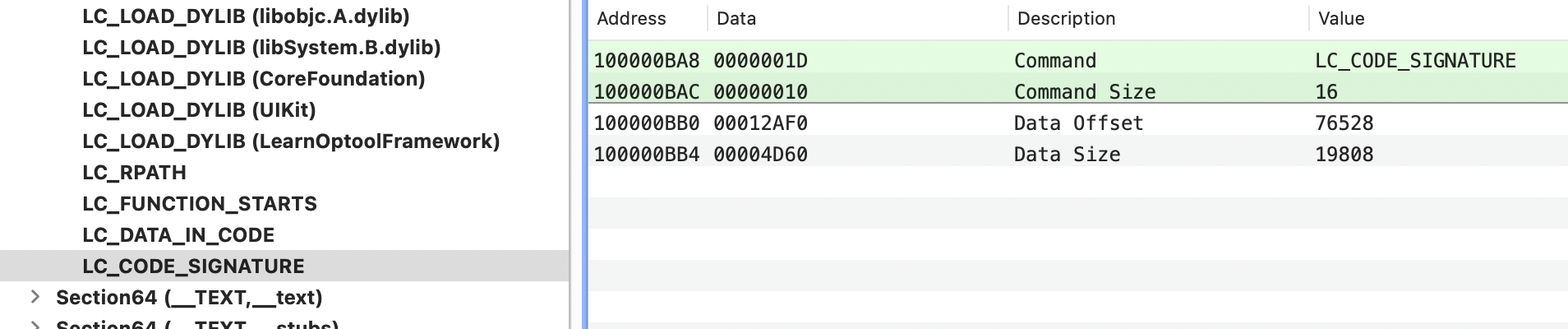
对macho文件有一定理解后,了解下optool是如何给macho文件增加动态库等功能的
optool 源码
环境
macOS 13.4 (22F66)
Xcode 14.3.1
0x0 编译
下载源码
sh
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/alexzielenski/optool.git修改下Deployment Target,比如改成11.0,不修改会报

当然可以从Xcode旧版本里找到libarclite_macos.x复制一个到对应目录下。
⌘ + B后,从Derived Data中找到编译后的二进制文件
libArgumentParser-Static.a 这个静态库主要是解析命令行参数的,而且链接后会在optool中,可以忽略
0x1 命令到源码分析
注入动态库
sh
# optool install -c <command> -p <payload> -t <target>
$ optool install -c load -p 动态库的地址 -t macho文件编译出一个非常简单的app,用MachOView查看可知Load Comamnds的LC_LOAD_DYLIB加载了Foundaiton,libobjc.A.dylib... UIKit这些系统库
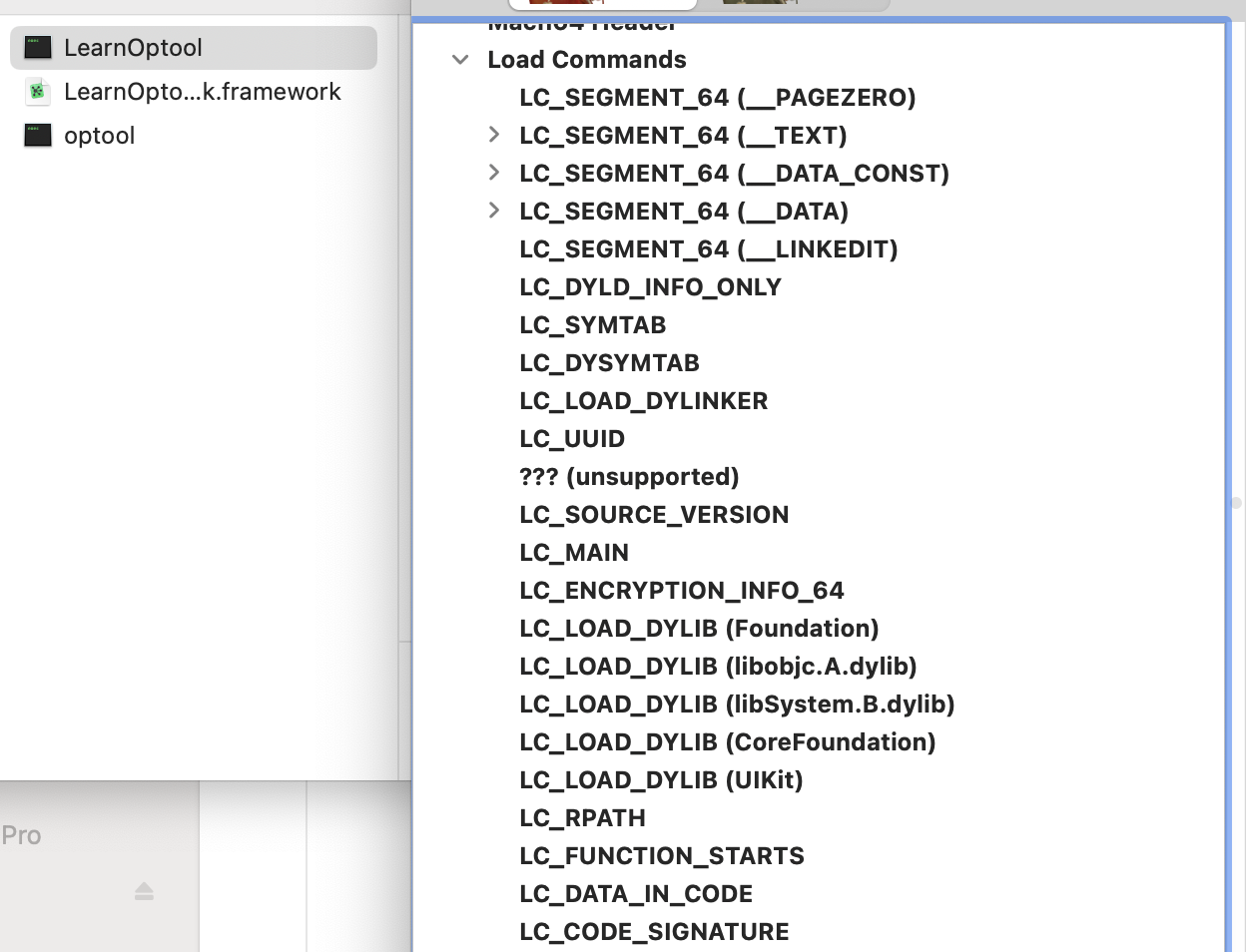
现在追加一个LearnOptionFramework
sh
./optool install -c load -p LearnOptoolFramework.framework/LearnOptoolFramework -t LearnOptool_patch_cmd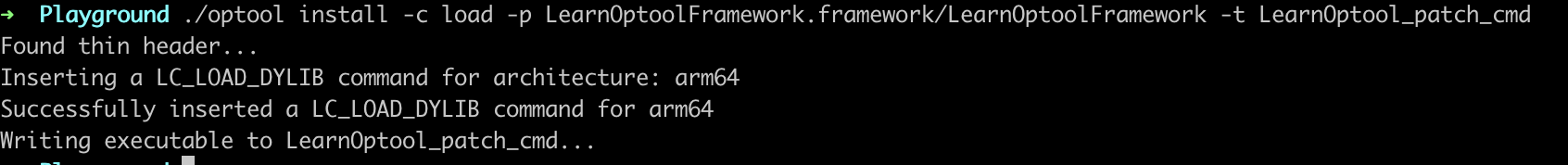
再次用MachOView查看,看出Load Commands增加了LearnOptoolFramework

源码分析
打开Xcode工程,工程代码结构简单
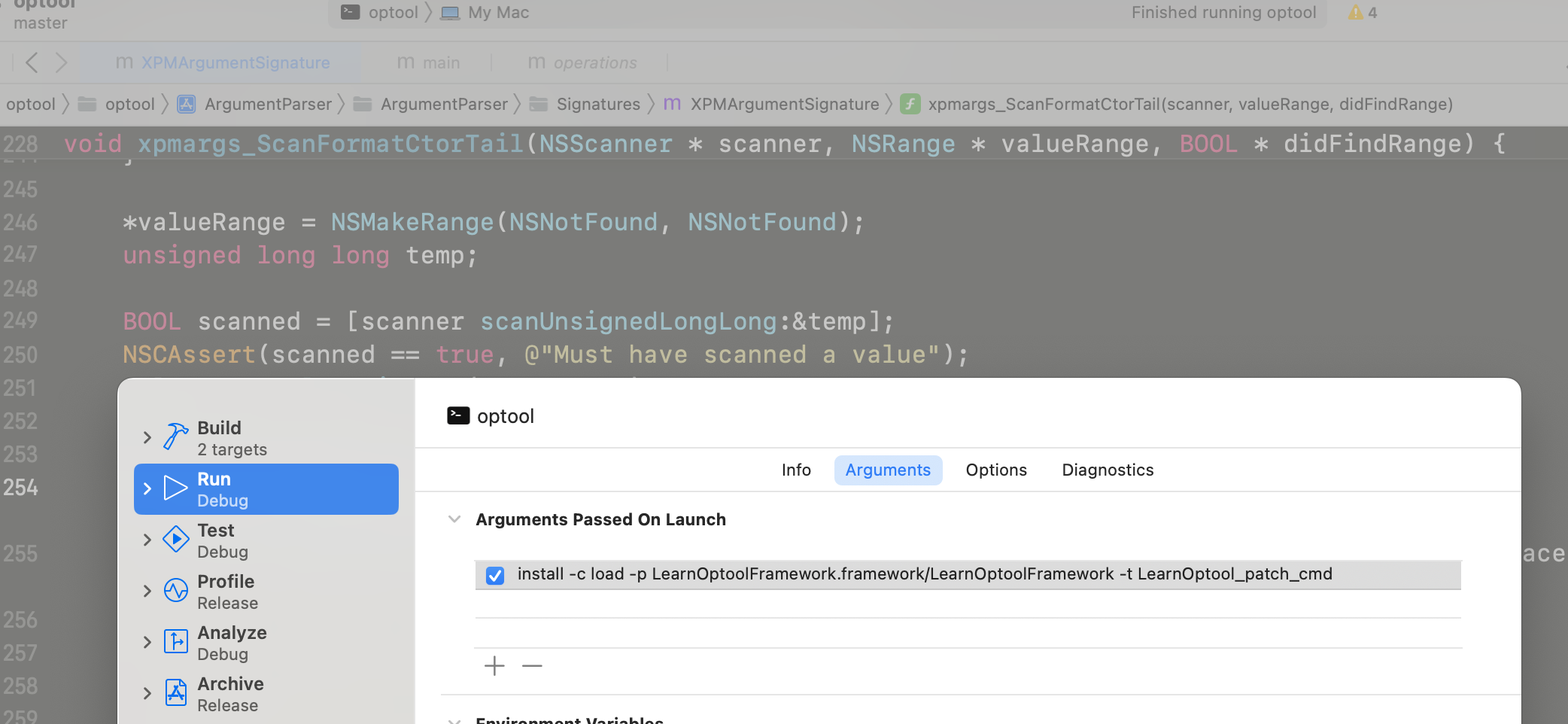
通过启动传参来调试添加动态库的过程
从main函数开始看,前面部分是解析参数的
objc
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
BOOL showHelp = NO;
// Flags
XPMArgumentSignature *weak = [XPMArgumentSignature argumentSignatureWithFormat:@"[-w --weak]"];
XPMArgumentSignature *resign = [XPMArgumentSignature argumentSignatureWithFormat:@"[--resign]"];
XPMArgumentSignature *target = [XPMArgumentSignature argumentSignatureWithFormat:@"[-t --target]={1,1}"];
...
XPMArgumentPackage *package = [[NSProcessInfo processInfo] xpmargs_parseArgumentsWithSignatures:@[resign, command, strip, restore, install, uninstall, output, backup, aslr, help, unrestrict, rename]];
NSString *targetPath = [package firstObjectForSignature:target];
...上面这部分是建立命令行解析的规则,比如是这样的字符串 [-t --target]={1,1}
objc
XPMArgumentSignature *target = [XPMArgumentSignature argumentSignatureWithFormat:@"[-t --target]={1,1}"];进入
objc
+ (id)argumentSignatureWithFormat:(NSString *)format, ...
{
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
XPMArgumentSignature * signature = [XPMArgumentSignature argumentSignatureWithFormat:format arguments:args];
va_end(args);
return signature;
}这里会用到可变参数
可变参数
- va_list args:定义一个指向个数可变的参数列表指针;
- va_start(args, format)format是第一个可选参数前的固定参数,va_start 使指针指向第一个可选参数;
- va_arg(args, type)返回参数列表中指针args所指的参数,返回类型为type,并使指针args指向参数列表中下一个参数;
- va_end(ap) 清空参数列表,并置参数指针ap无效.
按流程走下去主要就是
objc
xpmargs_ScanFormatCtorHead(scanner, foundSwitches, foundAliases, &foundRange, &didFindRange);
...
for (NSString * s in [enclosedString componentsSeparatedByString:@" "]) {
if ([s hasPrefix:@"--"]) {
[switches addObject:[s substringFromIndex:2]];
} else if ([s hasPrefix:@"-"]) {
[switches addObject:[s substringFromIndex:1]];
} else {
[aliases addObject:s];
}
}
xpmargs_ScanFormatCtorTail(scanner, valueRange, didFindRange);整个要做的是如何识别[-t --target]={1,1},然后命令行传入能匹配成功。
命令行参数
通过NSProcessInfo 对象的arguments 获取这次传入的参数信息,
objc
@property (readonly, copy) NSArray<NSString *> *arguments;打印效果大致如下
sh
<__NSFrozenArrayM 0x600000c00c00>(
xxx/optool,
install,
-c,
load,
-p,
LearnOptoolFramework.framework/LearnOptoolFramework,
-t,
LearnOptool_patch_cmd
)根据规则解析出targetPath
objc
NSString *targetPath = [package firstObjectForSignature:target];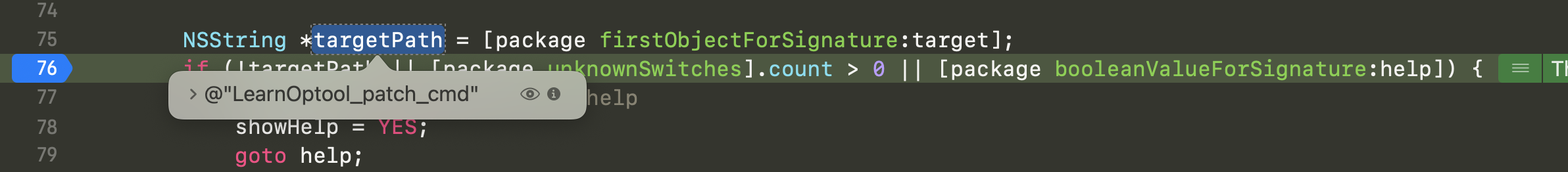
就是-t 参数传入的
如下所示,接着因为工具支持是否要备份,使用({})匿名函数来返回备份文件路径,target后面加_backup,因为没有使用到忽略。
objc
...
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle bundleWithPath:targetPath];
NSString *executablePath = [[bundle.executablePath ?: targetPath stringByExpandingTildeInPath] stringByResolvingSymlinksInPath];
NSString *backupPath = ({
NSString *bkp = [executablePath stringByAppendingString:@"_backup"];
if (bundle) {
NSString *vers = [bundle objectForInfoDictionaryKey:(NSString *)kCFBundleVersionKey];
if (vers)
bkp = [bkp stringByAppendingPathExtension:vers];
}
bkp;
});;紧接着是一段保护处理,也略过,然后读取executablePath文件到NSData对象中,然后创建一个可变的二进制对象,后面对binary进行操作
objc
...
NSData *originalData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:executablePath];
NSMutableData *binary = originalData.mutableCopy;
...
// 检查
if (!binary)
return OPErrorRead;然后自定义了一个thin_header
objc
// we pass around this header which includes some extra information
// and a 32-bit header which we used for both 32-bit and 64-bit files
// since the 64-bit just adds an extra field to the end which we don't need
struct thin_header {
uint32_t offset;
uint32_t size;
struct mach_header header;
};
objc
struct thin_header headers[4];
uint32_t numHeaders = 0;
headersFromBinary(headers, binary, &numHeaders);
if (numHeaders == 0) {
LOG("No compatible architecture found");
return OPErrorIncompatibleBinary;
}
...主要看下headersFromBinary这个函数
objc
// 这部分的逻辑主要是检查macho文件的魔数字段,然后确定是FAT,还是单独架构的文件,然后将填充到自定义的header结构体
struct thin_header *headersFromBinary(struct thin_header *headers, NSData *binary, uint32_t *amount) {
// In a MachO/FAT binary the first 4 bytes is a magic number
// which gives details about the type of binary it is
// CIGAM and co. mean the target binary has a byte order
// in reverse relation to the host machine so we have to swap the bytes
uint32_t magic = [binary intAtOffset:0];
bool shouldSwap = magic == MH_CIGAM || magic == MH_CIGAM_64 || magic == FAT_CIGAM;
#define SWAP(NUM) shouldSwap ? CFSwapInt32(NUM) : NUM
uint32_t numArchs = 0;
// a FAT file is basically a collection of thin MachO binaries
if (magic == FAT_CIGAM || magic == FAT_MAGIC) {
LOG("Found FAT Header");
// WE GOT A FAT ONE
struct fat_header fat = *(struct fat_header *)binary.bytes;
fat.nfat_arch = SWAP(fat.nfat_arch);
int offset = sizeof(struct fat_header);
// Loop through the architectures within the FAT binary to find
// a thin macho header that we can work with (x86 or x86_64)
for (int i = 0; i < fat.nfat_arch; i++) {
struct fat_arch arch;
arch = *(struct fat_arch *)([binary bytes] + offset);
arch.cputype = SWAP(arch.cputype);
arch.offset = SWAP(arch.offset);
struct thin_header macho = headerAtOffset(binary, arch.offset);
if (macho.size > 0) {
LOG("Found thin header...");
headers[numArchs] = macho;
numArchs++;
}
offset += sizeof(struct fat_arch);
}
// The binary is thin, meaning it contains only one architecture
} else if (magic == MH_MAGIC || magic == MH_MAGIC_64) {
// 根据设备的情况这个是这个,然后给thin_header赋值
struct thin_header macho = headerAtOffset(binary, 0);
if (macho.size > 0) {
LOG("Found thin header...");
numArchs++;
headers[0] = macho;
}
} else {
LOG("No headers found.");
}
*amount = numArchs;
return headers;
}headerAtOffset函数给thin_header赋值
objc
struct thin_header headerAtOffset(NSData *binary, uint32_t offset) {
struct thin_header macho;
macho.offset = offset;
macho.header = *(struct mach_header *)(binary.bytes + offset);
if (macho.header.magic == MH_MAGIC || macho.header.magic == MH_CIGAM) {
macho.size = sizeof(struct mach_header);
} else {
macho.size = sizeof(struct mach_header_64);
}
if (macho.header.cputype != CPU_TYPE_X86_64 && macho.header.cputype != CPU_TYPE_I386 && macho.header.cputype != CPU_TYPE_ARM && macho.header.cputype != CPU_TYPE_ARM64){
macho.size = 0;
}
return macho;
}上面这些准备工作执行完成后,可以开始修改二进制文件了。
开始遍历上面准备好的 thin_header 数组,里面有 mach_header 结构体
objc
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < numHeaders; i++) {
struct thin_header macho = headers[i];
...
else if ([package booleanValueForSignature:install]) {
NSString *lc = [package firstObjectForSignature:command];
uint32_t command = LC_LOAD_DYLIB;
if (lc)
command = COMMAND(lc);
if (command == -1) {
LOG("Invalid load command.");
return OPErrorInvalidLoadCommand;
}
if (insertLoadEntryIntoBinary(dylibPath, binary, macho, command)) {
LOG("Successfully inserted a %s command for %s", LC(command), CPU(macho.header.cputype));
} else {
LOG("Failed to insert a %s command for %s", LC(command), CPU(macho.header.cputype));
return OPErrorInsertFailure;
}根据下面这段COMMAND的宏,因为命令传的是load所以就是LC_LOAD_DYLIB,说明是一条加载动态库的指令,将待加载的动态库,二进制文件,macho文件头信息,加载命令都传到insertLoadEntryIntoBinary函数中
objc
#define COMMAND(str) ({ \
uint32_t cmd = -1; \
if ([str isEqualToString: @"reexport"]) \
cmd = LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB; \
else if ([str isEqualToString: @"weak"]) \
cmd = LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB; \
else if ([str isEqualToString: @"upward"]) \
cmd = LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB; \
else if ([str isEqualToString: @"load"]) \
cmd = LC_LOAD_DYLIB; \
cmd; \
})进入到 insertLoadEntryIntoBinary 函数,这段就是在处理macho来增加动态库加载的逻辑
objc
BOOL insertLoadEntryIntoBinary(NSString *dylibPath, NSMutableData *binary, struct thin_header macho, uint32_t type) {
// 异常保护
if (type != LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB &&
type != LC_LOAD_DYLIB) {
LOG("Invalid load command type");
return NO;
}
// parse load commands to see if our load command is already there
uint32_t lastOffset = 0;
// 是否重复添加
if (binaryHasLoadCommandForDylib(binary, dylibPath, &lastOffset, macho)) {
// there already exists a load command for this payload so change the command type
uint32_t originalType = *(uint32_t *)(binary.bytes + lastOffset);
if (originalType != type) {
LOG("A load command already exists for %s. Changing command type from %s to desired %s", dylibPath.UTF8String, LC(originalType), LC(type));
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(lastOffset, sizeof(type)) withBytes:&type];
} else {
LOG("Load command already exists");
}
return YES;
}
// create a new load command
// 新添加,创建加载动态库命令
unsigned int length = (unsigned int)sizeof(struct dylib_command) + (unsigned int)dylibPath.length;
// 我添加的dylibPath.length = 51,整个length = 75, padding = 5
unsigned int padding = (8 - (length % 8));
// check if data we are replacing is null
// 获取要添加command的位置的内容
NSData *occupant = [binary subdataWithRange:NSMakeRange(macho.header.sizeofcmds + macho.offset + macho.size,
length + padding)];
// All operations in optool try to maintain a constant byte size of the executable
// so we don't want to append new bytes to the binary (that would break the executable
// since everything is offset-based--we'd have to go in and adjust every offset)
// So instead take advantage of the huge amount of padding after the load commands
// 比较如果非空,说明到了代码的内容部分,就有问题。添加命令只能在Load Command后面且在代码内容前
if (strcmp([occupant bytes], "\0")) {
NSLog(@"cannot inject payload into %s because there is no room", dylibPath.fileSystemRepresentation);
return NO;
}
LOG("Inserting a %s command for architecture: %s", LC(type), CPU(macho.header.cputype));
struct dylib_command command;
struct dylib dylib;
/*
* A variable length string in a load command is represented by an lc_str
* union. The strings are stored just after the load command structure and
* the offset is from the start of the load command structure. The size
* of the string is reflected in the cmdsize field of the load command.
* Once again any padded bytes to bring the cmdsize field to a multiple
* of 4 bytes must be zero.
* lc_str 的注释
*/
// 所以offset是dylib command的大小
dylib.name.offset = sizeof(struct dylib_command);
dylib.timestamp = 2; // load commands I've seen use 2 for some reason
dylib.current_version = 0;
dylib.compatibility_version = 0;
command.cmd = type;
command.dylib = dylib;
// 命令的长度等于内容 + 对齐
command.cmdsize = length + padding;
unsigned int zeroByte = 0;
NSMutableData *commandData = [NSMutableData data];
// 动态库 command的内容
[commandData appendBytes:&command length:sizeof(struct dylib_command)];
// 动态库的路径字符串
[commandData appendData:[dylibPath dataUsingEncoding:NSASCIIStringEncoding]];
// 默认补0
[commandData appendBytes:&zeroByte length:padding];
// remove enough null bytes to account of our inserted data
// 这部分内容用0覆盖,最后一个参数传0就是指定覆盖区间就是Range的length
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(macho.offset + macho.header.sizeofcmds + macho.size, commandData.length)
withBytes:0
length:0];
// insert the data
// 添加data
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(lastOffset, 0) withBytes:commandData.bytes length:commandData.length];
// fix the existing header
// 元数据的修改
macho.header.ncmds += 1;
macho.header.sizeofcmds += command.cmdsize;
// this is safe to do in 32bit because the 4 bytes after the header are still being put back
// 替换mach的header部分
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(macho.offset, sizeof(macho.header)) withBytes:&macho.header];
return YES;
}效果
最后是加载在LC_LOAD_DYLIB这块
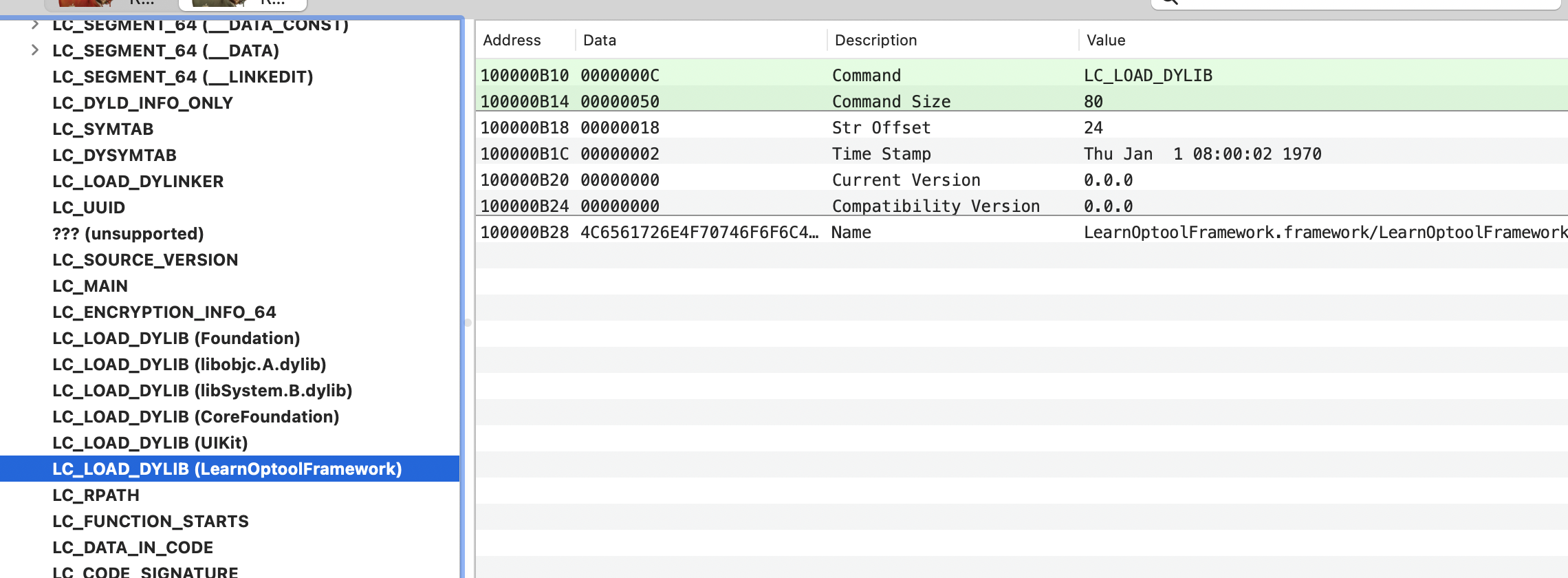
insertLoadEntryIntoBinary函数
objc
// 替换的时候有个lastOffset
[binary replaceBytesInRange:NSMakeRange(lastOffset, 0) withBytes:commandData.bytes length:commandData.length];
// 上面检测是否是重复添加时,会去计算
if (binaryHasLoadCommandForDylib(binary, dylibPath, &lastOffset, macho)) {
objc
...
// 只有这个LC_LOAD_DYLIB命令会修改loadOffset
case LC_LOAD_DYLIB: {
struct dylib_command command = *(struct dylib_command *)(binary.bytes + binary.currentOffset);
char *name = (char *)[[binary subdataWithRange:NSMakeRange(binary.currentOffset + command.dylib.name.offset, command.cmdsize - command.dylib.name.offset)] bytes];
if ([@(name) isEqualToString:dylib]) {
*lastOffset = (unsigned int)binary.currentOffset;
return YES;
}
binary.currentOffset += size;
loadOffset = (unsigned int)binary.currentOffset;
break;
}
...
// 这个lastOffset 就是最后一个LC_LOAD_DYLIB的位置
if (lastOffset != NULL)
*lastOffset = loadOffset;optool 添加有限制,但是LoadCommand末尾到代码部分的空间对添加几条命令还是足够的