1. 什么是线程局部存储:
线程局部存储(TLS,Thread-Local Storage):
- 线程局部存储(TLS)允许每个线程保存一份独立的数据副本,避免多个线程共享数据导致的竞争问题。
每个线程可以根据pthread_key_t 类型的 键 来 存储 和 访问 自己的私有数据。 - pthread_key_t:
pthread_key_t 是在POSIX线程库(pthread)中用于实现TLS的一种类型。
2. 如何使用POXIS线程局部存储:
(1)创建键:
cpp
int pthread_key_create(pthread_key_t *key, void (*destructor)
(void*));创建一个线程局部存储键,并绑定到一个特定的数据释放函数(可选)
- key: 用于存储创建的 pthread_key_t 键。
- destructor: 当线程退出时,如果 TLS 中有数据与该键关联,destructor 函数将被调用来释放该数据(这个参数可以是 NULL,表示不需要清理函数)。
(2)设置线程局部存储值:
cpp
int pthread_setspecific(pthread_key_t key, const void *value);- key: 用于存取数据的 pthread_key_t 键。
- value: 要设置的线程局部存储的值。
(3)获取线程局部存储值:
cpp
void *pthread_getspecific(pthread_key_t key);- key: 用于检索数据的 pthread_key_t 键。
- 返回值:返回与 key 关联的线程局部存储数据,如果没有数据,则返回 NULL。
(4)销毁键:
cpp
int pthread_key_delete(pthread_key_t key);3. 线程局部存储与加锁的关系:
线程局部存储(TLS)只适用于每个线程有独立数据的场景,可以避免线程间的冲突,但不适用于共享数据的情况;
加锁用于共享资源的情况,保证共享数据的访问是互斥的。
所以二者解决的是不同的问题, 适用于不同的场景,线程局部存储不能完全替代加锁。
4. WebRTC中ThreadManager的线程局部存储类型:
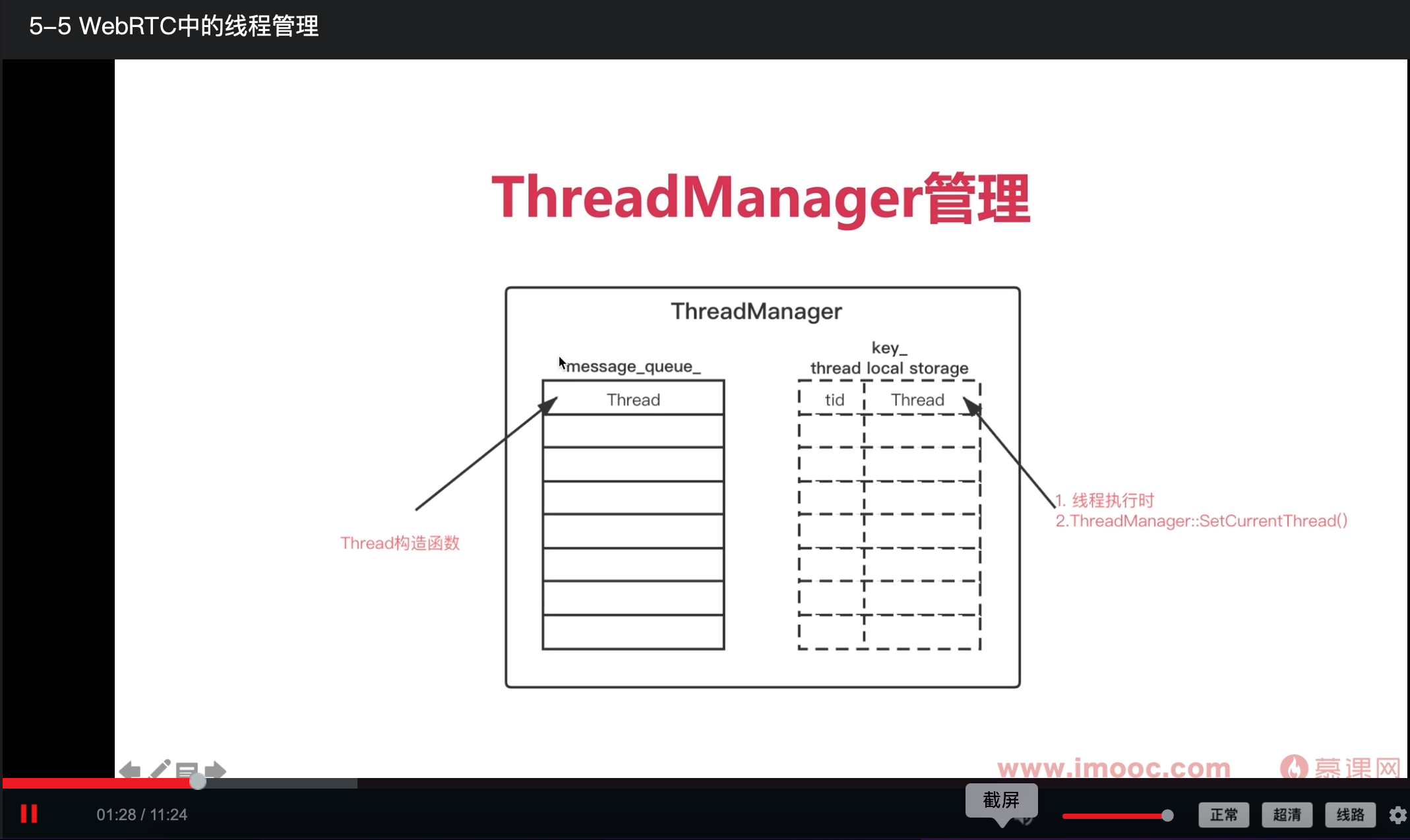
cpp
// src/rtc_base/thread.h
class ThreadManager
{
#if defined(WEBRTC_POSIX)
pthread_key_t key_;
#endif
};
// src/rtc_base/thread.cc
ThreadManager::ThreadManager()
{
pthread_key_create(&key_, nullptr);
}
Thread* ThreadManager::CurrentThread()
{
return static_cast<Thread*>(pthread_getspecific(key_));
}
void ThreadManager::SetCurrentThreadInternal(Thread* thread)
{
pthread_setspecific(key_, thread);
}5. 线程局部存储的demo小程序:
"key_"可以理解为是一个"存储区",而不是一个"键",key_中存储所有的线程与线程私有数据间的映射。
demo:
c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
pthread_key_t key;
void destructor(void *value) {
printf("Thread-specific data is being freed: %s\n", (char*)value);
}
void* thread_func_1(void* arg) {
pthread_setspecific(key, "Thread-specific data 111");
// Retrieve thread-specific data
char* value = pthread_getspecific(key);
printf("Thread-specific data 111: %s\n", value);
return NULL;
}
void* thread_func_2(void* arg) {
pthread_setspecific(key, "Thread-specific data 222");
// Retrieve thread-specific data
char* value = pthread_getspecific(key);
printf("Thread-specific data 111: %s\n", value);
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread1, thread2;
// Create a key with a destructor function
pthread_key_create(&key, destructor);
// Create threads
pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, thread_func_1, NULL);
pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, thread_func_2, NULL);
// Wait for threads to finish
pthread_join(thread1, NULL);
pthread_join(thread2, NULL);
// Delete the key
pthread_key_delete(key);
return 0;
}