
缓存是 分布式系统 的 重要组件,用于解决数据库数据 的高并发 访问问题。在用户访问大的网站,缓存能提高服务器访问性能,减少数据库的压力,提高用户体验。
本章讲解springboot的缓存管理,完成springboot与redis缓存中间件的整合作用
6.1springboot默认缓存管理
spring框架管理缓存的核心:将缓存应用在操作数据的方法中,减少啦操作数据的次数,也不会对程序造成什么干扰。
springboot继承啦spring框架的缓存管理功能,通过使用注解进行缓存的支持,springboot可以启动缓存管理 的 自动化配置,下面讲解springboot默认的缓存管理。
6.1.1 基础环境搭建
我们需要结合数据库的访问操作对springboot的缓存管理进行讲解:
我们先搭建环境:
1.准备数据:
这里使用第三章的springbootdata数据库。
2.创建项目:
搭建相关的数据实体类。
package com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
@Entity(name="t_comment") //设置ORM实体类,并指定映射表的名字
public class Comment {
@jakarta.persistence.Id
@Id//标注映射对应的主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //设置id自增策略
private long id;
private String content;
private String author;
@Column(name = "a_id")
private Integer aId;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"id=" + id +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", aId=" + aId +
'}';
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getaId() {
return aId;
}
public void setaId(Integer aId) {
this.aId = aId;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}3.编写数据库操作的Repository接口文件。
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public interface Repositry extends JpaRepository<Comment,Integer> {
//根据评论id修改评论作者的author
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("update t_comment c set c.author= ?1 where c.id = ?2")
public int updateComment(String author, Integer id);
}4.编写业务操作类Service文件。
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain.Comment;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.repository.Repositry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
//自定义一个数据操作类,注入实体类对象完成数据的操作
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private Repositry repositry;
public Comment findById(int comment_id) {
Optional<Comment> comment1 = repositry.findById(comment_id);
if (comment1.isPresent()) {
return comment1.get();
}
return null;
}
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
repositry.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(),comment.getaId());
return comment;
}
public int deleteComment(int comment_id) {
repositry.deleteById(comment_id);
return comment_id;
}
}5.编写web访问层:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter06.controller;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain.Comment;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.service.CommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class CommentController {
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public Comment findById(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id){
Comment comment = commentService.findById(comment_id);
return comment;
}
@GetMapping("/update/{id}/{author}")
public Comment updateComment(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id,
@PathVariable("author") String author){
Comment comment = commentService.findById(comment_id);
comment.setAuthor(author);
Comment updateComment = commentService.updateComment(comment);
return updateComment;
}
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public void deleteComment(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id){
commentService.deleteComment(comment_id);
}
}6.在配置文件编写连接数据库的配置信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootdata?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=sjk1234
spring.jpa.show-sql=true项目测试:
启动项目,http://localhost:8080/get/1
这个时候不断刷新浏览器,控制台会一直执行对应的sql语句,随着时间积累,系统的而用户不断增加,数据模型也会越来越大,体验感就会下降啦,这个时候使用缓存是最好的解决办法。
6.1.2 springboot默认缓存体验
接下来体验springboot默认的缓存使用效果
1。在启动类开启springboot基于注解的缓存管理支持
@EnableCaching。2.在数据操作方法上加注解进行缓存管理:
//这个注解将 方法返回结果 Comment 存放在 缓存中的 comment的名称空间中,
// 对应缓存的唯一标识(即缓存数据对应的主键key),默认为方法参数comment_id的值
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment")
public Comment findById(int comment_id) {
Optional<Comment> comment1 = repositry.findById(comment_id);
if (comment1.isPresent()) {
return comment1.get();
}
return null;
}进行测试:
这时候一直刷新浏览器,访问同一个用户评论信息,查询结果就只有一个,控制台也只有一条sql语句。
数据库只执行啦一次sql查询语句,说明默认的缓存支持已经生效啦。
6.2 springboot缓存注解介绍
上面我们通过注解进行啦缓存的管理,还有很多缓存注解以及注解熟悉可以配置优化缓存管理。下面我们一一讲解
1.@EnableCaching注解:springboot继承spring框架的,该注解通常配置在项目启动类上,用于开启 基于注解的缓存支持。
2.@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment") 这个注解可以作用在类或者方法上(通常用在数据擦查询方法),对查询出来的结果进行缓存存储。
执行顺序:1.进行缓存查询:如果缓存中没有对应的数据 就进行方法查询,将结果进行存储。如果有对应的数据就直接使用缓存的数据。
这个注解的属性很多,都是用于对缓存存储进行相关的配置。
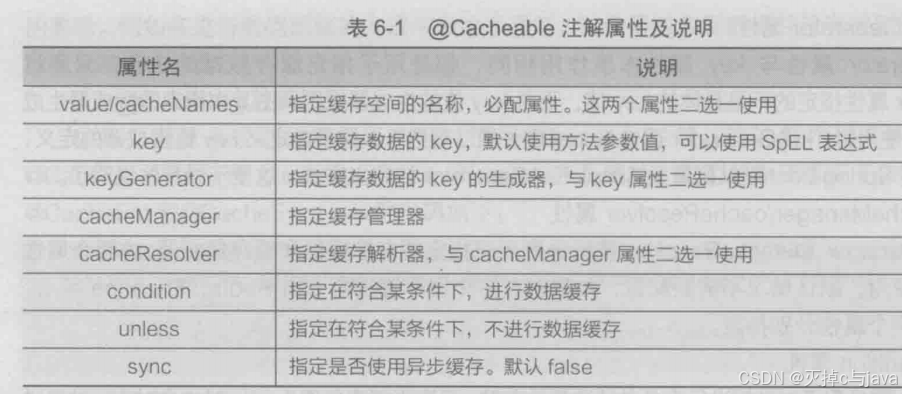
接下来我们一一讲解:
1.第一个属性:也就是给缓存空间起名字,可以同时给多个缓存空间起名字,也可以省略属性名,直接指定缓存空间的名称。使用示例 ,
,
2.第二个属性:key:指定缓存数据对应的唯一标识,缓存数据本质是map类型的数据,key指定唯一标识,value用于指定缓存的数据。默认使用方法的参数值。也可以使用表达式:
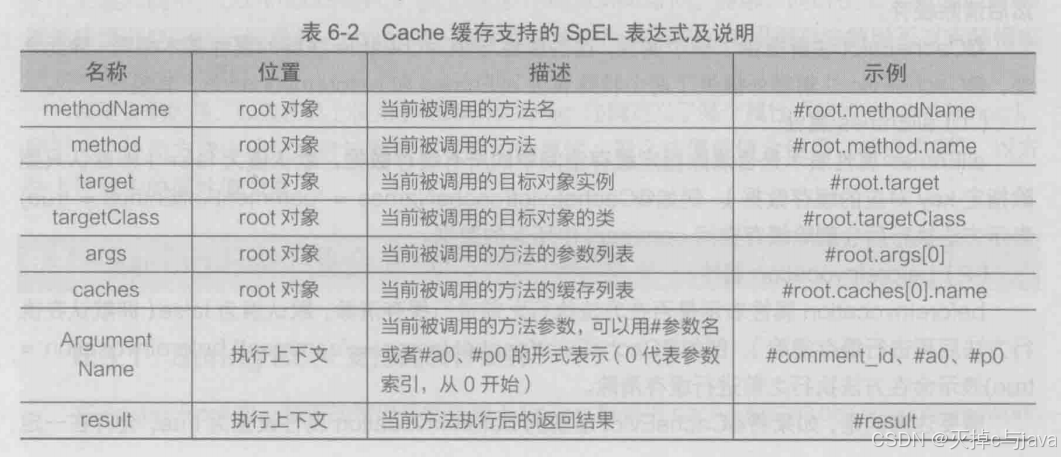
3.第三个属性:它的本质和key属性作用一样,只不过它是指定key值的生成器的规则,由其中指定的生成器生成具体的key值。这个属性跟key属性使用时两个选一个。
4.第四个属性:
5.第五个属性:用于对数据选择存储,指定条件为真时,才会对存储结果进行缓存。
- unless属性:这个属性作用与第五个属性相同,不过它 与第五个属性使用方式相反。

3.@CachePut注解:这个注解可以作用在类或者方法上(用于数据更新方法),作用是更新缓存数据。:执行流程:1.方法调用,2.将方法结果更新到缓存中
4.@CacheEvict注解:与上相同,通常用在数据删除方法上。删除缓存数据。执行流程与上边的类似


具体进行说明:


一个属性清除指定缓存空间中的所有数缓存数据。另一个属性看是否在方法执行前进行缓存清除。
5.@Caching注解
用于处理复杂规则的数据缓存,作用于类或者方法上,这个注解包含三个属性:cacheable。put,evict属性。它们作用等于:前面讲解的2,3,4注解。
使用案例:

6.@CacheConfig注解

6.3 springboot整合redis缓存实现
6.3.1 springboot支持的缓存组件
springboot中的数据存储管理依赖spring框架的cache相关的 缓存管理接口。
在程序中没设有 缓存解析器 或者 相关的 缓存管理组件,就以此启动以下缓存组件:

在项目中添加 某个缓存管理组件(如redis)后,会对应选择和启动对应的缓存管理器,如果项目中 同时添加多个缓存组件,且没指定 缓存管理器 或 缓存解析器 ,springboot就会先启动指定的缓存组件并进行缓存管理。

6.3.2基于注解的redis缓存实现
在6.1节代码基础上进行实现:
引入redis缓存组件:
1.添加对应的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>2.redis服务连接配置:
使用第三方缓存组件进行缓存管理,需要在第三方数据库搭建数据仓库进行缓存存储。
所以这里要连接上redis
3.使用使用对应的注解定制缓存管理:
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private Repositry repositry;
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment",unless = "#result==null")//在方法上添加缓存管理,没有标记key值,默认使用方法参数值作为key值,unless = "#result==null"表示值为空的时候不进行数据缓存
public Comment findById(int comment_id) {
Optional<Comment> comment1 = repositry.findById(comment_id);
if (comment1.isPresent()) {
return comment1.get();
}
return null;
}
@CachePut(cacheNames = "comment",key = "#result.id")//在方法上添加缓存管理,数据更新的方法必须设置key值
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
repositry.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(),comment.getaId());
return comment;
}
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "comment")//在方法上添加缓存管理
public int deleteComment(int comment_id) {
repositry.deleteById(comment_id);
return comment_id;
}
}4.基于注解的redis查询缓存测试
前面进以及对项目进行的操作:添加redis的缓存依赖,redis连接配置,
使用@EnableCaching进行啦缓存管理啦,接下来就进行测试。我在这里测试没有成功。之后再来解决bug
第四步按理讲是会报错需要序列化缓存对象
第五步:讲缓存对象实现序列化:
提示:一些基本数据类型,以及实现啦序列化接口,所以就不需要序列化。
下面我们对ORM实体类进行序列化:
让这个类实现jdk的序列化接口就好啦。
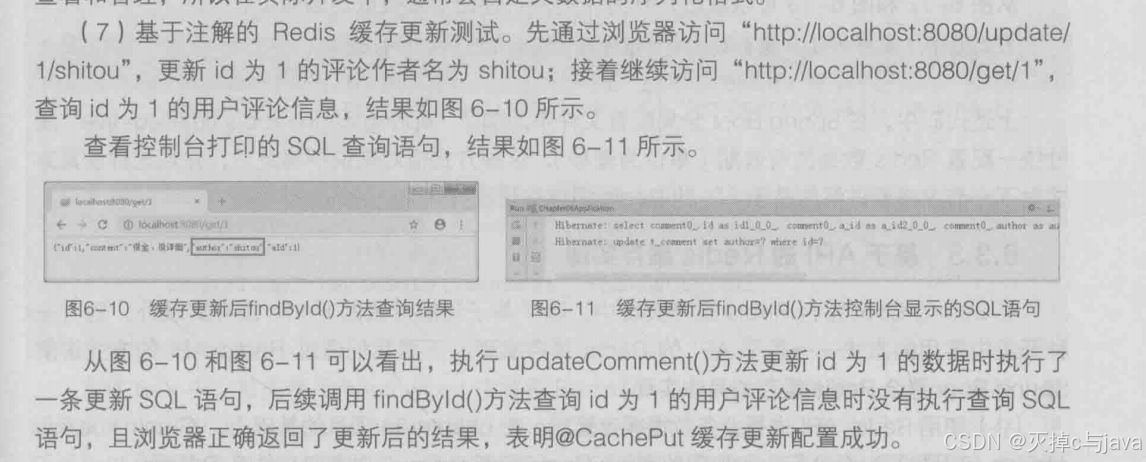
Serializable6.再次进行测试:
你执行查询请求之后,会出现查询结果,并且再redis客户端有对应的数据。
key值是"名称空间comment::+参数值"(comment::1)的形式呈现的。value值以序列化后的HEX格式存储的。这样的序列化是不行的,在实际开发中会自定义数据序列化格式以满足开发需求。
其他功能的缓存测试大家自行查看

6.3.3基于api的redis缓存实现
1.使用redis api进行业务数据缓存管理:
在上边的项目基础上进行操作。
在service包编写业务处理类:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter06.service;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain.Comment;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.repository.Repositry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class ApiCommentService {
@Autowired
private Repositry repositry;
//RedisTemplate是可以直接进行redis操作的javaapi,可直接注入使用
//这个api可以操作对象类型数据,它的子类可以针对字符串类型的数据操作。
//这个api可以进行数据缓存查询,更新,修改,删除,设置缓存有效期等。
@Qualifier("redisTemplate")
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// 查询缓存
public Comment findById(int comment_id) {
Object object = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("comment"+comment_id);
if(object != null) {
return (Comment) object;
}else {
Optional<Comment> optional=repositry.findById(comment_id);
if (optional.isPresent()) {
Comment comment=optional.get();
//这条语句解读:设置啦缓存数据,设置key值,缓存有效时间等
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment_id,comment,1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
return comment;
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
//更新缓存
public Comment update(Comment comment) {
repositry.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(), comment.getaId());
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment.getaId(),comment);
return comment;
}
//删除缓存
public void deleteById(int comment_id) {
repositry.deleteById(comment_id);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment_id,null);
}
}2.编写访问的controller文件:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter06.controller;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.domain.Comment;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter06.service.ApiCommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")//路径映射
public class ApiCommentController {
@Autowired
private ApiCommentService apiCommentService;
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public Comment findById(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id){
Comment comment = apiCommentService.findById(comment_id);
return comment;
}
@GetMapping("/get/{id}/{author}")
public Comment update(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id,
@PathVariable("author") String author) {
Comment comment = apiCommentService.findById(comment_id);
comment.setAuthor(author);
Comment updatedComment = apiCommentService.update(comment);
return updatedComment;
}
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable("id") int comment_id) {
apiCommentService.deleteById(comment_id);
}
}3.相关的配置:
使用api的方式整合redis不需要在启动类添加缓存管理的注解,
其他的序列化,引入依赖于redis的连接配置都与上面的一致。
接下来就可以测试啦。
6.4 自定义redis缓存序列化机制
这里的内容大家可以另看其他文章把
6.5 本章小结
通过本章学习希望理解springboot的缓存管理,以及使用springboot整合redis完成数据的缓存
6.6习题

