框架设计前瞻
设计思想及编程范式
命令式和声明式
从范式上来看,视图层框架通常分为命令式和声明式,它们各有优缺点
命令式
概念
早年间流行的 jQuery 就是典型的命令式框架。命令式框架的一大特点就是关注过程。例如,我们把下面这段话翻译成对应的代码
txt
获取 id 为 app 的 div 标签
它的文本内容为 hello word
为其绑定点击事件
当点击时弹出提示:OK使用原生的 JavaScript 对应的代码为
js
const div = document.querySelector('#app') // 获取 div
div.innerText = 'hello vue3' // 设置文本内容
div.addEventListener('click', () => { alert('ok') }) // 绑定点击事件完整的叙述了所要经历的全部流程
编程式
与命令式框架更加关注过程不同,声明式框架更加关注结果
vue
<div @click="() => alert('ok')">hello vue3</div>可以看到,我们提供的是一个"结果",至于如何实现这个"结果",我们并不关心
编程式 VS 命令式
命令式和声明式各有优缺点,在框架设计方面,则体现在性能 与可维护性之间的权衡
声明式代码的性能不优于命令式代码的性能
性能
假设现在我们要将 div 标签的文本内容修改为 hello vue3,那么如何用命令式代码实现呢?很简单,因为我们明确知道要修改的是什么,所以直接调用相关命令操作即可
js
div.textContent = 'hello vue3' // 直接修改还有没有其他办法比上面这句代码的性能更好?答案是"没有
理论上命令式代码可以做到极致的性能优化,因为我们明确知道哪些发生了变更,只做必要的修改就行了。但是声明式代码不一定能做到这一点,因为它描述的是结果
vue
<!-- 之前: -->
<div @click="() => alert('ok')">hello world</div>
<!-- 之后: -->
<div @click="() => alert('ok')">hello vue3</div>为了实现最优的更新性能,它需要找到前后的差异并只更新变化的地方,但是最终完成这次更新的代码仍然是:
js
div.textContent = 'hello vue3' // 直接修改如果我们把直接修改的性能消耗定义为 A,把找出差异的性能消耗定义为 B,
那么有:
命令式代码的更新性能消耗 = A声明式代码的更新性能消耗 = B + A
声明式代码会比命令式代码多出找出差异的性能消耗,因此最理想的情况是,当找出差异的性能消耗为 0 时,声明式代码与命令式代码的性能相同,但是无法做到超越,毕竟框架本身就是封装了命令式代码才实现了面向用户的声明式。这符合前文中给出的性能结论:声明式代码的性能不优于命令式代码的性能
可维护性
Vue选择使用声明式的原因就是声明式代码的可维护性更强
在采用命令式代码开发的时候,我们需要维护实现目标的整个过程,包括要手动完成 DOM 元素的创建、更新、删除等工作
而声明式代码展示的就是我们要的结果,看上去更加直观,至于做事儿的过程,并不需要我们关心,Vue.js都为我们封装好了
编译时
所谓编译时就是在代码构建阶段和组件进行静态分析和转换的过程,在这一阶段会被转化为JavaScript识别执行的代码
假设我们现在设计了一个框架,它提供一个 Render 函数 ,依据提供的树形结构的对象数据,Render 函数会递归的将数据渲染成 浏览器识别的 DOM 元素
js
const obj = {
tag: 'div',
children: [
{ tag: 'span': children: 'hello vue3' }
]
}- tag 代表标签名
- children 表示子节点 (children既可以是一个数组也可以是一段文本)
render 函数实现
js
function Render(obj, root) {
const el = document.createElement(obj.tag)
if (typeof obj.children === 'string') {
const text = document.createTextNode(obj.children)
el.appendChild(text)
} else if (obj.children) {
// 数组,递归调用 Render,使用 el 作为 root 参数
obj.children.forEach((child) => Render(child, el))
}
// 将元素添加到 root
root.appendChild(el)
}使用函数
js
const obj = {
tag: 'div',
children: [
{ tag: 'span', children: 'hello world' }
]
}
//渲染到 body 下
Render(obj, document.body)在使用时直接为 Render 的渲染函数提供了一个树形结构的数据对象,那么就必须按照使用方式的要求传入数据,其他的数据形式并不支持
那么这个 Render 函数就是一个纯运行时的框架
扩展一下引入编译实现,把 html标签编译成树形结构的数据对象
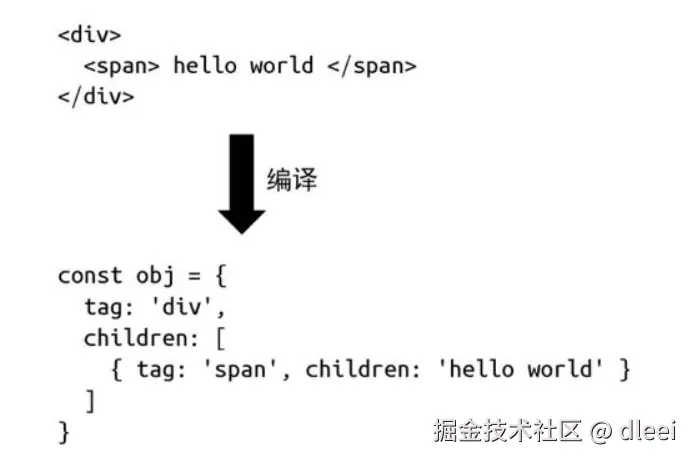
Compiler
它的作用就是把 HTML 字符串编译成树型结构的数据对象
js
const html = `
<div>
<span>hello vue3</span>
</div>
`
// 调用 Compiler 得到编译后的树形结构的对象
const obj = Compiler(html)
// 调用 render 进行渲染
Render(obj, document.body)这样就是一个 编译时+ 运行时 框架的简单实现
它既支持运行时,用户可以直接提供数据对象从而无须编译;又支持编译时,用户可以提供 HTML 字符串,我们将其编译为数据对象后再交给运行时处理
既然编译器可以把 HTML 字符串编译成数据对象,那么能不能直接编译成命令式代码,自然是可以的

这样我们只需要一个 Compiler 函数就可以了,连 Render 都不需要了。其实这就变成了一个纯编译时的框架,因为我们不支持任何运行时内容,用户的代码通过编译器编译后才能运行
运行时
运行时在浏览器实际执行代码的阶段,负责处理动态逻辑,如响应式数据更新、组件实例化、虚拟 DOM 的对比(Diff)和 DOM 更新
各自优缺点
运行时的框架由于没有编译的过程,无法分析用户提供的内容,加入编译过程,我们就可以依据用户提供的内容进行分析哪些内容需要改变,哪些内容未来可能需要改变,在编译时提取需要的信息传递给 Render 函数
假如框架是一个纯编译时的,它可以直接分析用户提供的内容,直接将其编译成可执行的 JavaScript 代码,性能会更好,但是有损灵活性,就是用户提供的内容必须时编译后才能运行
其中 Svelte 就是纯编译时的框架,但是它的真实性能可能达不到理论高度。Vue.js 3 仍然保持了运行时 + 编译时的架构,在保持灵活性的基础上能够尽可能地去优化
源码下载
所有的核心代码全部在 packages 文件夹里面,使用的是 monorepo 进行的依赖管理
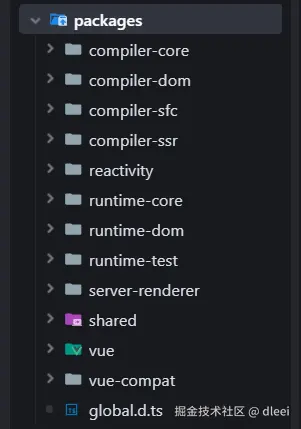
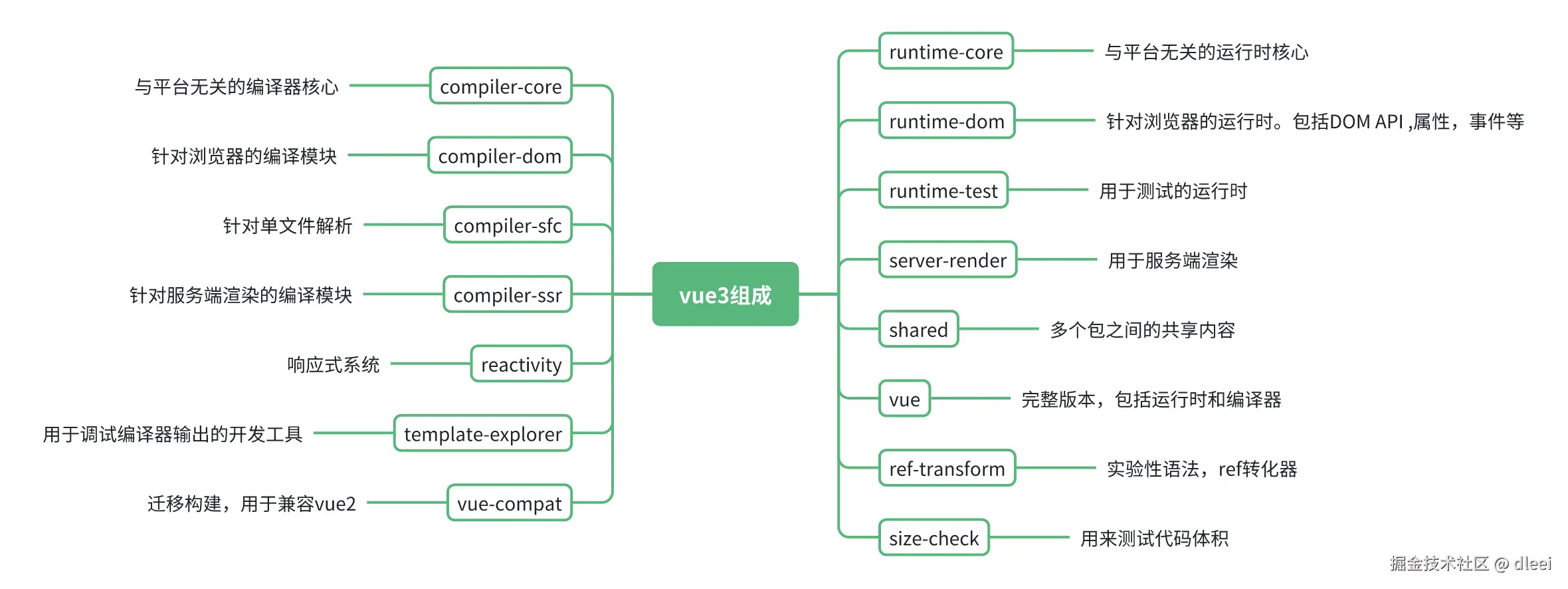
运行源代码
Vue使用的是 pnpm 作为的包管理工具
less
pnpm i // 下载依赖包
arduino
pnpm build // 对vue源代码进行打包打包后的 js 代码会全部在 packages/vue/dist 文件夹内
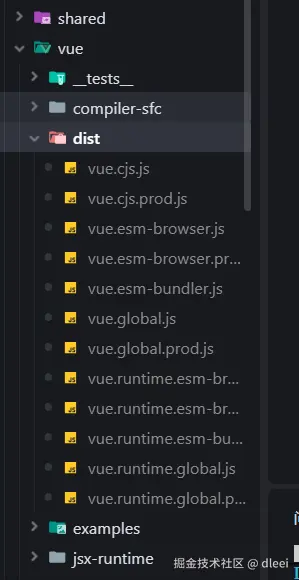
运行测试实例
examples文件夹里面的是 vue 官方提供的所有测试实例
我们可以选择新建一个来测试一下
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { reactive, effect } = Vue
const obj = reactive({
name: '张三',
})
effect(() => {
document.querySelector('#app').innerHTML = obj.name
})
setTimeout(() => {
obj.name = '李四'
}, 3000)
</script>
</body>
</html>在运行实例的时候需要启动一个服务,一个vscode插件 Live-Server
 运行时右键通过 Live Server 打开
运行时右键通过 Live Server 打开
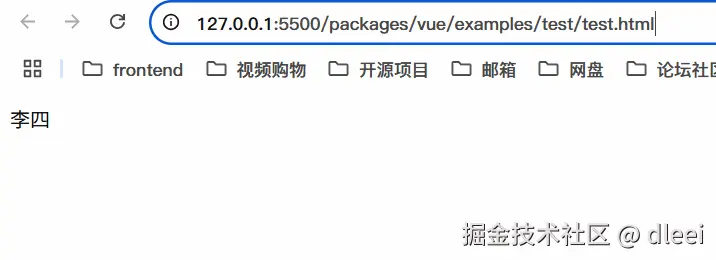
可以看到测试实例正常运行,说明我们打包之后的代码没有任何的问题
开启SourceMap
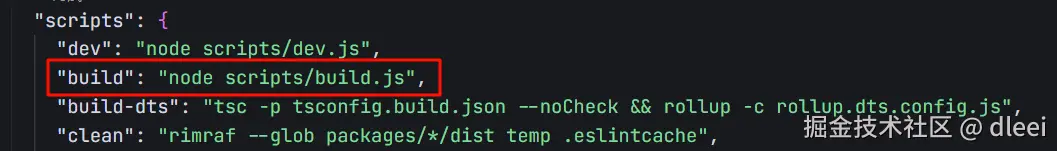
在我们执行 pnpm build 打包操作的时候运行的是 sctipts/build.js 文件
来到 build.js 文件,找到关于 sourcemap 的配置
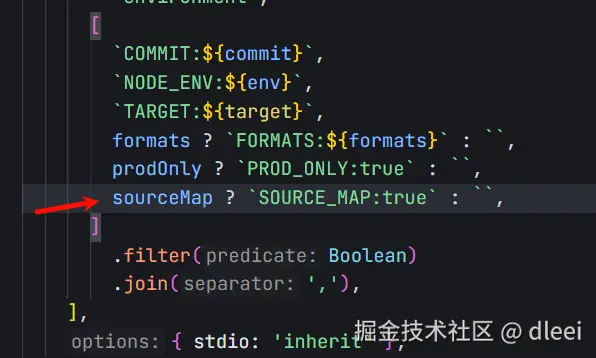
这个值是否为 true 表示对应是否开启 sourcemap
回到上方找到这个sourcemap 的值是哪里取到的

可以看到是在values里面取到的,接着找
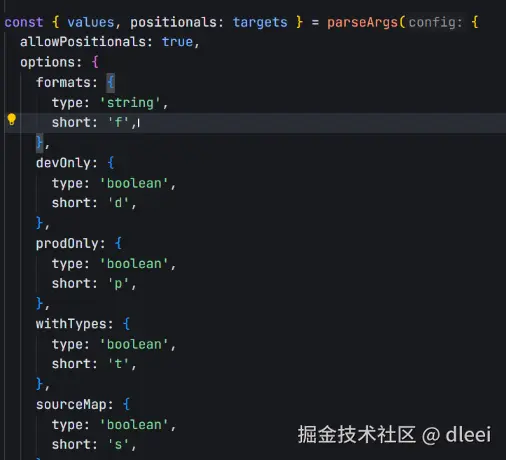
是在parseArgs 里面的,找一下
原来是node里面的工具函数,去看一下文档

简单来说就是parseArgs 会将命令行参数(如 --sourceMap 或 -s)解析为一个结构化对象,分为:
values: 包含所有解析后的选项(--开头的参数)。positionals: 包含所有位置参数(非选项参数)
如果你执行的是
bash
node scripts/build.js --sourceMap --formats esm那么被解析后的 values 对象就是
bash
{
formats: 'esm',
sourceMap: true,
// 其他未显式传递的选项默认为 undefined 或 false
}ok 回到最开始,这个传递进来的 sourcemap 的参数是被 exec 函数处理了
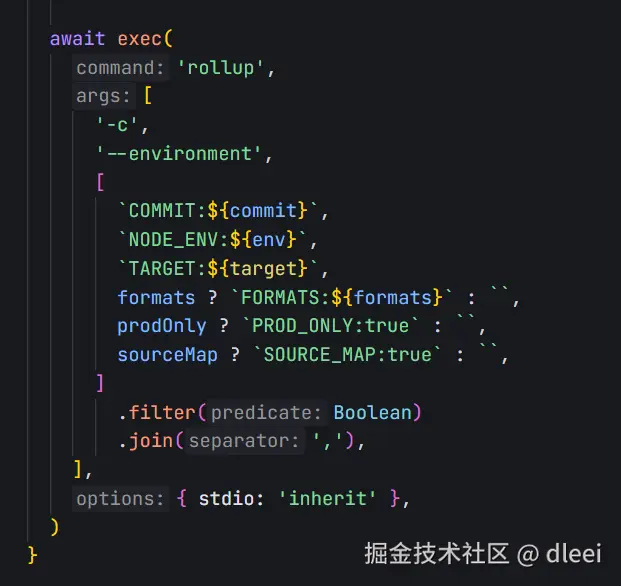
看一下 exec 函数的定义
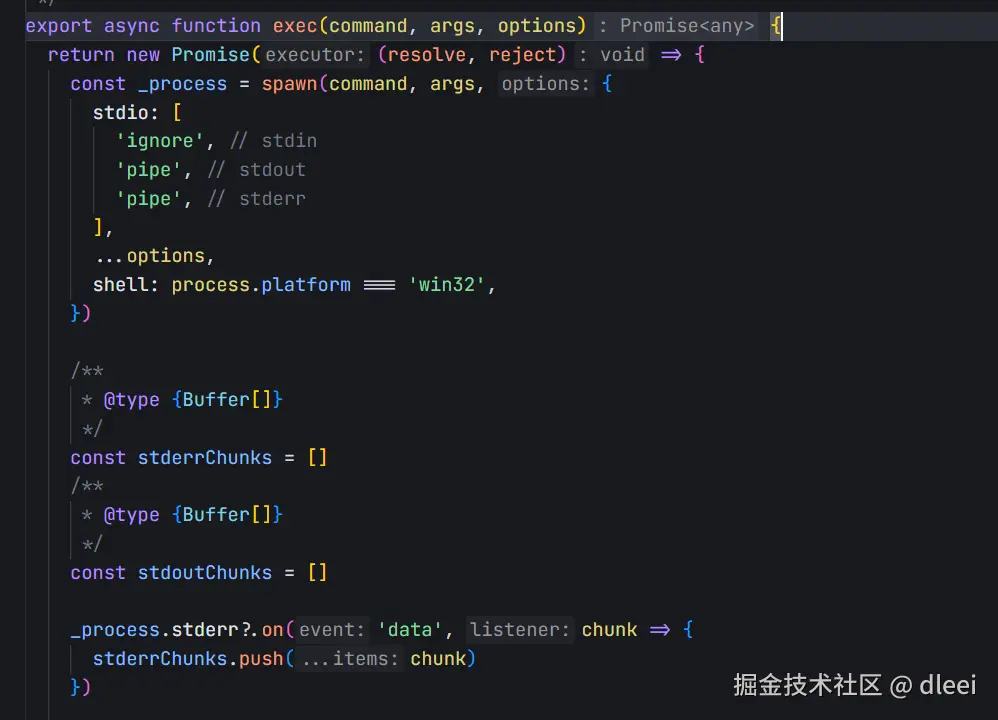
这里就是通过 node 的子进程 执行了rollup 的命令 [ ] 里面是传递给 rollup 对应的一些参数,其中就包括 SourceMap 的配置
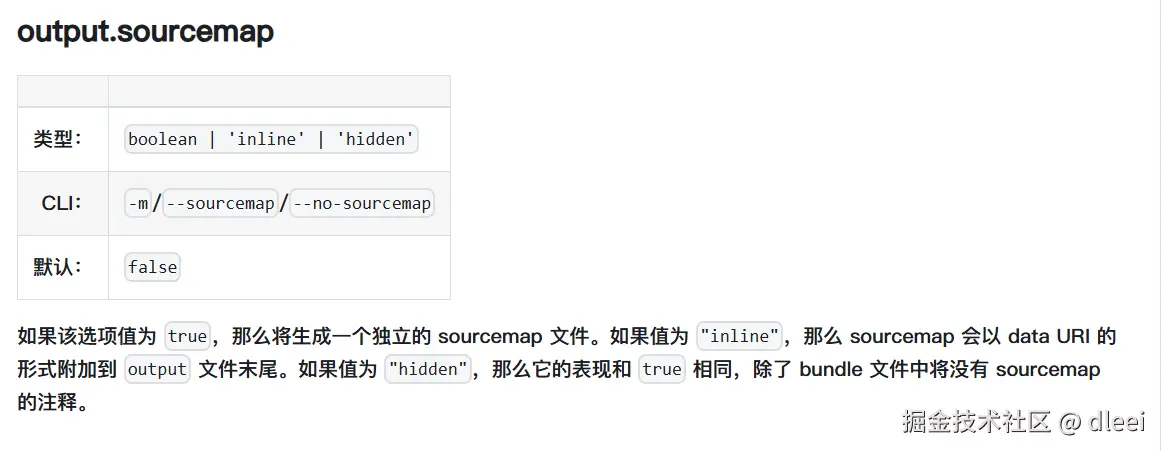
那么我们就可以通过 process.env 访问进程中的变量,从而设置给 rollup 的配置项开启 SourceMap
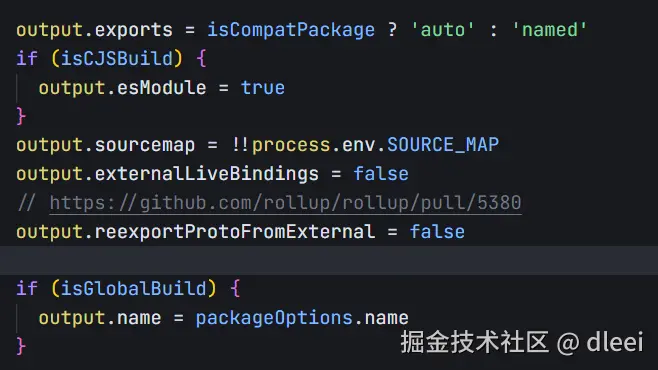
源码debugger
因为我们已经对vue源码开启了sourcemap ,我们重新打包一下
然后新建一个测试实例
html
// examples/test.html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { createApp, ref, onMounted } = Vue
createApp({
setup() {
const title = ref('hello VUE3')
onMounted(() => {
document.querySelector('#app').innerHTML = title.value
})
return { title }
},
}).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>我们在 onMounted 里面加一个断点,测试一下,你也可以选择你自己喜欢的方式在编辑器里面通过lunch.json配置调试或是debugger都可以
 我们在右边可以看到代码对应的执行流程
我们在右边可以看到代码对应的执行流程
搭建我们自己的vue
初始化
这里我们只实现部分功能,主要关注三个部分
- 运行时
- 编译时
- 响应式
bash
npm init -y
配置ts支持
安装
bash
pnpm i typescript -g
// 查看安装
tsc -v
// 初始化 ts 配置文件
tsc --init基础配置,这里只是开启配置了一部分
json
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Visit https://aka.ms/tsconfig to read more about this file */
/* Projects */
// "incremental": true, /* Save .tsbuildinfo files to allow for incremental compilation of projects. */
// "composite": true, /* Enable constraints that allow a TypeScript project to be used with project references. */
// "tsBuildInfoFile": "./.tsbuildinfo", /* Specify the path to .tsbuildinfo incremental compilation file. */
// "disableSourceOfProjectReferenceRedirect": true, /* Disable preferring source files instead of declaration files when referencing composite projects. */
// "disableSolutionSearching": true, /* Opt a project out of multi-project reference checking when editing. */
// "disableReferencedProjectLoad": true, /* Reduce the number of projects loaded automatically by TypeScript. */
/* Language and Environment */
"target": "es2016", /* Set the JavaScript language version for emitted JavaScript and include compatible library declarations. */
"lib": ["ESNext","DOM"], /* Specify a set of bundled library declaration files that describe the target runtime environment. */
// "jsx": "preserve", /* Specify what JSX code is generated. */
// "libReplacement": true, /* Enable lib replacement. */
// "experimentalDecorators": true, /* Enable experimental support for legacy experimental decorators. */
// "emitDecoratorMetadata": true, /* Emit design-type metadata for decorated declarations in source files. */
// "jsxFactory": "", /* Specify the JSX factory function used when targeting React JSX emit, e.g. 'React.createElement' or 'h'. */
// "jsxFragmentFactory": "", /* Specify the JSX Fragment reference used for fragments when targeting React JSX emit e.g. 'React.Fragment' or 'Fragment'. */
// "jsxImportSource": "", /* Specify module specifier used to import the JSX factory functions when using 'jsx: react-jsx*'. */
// "reactNamespace": "", /* Specify the object invoked for 'createElement'. This only applies when targeting 'react' JSX emit. */
// "noLib": true, /* Disable including any library files, including the default lib.d.ts. */
// "useDefineForClassFields": true, /* Emit ECMAScript-standard-compliant class fields. */
// "moduleDetection": "auto", /* Control what method is used to detect module-format JS files. */
/* Modules */
"module": "NodeNext", /* Specify what module code is generated. */
"rootDir": "./", /* Specify the root folder within your source files. */
"moduleResolution": "nodenext", /* Specify how TypeScript looks up a file from a given module specifier. */
// "baseUrl": "./", /* Specify the base directory to resolve non-relative module names. */
// "paths": {}, /* Specify a set of entries that re-map imports to additional lookup locations. */
// "rootDirs": [], /* Allow multiple folders to be treated as one when resolving modules. */
// "typeRoots": [], /* Specify multiple folders that act like './node_modules/@types'. */
// "types": [], /* Specify type package names to be included without being referenced in a source file. */
// "allowUmdGlobalAccess": true, /* Allow accessing UMD globals from modules. */
// "moduleSuffixes": [], /* List of file name suffixes to search when resolving a module. */
// "allowImportingTsExtensions": true, /* Allow imports to include TypeScript file extensions. Requires '--moduleResolution bundler' and either '--noEmit' or '--emitDeclarationOnly' to be set. */
// "rewriteRelativeImportExtensions": true, /* Rewrite '.ts', '.tsx', '.mts', and '.cts' file extensions in relative import paths to their JavaScript equivalent in output files. */
// "resolvePackageJsonExports": true, /* Use the package.json 'exports' field when resolving package imports. */
// "resolvePackageJsonImports": true, /* Use the package.json 'imports' field when resolving imports. */
// "customConditions": [], /* Conditions to set in addition to the resolver-specific defaults when resolving imports. */
// "noUncheckedSideEffectImports": true, /* Check side effect imports. */
"resolveJsonModule": true, /* Enable importing .json files. */
// "allowArbitraryExtensions": true, /* Enable importing files with any extension, provided a declaration file is present. */
// "noResolve": true, /* Disallow 'import's, 'require's or '<reference>'s from expanding the number of files TypeScript should add to a project. */
/* JavaScript Support */
// "allowJs": true, /* Allow JavaScript files to be a part of your program. Use the 'checkJS' option to get errors from these files. */
// "checkJs": true, /* Enable error reporting in type-checked JavaScript files. */
// "maxNodeModuleJsDepth": 1, /* Specify the maximum folder depth used for checking JavaScript files from 'node_modules'. Only applicable with 'allowJs'. */
/* Emit */
// "declaration": true, /* Generate .d.ts files from TypeScript and JavaScript files in your project. */
// "declarationMap": true, /* Create sourcemaps for d.ts files. */
// "emitDeclarationOnly": true, /* Only output d.ts files and not JavaScript files. */
"sourceMap": false, /* Create source map files for emitted JavaScript files. */
// "inlineSourceMap": true, /* Include sourcemap files inside the emitted JavaScript. */
// "noEmit": true, /* Disable emitting files from a compilation. */
// "outFile": "./", /* Specify a file that bundles all outputs into one JavaScript file. If 'declaration' is true, also designates a file that bundles all .d.ts output. */
// "outDir": "./", /* Specify an output folder for all emitted files. */
"removeComments": true, /* Disable emitting comments. */
// "importHelpers": true, /* Allow importing helper functions from tslib once per project, instead of including them per-file. */
"downlevelIteration": true, /* Emit more compliant, but verbose and less performant JavaScript for iteration. */
// "sourceRoot": "", /* Specify the root path for debuggers to find the reference source code. */
// "mapRoot": "", /* Specify the location where debugger should locate map files instead of generated locations. */
// "inlineSources": true, /* Include source code in the sourcemaps inside the emitted JavaScript. */
// "emitBOM": true, /* Emit a UTF-8 Byte Order Mark (BOM) in the beginning of output files. */
// "newLine": "crlf", /* Set the newline character for emitting files. */
// "stripInternal": true, /* Disable emitting declarations that have '@internal' in their JSDoc comments. */
// "noEmitHelpers": true, /* Disable generating custom helper functions like '__extends' in compiled output. */
// "noEmitOnError": true, /* Disable emitting files if any type checking errors are reported. */
// "preserveConstEnums": true, /* Disable erasing 'const enum' declarations in generated code. */
// "declarationDir": "./", /* Specify the output directory for generated declaration files. */
/* Interop Constraints */
// "isolatedModules": true, /* Ensure that each file can be safely transpiled without relying on other imports. */
// "verbatimModuleSyntax": true, /* Do not transform or elide any imports or exports not marked as type-only, ensuring they are written in the output file's format based on the 'module' setting. */
// "isolatedDeclarations": true, /* Require sufficient annotation on exports so other tools can trivially generate declaration files. */
// "erasableSyntaxOnly": true, /* Do not allow runtime constructs that are not part of ECMAScript. */
// "allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true, /* Allow 'import x from y' when a module doesn't have a default export. */
"esModuleInterop": true, /* Emit additional JavaScript to ease support for importing CommonJS modules. This enables 'allowSyntheticDefaultImports' for type compatibility. */
// "preserveSymlinks": true, /* Disable resolving symlinks to their realpath. This correlates to the same flag in node. */
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, /* Ensure that casing is correct in imports. */
/* Type Checking */
"strict": true, /* Enable all strict type-checking options. */
"noImplicitAny": true, /* Enable error reporting for expressions and declarations with an implied 'any' type. */
// "strictNullChecks": true, /* When type checking, take into account 'null' and 'undefined'. */
// "strictFunctionTypes": true, /* When assigning functions, check to ensure parameters and the return values are subtype-compatible. */
// "strictBindCallApply": true, /* Check that the arguments for 'bind', 'call', and 'apply' methods match the original function. */
// "strictPropertyInitialization": true, /* Check for class properties that are declared but not set in the constructor. */
// "strictBuiltinIteratorReturn": true, /* Built-in iterators are instantiated with a 'TReturn' type of 'undefined' instead of 'any'. */
// "noImplicitThis": true, /* Enable error reporting when 'this' is given the type 'any'. */
// "useUnknownInCatchVariables": true, /* Default catch clause variables as 'unknown' instead of 'any'. */
// "alwaysStrict": true, /* Ensure 'use strict' is always emitted. */
"noUnusedLocals": true, /* Enable error reporting when local variables aren't read. */
"noUnusedParameters": true, /* Raise an error when a function parameter isn't read. */
// "exactOptionalPropertyTypes": true, /* Interpret optional property types as written, rather than adding 'undefined'. */
// "noImplicitReturns": true, /* Enable error reporting for codepaths that do not explicitly return in a function. */
// "noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true, /* Enable error reporting for fallthrough cases in switch statements. */
// "noUncheckedIndexedAccess": true, /* Add 'undefined' to a type when accessed using an index. */
// "noImplicitOverride": true, /* Ensure overriding members in derived classes are marked with an override modifier. */
// "noPropertyAccessFromIndexSignature": true, /* Enforces using indexed accessors for keys declared using an indexed type. */
// "allowUnusedLabels": true, /* Disable error reporting for unused labels. */
// "allowUnreachableCode": true, /* Disable error reporting for unreachable code. */
/* Completeness */
// "skipDefaultLibCheck": true, /* Skip type checking .d.ts files that are included with TypeScript. */
"skipLibCheck": true /* Skip type checking all .d.ts files. */
},
"include": ["packages/*/src"],
}具体所有详细配置查看tsconfig.json 配置详解
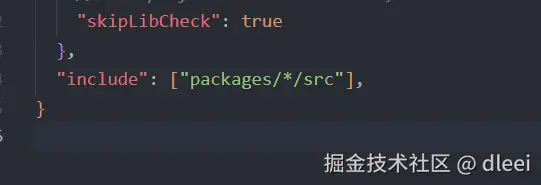
这个include 配置项的意思是项目的入口文件
表示匹配 packages 文件夹里面的所有文件的 src 文件夹里面的所有文件
所以需要我们在packages 文件夹里面的每一个模块文件里面都添加一个 src 文件夹,所有的代码都写在 src 文件夹里面
格式化工具
prettire
arduino
/** .prettierrc.js
* 在VSCode中安装prettier插件 打开插件配置填写`.prettierrc.js` 将本文件作为其代码格式化规范
* 在本文件中修改格式化规则,不会同时触发改变ESLint代码检查,所以每次修改本文件需要重启VSCode,ESLint检查才能同步代码格式化
* 需要相应的代码格式化规范请自行查阅配置,下面为默认项目配置
*/
module.exports = {
// plugins: ["prettier-plugin-tailwindcss"],
// 指定每个缩进级别的空格数
tabWidth: 2,
// 使用制表符而不是空格缩进行
useTabs: false,
// 在语句末尾是否需要分号
semi: true,
// 是否使用单引号
singleQuote: false,
// 更改引用对象属性的时间 可选值"<as-needed|consistent|preserve>"
quoteProps: "as-needed",
// 在JSX中使用单引号而不是双引号
jsxSingleQuote: false,
// 多行时尽可能打印尾随逗号。(例如,单行数组永远不会出现逗号结尾。) 可选值"<none|es5|all>",默认none
trailingComma: "es5",
// 在对象文字中的括号之间打印空格
bracketSpacing: true,
// jsx 标签的反尖括号需要换行
jsxBracketSameLine: false,
// 在单独的箭头函数参数周围包括括号 always:(x) => x \ avoid:x => x
arrowParens: "always",
// 这两个选项可用于格式化以给定字符偏移量(分别包括和不包括)开始和结束的代码
rangeStart: 0,
rangeEnd: Infinity,
// 指定要使用的解析器,不需要写文件开头的 @prettier
requirePragma: false,
// 不需要自动在文件开头插入 @prettier
insertPragma: false,
// 使用默认的折行标准 always\never\preserve
proseWrap: "preserve",
// 指定HTML文件的全局空格敏感度 css\strict\ignore
htmlWhitespaceSensitivity: "css",
// Vue文件脚本和样式标签缩进
vueIndentScriptAndStyle: false,
//在 windows 操作系统中换行符通常是回车 (CR) 加换行分隔符 (LF),也就是回车换行(CRLF),
//然而在 Linux 和 Unix 中只使用简单的换行分隔符 (LF)。
//对应的控制字符为 "\n" (LF) 和 "\r\n"(CRLF)。auto意为保持现有的行尾
// 换行符使用 lf 结尾是 可选值"<auto|lf|crlf|cr>"
endOfLine: "auto",
};这里仅作为源码学习,是否需要添加 eslint 检测按照自己的需求即可,这里为了不增加复杂度就不添加
在编辑器中开启在保存时格式化文件

打包工具
vue2和vue3都是用的rollup作为代码打包的工具
配置
json
import resolve from '@rollup/plugin-node-resolve'
import commonjs from '@rollup/plugin-commonjs'
import typescript from '@rollup/plugin-typescript'
export default [
{
// 入口文件
input: 'packages/vue/src/index.ts',
// 打包出口
output: [
{
// 打包后的文件名
file: 'packages/vue/dist/vue.js',
// 打包后的文件格式
format: 'iife',
// 打包后的文件是否生成sourceMap
sourcemap: true,
// 打包后的文件是否生成全局变量
name: 'Vue',
},
],
// 插件
plugins:[
typescript({
sourcemap: true,
}),
// 模块导入路径补全
resolve(),
// 将commonjs转换为esm
commonjs()
]
},
]具体所有详情配置项查看文档 配置
插件安装
bash
pnpm i rollup @rollup/plugin-commonjs @rollup/plugin-node-resolve @rollup/plugin-typescript tslib typescript -D在 script 里面添加一个打包命令
json
"scripts": {
"build": "rollup -c"
},
检查是否配置有效
我们在 packages/vue/src/index.ts 里面随便写一点代码
ts
console.log('Hello this is my vue')我们运行打包一下试试
bash
pnpm build
vue2响应式核心
vue2中的实现响应式是利用的 Object.defineproperty 来实现的
Object.defineProperty() 静态方法直接在对象上定义新属性,或修改对象上的现有属性,并返回该对象
参数
-
obj要定义属性的对象。
-
prop一个字符串或
Symbol,指定要定义或修改的属性的键。 -
descriptor正在定义或修改的属性的描述符。
返回值
传递给函数的对象,添加或修改了指定的属性
js
const product = {
name: 'iphone',
price: 1000,
quantity: 10,
}
// Object.defineproperty() 方法
/**
* 1. 第一个参数是要定义属性的对象
* 2. 第二个参数是要定义或修改的属性的名称
* 3. 第三个参数是一个描述符对象,用于描述属性的行为
* 4. 描述符对象的属性
* get方法在读取属性时调用,set方法在设置属性时调用
* 5. value: 属性的值
* 6. writable: 是否可以修改属性的值
* 7. enumerable: 是否可以枚举属性
*/
// 使用闭包存储内部的价格
let _price = product.price
Object.defineProperty(product, 'price', {
get() {
console.log('get price')
return _price
},
set(newVal) {
console.log('set price')
_price = newVal
},
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
})
const effect = {
getPrice() {
console.log(product.price)
},
setPrice() {
product.price = 2000
}
}
effect.getPrice()
effect.setPrice()
effect.getPrice() 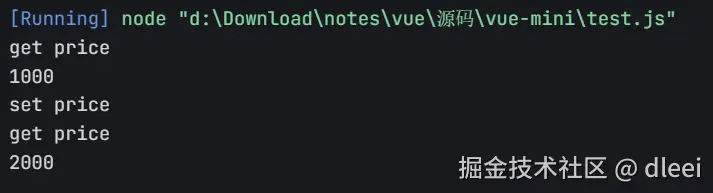
第一次调用 getPrice 会返回 get price 和 当前的 1000 初始值
第二次调用 setPrice 会返回 set price
第三次调用 getPrice 同样会触发 get price 但是现在返回的是 2000 ,里面的 price 已经被我们上一步的 setPrice 修改掉了
这也是vue2中实现响应式原理的主要核心就是利用 Object.defineproperty() 方法来实现数据劫持,当我们在访问属性和设置属性的时候对数据进行操作
VUE2实现响应式缺陷
对象
Vue 无法检测 property 的添加或移除。由于 Vue 会在初始化实例时对 property 执行 getter/setter 转化,所以 property 必须在 data 对象上存在才能让 Vue 将它转换为响应式的
js
var vm = new Vue({
data:{
a:1
}
})
// `vm.a` 是响应式的
vm.b = 2
// `vm.b` 是非响应式的对于已经创建的实例,Vue 不允许动态添加根级别的响应式 property。但是,可以使用 Vue.set(object, propertyName, value) 方法向嵌套对象添加响应式 property
js
Vue.set(vm.someObject, 'b', 2)还可以使用 vm.$set 实例方法,这也是全局 Vue.set 方法的别名:
js
this.$set(this.someObject,'b',2)有时你可能需要为已有对象赋值多个新 property,比如使用 Object.assign() 或 _.extend()。但是,这样添加到对象上的新 property 不会触发更新。在这种情况下,你应该用原对象与要混合进去的对象的 property 一起创建一个新的对象
js
// 代替 `Object.assign(this.someObject, { a: 1, b: 2 })`
this.someObject = Object.assign({}, this.someObject, { a: 1, b: 2 })数组
Vue 不能检测以下数组的变动:
- 当你利用索引直接设置一个数组项时,例如:
vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue - 当你修改数组的长度时,例如:
vm.items.length = newLength
js
var vm = new Vue({
data: {
items: ['a', 'b', 'c']
}
})
vm.items[1] = 'x' // 不是响应性的
vm.items.length = 2 // 不是响应性的为了解决第一类问题,以下两种方式都可以实现和 vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue 相同的效果,同时也将在响应式系统内触发状态更新
js
// Vue.set
Vue.set(vm.items, indexOfItem, newValue)
js
// Array.prototype.splice
vm.items.splice(indexOfItem, 1, newValue)你也可以使用 vm.$set 实例方法,该方法是全局方法 Vue.set 的一个别名:
js
vm.$set(vm.items, indexOfItem, newValue)为了解决第二类问题,你可以使用 splice:
js
vm.items.splice(newLength)vue3响应式核心
vue3使用的是 proxy 为另一个对象创建代理,该代理可以拦截并重新定义该对象的基本操作

js
const product = {
name: 'iphone',
price: 1000,
quantity: 10,
}
/**
* Proxy 代理对象
* 它是一个类需要 new 实例化
* 参数
* 1. 被代理的对象
* 2. 代理对象的配置项
* get: 读取属性时触发
* set: 修改属性时触发
* has: in 操作符时触发
* deleteProperty: delete 操作符时触发
* ownKeys: Object.keys() 时触发
* getOwnPropertyDescriptor: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()时触发
*/
const p = new Proxy(product, {
/**
* 参数
* 1. target 被代理的对象
* 2. key 被访问的代理对象的属性名
* 3. receiver 代理对象Proxy实例本身
*/
get(target, key) {
return target[key]
},
/**
* 参数
* 1. target 被代理的对象
* 2. key 被访问的代理对象的属性名
* 3. newValue 被修改的新值
* 4. receiver 代理对象Proxy实例本身
*/
set(target, key, newValue) {
target[key] = newValue
return true // 必须返回一个boolean值, 表示是否修改成功
},
})
console.log(p.name) // iphone
p.name = 'ipad'
console.log(p.name) // ipad代理通常与 Reflect 对象一起使用,该对象提供了一些与 Proxy 同名的方法。Reflect 方法提供了用于调用相应对象内部方法的反射语义

js
const p = {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
get fullName() {
// get 的作用是可以在读取 fullName 的时候执行函数 p.fullName 而不是 p.fullName()
return this.firstName + this.lastName
},
}
const p2 = {
firstName: '李',
lastName: '四',
get fullName() {
return this.firstName + this.lastName
},
}
/**
* Reflect 反射
* 提供的方法于 Proxy的handler 方法命名相同
* 主要使用的静态方法有:
* Reflect.get(target, key, receiver) 读取属性
* Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver) 设置属性
* Reflect.has(target, key) 判断是否有属性
* Reflect.deleteProperty(target, key) 删除属性
* get方法参数
* target: 需要取值的目标对象
* key: 需要获取的值的键值
* receiver: 可选, 如果target对象中指定了getter,receiver则为 getter 调用时的this值
* 返回值: 读取的属性值
* set 方法参数
* target: 需要设置的目标对象
* key: 设置的属性的名称
* value: 需要设置的值
* receiver: 可选, 如果target对象中指定了setter,receiver则为 setter 调用时的this值
* 返回值: 一个布尔值, 表示是否设置成功
*/
console.log(Reflect.get(p, 'fullName')) // 张三
console.log(Reflect.get(p2, 'fullName', p2)) // 李四
Reflect.set(p, 'firstName', '王')
console.log(p.fullName) // 王三
为什么使用Reflect来修改值而不是proxy的方法:question:
- 确保正确的
this上下文
当通过 Proxy 代理访问对象的属性时,如果属性是 getter/setter 或方法,直接通过 target[key] 访问可能会导致 this 指向原始对象而非代理对象,从而破坏响应性。 Reflect 方法通过传递 receiver 参数 (通常是代理对象本身)解决了这一问题,确保 this 始终指向代理对象,保持响应式链路的完整性。
js
const obj = {
_value: 0,
get value() {
return this._value; // this 应该指向代理对象,而非原始对象
},
};
const proxy = new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, key, receiver) {
// 错误:直接返回 target[key],this 指向原始对象 obj
// return target[key];
// 正确:通过 Reflect 传递 receiver,this 指向代理对象 proxy
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver);
},
});
console.log(proxy.value); // 正确触发代理的 get 逻辑,保持 this 正确- 处理继承与原型链
如果对象的属性定义在其原型链上(如继承自父类),直接通过 target[key] 访问可能无法正确触发代理拦截。 Reflect 方法会沿着原型链查找属性,确保所有层级的属性访问都能被代理捕获,避免响应式系统的"漏洞"。
js
const parent = { value: 42 };
const child = Object.create(parent); // child 继承自 parent
const proxy = new Proxy(child, {
get(target, key, receiver) {
// 直接返回 target[key] 无法拦截原型链上的属性访问
// return target[key];
// 使用 Reflect 可以正确触发原型链查找,并被代理捕获
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver);
},
});
console.log(proxy.value); // 正确触发代理的 get 逻辑3.统一化操作与边缘情况处理
Reflect API 的设计目标之一是与 Proxy 的陷阱方法一一对应,且行为高度规范化 。直接操作对象属性可能在某些边缘场景(如属性为 Symbol、属性不可配置、严格模式下的 set 返回值等)导致不一致的行为,而 Reflect 方法严格遵循语言规范,确保行为一致性。
例如:
- 直接通过
target[key] = value赋值时,若属性是只读的,在严格模式下会抛出错误,但Proxy的set陷阱需要返回一个布尔值表示是否赋值成功。使用Reflect.set()可以直接返回布尔值,避免手动处理这些复杂情况。
js
const obj = {};
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'readOnlyProp', { value: 42, writable: false });
const proxy = new Proxy(obj, {
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
// 直接赋值会抛出错误(严格模式下),且无法返回布尔值
// target[key] = value;
// 使用 Reflect.set() 自动处理错误并返回布尔值
return Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
},
});
proxy.readOnlyProp = 100; // 静默失败,返回 false(非严格模式)4.与 Proxy 的协作性
Proxy 的陷阱方法(如 get 和 set)与 Reflect 方法参数结构完全匹配,使得代码更简洁且易于维护。例如:
Reflect.get(target, key, receiver)的参数与Proxy的get陷阱参数(target, key, receiver)完全一致,可直接透传。
js
const proxy = new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, key, receiver) {
track(key); // 依赖收集
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver); // 直接透传参数
},
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
trigger(key); // 触发更新
return Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
},
});本文为个人学习记录,内容会根据学习进度不定期补充和更新,难免存在一定的疏漏或错误。若发现任何问题,恳请指正与建议