一、设置视图的宽高
1.在XML文件中设置视图宽高
视图宽度通过属性android:layout_width表达,视图高度通过属性android:layout_height表达,宽高的取值主要有下列三种:
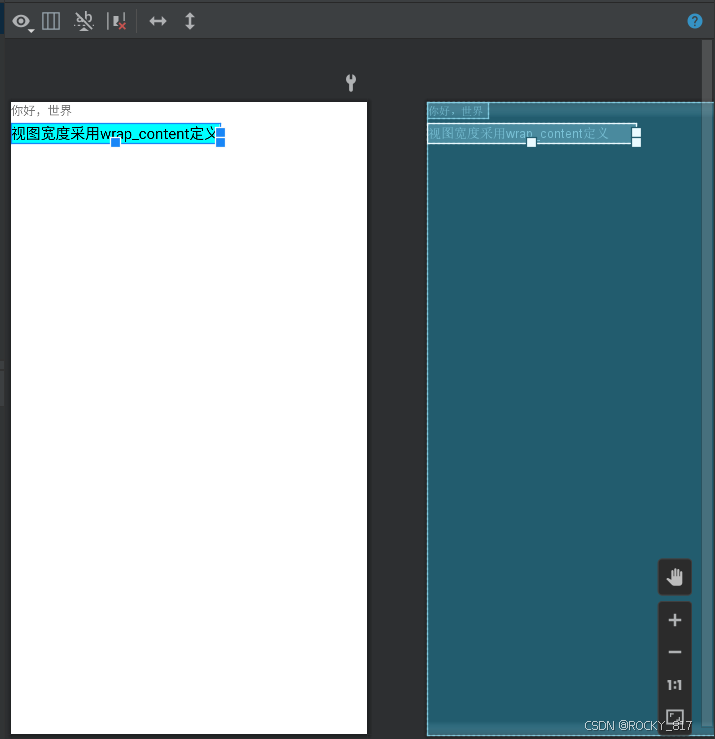
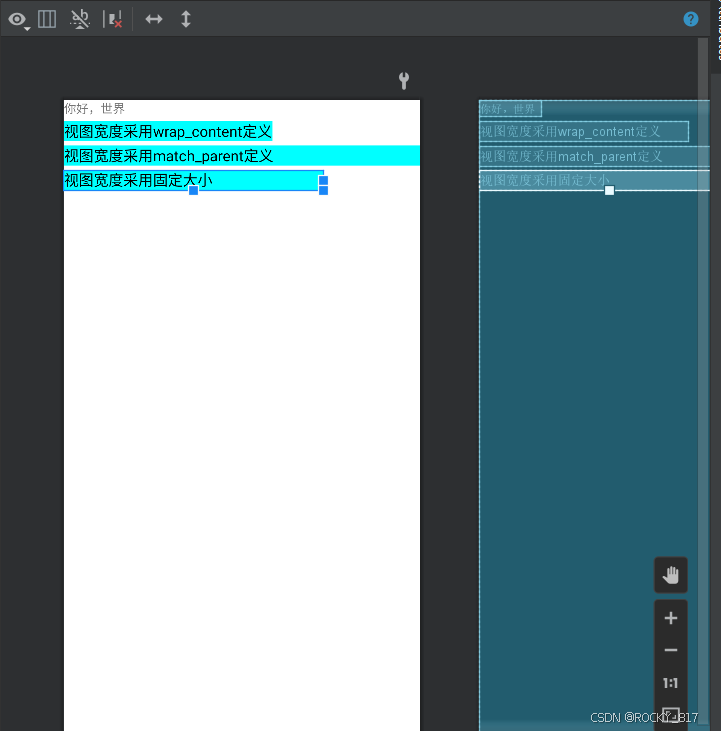
(1)wrap_content:表示与内容自适应。对于文本视图来说,内部文字需要多大的显示空间,当前视图就要占据多大的尺寸。但最宽不能超过上级视图的宽度,一旦超过就要换行;最高不能超过上级视图的高度,一旦超过就会隐藏。
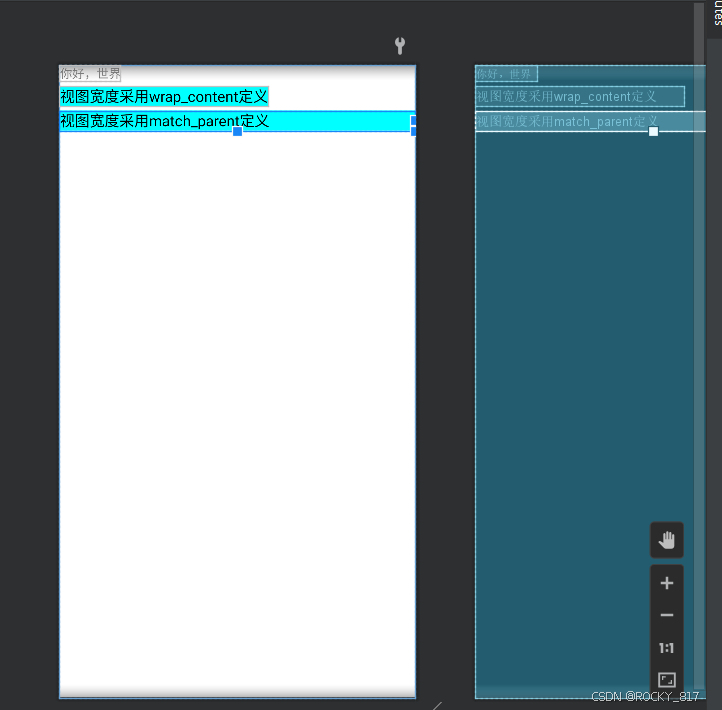
(2)match_parent:表示与上级视图保持一致。上级视图的尺寸有多大,当前视图的尺寸就有多大。
XML
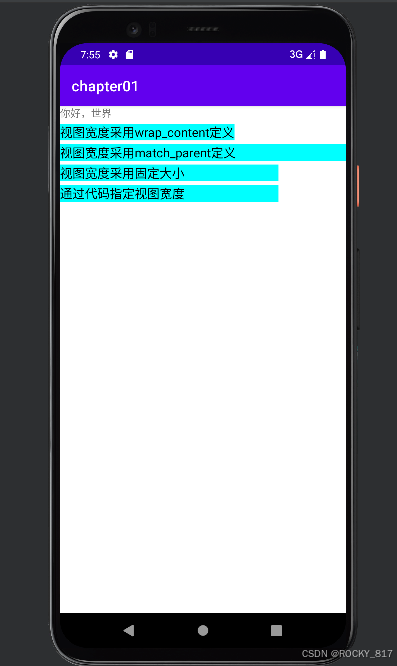
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
android:text="视图宽度采用match_parent定义"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="17sp"
/>
(3)以dp为单位的具体尺寸。
XML
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
android:text="视图宽度采用固定大小"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="17sp"
/>
2.在代码中设置视图宽高
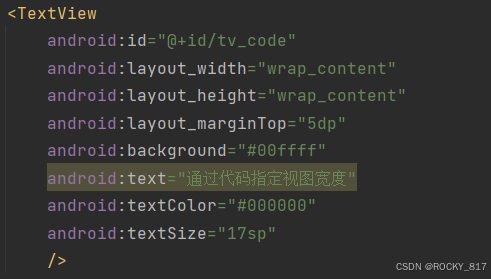
首先确保XML中的宽高属性值为wrap_content,这样才允许在代码中修改宽高
XML
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_code"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
android:text="通过代码指定视图宽度"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="17sp"
/>接着打开该页面对应的Java代码,依序执行以下三个步骤:
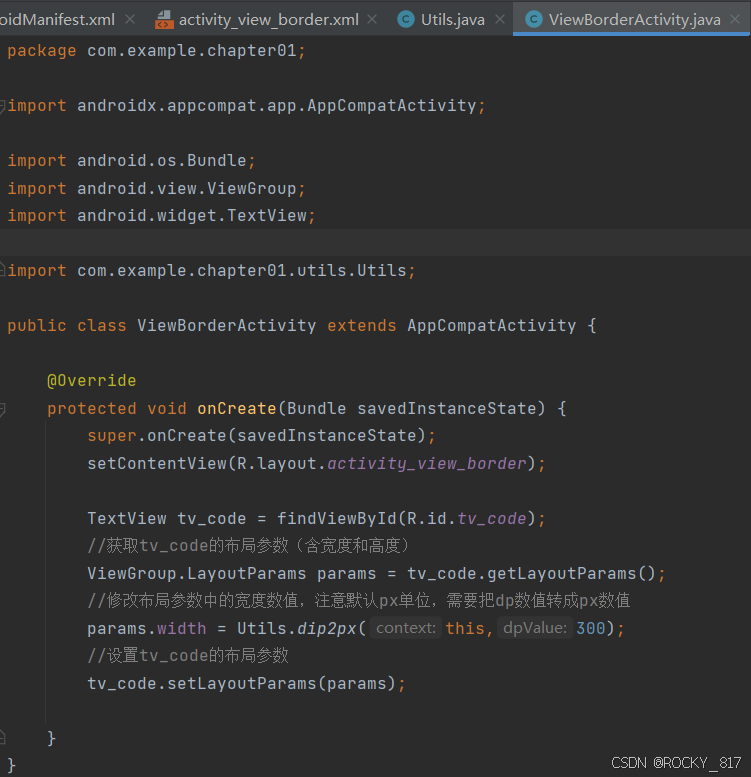
(1)调用控件对象的getLayoutParams方法,获取该控件的布局参数
(2)布局参数的width属性表示宽度,height属性表示高度,修改这两个属性值
(3)调用控件对象的setLayoutParams方法,填入修改后的布局参数使之生效
java
package com.example.chapter01.utils;
import android.content.Context;
public class Utils {
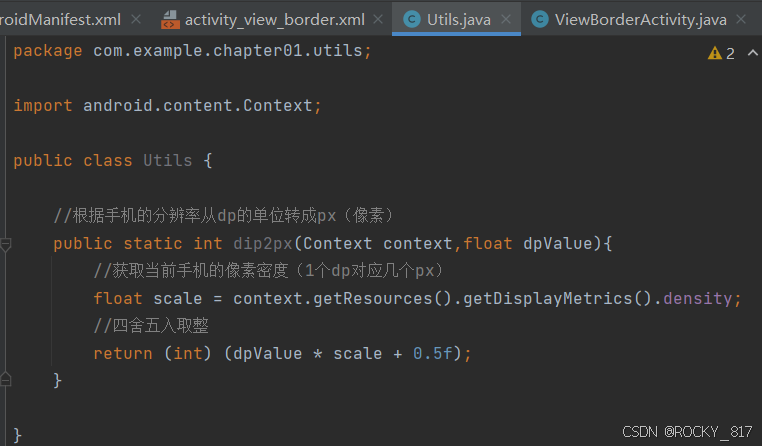
//根据手机的分辨率从dp的单位转成px(像素)
public static int dip2px(Context context,float dpValue){
//获取当前手机的像素密度(1个dp对应几个px)
float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
//四舍五入取整
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
}
java
package com.example.chapter01;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.chapter01.utils.Utils;
public class ViewBorderActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_view_border);
TextView tv_code = findViewById(R.id.tv_code);
//获取tv_code的布局参数(含宽度和高度)
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = tv_code.getLayoutParams();
//修改布局参数中的宽度数值,注意默认px单位,需要把dp数值转成px数值
params.width = Utils.dip2px(this,300);
//设置tv_code的布局参数
tv_code.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}调试运行:
二、设置视图的间距
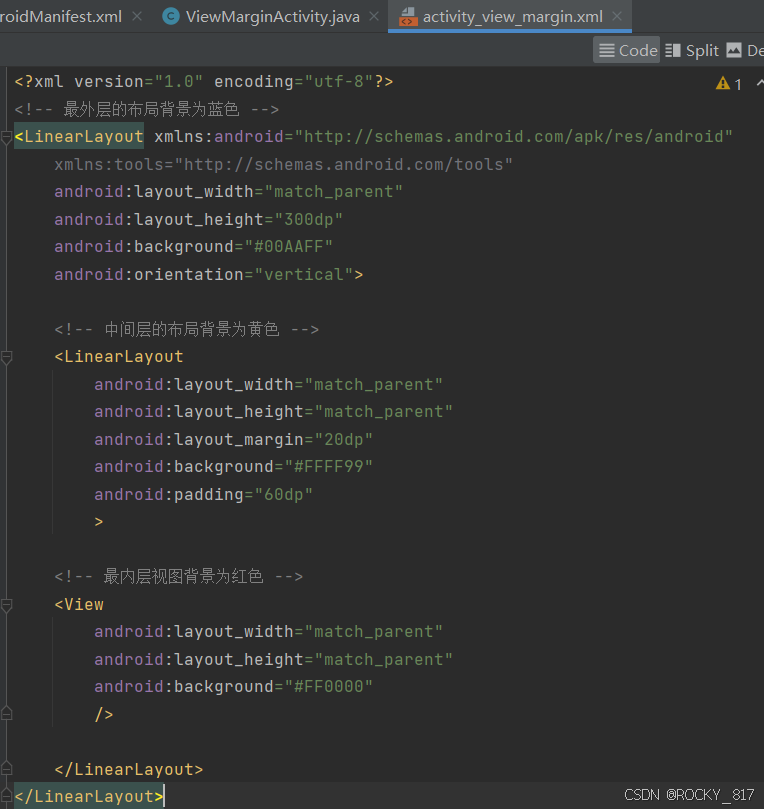
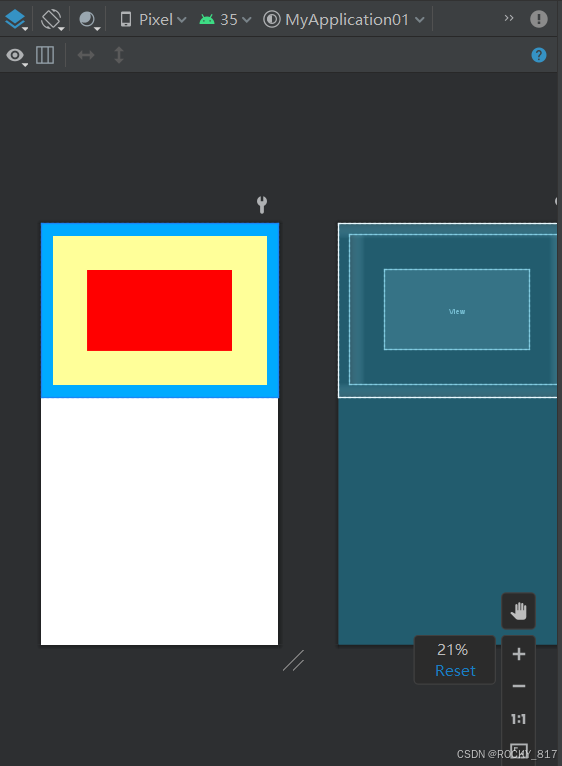
设置视图的间距有两种方式:
1.采用layout_margin属性,它指定了当前视图与周围平级视图之间的距离。包括layout_margin、layout_marginLeft、layout_marginTop、layout_marginRight、layout_marginBottom
注意:layout_margin 不单单用于文本视图,还可用于所有视图,包括各类布局和各类控件。
2.采用padding属性,它指定了当前视图与内部下级视图之间的距离。包括padding、paddingLeft、paddingTop、paddingRight、paddingBottom
设置以下视图:

示例:
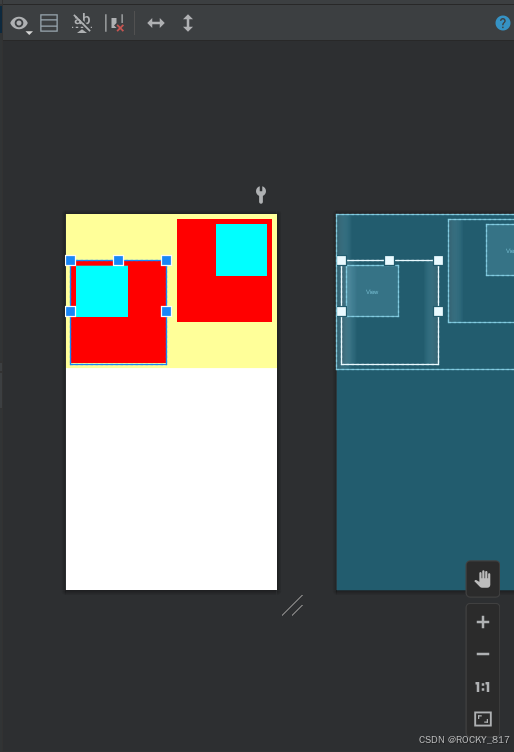
三、设置视图的对齐方式
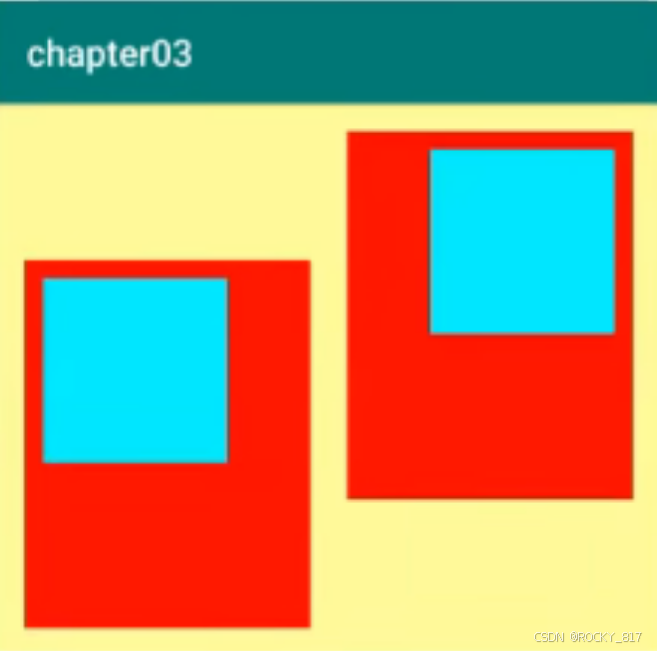
设置视图的对齐方式有两种途径:
1.采用layout_gravity属性,它指定了当前视图相对于上级视图的对齐方式。
2.采用gravity属性,它指定了下级视图相对于当前视图的对齐方式。
layout_gravity与gravity的取值包括:left、top、right、bottom,还可以用竖线连接各取值,例如"leftltop"表示即靠左又靠上,也就是朝左上角对齐。
(一个管自己在父容器中的位置,一个管子元素)
设置以下视图:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#ffff99"
android:orientation="horizontal">
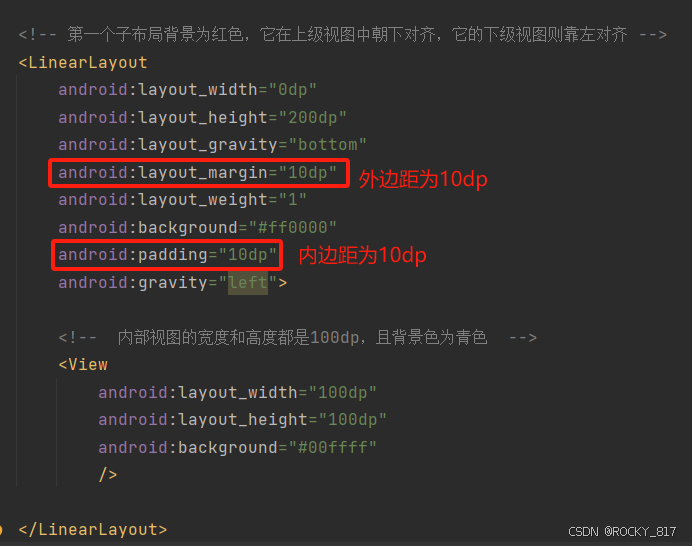
<!-- 第一个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝下对齐,它的下级视图则靠左对齐 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:padding="10dp"
android:gravity="left">
<!-- 内部视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 第二个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝上对齐,它的下级视图则靠右对齐 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:padding="10dp"
android:gravity="right">
<!-- 内部视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>