前置知识
什么是HID?
HID(Human Interface Device)是直接与人交互的电子设备,通过标准化协议实现用户与计算机或其他设备的通信,典型代表包括键盘、鼠标、游戏手柄等。
为什么HID要与qt进行通信?
我这里的应用场景是数位板与我自己写的上位机进行通信,用户可以在上位机软件中手动设置数位板上按键代表的快捷键。
如何知道当前HID设备的VID,PID?
- 打开 设备管理器 ,找到您的设备(通常在 人体学输入设备 或 通用串行总线设备 类别下)。
- 右键点击设备 -> 属性 -> 事件选项卡
如何通信?
1. 引入 hidapi 库
hidapi库是一个第三方库需要下载。下载完编译之后把 hidapi.h,hidapi.dll ,hidapi.lib放到项目根目录下。
hid设备初始化有以下几个步骤:
2. 初始化 hidapi
cpp
hid_init()3. 枚举和选择设备
cpp
void enumerateDevices() {
struct hid_device_info *devs = hid_enumerate(0x0, 0x0); // 参数为VID和PID,0x0表示匹配所有
struct hid_device_info *cur_dev = devs;
while (cur_dev) {
printf("Device Found\n type: %04hx %04hx\n path: %s\n serial_number: %ls",
cur_dev->vendor_id, cur_dev->product_id, cur_dev->path, cur_dev->serial_number);
printf("\n");
printf(" Manufacturer: %ls\n", cur_dev->manufacturer_string);
printf(" Product: %ls\n", cur_dev->product_string);
printf(" Release: %hx\n", cur_dev->release_number);
printf(" Interface Number: %d\n\n", cur_dev->interface_number);
cur_dev = cur_dev->next;
}
hid_free_enumeration(devs);
}4. 打开设备
cpp
hid_device *handle;
handle = hid_open(0x1234, 0x5678, NULL); // 替换为设备的VID和PID5. 设置非阻塞模式(可选)
cpp
int res = hid_set_nonblocking(handle, 1); // 参数为1表示非阻塞模式
if (res < 0) {
// 处理设置失败的情况
}6. 读取和写入数据
cpp
// 读取数据
unsigned char buf[256];
int res = hid_read(handle, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (res < 0) {
// 处理读取错误
} else {
// 处理读取到的数据
}
// 写入数据
unsigned char data[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x02}; // 示例数据
res = hid_write(handle, data, sizeof(data));
if (res < 0) {
// 处理写入错误
}7. 关闭设备和释放资源
cpp
hid_close(handle);
hid_exit();示例代码整合
cpp
void MainWindow::HidInit()
{
// 1. 初始化HIDAPI
if (hid_init() != 0) {
qDebug() << "[错误] HIDAPI初始化失败";
return;
}
else{
qDebug() << "[正确] HIDAPI初始化成功";
}
// 2. 枚举设备
qDebug() << "[调试] 开始枚举HID设备...";
hid_device_info *devs = hid_enumerate(0x0, 0x0);
if (!devs) {
qDebug() << "[错误] 无法枚举HID设备,可能没有HID设备连接";
hid_exit();
return;
}
hid_device_info *cur_dev = devs;
char* devicePath = nullptr;
bool deviceFound = false;
int deviceCount = 0; // 用于统计发现的HID设备数量
qDebug() << "[调试] 开始遍历HID设备列表...";
while (cur_dev) {
deviceCount++;
// 打印所有HID设备信息,用于调试
qDebug().nospace() << "[调试] 设备 #" << deviceCount
<< ": VID=0x" << QString::number(cur_dev->vendor_id, 16).toUpper()
<< ", PID=0x" << QString::number(cur_dev->product_id, 16).toUpper();
// << ", 路径=" << QString::fromWCharArray(cur_dev->path);
if (cur_dev->vendor_id == TARGET_VID && cur_dev->product_id == TARGET_PID) {
devicePath = _strdup(cur_dev->path);
deviceFound = true;
qDebug() << "\n[信息] 找到目标设备:";
qDebug() << "路径:" << devicePath;
qDebug() << "制造商:" << (cur_dev->manufacturer_string ? QString::fromWCharArray(cur_dev->manufacturer_string) : "N/A");
qDebug() << "产品名:" << (cur_dev->product_string ? QString::fromWCharArray(cur_dev->product_string) : "N/A");
qDebug() << "接口号:" << cur_dev->interface_number;
break;
}
cur_dev = cur_dev->next;
}
qDebug() << "[调试] 遍历完成,共发现" << deviceCount << "个HID设备";
hid_free_enumeration(devs);
if (!deviceFound) {
qDebug() << "[错误] 未找到目标设备 (VID: 0x" << QString::number(TARGET_VID, 16).toUpper()
<< ", PID: 0x" << QString::number(TARGET_PID, 16).toUpper() << ")";
hid_exit();
return;
}
// 3. 打开设备
qDebug() << "[调试] 尝试打开目标设备...";
hid_device* handle = hid_open_path(devicePath);
if (!handle) {
qDebug() << "[错误] 无法打开设备:" << QString::fromWCharArray(hid_error(nullptr));
free(devicePath);
hid_exit();
return;
}
// 3. 打开设备
handle = hid_open_path(devicePath);
if (!handle) {
qDebug() << "[错误] 无法打开设备:" << QString::fromWCharArray(hid_error(nullptr));
free(devicePath);
hid_exit();
return;
}
// 设置非阻塞模式
hid_set_nonblocking(handle, 1);
qDebug() << "\n[信息] 设备已成功打开";
// 4. 尝试通信
const int REPORT_SIZE = 65; // 64字节数据 + 1字节报告ID
unsigned char buf[REPORT_SIZE] = {0};
// 尝试不同报告ID (0x00-0xFF)
for (int report_id = 0x00; report_id <= 0xFF; report_id++) {
// 4.1 尝试特性报告
buf[0] = report_id;
buf[1] = 0x01; // 示例命令
qDebug() << "\n[调试] 尝试报告ID: 0x" << QString::number(report_id, 16).toUpper();
int res = hid_send_feature_report(handle, buf, REPORT_SIZE);
if (res > 0) {
qDebug() << "[成功] 特性报告发送成功 (ID: 0x"
<< QString::number(report_id, 16).toUpper() << ")";
break;
} else if (report_id == 0xFF) {
qDebug() << "[警告] 所有特性报告尝试失败";
}
// 4.2 尝试输出报告
res = hid_write(handle, buf, REPORT_SIZE);
if (res > 0) {
qDebug() << "[成功] 输出报告发送成功 (ID: 0x"
<< QString::number(report_id, 16).toUpper() << ")";
break;
} else if (report_id == 0xFF) {
qDebug() << "[警告] 所有输出报告尝试失败";
}
}
// 5. 读取响应 (5秒超时)
qDebug() << "\n[信息] 等待设备响应...";
int timeout_ms = 5000;
QElapsedTimer timer;
timer.start();
while (timer.elapsed() < timeout_ms) {
int res = hid_read(handle, buf, REPORT_SIZE);
if (res > 0) {
qDebug() << "[成功] 收到" << res << "字节数据:";
// 打印接收到的数据 (十六进制格式)
QString hexData;
for (int i = 0; i < res; i++) {
hexData += "0x" + QString::number(buf[i], 16).toUpper().rightJustified(2, '0') + " ";
if ((i+1) % 8 == 0) hexData += "\n";
}
qDebug() << hexData;
break;
} else if (res == 0) {
QThread::msleep(100); // 避免CPU占用过高
} else {
qDebug() << "[错误] 读取失败:" << QString::fromWCharArray(hid_error(handle));
break;
}
}
if (timer.elapsed() >= timeout_ms) {
qDebug() << "[警告] 读取超时,未收到响应";
}
// 6. 清理资源
hid_close(handle);
free(devicePath);
hid_exit();
qDebug() << "\n[信息] HID通信结束";
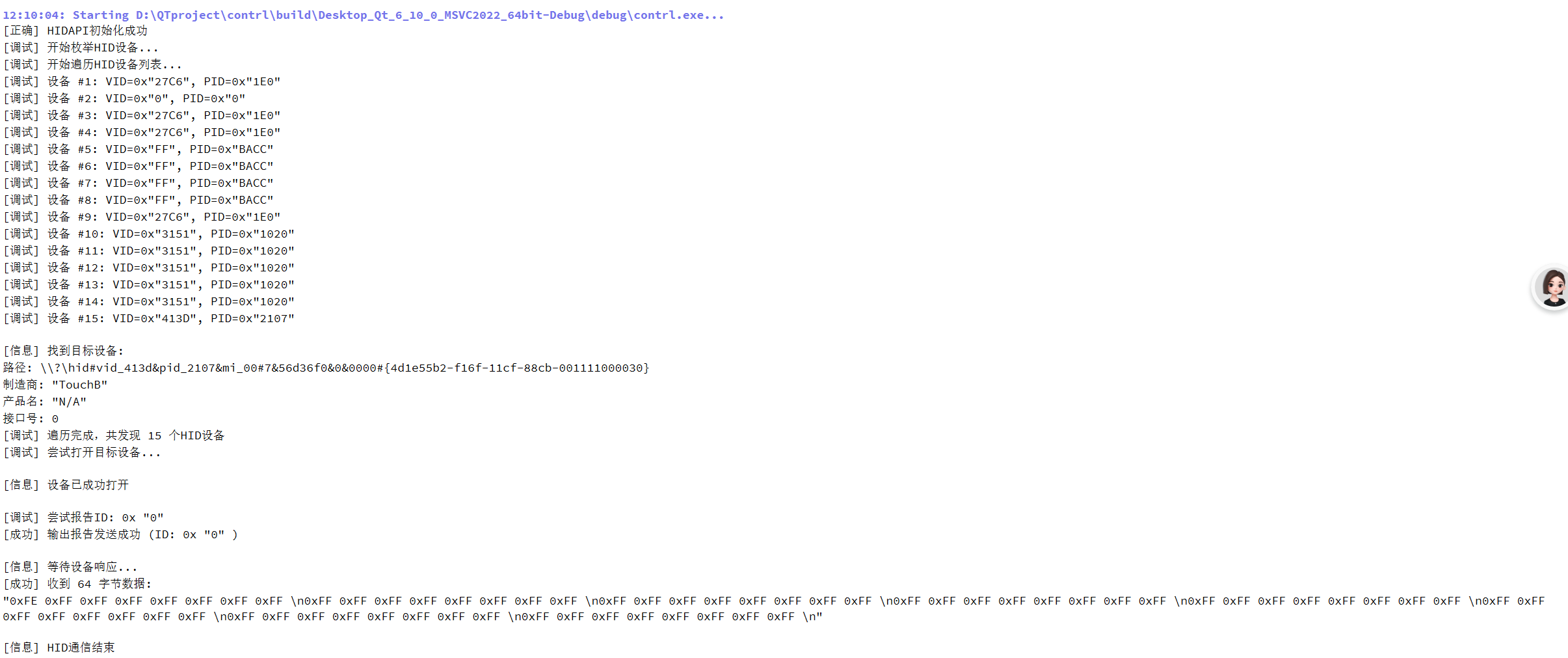
}运行效果演示(我接入的是wacom数位板):
全是0xFF为未激活状态(初始状态)。
总结操作流程
- 确认设备功能与协议:明确设备是输入型(主动上报)还是命令型(需指令触发)。
- 发送测试指令:若无文档,通过简单指令试探设备响应模式。
- 解析数据结构:根据响应数据的变化规律,逆向推导字节含义(如坐标、状态、校验等)。
- 编写业务逻辑:基于解析结果,实现数据处理或控制功能(如鼠标模拟、设备配置等)。
解析报告数据
如何解析
用以下结构来存储报告:
cpp
struct TabletData {
quint8 reportId; // 报告ID
quint16 x; // X坐标(0-最大值)
quint16 y; // Y坐标(0-最大值)
quint16 pressure; // 压力值(0-最大值)
QList<int> buttons; // 按下的按钮列表(按钮编号从1开始)
};创建一个TabletData 类型的函数:
该函数对报告进行解析,第0字节是报告ID,第1字节是按钮位置........
cpp
TabletData HidManager::parseTabletData(const QByteArray& data) {
TabletData result;
if (data.isEmpty()) return result;
result.reportId = data[0];
switch (result.reportId) {
case 0x11: // 按钮报告(假设按钮在字节1-2)
for (int byteIdx = 1; byteIdx < 3; byteIdx++) {
if (byteIdx >= data.size()) break;
unsigned char byte = data[byteIdx];
for (int bitIdx = 0; bitIdx < 8; bitIdx++) {
if ((byte & (1 << bitIdx)) != 0) { // 1表示按下
result.buttons.append((byteIdx - 1) * 8 + bitIdx + 1);
}
}
}
break;
case 0x10: // **关键修改**:坐标/压力报告ID改为0x10
// 解析坐标和压力(假设坐标在字节1-4,压力在字节5-6)
if (data.size() >= 5) {
// 小端序解析:低字节在前,高字节在后
result.x = static_cast<quint16>(data[1]) | (static_cast<quint16>(data[2]) << 8);
result.y = static_cast<quint16>(data[3]) | (static_cast<quint16>(data[4]) << 8);
}
if (data.size() >= 7) {
result.pressure = static_cast<quint16>(data[5]) | (static_cast<quint16>(data[6]) << 8);
}
result.buttons.clear(); // 坐标报告不含按钮,清空列表
break;
default:
qWarning() << "未知报告ID:" << QString::number(result.reportId, 16);
break;
}
return result;
}写一个打印输出函数
cpp
void HidManager::handleHidData(const QByteArray& data)
{
// 数据为空或与上次完全相同则直接返回
static QByteArray lastDataFrame;
if (data.isEmpty() || data == lastDataFrame) return;
lastDataFrame = data;
// 解析数据到结构体
TabletData currentData = parseTabletData(data);
// 打印原始数据和解析结果(调试用)
if (debugMode) { // 可添加调试开关
QString hexData;
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
hexData += "0x" + QString::number((unsigned char)data[i], 16).toUpper().rightJustified(2, '0') + " ";
if ((i+1) % 8 == 0) hexData += "\n";
}
qDebug() << "收到新数据:" << hexData;
qDebug() << "解析后数据:"
<< "报告ID:" << QString::number(currentData.reportId, 16)
<< "坐标: (" << currentData.x << ", " << currentData.y << ")"
<< "压力:" << currentData.pressure
<< "按钮:" << currentData.buttons;
}
// 静态变量存储上次数据,用于检测变化
static TabletData lastData;
// 检查关键数据是否变化(按钮、坐标、压力)
bool isButtonChanged = (currentData.buttons != lastData.buttons);
bool isPositionChanged = (currentData.x != lastData.x || currentData.y != lastData.y);
bool isPressureChanged = (currentData.pressure != lastData.pressure);
// 根据变化类型发送不同信号
if (isButtonChanged) {
emit buttonStateChanged(currentData.buttons);
}
if (isPositionChanged || isPressureChanged) {
emit tabletMoved(currentData.x, currentData.y, currentData.pressure);
}
// 更新上次数据缓存
lastData = currentData;
}打印输出:
拿wacom数位板举例。以下是连接wacom数位板之后,数位笔滑动之后wacom数位板发送过来的报告:
解析内容
报告第一个字节为报告ID, 用来区分用户进行的是什么操作**。**
当报告ID为0X10时代表坐标移动
当报告ID为0X11时代表按键按下
例:
按下第一个按键,此时报告ID为0x11,表示按键事件发生。此时第2个字节发生了变化,也就是第一个字节被按下了:

当用数位笔在数位板上滑动之后收到如下报告:
报告ID为0x10,表示坐标发生变化。坐标在字节1-4,压力在字节5-6:



HID设备按键与Qt界面UI按键的快捷键绑定实现
流程图