前言
前面我们完成了量产工具的显示系统和输入系统,见
量产工具(一)------显示系统
量产工具(二)------输入系统
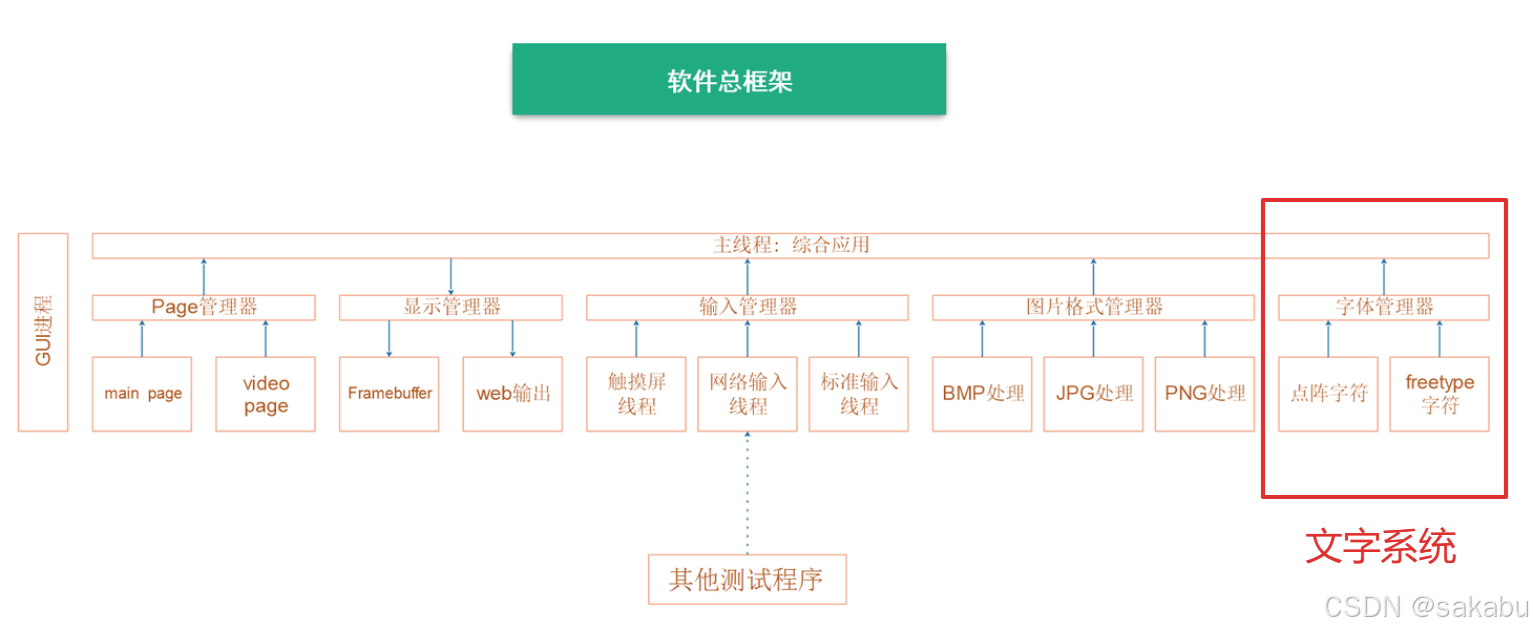
这节我们来实现文字系统,套路和前两节类似,先抽象出数据结构然后再对代码进行封装。
数据结构抽象
使用点阵绘制文字时:每个文字的大小一样,前后文件互不影响

使用Freetype绘制文字时:大小可能不同,前面文字会影响后面文字
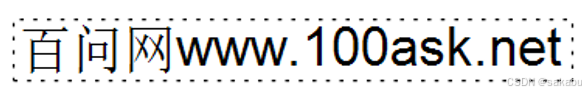
既然我们能支持比较复杂的Freetype,自然能支持比较简单的点阵字体。
对于单个Freetype字符,格式如下:
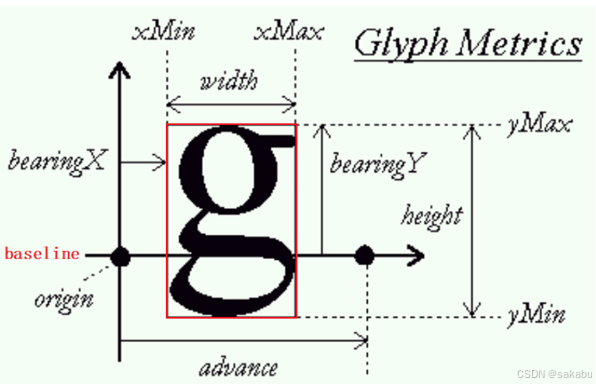
我们要抽象出一个结构体 FontBitMap ,能描述一个"字符":位置、大小、位图;我们还要抽象出一个结构体 FontOpr ,能描述字体的操作,比如Freetype的操作、固定点阵字体的操作。
FontBitMap
结构如下:
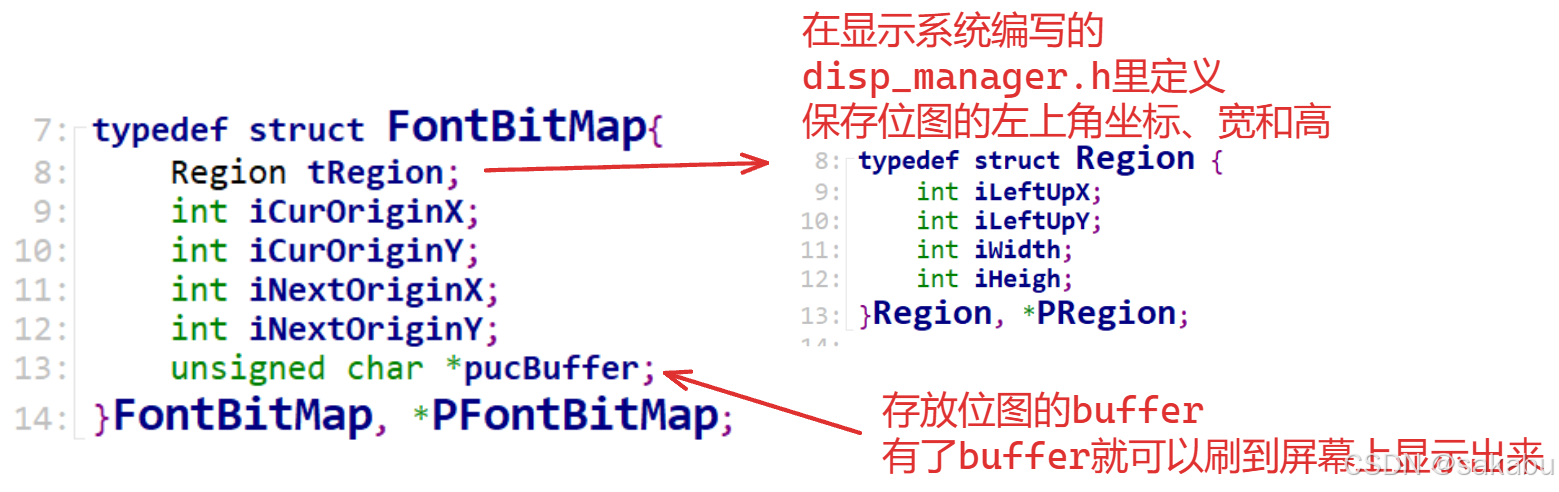
为了让代码更加美观,这里的坐标信息就用了之前定义的 Region 结构体,它用来描述位图的区域信息。
值得注意的是 FontBitMap结构体里的带 Origin 后缀的参数,它用来描述Freetype里的基点,之所以Freetype会看起来比较紧凑,是因为下一个字符的基点是根据前一个字符的基点来计算的。
FontOpr
结构如下:

底层代码需要实现这三个函数,后面也会有管理层,底层需要把自己注册到管理链表里,上层代码就可以直接调用底层代码而无需关心细节。这就是面向对象的编程思想。
font_manager.h
cpp
#ifndef _FONT_MANAGER_H
#define _FONT_MANAGER_H
/*对于一些要复用的结构体和定义,避免重复包含,放在一个通用头文件里*/
#include <common.h>
typedef struct FontBitMap{
/*后面会将Region结构体从之前的头文件剪切到common.h里*/
Region tRegion;
int iCurOriginX;
int iCurOriginY;
int iNextOriginX;
int iNextOriginY;
unsigned char *pucBuffer;
}FontBitMap, *PFontBitMap;
typedef struct FontOpr{
char *name;
int (*FontInit)(char *aFineName);
int (*SetFontSize)(int iFontSize);
int (*GetFontBitMap)(unsigned char dwCode, PFontBitMap ptFontBitMap);
struct FontOpr *ptNext;
}FontOpr, *PFontOpr;
void RegisterFont(PFontOpr ptFontOpr);
void FontsRegister(void);
int SelectAndInitFont(char *aFontOprName, char *aFontFileName);
int SetFontSize(int iFontSize);
int GetFontBitMap(unsigned char dwCode, PFontBitMap ptFontBitMap);
#endif实现Freetype代码
现在我们来实现freetype的代码,从某个字体库文件里得到字符的点阵。freetype知识点比较多且相对复杂,可以先去看这篇博客:使用freetype显示文字。
freetype.c
cpp
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <font_manager.h>
#include <ft2build.h>
#include FT_FREETYPE_H
#include FT_GLYPH_H
//储存FreeType库中的字体面(face)
static FT_Face g_tFace;
//默认字体大小
static int g_iDefaultFontSize = 12;
/* 初始化FreeType字体库 */
static int FreeTypeFontInit(char *aFineName)
{
FT_Library library;
int error;
//初始化FreeType库
error = FT_Init_FreeType( &library ); /* initialize library */
if (error)
{
printf("FT_Init_FreeType err\n");
return -1;
}
//从指定文件创建字体面
error = FT_New_Face(library, aFineName, 0, &g_tFace ); /* create face object */
if (error)
{
printf("FT_New_Face err\n");
return -1;
}
//设置字体大小
FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes(g_tFace, g_iDefaultFontSize, 0);
return 0;
}
/* 设置字体大小 */
static int FreeTypeSetFontSize(int iFontSize)
{
//设置字体大小
FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes(g_tFace, iFontSize, 0);
return 0;
}
/* 获取字体位图 */
static int FreeTypeGetFontBitMap(unsigned int dwCode, PFontBitMap ptFontBitMap)
{
int error;
FT_Vector pen;
FT_GlyphSlot slot = g_tFace->glyph;
//设置当前光标位置,单位为1/64像素
pen.x = ptFontBitMap->iCurOriginX * 64; /* 单位: 1/64像素 */
pen.y = ptFontBitMap->iCurOriginY * 64; /* 单位: 1/64像素 */
/* 转换:transformation设置变换矩阵 */
FT_Set_Transform(g_tFace, 0, &pen);
/* 加载位图: load glyph image into the slot (erase previous one) */
error = FT_Load_Char(g_tFace, dwCode, FT_LOAD_RENDER);
if (error)
{
printf("FT_Load_Char error\n");
return -1;
}
//获取字符位图缓冲区
ptFontBitMap->pucBuffer = slot->bitmap.buffer;
//设置字体位图的区域信息
ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iLeftUpX = slot->bitmap_left;
ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iLeftUpY = ptFontBitMap->iCurOriginY*2 - slot->bitmap_top;
ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iWidth = slot->bitmap.width;
ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iHeigh = slot->bitmap.rows;
ptFontBitMap->iNextOriginX = ptFontBitMap->iCurOriginX + slot->advance.x / 64;
ptFontBitMap->iNextOriginY = ptFontBitMap->iCurOriginY;
return 0;
}
/* 定义一个字体操作结构体 */
static FontOpr g_tFreetypeOpr = {
.name = "freetype",
.FontInit = FreeTypeFontInit,
.SetFontSize = FreeTypeSetFontSize,
.GetFontBitMap = FreeTypeGetFontBitMap,
};
//注册FreeType字体操作结构体
void FreetypeRegister(void)
{
RegisterFont(&g_tFreetypeOpr);
}文字管理
参照下图实现 font_manager.c ,向上层提供更简单的接口函数:
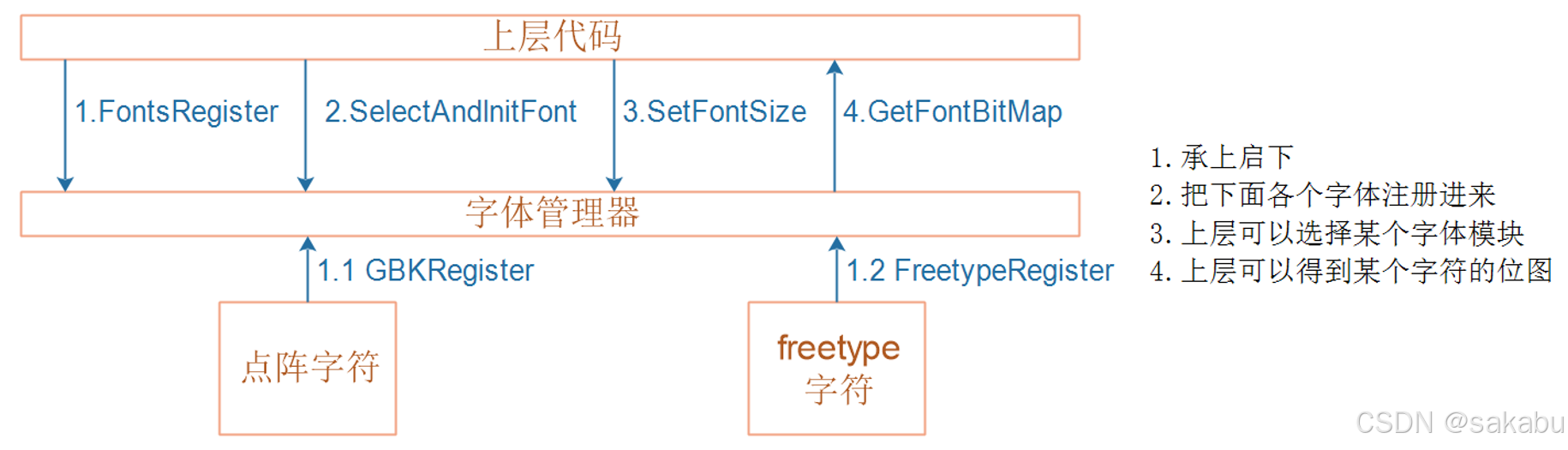
套路和我们之前的管理单元一样,都是对底层函数进一步封装,上层代码调用管理单元的代码而无需关心内部细节,这就是面向对象的编程思想。
font_manager.c
cpp
#include <font_manager.h>
#include <string.h>
//指向注册链表的头
static PFontOpr g_ptFonts = NULL;
//指向当前默认的字体的操作系统
static PFontOpr g_ptDefaulFontOpr = NULL;
//注册一个新的字体操作结构体到链表中
void RegisterFont(PFontOpr ptFontOpr)
{
ptFontOpr->ptNext = g_ptFonts;
g_ptFonts = ptFontOpr;
}
//注册字体操作系统,这里显示注册了FreeType字体
void FontsRegister(void)
{
extern void FreetypeRegister(void);
FreetypeRegister();
}
//选择并初始一个字体操作结构体
int SelectAndInitFont(char *aFontOprName, char *aFontFileName)
{
PFontOpr ptTmp = g_ptFonts;
while (ptTmp)
{
//比较操作结构体的名称,找到匹配的结构体
if (strcmp(ptTmp->name, aFontOprName) == 0)
break;
ptTmp = ptTmp->ptNext;
}
//没找到,返回
if (!ptTmp)
return -1;
//记录一下默认的字体操作结构体
g_ptDefaulFontOpr = ptTmp;
//调用结构体的初始化函数,初始化字体
return ptTmp->FontInit(aFontFileName);
}
//设置当前默认字体的字体大小
int SetFontSize(int iFontSize)
{
return g_ptDefaulFontOpr->SetFontSize(iFontSize);
}
//获取当前默认字体的字符位图
int GetFontBitMap(unsigned int dwCode, PFontBitMap ptFontBitMap)
{
return g_ptDefaulFontOpr->GetFontBitMap(dwCode, ptFontBitMap);
}单元测试
目录结构如下:
我们要将freetype生成的字体在LCD上显示出来,在 disp_manager.c 中还要实现一个绘制函数: DrawFontBitMap
DrawFontBitMap
cpp
void DrawFontBitMap(PFontBitMap ptFontBitMap, unsigned int dwColor)
{
int i, j, p, q;
int x = ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iLeftUpX;
int y = ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iLeftUpY;
int x_max = x + ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iWidth;
int y_max = y + ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iHeigh;
int width = ptFontBitMap->tRegion.iWidth;
unsigned char *buffer = ptFontBitMap->pucBuffer;//字符点阵数据
for ( j = y, q = 0; j < y_max; j++, q++ )
{
for ( i = x, p = 0; i < x_max; i++, p++ )
{
if ( i < 0 || j < 0 ||
i >= g_tDispBuff.iXres || j >= g_tDispBuff.iYres )
continue;
if (buffer[q * width + p])//根据字符点阵数据描点
PutPixel(i, j, dwColor);
}
}
}接着在unittest.c目录下新建 font_test.c 文件,编写单元测试代码。
font_test.c
cpp
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <disp_manager.h>
#include <font_manager.h>
#define FONTDATAMAX 4096
/*此处忽略了点阵数据
static const unsigned char fontdata_8x16[FONTDATAMAX] = {};
*/
/**********************************************************************
* 函数名称: lcd_put_ascii
* 功能描述: 在LCD指定位置上显示一个8*16的字符
* 输入参数: x坐标,y坐标,ascii码
* 输出参数: 无
* 返 回 值: 无
* 修改日期 版本号 修改人 修改内容
* -----------------------------------------------
* 2020/05/12 V1.0 zh(angenao) 创建
***********************************************************************/
void lcd_put_ascii(int x, int y, unsigned char c)
{
unsigned char *dots = (unsigned char *)&fontdata_8x16[c*16];
int i, b;
unsigned char byte;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
byte = dots[i];
for (b = 7; b >= 0; b--)
{
if (byte & (1<<b))
{
/* show */
PutPixel(x+7-b, y+i, 0xffffff); /* 白 */
}
else
{
/* hide */
PutPixel(x+7-b, y+i, 0); /* 黑 */
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
PDispBuff ptBuffer;
int error;
FontBitMap tFontBitMap;
char *str= "www.100ask.net";
int i = 0;
int lcd_x;
int lcd_y;
int font_size;
//检查输入参数数目
if (argc != 5)
{
printf("Usage: %s <font_file> <lcd_x> <lcd_y> <font_size>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
lcd_x = strtol(argv[2], NULL, 0);//将输入参数从字符串形式变成数字形式
lcd_y = strtol(argv[3], NULL, 0);//将输入参数从字符串形式变成数字形式
font_size = strtol(argv[4], NULL, 0);//将输入参数从字符串形式变成数字形式
//初始化显示设备
DisplayInit();
SelectDefaultDisplay("fb");
InitDefaultDisplay();
ptBuffer = GetDisplayBuffer();
//注册初始化字体
FontsRegister();
error = SelectAndInitFont("freetype", argv[1]);
if (error)
{
printf("SelectAndInitFont err\n");
return -1;
}
//设置字体大小
SetFontSize(font_size);
//循环各个字符
while (str[i])
{
tFontBitMap.iCurOriginX = lcd_x;
tFontBitMap.iCurOriginY = lcd_y;
/* get bitmap 获得字符位图*/
error = GetFontBitMap(str[i], &tFontBitMap);
if (error)
{
printf("SelectAndInitFont err\n");
return -1;
}
/* draw on buffer */
DrawFontBitMap(&tFontBitMap, 0xff0000);
/* flush to lcd/web */
FlushDisplayRegion(&tFontBitMap.tRegion, ptBuffer);
lcd_x = tFontBitMap.iNextOriginX;//移动光标,进行下一个字符的描绘
lcd_y = tFontBitMap.iNextOriginY;//移动光标,进行下一个字符的描绘
i++;
}
return 0;
}在include目录下面新建一个我们之前提到的 common.h 头文件,里面定义了我们经常会用到的结构体和某些宏。
common.h
cpp
#ifndef _COMMON_H
#define _COMMON_H
#ifndef NULL
#define NULL (void *)0
#endif
typedef struct Region {
int iLeftUpX; //区域左上角的X坐标
int iLeftUpY; //区域左上角的Y坐标
int iWidth; //区域宽度
int iHeigh; //区域高度
}Region, *PRegion;
#endifunittest目录下的Makefile
EXTRA_CFLAGS :=
CFLAGS_file.o :=
#obj-y += disp_test.o
#obj-y += input_test.o
obj-y += font_test.o
font目录下的Makefile
EXTRA_CFLAGS :=
CFLAGS_file.o :=
obj-y += font_manager.o
obj-y += freetype.o
这里注意,顶层目录下的makefile还要链接freetype库,否则make会报错。

运行结果
Ubuntu交叉编译后,开发板共享文件系统。

 下方彩色的是lvgl的页面,忽略即可,可以看到成功显示一行字体
下方彩色的是lvgl的页面,忽略即可,可以看到成功显示一行字体
至此量产工具第三部分------文字系统就完成了,下一篇我会更新第四部分------UI系统。希望大家多多点赞支持。