假设有这样一个请求:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/register?name=zhangsan&password=123&email=zhangsan@powernode.com 在SpringMVC中应该如何获取请求提交的数据呢?
在SpringMVC中又应该如何获取请求头信息呢?
在SpringMVC中又应该如何获取客户端提交的Cookie数据呢?
一、准备
1.创建模块,添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.powernode.springmvc</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc-003</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!--springmvc依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>6.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!--logback依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--servlet依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--thymeleaf和spring6整合的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring6</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>21</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>21</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
</project>2.添加web支持

3.编写web.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_6_0.xsd"
version="6.0">
<!--前端控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--通过初始化参数来指定springmvc配置文件的路径和名字。-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--在服务器启动的时候初始化DispatcherServlet,提高第一次访问的效率-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>4.创建UserController

5.编写springmvc.xml

6.编写register.html文件

7.部署测试

二、使用原生的Servlet API进行获取
原生的Servlet API指的是:HttpServletRequest 在SpringMVC当中,一个Controller类中的方法参数上如果有HttpServletRequest,SpringMVC会自动将**当前请求对象**传递给这个参数,因此我们可以通过这个参数来获取请求提交的数据。测试一下。
在 register.html 中准备一个注册的表单:

接下来在控制器添加一个方法来处理这个注册的请求:

提供视图页面:

测试:


这样通过Servlet原生的API获取到提交的数据。但是这种方式不建议使用,因为方法的参数依赖Servlet原生API,Controller的测试将不能单独测试,必须依赖WEB服务器才能测试。另外,换句话说,如果在SpringMVC中使用了原生的Servlet,你为什么还要用SpringMVC框架呢!!!!!
三、使用RequestParam注解标注
1.RequestParam注解的基本使用
RequestParam注解作用:将请求参数与方法上的形参映射。



注意:对于@RequestParam注解来说,属性有value和name,这两个属性的作用相同,都是用来指定提交数据的name。

2.RequestParam注解的required属性

required属性用来设置该方法参数是否为必须的。
默认情况下,这个参数为 `true`,表示方法参数是必需的。如果请求中缺少对应的参数,则会抛出异常。
可以将其设置为`false`,false表示不是必须的,如果请求中缺少对应的参数,则方法的参数为null。
测试,修改register方法,如下:
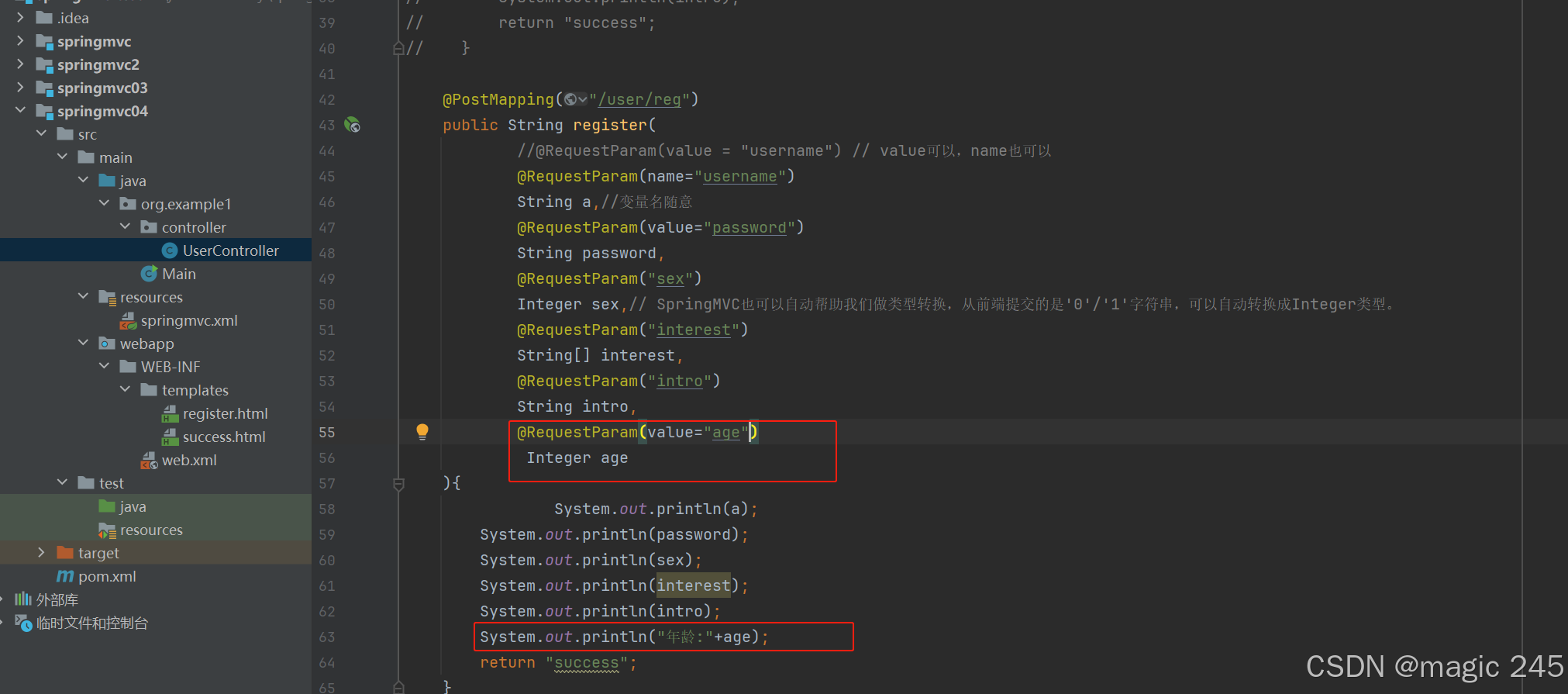
添加了一个 age 形参,没有指定 required 属性时,默认是true,表示必需的,但前端表单中没有年龄age,我们来看报错信息:


错误信息告诉我们:参数age是必需的。没有提供这个请求参数,HTTP状态码 400
如果将 required 属性设置为 false。则该参数则不是必须的,如果请求参数仍然未提供时,我们来看结果:



通过测试得知,如果一个参数被设置为不是必需的,当没有提交对应的请求参数时,形参默认值null
3.RequestParam注解的defaultValue属性
defaultValue属性用来设置形参的默认值,当`没有提供对应的请求参数`或者`请求参数的值是空字符串""`的时候,方法的形参会采用默认值。




四、依靠控制器方法上的形参名来接收
@RequestParam 这个注解是可以省略的,如果方法形参的名字和提交数据时的name相同,则 @RequestParam 可以省略。

但有一个前提:如果你采用的是Spring6+版本,你需要在pom.xml文件中指定编译参数'-parameter',配置如下:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.12.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>21</source>
<target>21</target>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>注意:如果你使用的是Spring5的版本,以上的配置是不需要的。
Controller中的方法只需要这样写:形参的名字必须和提交的数据的name一致!!!!! 
测试结果


五、使用POJO类/JavaBean接收请求参数
以上方式大家可以看到,当提交的数据非常多时,方法的形参个数会非常多,这不是很好的设计。
在SpringMVC中也可以使用POJO类/JavaBean来接收请求参数。不过有一个非常重要的要求:POJO类的属性名必须和请求参数的参数名保持一致。提供以下的JavaBean:
package org.example1.pojo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer sex;
private String[] interest;
private String intro;
private Integer age;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(Integer sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String[] getInterest() {
return interest;
}
public void setInterest(String[] interest) {
this.interest = interest;
}
public String getIntro() {
return intro;
}
public void setIntro(String intro) {
this.intro = intro;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
", interest=" + Arrays.toString(interest) +
", intro='" + intro + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}在控制器方法的形参位置上使用javabean来接收请求参数:

执行结果:


底层的实现原理:反射机制。先获取请求参数的名字,因为请求参数的名字就是JavaBean的属性名,通过这种方式给对应的属性赋值。
请求参数是否可以赋值到JavaBean对应的属性上,不是取决于属性名,而是setter方法名。
六、RequestHeader注解
该注解的作用是:将请求头信息映射到方法的形参上。 和RequestParam注解功能相似,RequestParam注解的作用:将请求参数映射到方法的形参上。 当然,对于RequestHeader注解来说,也有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,和RequestParam一样,这里就不再赘述了。
测试:

执行结果:


七、CookieValue注解
该注解的作用:将请求提交的Cookie数据映射到方法形参上 同样是有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue
前端页面中编写发送cookie的代码:
<script type="text/javascript">
function sendCookie(){
document.cookie = "id=123456789; expires=Thu, 18 Dec 2025 12:00:00 UTC; path=/";
document.location = "/springmvc/user/reg";
}
</script>
<button onclick="sendCookie()">向服务器端发送Cookie</button>后端UserController代码:


八、请求的中文乱码问题
1.get请求乱码
get请求数据在URI后面提交,这个乱码问题怎么解决呢?
解决办法是找到 CATALINA_HOME/config/server.xml文件,找到其中配置端口号的标签<Connector>,在该标签中添加 URIEncoding="UTF-8"。
但是对于高版本的Tomcat服务器来说,是不需要设置的,例如Tomcat10,Tomcat9,有如下的默认配置,在默认情况下URIEncoding使用的就是UTF-8的编码方式。

但对于低版本的Tomcat服务器,例如:Tomcat8。URIEncoding的默认配置是ISO-8859-1,因此在Tomcat8中需要手动配置server.xml文件:

配置如下:


2.post请求乱码
post请求是解决请求体的中文乱码问题。解决办法大家都知道:
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");同样,对于高版本的Tomcat10服务器来说,针对请求体中的字符编码也是配置好的,默认也是采用了UTF-8,中文乱码问题也解决了,在这个文件中配置的:apache-tomcat-10.1.19\conf\web.xml 配置内容如下

通过以上配置可以看到,Tomcat10对请求和响应都设置了默认的字符编码方式为UTF-8 一定要注意:Tomcat9以及之前的版本,以上的配置是没有的。
有可能很多同学使用的不是Tomcat10,如果不是Tomcat10,则会出现乱码问题,我们来模拟一下乱码的产生,将apache-tomcat-10.1.19\conf\web.xml文件中的UTF-8配置修改为ISO-8859-1:

一定要重启Tomcat10,新的配置才能生效
怎么样才能在DispatcherServlet之前执行request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8")呢?没错,我相信大家想到了:过滤器Filter。过滤器Filter可以在Servlet执行之前执行。有同学又说了:监听器不行吗?不行。因为我们需要对每一次请求解决乱码,而监听器只在服务器启动阶段执行一次。因此这里解决每一次请求的乱码问题,应该使用过滤器Filter。并且,告诉大家一个好消息,SpringMVC已经将这个字符编码的过滤器提前写好了,我们直接配置好即可:CharacterEncodingFilter,我们一起看一下它的源码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import jakarta.servlet.FilterChain;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
/**
* Servlet Filter that allows one to specify a character encoding for requests.
* This is useful because current browsers typically do not set a character
* encoding even if specified in the HTML page or form.
*
* <p>This filter can either apply its encoding if the request does not already
* specify an encoding, or enforce this filter's encoding in any case
* ("forceEncoding"="true"). In the latter case, the encoding will also be
* applied as default response encoding (although this will usually be overridden
* by a full content type set in the view).
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 15.03.2004
* @see #setEncoding
* @see #setForceEncoding
* @see jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#setCharacterEncoding
* @see jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse#setCharacterEncoding
*/
public class CharacterEncodingFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Nullable
private String encoding;
private boolean forceRequestEncoding = false;
private boolean forceResponseEncoding = false;
/**
* Create a default {@code CharacterEncodingFilter},
* with the encoding to be set via {@link #setEncoding}.
* @see #setEncoding
*/
public CharacterEncodingFilter() {
}
/**
* Create a {@code CharacterEncodingFilter} for the given encoding.
* @param encoding the encoding to apply
* @since 4.2.3
* @see #setEncoding
*/
public CharacterEncodingFilter(String encoding) {
this(encoding, false);
}
/**
* Create a {@code CharacterEncodingFilter} for the given encoding.
* @param encoding the encoding to apply
* @param forceEncoding whether the specified encoding is supposed to
* override existing request and response encodings
* @since 4.2.3
* @see #setEncoding
* @see #setForceEncoding
*/
public CharacterEncodingFilter(String encoding, boolean forceEncoding) {
this(encoding, forceEncoding, forceEncoding);
}
/**
* Create a {@code CharacterEncodingFilter} for the given encoding.
* @param encoding the encoding to apply
* @param forceRequestEncoding whether the specified encoding is supposed to
* override existing request encodings
* @param forceResponseEncoding whether the specified encoding is supposed to
* override existing response encodings
* @since 4.3
* @see #setEncoding
* @see #setForceRequestEncoding(boolean)
* @see #setForceResponseEncoding(boolean)
*/
public CharacterEncodingFilter(String encoding, boolean forceRequestEncoding, boolean forceResponseEncoding) {
Assert.hasLength(encoding, "Encoding must not be empty");
this.encoding = encoding;
this.forceRequestEncoding = forceRequestEncoding;
this.forceResponseEncoding = forceResponseEncoding;
}
/**
* Set the encoding to use for requests. This encoding will be passed into a
* {@link jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#setCharacterEncoding} call.
* <p>Whether this encoding will override existing request encodings
* (and whether it will be applied as default response encoding as well)
* depends on the {@link #setForceEncoding "forceEncoding"} flag.
*/
public void setEncoding(@Nullable String encoding) {
this.encoding = encoding;
}
/**
* Return the configured encoding for requests and/or responses.
* @since 4.3
*/
@Nullable
public String getEncoding() {
return this.encoding;
}
/**
* Set whether the configured {@link #setEncoding encoding} of this filter
* is supposed to override existing request and response encodings.
* <p>Default is "false", i.e. do not modify the encoding if
* {@link jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getCharacterEncoding()}
* returns a non-null value. Switch this to "true" to enforce the specified
* encoding in any case, applying it as default response encoding as well.
* <p>This is the equivalent to setting both {@link #setForceRequestEncoding(boolean)}
* and {@link #setForceResponseEncoding(boolean)}.
* @see #setForceRequestEncoding(boolean)
* @see #setForceResponseEncoding(boolean)
*/
public void setForceEncoding(boolean forceEncoding) {
this.forceRequestEncoding = forceEncoding;
this.forceResponseEncoding = forceEncoding;
}
/**
* Set whether the configured {@link #setEncoding encoding} of this filter
* is supposed to override existing request encodings.
* <p>Default is "false", i.e. do not modify the encoding if
* {@link jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getCharacterEncoding()}
* returns a non-null value. Switch this to "true" to enforce the specified
* encoding in any case.
* @since 4.3
*/
public void setForceRequestEncoding(boolean forceRequestEncoding) {
this.forceRequestEncoding = forceRequestEncoding;
}
/**
* Return whether the encoding should be forced on requests.
* @since 4.3
*/
public boolean isForceRequestEncoding() {
return this.forceRequestEncoding;
}
/**
* Set whether the configured {@link #setEncoding encoding} of this filter
* is supposed to override existing response encodings.
* <p>Default is "false", i.e. do not modify the encoding.
* Switch this to "true" to enforce the specified encoding
* for responses in any case.
* @since 4.3
*/
public void setForceResponseEncoding(boolean forceResponseEncoding) {
this.forceResponseEncoding = forceResponseEncoding;
}
/**
* Return whether the encoding should be forced on responses.
* @since 4.3
*/
public boolean isForceResponseEncoding() {
return this.forceResponseEncoding;
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String encoding = getEncoding();
if (encoding != null) {
if (isForceRequestEncoding() || request.getCharacterEncoding() == null) {
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
if (isForceResponseEncoding()) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}最核心的方法是:
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String encoding = getEncoding();
if (encoding != null) {
if (isForceRequestEncoding() || request.getCharacterEncoding() == null) {
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
if (isForceResponseEncoding()) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}分析以上核心方法得知该过滤器对请求和响应都设置了字符编码方式。
-
当
强行使用请求字符编码方式为true时,或者请求对象的字符编码方式为null时,设置请求的字符编码方式。 -
当
强行使用响应字符编码方式为true时,设置响应的字符编码方式。
根据以上代码,可以得出以下配置信息,在web.xml文件中对过滤器进行如下配置:
<!--字符编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>注意:针对于我们当前的Tomcat10的配置来说,它有默认的字符集ISO-8859-1,因此以下在web.xml文件中的配置是不能缺少的:
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>如果缺少它,仍然是会存在乱码问题的。自行测试一下!!!!