语义化更易读,seo;搜索引擎优化
块级元素:独占一行,不管内容长度
内联元素:紧跟着排列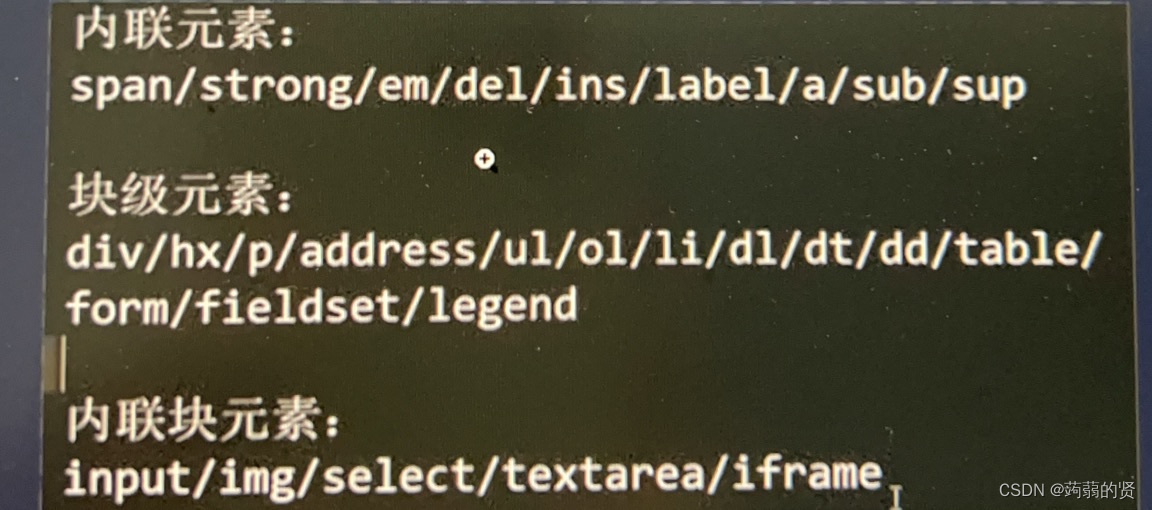
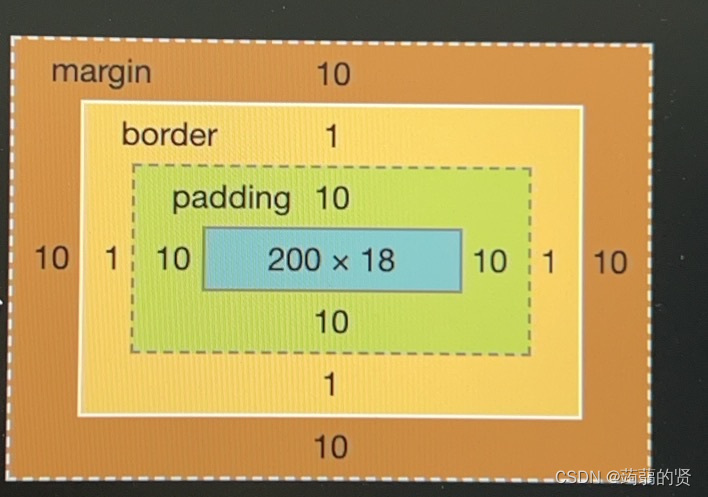
盒模型:
标准盒模型,内容即为长宽,内外边距,框都不算。
怪异盒模型,内边距+内容+框=宽
标准盒模型写width:200px
得到的box-sizing大于200,
加上一句box-sizing:border-box。就缩到200了
不加的话就是默认content-box(内容占据全部的width)

margin合并
当两个div有低外边距和顶外边距时,会造成盒子塌陷。
html
<body>
<div>第一个盒子</div>
<div>第二个盒子</div>
</body>
<style>
div {
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 1;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
border: 1px solid #fcfcfc;
}
</style>在两个div之间插入空div,也会合并。
margin负值

BFC:Block formatting context(块级格式化上下文)
形成独立的渲染区域,内部原元素的渲染不会影响外界,用于清除浮动

正常div先写img,加上float:left,再写<p>,文字正常,但是整个div高度很小,造成图片浮动

加上
.bfc {
overflow: hidden;
}

还是有问题:p占满了整个页面

解决方案:p也加上bfc

圣杯布局


html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div id="header">header</div>
<div id="content">
<div id="center" class="column">center</div>
<div id="left" class="column">left</div>
<div id="right" class="column">right</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">footer </div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
div {
text-align: center;
}
#header {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
#content {
padding-left: 300px;
padding-right: 200px;
}
#content #center {
background-color: #ddd;
width: 100%;
}
#content #left {
background-color: yellow;
width: 300px;
margin-left: -100%;
/* 拖到上面 */
position: relative;
right: 300px;
/* 继续左拖300px */
}
#content #right {
background-color: green;
width: 200px;
margin-right: -200px;
}
#content .column {
float: left;
}
#footer {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
clear: both;
/* 清除浮动 */
}
</style>
</html>flex骰子布局
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="continer">
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.continer {
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #000;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.point {
background-color: black;
border-radius: 50%;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin: 7px;
}
.point:nth-child(2) {
align-self: center;
}
.point:nth-child(3) {
align-self: flex-end;
}
</style>
</html>
row-reserve是从右往左排列

space-between是左右靠边分布
space-around是等距离分布

baseline:不是靠近最底下。是靠近基线,而交叉轴和主轴的基线从左上角开始。
示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="continer">
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
<div class="point"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.continer {
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #000;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
justify-content: flex-start;
align-items: flex-start;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.point {
background-color: black;
border-radius: 50%;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin: 0;
}
/* .point:nth-child(2) {
align-self: center;
}
.point:nth-child(3) {
align-self: flex-end;
} */
</style>
</html>
relative和absolte定位

relative相对于自身,absolute相对于上一个父元素
在CSS中,relative和absolute是用于定位元素的两种方式
relative(相对定位)是相对于元素自身原来的位置进行定位。当你对一个元素使用position: relative后,可以通过top、bottom、left、right属性来移动这个元素。元素原来占据的空间仍然会保留,其他元素不会占据它原来的位置。例如,设置一个元素position: relative和top: 10px,这个元素会相对于它原来的位置向下移动10像素。
absolute(绝对定位)是相对于最近的已定位祖先元素(position属性值为relative、absolute或者fixed)来定位。如果没有已定位的祖先元素,那么它会相对于文档根元素(<html>)进行定位。当一个元素使用position: absolute时,它会脱离文档流,原来占据的空间不会被保留,其他元素会填补它原来的位置。比如,在一个相对定位的容器中有一个绝对定位的元素,这个绝对定位元素会以容器的左上角为参照点(如果没有其他偏移量设置)进行定位。
水平居中

html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="item1">hello world</div>
<div class="continer">
<div class="item2">hello world</div>
</div>
<div class="continer">
<div class="item3">hello world</div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.continer {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: gray;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.item1 {
text-align: center;
background-color: gray;
}
.continer .item2 {
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: pink;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.item3 {
position: absolute;
background-color: yellow;
top: 250px;
left: 50px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -150px;
}
</style>
</html>
垂直居中


line-heigh继承

当1情况,直接继承50px,
当2情况,继承1.5*自身行高
当3情况,继承2*父元素行高。
rem?

