示例
openExample('graphics/ReturnAllGraphicsObjectsExample')
openExample('graphics/FindAllLineObjectsExample')
openExample('graphics/FindObjectsWithSpecifiedPropertyValuesExample')
openExample('graphics/FindObjectsWithoutSpecificPropertyValuesExample')
openExample('graphics/FindObjectsUsingRegularExpressionExample')
openExample('graphics/FindAllObjectsWithSpecifiedPropertyExample')
openExample('graphics/FindAllLineObjectsInCurrentAxesExample')
openExample('graphics/ReturnAllObjectsInCurrentFigureExample')
openExample('graphics/RestrictSearchDepthExample')
另请参阅 copyobj, findall, findobj, gcf, gca, gcbo, gco, get, regexp,
set, groot
已在 R2006a 之前的 MATLAB 中引入
findobj 的文档
doc findobj
findobj 的其他用法
handle/findobj qrandstream/findobj这个函数的功能非常强大,可以通过各种条件来查找对象,例如查找所有的Line对象,查找所有的Axes对象,查找所有的Figure对象等等。还能通过设置逻辑条件,正则表达式等等来查找对象。
图像窗口
图像窗口的创建,可以用下面的函数来实现:
gcffigurefigure('Name', 'xxx')
这些函数返回一个Figure对象,可以通过get和set来查看和修改属性。属性的修改,也能够用过f.Name = 'xxx'这样的方式来实现。此外,调用操作坐标系的函数以及绘图函数(自动调用坐标系创建),也会自动修改图形窗口的属性。
matlab
f = gcf;
get(f)得到所有属性的列表如下,可以自己查看。
Alphamap: [0 0.0159 0.0317 0.0476 0.0635 0.0794 0.0952 0.1111 0.1270 0.1429 0.1587 0.1746 0.1905 ... ] (1x64 double)
BeingDeleted: off
BusyAction: 'queue'
ButtonDownFcn: ''
Children: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
Clipping: on
CloseRequestFcn: 'closereq'
Color: [0.9400 0.9400 0.9400]
Colormap: [256x3 double]
ContextMenu: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
CreateFcn: ''
CurrentAxes: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
CurrentCharacter: ''
CurrentObject: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
CurrentPoint: [0 0]
DeleteFcn: ''
DockControls: on
FileName: ''
GraphicsSmoothing: on
HandleVisibility: 'on'
Icon: ''
InnerPosition: [680 458 560 420]
IntegerHandle: on
Interruptible: on
InvertHardcopy: on
KeyPressFcn: ''
KeyReleaseFcn: ''
MenuBar: 'figure'
Name: ''
NextPlot: 'add'
Number: 1
NumberTitle: on
OuterPosition: [676 454 568 454]
PaperOrientation: 'portrait'
PaperPosition: [0 0 5.8333 4.3750]
PaperPositionMode: 'manual'
PaperSize: [8.2677 11.6929]
PaperType: 'A4'
PaperUnits: 'inches'
Parent: [1x1 Root]
Pointer: 'arrow'
PointerShapeCData: [16x16 double]
PointerShapeHotSpot: [1 1]
Position: [680 458 560 420]
Renderer: 'opengl'
RendererMode: 'auto'
Resize: on
Scrollable: off
SelectionType: 'normal'
SizeChangedFcn: ''
Tag: ''
ToolBar: 'auto'
Type: 'figure'
Units: 'pixels'
UserData: []
Visible: off
WindowButtonDownFcn: ''
WindowButtonMotionFcn: ''
WindowButtonUpFcn: ''
WindowKeyPressFcn: ''
WindowKeyReleaseFcn: ''
WindowScrollWheelFcn: ''
WindowState: 'normal'
WindowStyle: 'normal' 同时,可以通过help来查看这个函数的帮助。
matlab
help figure figure - 创建图窗窗口
此 MATLAB 函数 使用默认属性值创建一个新的图窗窗口。生成的图窗为当前图窗。
语法
figure
figure(Name,Value)
f = figure(___)
figure(f)
figure(n)
输入参数
f - 目标图窗
Figure 对象
n - 目标图窗编号
整数标量值
名称-值参数
Name - 名称
'' (默认值) | 字符向量 | 字符串标量
Color - 背景色
RGB 三元组 | 十六进制颜色代码 | 'r' | 'g' | 'b'
Position - 可绘制区域的位置和大小
[left bottom width height]
Units - 测量单位
'pixels' (默认值) | 'normalized' | 'inches' | 'centimeters' |
'points' | 'characters'
另请参阅 axes, gcf, gca, clf, cla, shg, Figure 属性
已在 R2006a 之前的 MATLAB 中引入
figure 的文档
doc figure
坐标系对象
同样,坐标系对象的创建,可以用下面的函数来实现:
gcaaxes
这些函数返回一个Axes对象,可以通过get和set来查看和修改属性。属性的修改,也能够用过a.XLim = [0, 1]这样的方式来实现。此外,调用绘图函数,也会自动修改坐标系的属性。
matlab
a = gca;
get(a) ALim: [0 1]
ALimMode: 'auto'
AlphaScale: 'linear'
Alphamap: [0 0.0159 0.0317 0.0476 0.0635 0.0794 0.0952 0.1111 0.1270 0.1429 0.1587 0.1746 0.1905 ... ] (1x64 double)
AmbientLightColor: [1 1 1]
BeingDeleted: off
Box: off
BoxStyle: 'back'
BusyAction: 'queue'
ButtonDownFcn: ''
CLim: [0 1]
CLimMode: 'auto'
CameraPosition: [0.5000 0.5000 9.1603]
CameraPositionMode: 'auto'
CameraTarget: [0.5000 0.5000 0.5000]
CameraTargetMode: 'auto'
CameraUpVector: [0 1 0]
CameraUpVectorMode: 'auto'
CameraViewAngle: 6.6086
CameraViewAngleMode: 'auto'
Children: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
Clipping: on
ClippingStyle: '3dbox'
Color: [1 1 1]
ColorOrder: [7x3 double]
ColorOrderIndex: 1
ColorScale: 'linear'
Colormap: [256x3 double]
ContextMenu: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
CreateFcn: ''
CurrentPoint: [2x3 double]
DataAspectRatio: [1 1 1]
DataAspectRatioMode: 'auto'
DeleteFcn: ''
FontAngle: 'normal'
FontName: 'Helvetica'
FontSize: 10
FontSizeMode: 'auto'
FontSmoothing: on
FontUnits: 'points'
FontWeight: 'normal'
GridAlpha: 0.1500
GridAlphaMode: 'auto'
GridColor: [0.1500 0.1500 0.1500]
GridColorMode: 'auto'
GridLineStyle: '-'
GridLineWidth: 0.5000
GridLineWidthMode: 'auto'
HandleVisibility: 'on'
HitTest: on
InnerPosition: [0.1300 0.1100 0.7750 0.8150]
InteractionOptions: [1x1 matlab.graphics.interaction.interactionoptions.InteractionOptions]
Interactions: [1x1 matlab.graphics.interaction.interface.DefaultAxesInteractionSet]
Interruptible: on
LabelFontSizeMultiplier: 1.1000
Layer: 'bottom'
Layout: [0x0 matlab.ui.layout.LayoutOptions]
Legend: [0x0 GraphicsPlaceholder]
LineStyleCyclingMethod: 'aftercolor'
LineStyleOrder: '-'
LineStyleOrderIndex: 1
LineWidth: 0.5000
MinorGridAlpha: 0.2500
MinorGridAlphaMode: 'auto'
MinorGridColor: [0.1000 0.1000 0.1000]
MinorGridColorMode: 'auto'
MinorGridLineStyle: ':'
MinorGridLineWidth: 0.5000
MinorGridLineWidthMode: 'auto'
NextPlot: 'replace'
NextSeriesIndex: 1
OuterPosition: [0 0 1 1]
Parent: [1x1 Figure]
PickableParts: 'visible'
PlotBoxAspectRatio: [1 0.7903 0.7903]
PlotBoxAspectRatioMode: 'auto'
Position: [0.1300 0.1100 0.7750 0.8150]
PositionConstraint: 'outerposition'
Projection: 'orthographic'
Selected: off
SelectionHighlight: on
SortMethod: 'childorder'
Subtitle: [1x1 Text]
SubtitleFontWeight: 'normal'
Tag: ''
TickDir: 'in'
TickDirMode: 'auto'
TickLabelInterpreter: 'tex'
TickLength: [0.0100 0.0250]
TightInset: [0.0435 0.0532 0.0170 0.0202]
Title: [1x1 Text]
TitleFontSizeMultiplier: 1.1000
TitleFontWeight: 'normal'
TitleHorizontalAlignment: 'center'
Toolbar: [1x1 AxesToolbar]
Type: 'axes'
Units: 'normalized'
UserData: []
View: [0 90]
Visible: on
XAxis: [1x1 NumericRuler]
XAxisLocation: 'bottom'
XColor: [0.1500 0.1500 0.1500]
XColorMode: 'auto'
XDir: 'normal'
XGrid: off
XLabel: [1x1 Text]
XLim: [0 1]
XLimMode: 'auto'
XLimitMethod: 'tickaligned'
XMinorGrid: off
XMinorTick: off
XScale: 'linear'
XTick: [0 0.1000 0.2000 0.3000 0.4000 0.5000 0.6000 0.7000 0.8000 0.9000 1]
XTickLabel: {11x1 cell}
XTickLabelMode: 'auto'
XTickLabelRotation: 0
XTickLabelRotationMode: 'auto'
XTickMode: 'auto'
YAxis: [1x1 NumericRuler]
YAxisLocation: 'left'
YColor: [0.1500 0.1500 0.1500]
YColorMode: 'auto'
YDir: 'normal'
YGrid: off
YLabel: [1x1 Text]
YLim: [0 1]
YLimMode: 'auto'
YLimitMethod: 'tickaligned'
YMinorGrid: off
YMinorTick: off
YScale: 'linear'
YTick: [0 0.1000 0.2000 0.3000 0.4000 0.5000 0.6000 0.7000 0.8000 0.9000 1]
YTickLabel: {11x1 cell}
YTickLabelMode: 'auto'
YTickLabelRotation: 0
YTickLabelRotationMode: 'auto'
YTickMode: 'auto'
ZAxis: [1x1 NumericRuler]
ZColor: [0.1500 0.1500 0.1500]
ZColorMode: 'auto'
ZDir: 'normal'
ZGrid: off
ZLabel: [1x1 Text]
ZLim: [0 1]
ZLimMode: 'auto'
ZLimitMethod: 'tickaligned'
ZMinorGrid: off
ZMinorTick: off
ZScale: 'linear'
ZTick: [0 0.5000 1]
ZTickLabel: ''
ZTickLabelMode: 'auto'
ZTickLabelRotation: 0
ZTickLabelRotationMode: 'auto'
ZTickMode: 'auto'
默认创建的笛卡尔坐标系,两个坐标轴的范围都是[0, 1],可以通过a.XLim和a.YLim来查看和修改。

matlab
help axes axes - 创建笛卡尔坐标区
此 MATLAB 函数 在当前图窗中创建默认的笛卡尔坐标区,并将其设置为当前坐标区。通常情况
下,您不需要在绘图之前创建坐标区,因为如果不存在坐标区,图形函数会在绘图时自动创建坐标
区。
语法
axes
axes(Name,Value)
axes(parent,Name,Value)
ax = axes(___)
axes(cax)
输入参数
parent - 父容器
Figure 对象 | Panel 对象 | Tab 对象 | TiledChartLayout 对象 |
GridLayout 对象
cax - 要设置为当前坐标区的坐标区
Axes 对象 | PolarAxes 对象 | GeographicAxes 对象 | 独立可视化
名称-值参数
Position - 大小和位置,不包括标签边距
[0.1300 0.1100 0.7750 0.8150] (默认值) | 四元素向量
OuterPosition - 大小和位置,包括标签和边距
[0 0 1 1] (默认值) | 四元素向量
Units - 位置单位
"normalized" (默认值) | "inches" | "centimeters" | "points" |
"pixels" | "characters"
示例
openExample('graphics/DefineMultipleAxesInFigureWindowExample')
openExample('graphics/MakeSpecificAxesTheCurrentAxesExample')
openExample('graphics/CreateAxesInUITabsExample')
另请参阅 Axes 属性, axis, cla, gca, figure, clf, tiledlayout, nexttile,
polaraxes
已在 R2006a 之前的 MATLAB 中引入
axes 的文档
doc axes对于Axes所有属性和设置的例子,文档同样列写得非常齐全。
一个坐标系绘制多个图形
当我们调用plot函数时,可以直接提供多组数据,此时,Matlab会自动绘制多个图形,每个图形对应一组数据。返回的也是对应的图形对象的句柄。
可以通过对句柄的操作,来修改图形的属性,例如颜色,线型,线宽等等。
matlab
x = 0:0.1:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
h = plot(x, y1, x, y2);
h(1).Color = 'r';
h(2).Color = 'b';
h(1).LineWidth = 1;
h(2).LineWidth = 4;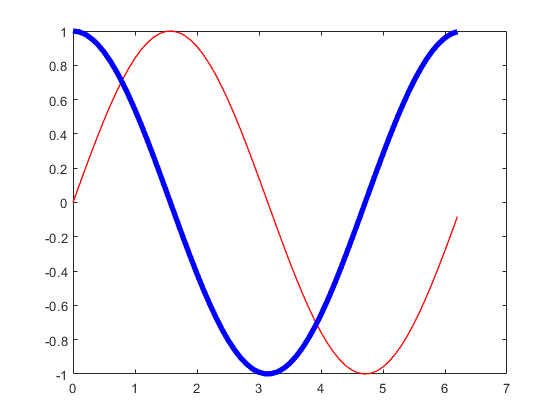
另外,我们也能通过hold('off')和hold('on')来控制是否保留原有的图形,这样也可以实现在一个坐标系中绘制多个图形。
绘制完毕图像,或者导入通过savefig保存的图像之后,还能通过findobj来查找图形对象,然后对其进行操作。
matlab
x = 0:0.1:2*pi;
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);
plot(x, y1)
hold('on');
plot(x, y2);
% savefig('test.fig')
% close('all')
% openfig('test.fig')
h = findobj(gca, 'Type', 'line');
h(1).Color = 'r';
h(2).Color = 'b';
h(1).LineWidth = 4;
h(2).LineWidth = 1;

多坐标系绘图
把多个坐标系放在一个图形中,在发表论文的过程中是很常规的操作。以前Matlab采用的是subplot函数,现在推荐使用tiledlayout和nexttile函数。
matlab
% subplot example
f = figure;
a1 = subplot(2, 1, 1);
x = 0:0.1:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
plot(a1, x, y);
a2 = subplot(2, 1, 2);
y = cos(x);
plot(a2, x, y);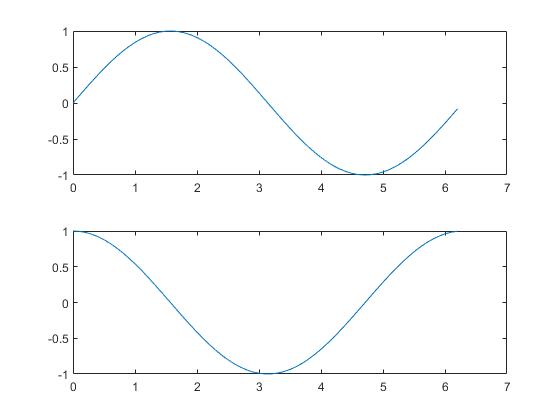
用新的工具,可以更加方便的控制坐标系的位置和大小,以及坐标系之间的间距。这个工具的使用方法,可以参考doc tiledlayout和doc nexttile。
下面是一个非常简单的例子,展示了如何使用这个工具。
matlab
tiledlayout(2,2);
[X,Y,Z] = peaks(20);
% Tile 1
nexttile
surf(X,Y,Z)
% Tile 2
nexttile
contour(X,Y,Z)
% Tile 3
nexttile
imagesc(Z)
% Tile 4
nexttile
plot3(X,Y,Z)可以看到,每个Axes都是一个独立可以进行二维乃至三维绘图的区域。从这一点上来看,Matlab的绘图功能的确比Python的matplotlib要强不少。

更加复杂的布局方式,还可以通过,nexttile([2, 2])这样的方式来实现多行多列的子图。
matlab
scores = [444 460 380
387 366 500
365 451 611
548 412 452];
strikes = [9 6 5
6 4 8
4 7 16
10 9 8];
t = tiledlayout('flow');
% Team 1
nexttile
plot([1 2 3 4],strikes(:,1),'-o')
title('Team 1 Strikes')
% Team 2
nexttile
plot([1 2 3 4],strikes(:,2),'-o')
title('Team 2 Strikes')
% Team 3
nexttile
plot([1 2 3 4],strikes(:,3),'-o')
title('Team 3 Strikes')
% 设置两行三列的子图
nexttile([2 3]);
bar([1 2 3 4],scores)
legend('Team 1','Team 2','Team 3','Location','northwest')
% Configure ticks and axis labels
xticks([1 2 3 4])
xlabel('Game')
ylabel('Score')
% Add layout title
title(t,'April Bowling League Data')tiledlayout可以通过参数设置横向、纵向、流式布局等等,具体的参数可以参考doc tiledlayout。最后那个nexttile([2 3])的参数,可以设置子图的大小,这个参数是一个二维数组,第一个元素是行数,第二个元素是列数。

同样,我们也能通过help和doc来查看这些函数的帮助。
doc tiledlayoutdoc nexttiledoc tilenumdoc tilerowcol
这四个函数全部需要R2022b以后的版本。
实际上,这个话题值得单独开一个帖子来讨论。