纯C#软实现openGL(V0.1),黑盒变白盒
为了彻底掌握openGL,做一个openGL的软实现(命名为SoftGLImpl)是必要的。(而非仅仅调用opengl32.dll)
openGL API的每个函数,都是在按下述方式执行3D渲染算法:
csharp
using GLsizei = System.Int32;
using GLuint = System.UInt32;
using GLenum = System.UInt32;
public unsafe partial class SoftGL { // class for openGL API
// 以glGenBuffers为例
static void glGenBuffers(GLsizei n, GLuint[] names) {
RenderContext? context = SoftGLImpl.SoftGL.GetCurrentContextObj();
if (context == null) { return; }// 若不先创建openGL上下文,则直接调用此API是无效的。
context.GenBuffers(n, names);// 安排数据,保存到openGL上下文中。
}
// 以glDrawElements为例
public static void glDrawElements(GLenum mode, GLsizei count, GLenum type, IntPtr indices) {
RenderContext? context = SoftGLImpl.SoftGL.GetCurrentContextObj();
if (context == null) { return; }// 若不先创建openGL上下文,则直接调用此API是无效的。
context.DrawElements(mode, count, type, indices);// 执行渲染过程,结果将被保存到openGL上下文中。
}
}这些函数的作用,要么是安排buffer/shader/texture数据、各种选项,要么是执行渲染过程。整个渲染过程(pipeline)如下图所示:
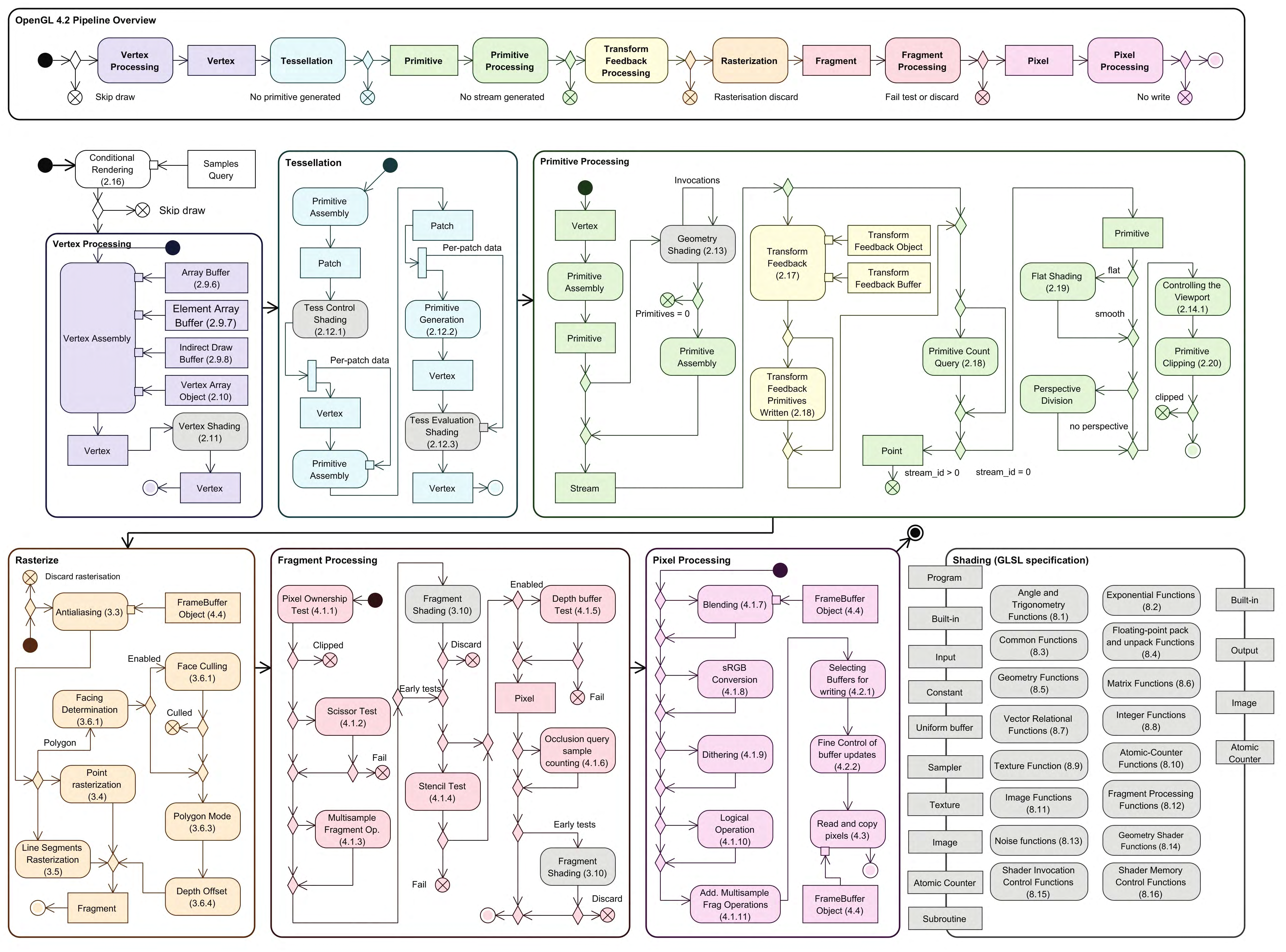
实现openGL就是要实现图中的全部过程。本文重点介绍下列问题:
- 如何让shader运行起来
- 如何实现pipeline各步骤中的算法
- 如何提升纯C#软实现的效率
如何让shader运行起来
所谓modern openGL,其核心特点是利用shader并行计算的办法来提高3D图形渲染的效率和效果。shader是一段GLSL代码,类似C语言,所以我必须做一个简单的编译器。https://www.cnblogs.com/bitzhuwei/p/18631231是我做好的GLSL编译器前端。这样,我就可以用下面的思路解决"如何让shader运行起来"的问题:
csharp
// 1. 解析shader字符串,得到其语义信息
var parser = new ShaderParser();
string source = File.ReadAllText("blinnphong.vert");
List<Token> tokens = parser.Analyze(source);
SyntaxTree tree = parser.Parse(tokens);
var translation_unit = parser.Extract(tree, tokens, source);
// 2. 将语义信息转换为C#代码
var builder = new StringBuilder();
using (var writer = new StringWriter(builder)) {
var config = new BlankConfig(inlineBlank: 0, forceNewline: false);
var context = new FormatContext(tabUnit: 4, tabCount: 0, tokens);
translation_unit.Transform(config, writer, context);
}
var csCode = builder.ToString();
// 3. 动态编译C#代码并调用,即模拟GPU运行shader的过程
var script = CSharpScript.Create<VertexShaderCode>(csCode);
var result = await script.RunAsync();主要的工作量在于:
-
编写GLSL编译器前端
详情可参考https://www.cnblogs.com/bitzhuwei/p/18683262/my-own-parsers。
-
根据语法树生成C#版的shader代码。由于GLSL和C#的语法书写差异,需要处理下列差异:
点击查看代码
csharp
// from GLSL
struct { mat4 model; mat4 view; mat4 projection; } va[3], vb;
// to C#
struct struct0 { mat4 model; mat4 view; mat4 projection; }
struct0[] va = new struct0[3]; struct0 vb;
// from GLSL
layout(origin_upper_left, pixel_center_integer) in vec4 gl_FragCoord;
// to C#
[layout(values = [origin_upper_left, pixel_center_integer])]
[In]
vec4 gl_FragCoord;
// from GLSL
layout(std140, binding = 2) uniform Camera {
mat4 view;
mat4 projection;
};
// to C#
[layout(binding = 2, values = [std140])]
[uniform]
struct Camera字 {
mat4 view;
mat4 projection;
}
Camera字 Camera;- 为C#版的shader代码提供底层支持,这包括实现GLSL内置的变量(
gl_VertexID、gl_FragCoord等)、类型(vec4、mat4等)、函数(max、pow、mix)。
pipeline各步骤中的算法
pipeline很长,里面涉及的算法很多。每次调用glDrawElements()都是在执行pipeline。下面我们详细解释这里的各个步骤。
csharp
public static void glDrawElements(GLenum mode, GLsizei count, GLenum type, IntPtr indices) {
var context = SoftGL.GetCurrentContextObj();
if (context == null) { return; }
if (!Enum.IsDefined(typeof(DrawTarget), mode) || !Enum.IsDefined(typeof(DrawElementsType), type))
{ context.lastErrorCode = (uint)(ErrorCode.InvalidEnum); return; }
if (count < 0) { context.lastErrorCode = (uint)(ErrorCode.InvalidValue); return; }
// TODO: GL_INVALID_OPERATION is generated if a geometry shader is active
// and mode is incompatible with the input primitive type of the geometry shader in the currently installed program object.
// TODO: GL_INVALID_OPERATION is generated
// if a non-zero buffer object name is bound to an enabled array
// or the element array and the buffer object's data store is currently mapped.
var vao = context.currentVertexArrayObject; // data structure.
if (vao == null) { return; }
var program = context.currentShaderProgram; // algorithm.
if (program == null) { return; }
var indexBuffer = context.target2CurrentBuffer[(GLenum)BindBufferTarget.ElementArrayBuffer];
if (indexBuffer == null) { return; }
// execute vertex shader for each vertex!
Dictionary<uint, VertexCodeBase> vertexID2Shader = VertexShaderStage(
count, (DrawElementsType)type, indices, vao, program, indexBuffer);
var framebuffer = context.target2CurrentFramebuffer[(GLenum)BindFramebufferTarget.Framebuffer];
ClipSpace2NormalDeviceSpace(vertexID2Shader);
// linear interpolation.
ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList = LinearInterpolation(
context, (DrawTarget)mode, count, (DrawElementsType)type, indices, vao, program, indexBuffer, vertexID2Shader);
// execute fargment shader for each fragment!
FragmentShaderStage(program, fragmentList);
// TODO: Scissor test
// TODO: Multisampel fragment operations
// TODO: Stencil test
DepthTest(context, fragmentList);
// TODO: Blending
// TODO: Dithering
// TODO: Logical operations
// write fragments to framebuffer's colorbuffer attachment(s).
WriteFragments2Framebuffer(context, framebuffer, fragmentList);
}
private static void WriteFragments2Framebuffer(RenderContext context, GLFramebuffer framebuffer, ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList) {
if (framebuffer.ColorbufferAttachments == null) { return; }
uint[] drawBufferIndexes = framebuffer.DrawBuffers.ToArray();
Func<int, IntPtr, Fragment, bool> hasValidDepth;
var depthBuffer = framebuffer.DepthbufferAttachment;
GCHandle pin = new GCHandle(); IntPtr pDepthBuffer = IntPtr.Zero;
if (depthBuffer == null) { hasValidDepth = alwaysHasValidDepth; }
else {
switch (depthBuffer.Format) {
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT: hasValidDepth = hasValidDepth32float; break;
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT24: hasValidDepth = hasValidDepth24uint; break;
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT32: hasValidDepth = hasValidDepth32float; break;
default: throw new Exception("bug, fix this!");
}
pin = GCHandle.Alloc(depthBuffer.DataStore, GCHandleType.Pinned);
pDepthBuffer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
}
int width = context.viewport.w;
foreach (var fragment in fragmentList) {
if (fragment.discard) { continue; }
if (fragment.outVariables == null) { continue; }
if (!hasValidDepth(width, pDepthBuffer, fragment)) { continue; }
for (int i = 0; i < fragment.outVariables.Length && i < drawBufferIndexes.Length; i++) {
PassBuffer outVar = fragment.outVariables[i];
var attachment = framebuffer.ColorbufferAttachments[drawBufferIndexes[i].ToIndex()];
if (attachment != null) {
attachment.Set((int)fragment.gl_FragCoord.x, (int)fragment.gl_FragCoord.y, outVar);
}
}
}
}
private static int ByteLength(DrawElementsType type) {
int result = 0;
switch (type) {
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedByte: result = sizeof(byte); break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedShort: result = sizeof(ushort); break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedInt: result = sizeof(uint); break;
default: throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(typeof(DrawElementsType));
}
return result;
}vertex processing
这一步的任务:
①预备:找到要处理的vertex,为其挨个编号;
②计算:为每个vertex分别调用vertex shader的main()函数;
③持有:保存②的计算结果,供下一步使用。
点击查看代码 vertex processing
csharp
// vertex processing
private static unsafe Dictionary<uint, VertexCodeBase> VertexShaderStage(
int count, // how many elements to be rendered
DrawElementsType type,
IntPtr indices, // an offset of the first index in the buffer currently bound to GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER
GLVertexArrayObject vao, GLProgram program, GLBuffer indexBuffer) {
var vs = program.VertexShader;
uint vertexCount = GetVertexCount(vao, indexBuffer, type);
// gl_VertexID -> shader object
var vertexID2Shader = new Dictionary<uint, VertexCodeBase>((int)vertexCount);
// execute vertex shader for each vertex.
byte[] indexData = indexBuffer.Data;
int indexLength = indexData.Length / ByteLength(type);
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(indexData, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
int indexID = indices.ToInt32() / ByteLength(type);
for (var c = 0; c < count && indexID < indexLength; indexID++, c++) {
uint gl_VertexID = GetVertexID(pointer, type, indexID);
var instance = vs.CreateCodeInstance() as VertexCodeBase; // an executable vertex shader.
vertexID2Shader.Add(gl_VertexID, instance);
instance.gl_VertexID = (int)gl_VertexID; // setup gl_VertexID.
// setup "in SomeType varName;" vertex attributes.
Dictionary<uint, VertexAttribDesc> locVertexAttribDict = vao.LocVertexAttribDict;
foreach (PassVariable inVar in vs.name2inVar.Values) {
if (locVertexAttribDict.TryGetValue(inVar.location, out var desc)) {
byte[] dataStore = desc.vbo.Data;
int byteIndex = desc.GetDataIndex(gl_VertexID);
VertexAttribType vertexAttribType = (VertexAttribType)desc.dataType;
var value = dataStore.ToStruct(inVar.fieldInfo.FieldType, byteIndex);
inVar.fieldInfo.SetValue(instance, value);
}
}
// setup "uniform SomeType varName;" in vertex shader.
Dictionary<string, UniformValue> nameUniformDict = program.name2Uniform;
foreach (UniformVariable uniformVar in vs.Name2uniformVar.Values) {
string name = uniformVar.fieldInfo.Name;
if (nameUniformDict.TryGetValue(name, out var obj)) {
if (obj.value != null) {
uniformVar.fieldInfo.SetValue(instance, obj.value);
}
}
}
instance.main(); // execute vertex shader code.
}
pin.Free();
return vertexID2Shader;
}
// Get the vertex id at specified <paramref name="indexID"/> of the array represented by <paramref name="pointer"/>.
// The <paramref name="type"/> indicates the type of the array(byte[], ushort[] or uint[]).
private static unsafe uint GetVertexID(IntPtr pointer, DrawElementsType type, int indexID) {
uint gl_VertexID = uint.MaxValue;
switch (type) {
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedByte: {
byte* array = (byte*)pointer;
gl_VertexID = array[indexID];
}
break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedShort: {
ushort* array = (ushort*)pointer;
gl_VertexID = array[indexID];
}
break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedInt: {
uint* array = (uint*)pointer;
gl_VertexID = array[indexID];
}
break;
default: throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(typeof(DrawElementsType));
}
return gl_VertexID;
}
// How many vertexIDs are there in the specified <paramref name="byteArray"/>.
private static uint GetVertexIDCount(byte[] byteArray, DrawElementsType type) {
uint result = 0;
uint byteLength = (uint)byteArray.Length;
switch (type) {
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedByte: result = byteLength; break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedShort: result = byteLength / 2; break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedInt: result = byteLength / 4; break;
default: throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(typeof(DrawElementsType));
}
return result;
}
// Gets the maximum vertexID in the specified <paramref name="byteArray"/>.
private static unsafe uint GetMaxVertexID(byte[] byteArray, DrawElementsType type) {
int byteLength = byteArray.Length;
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(byteArray, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
uint gl_VertexID = 0;
switch (type) {
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedByte: {
byte* array = (byte*)pointer;
for (int i = 0; i < byteLength; i++) {
if (gl_VertexID < array[i]) { gl_VertexID = array[i]; }
}
}
break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedShort: {
ushort* array = (ushort*)pointer;
int length = byteLength / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (gl_VertexID < array[i]) { gl_VertexID = array[i]; }
}
}
break;
case DrawElementsType.UnsignedInt: {
uint* array = (uint*)pointer;
int length = byteLength / 4;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (gl_VertexID < array[i]) { gl_VertexID = array[i]; }
}
}
break;
default: throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(typeof(DrawElementsType));
}
pin.Free();
return gl_VertexID;
}
private static uint GetVertexCount(GLVertexArrayObject vao, GLBuffer indexBuffer, DrawElementsType type) {
uint vertexCount = 0;
VertexAttribDesc[] descs = vao.LocVertexAttribDict.Values.ToArray();
if (descs.Length > 0) {
int c = descs[0].GetVertexCount();
if (c >= 0) { vertexCount = (uint)c; }
}
else {
uint maxvertexID = GetMaxVertexID(indexBuffer.Data, type);
uint vertexIDCount = GetVertexIDCount(indexBuffer.Data, type);
vertexCount = Math.Min(maxvertexID, vertexIDCount);
}
return vertexCount;
}tessellation
primitive processing
transform feedback processing
rasterization
上一步得到了用vertex和其他参数描述的POINTS、LINES、TRIANGLES、QUADS,这一步要计算出它们会出现在哪些像素点上。
POINTS的光栅化
POINTS的光栅化过程最简单,因为不需要插值。
csharp
private static unsafe ConcurrentBag<Fragment> LinearInterpolationPoints(RenderContext context, int count, DrawElementsType type, IntPtr indices, GLVertexArrayObject vao, GLProgram program, GLBuffer indexBuffer, Dictionary<uint, VertexCodeBase> vertexID2Shader) {
var result = new System.Collections.Concurrent.ConcurrentBag<Fragment>();
byte[] indexData = indexBuffer.Data;
int indexLength = indexData.Length / ByteLength(type);
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(indexData, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
ivec4 viewport = context.viewport;
int indexID = indices.ToInt32() / ByteLength(type);
for (var c = 0; c < count && indexID < indexLength; indexID++, c++) {
uint gl_VertexID = GetVertexID(pointer, type, indexID);
var shaderObj = vertexID2Shader[gl_VertexID];
var fragCoord = new vec3(
(shaderObj.gl_Position.x + 1) / 2.0f * viewport.z + viewport.x,
(shaderObj.gl_Position.y + 1) / 2.0f * viewport.w + viewport.y,
(shaderObj.gl_Position.z + 1) / 2.0f * (float)(context.depthRangeFar - context.depthRangeNear)
+ (float)context.depthRangeNear);
var fragment = new Fragment(fragCoord, shaderObj);
result.Add(fragment);
}
pin.Free();
return result;
}LINES的光栅化
上一步得到的是LINE的两个端点的位置,现在需要通过插值确定LINE会出现在哪些像素Fragment上。
这用到了Bresenham算法。本项目提供了一个展示此算法效果的demo,如下图所示:
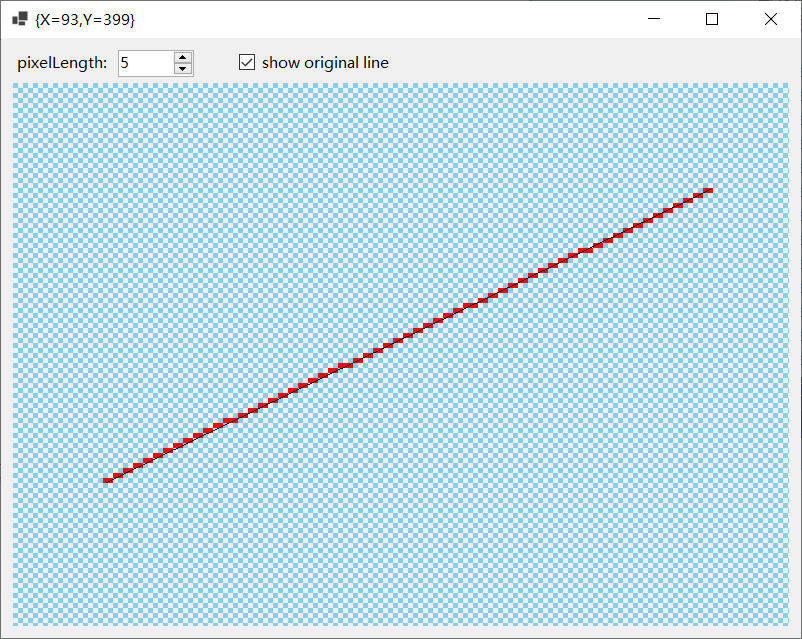
点击查看代码 Bresenham算法对LINE插值
csharp
private static void FindPixelsAtLine(vec3 start, vec3 end, List<Pixel3> pixels) {
if (start.x < end.x) { DoFindPixelsAtLine(start, end, pixels); }
else { DoFindPixelsAtLine(end, start, pixels); }
}
// from left(start) to right(end)
private static void DoFindPixelsAtLine(vec3 start, vec3 end, List<Pixel3> pixels) {
// now start.X <= end.X
if (start.y < end.y) { FindPixelsAtLine1(start, end, pixels); }
else { FindPixelsAtLine2(start, end, pixels); }
}
// from (0, height - 1)(start) to (width - 1, 0)(end)
private static void FindPixelsAtLine2(vec3 start, vec3 end, List<Pixel3> pixels) {
var x0 = (int)start.x; var y0 = (int)start.y;
var x1 = (int)end.x; var y1 = (int)end.y;
float dx = x1 - x0, dy = y0 - y1;
if (dx >= dy) {
float p = dy + dy - dx;
for (; x0 <= x1; x0++) {
var a = (x0 + 0.5f - start.x) / (end.x - start.x);
if (x0 == x1) { y0 = y1; }
pixels.Add(new Pixel3(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z)));
if (p > 0) {
y0 -= 1;
p = p + dy + dy - dx - dx;
}
else {
p = p + dy + dy;
}
}
}
else {
float p = dx + dx - dy;
for (; y0 >= y1; y0--) {
var a = (y0 + 0.5f - end.y) / (start.y - end.y);
if (y0 == y1) { x0 = x1; }
pixels.Add(new Pixel3(x0, y0, end.z + a * (start.z - end.z)));
if (p >= 0) {
x0 += 1;
p = p + dx + dx - dy - dy;
}
else {
p = p + dx + dx;
}
}
}
}
// from (0, 0)(start) to (width - 1, height - 1)(end)
private static void FindPixelsAtLine1(vec3 start, vec3 end, List<Pixel3> pixels) {
var x0 = (int)start.x; var y0 = (int)start.y;
var x1 = (int)end.x; var y1 = (int)end.y;
float dx = x1 - x0, dy = y1 - y0;
if (dx >= dy) {
float p = dy + dy - dx;
for (; x0 <= x1; x0++) {
var a = (x0 + 0.5f - start.x) / (end.x - start.x);
if (x0 == x1) { y0 = y1; }
pixels.Add(new Pixel3(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z)));
if (p >= 0) {
y0 += 1;
p = p + dy + dy - dx - dx;
}
else {
p = p + dy + dy;
}
}
}
else {
float p = dx + dx - dy;
for (; y0 <= y1; y0++) {
var a = (y0 + 0.5f - start.y) / (end.y - start.y);
if (y0 == y1) { x0 = x1; }// the last pixel
pixels.Add(new Pixel3(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z)));
if (p >= 0) {
x0 += 1;
p = p + dx + dx - dy - dy;
}
else {
p = p + dx + dx;
}
}
}
}TRIANGLES的光栅化
上一步得到的是TRIANGLE的三个端点的位置,现在需要通过插值确定TRIANGLE会出现在哪些像素Fragment上。
用Bresenham算法确定每一列里最上一个和最下一个像素的位置,就可以逐列确定全部Fragment,且便于并行计算。当然,也可以逐行扫描。
本项目提供了一个展示此算法效果的demo,如下图所示:
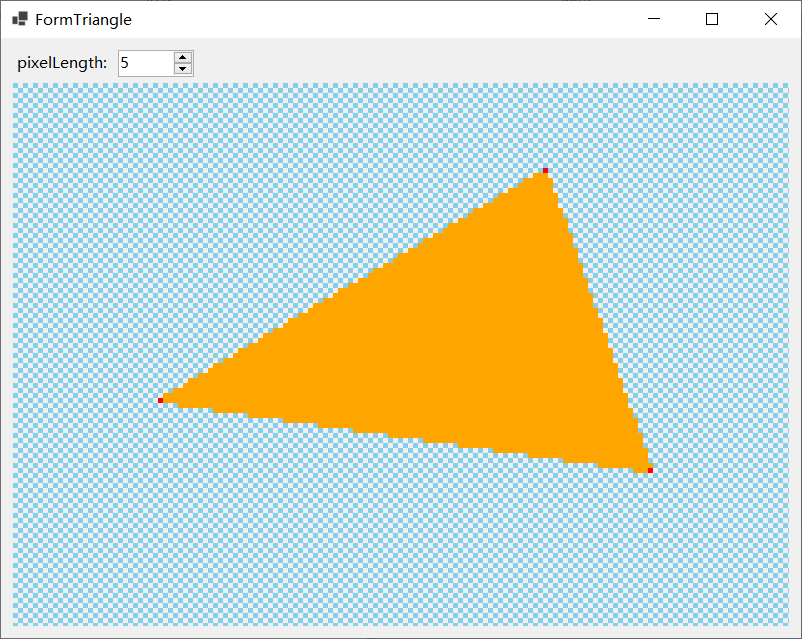
点击查看代码 借助Bresenham算法逐列扫描Fragment
csharp
unsafe private static void FindFragmentsInTriangle(
vec3 fragCoord0, vec3 fragCoord1, vec3 fragCoord2,
VertexCodeBase endpoints0, VertexCodeBase endpoints1, VertexCodeBase endpoints2,
ConcurrentBag<Fragment> result) {
int left = (int)fragCoord0.x, right = left;
if (left > (int)fragCoord1.x) { left = (int)fragCoord1.x; }
if (left > (int)fragCoord2.x) { left = (int)fragCoord2.x; }
if (right < (int)fragCoord1.x) { right = (int)fragCoord1.x; }
if (right < (int)fragCoord2.x) { right = (int)fragCoord2.x; }
var scanlines = new Scanline[right - left + 1];// we'll find the vertial scanlines
LocateScanlines(fragCoord0, fragCoord1, left, scanlines);
LocateScanlines(fragCoord1, fragCoord2, left, scanlines);
LocateScanlines(fragCoord2, fragCoord0, left, scanlines);
var matrix = new mat3(fragCoord0, fragCoord1, fragCoord2);
var inverseMat = CodeBase.inverse(matrix);
// way #1
for (int i = 0; i < scanlines.Length; i++) {
var scanline = scanlines[i];
var min = scanline.start; var max = scanline.end;
for (int y = min.y; y <= max.y; y++) {
float a = (min.y != max.y) ? (y + 0.5f - min.y) / (max.y - min.y) : (0);
float z = min.depth + a * (max.depth - min.depth);
var pixel = new vec3(min.x + 0.5f, y + 0.5f, z);// pixel.x += 0.5f; pixel.y += 0.5f;
vec3 p012 = inverseMat * pixel;
var fragment = new Fragment(pixel, endpoints0, endpoints1, endpoints2, p012.x, p012.y, p012.z);
result.Add(fragment);
}
}
}
private static void LocateScanlines(vec3 start, vec3 end,
int left, Scanline[] scanlines) {
if (start.x < end.x) { DoLocateScanlines(start, end, left, scanlines); }
else { DoLocateScanlines(end, start, left, scanlines); }
}
private static void DoLocateScanlines(vec3 start, vec3 end, int left, Scanline[] scanlines) {
// now start.x <= end.x
if (start.y < end.y) { LocateScanlines1(start, end, left, scanlines); }
else { LocateScanlines2(start, end, left, scanlines); }
}
// from (0, height - 1)(start) to (width - 1, 0)(end)
private static void LocateScanlines2(vec3 start, vec3 end, int left, Scanline[] scanlines) {
var x0 = (int)start.x; var y0 = (int)start.y;
var x1 = (int)end.x; var y1 = (int)end.y;
float dx = x1 - x0, dy = y0 - y1;
if (dx >= dy) {
float p = dy + dy - dx;
for (; x0 <= x1; x0++) {
var a = (x0 + 0.5f - start.x) / (end.x - start.x);
if (x0 == x1) { y0 = y1; }
{
var index = x0 - left;
scanlines[index].TryExtend(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z));
}
if (p > 0) {
y0 -= 1;
p = p + dy + dy - dx - dx;
}
else {
p = p + dy + dy;
}
}
}
else {
float p = dx + dx - dy;
for (; y0 >= y1; y0--) {
var a = (y0 + 0.5f - end.y) / (start.y - end.y);
if (y0 == y1) { x0 = x1; }
{
var index = x0 - left;
scanlines[index].TryExtend(x0, y0, end.z + a * (start.z - end.z));
}
if (p >= 0) {
x0 += 1;
p = p + dx + dx - dy - dy;
}
else {
p = p + dx + dx;
}
}
}
}
// from (0, 0)(start) to (width - 1, height - 1)(end)
private static void LocateScanlines1(vec3 start, vec3 end, int left, Scanline[] scanlines) {
var x0 = (int)start.x; var y0 = (int)start.y;
var x1 = (int)end.x; var y1 = (int)end.y;
float dx = x1 - x0, dy = y1 - y0;
if (dx >= dy) {
float p = dy + dy - dx;
for (; x0 <= x1; x0++) {
var a = (x0 + 0.5f - start.x) / (end.x - start.x);
if (x0 == x1) { y0 = y1; }
{
var index = x0 - left;
scanlines[index].TryExtend(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z));
}
if (p >= 0) {
y0 += 1;
p = p + dy + dy - dx - dx;
}
else {
p = p + dy + dy;
}
}
}
else {
float p = dx + dx - dy;
for (; y0 <= y1; y0++) {
var a = (y0 + 0.5f - start.y) / (end.y - start.y);
if (y0 == y1) { x0 = x1; }// the last pixel
{
var index = x0 - left;
scanlines[index].TryExtend(x0, y0, start.z + a * (end.z - start.z));
}
if (p >= 0) {
x0 += 1;
p = p + dx + dx - dy - dy;
}
else {
p = p + dx + dx;
}
}
}
}fragment processing
这一步为每个Fragment分别调用fragment shader的main()函数。在此之前,要将每个Fragment的数据传递给fragment shader的各个in变量。在此之后,要将fragment shader的各个out变量(通常只有1个)传递给Fragment。通过反射机制,这很好实现。
点击查看代码 为每个Fragment执行fragment shader
csharp
private static unsafe void FragmentShaderStage(GLProgram program, ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList) {
var fs = program.FragmentShader;
const BindingFlags flags = BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static;
var inFieldInfos = (from item in fs.codeType.GetFields(flags)
where item.IsDefined(typeof(InAttribute), true)
select item).ToArray();
var name2fielfInfo = new Dictionary<string, FieldInfo>();
foreach (var item in fragmentList.ElementAt(0).endpoints0.GetType().GetFields(flags)) {
name2fielfInfo.Add(item.Name, item);
}
foreach (var fragment in fragmentList) {
var instance = fs.CreateCodeInstance() as FragmentCodeBase; // an executable fragment shader.
Debug.Assert(instance != null);
instance.gl_FragCoord = fragment.gl_FragCoord; // setup fragment coordinate in window/screen space.
// setup "in SomeType varName;" vertex attributes.
foreach (var field in inFieldInfos) {
if (name2fielfInfo.TryGetValue(field.Name, out var endpointField)) {
var type = endpointField.FieldType; object value;
if (false) { }
else if (type == typeof(float)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Float); }
else if (type == typeof(vec2)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Vec2); }
else if (type == typeof(vec3)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Vec3); }
else if (type == typeof(vec4)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Vec4); }
else if (type == typeof(mat2)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Mat2); }
else if (type == typeof(mat3)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Mat3); }
else if (type == typeof(mat4)) { value = fragment.GetValue(endpointField, PassType.Mat4); }
else { throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(type); }
field.SetValue(instance, value);
}
}
// setup "uniform SomeType varName;" in fragment shader.
Dictionary<string, UniformValue> nameUniformDict = program.name2Uniform;
foreach (UniformVariable uniformVar in fs.Name2uniformVar.Values) {
string name = uniformVar.fieldInfo.Name;
if (nameUniformDict.TryGetValue(name, out var obj)) {
uniformVar.fieldInfo.SetValue(instance, obj.value);
}
}
instance.main(); // execute fragment shader code.
fragment.discard = instance.discard;
if (!instance.discard) {// if this fragment is not discarded.
PassVariable[] outVariables = fs.name2outVar.Values.ToArray();
var outBuffers = new PassBuffer[outVariables.Length];
for (int index = 0; index < outVariables.Length; index++) {
PassVariable outVar = outVariables[index];
var outBuffer = new PassBuffer(outVar.fieldInfo.FieldType.GetPassType(), 1);
var pointer = outBuffer.Mapbuffer();
var value = outVar.fieldInfo.GetValue(instance);
Debug.Assert(value != null);
switch (outBuffer.elementType) {
case PassType.Float: {// make sure no negtive values
var v = (float)value;
if (v < 0) { v = 0; } else if (v > 1) { v = 1; }
((float*)pointer)[0] = v >= 0 ? v : 0;
}
break;
case PassType.Vec2: {// make sure no negtive values
var v = (vec2)value;
if (v.x < 0) { v.x = 0; } else if (v.x > 1) { v.x = 1; }
if (v.y < 0) { v.y = 0; } else if (v.y > 1) { v.y = 1; }
((vec2*)pointer)[0] = v;
}
break;
case PassType.Vec3: {// make sure no negtive values
var v = (vec3)value;
if (v.x < 0) { v.x = 0; } else if (v.x > 1) { v.x = 1; }
if (v.y < 0) { v.y = 0; } else if (v.y > 1) { v.y = 1; }
if (v.z < 0) { v.z = 0; } else if (v.z > 1) { v.z = 1; }
((vec3*)pointer)[0] = v;
}
break;
case PassType.Vec4: {// make sure no negtive values
var v = (vec4)value;
if (v.x < 0) { v.x = 0; } else if (v.x > 1) { v.x = 1; }
if (v.y < 0) { v.y = 0; } else if (v.y > 1) { v.y = 1; }
if (v.z < 0) { v.z = 0; } else if (v.z > 1) { v.z = 1; }
if (v.w < 0) { v.w = 0; } else if (v.w > 1) { v.w = 1; }
((vec4*)pointer)[0] = v;
}
break;
case PassType.Mat2: ((mat2*)pointer)[0] = (mat2)value; break;
case PassType.Mat3: ((mat3*)pointer)[0] = (mat3)value; break;
case PassType.Mat4: ((mat4*)pointer)[0] = (mat4)value; break;
default: throw new NotDealWithNewEnumItemException(typeof(PassType));
}
outBuffer.Unmapbuffer();
outBuffers[index] = outBuffer;
}
fragment.outVariables = outBuffers;
}
}
}pixel processing
暂时只实现了深度测试功能。
点击查看代码 DepthTest
csharp
private static void DepthTest(RenderContext context, ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList) {
var framebuffer = context.target2CurrentFramebuffer[(GLenum)BindFramebufferTarget.DrawFramebuffer];
var depthBuffer = framebuffer.DepthbufferAttachment;
ivec4 viewport = context.viewport;
switch (depthBuffer.Format) {
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT: {// 32 bit -> float
DepthTest32float(viewport.w, depthBuffer, fragmentList);
}
break; // TODO: what should this be? ok, uint it is.
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT24: {// 24 bit -> uint
DepthTest24uint(viewport.w, depthBuffer, fragmentList);
}
break;
case GL.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT32: {// 32 bit -> float
DepthTest32float(viewport.w, depthBuffer, fragmentList);
}
break;
default: throw new Exception("invalid depth format!");
}
}
private static void DepthTest24uint(int width, IGLAttachable depthBuffer, ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList) {
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(depthBuffer.DataStore, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
var depthTestPlatform = (byte*)pointer;// [viewport.z, viewport.w];
foreach (var post in fragmentList) {
var x = (int)post.gl_FragCoord.x;
var y = (int)post.gl_FragCoord.y;
var coord = (y * width + x) * 3;
uint preDepth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { preDepth += (uint)(depthTestPlatform[coord + i] << i); }
var postDepth = (uint)post.gl_FragCoord.z * (1 << 24);
// TODO: switch (depthfunc(..)) { .. }
if (postDepth < preDepth) {// fragment is nearer.
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
depthTestPlatform[coord + i] = (byte)(postDepth >> i);
}
}
}
pin.Free();
}
private static void DepthTest32float(int width, IGLAttachable depthBuffer, ConcurrentBag<Fragment> fragmentList) {
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(depthBuffer.DataStore, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
var depthTestPlatform = (float*)pointer;// [viewport.z, viewport.w];
foreach (var post in fragmentList) {
var x = (int)post.gl_FragCoord.x;
var y = (int)post.gl_FragCoord.y;
var coord = y * width + x;
var preDepth = depthTestPlatform[coord];
// TODO: switch (depthfunc(..)) { .. }
if (post.gl_FragCoord.z < preDepth) {// fragment is nearer.
depthTestPlatform[coord] = post.gl_FragCoord.z;
}
}
pin.Free();
}如何提升纯C#软实现的效率
软实现本来就不把效率放在第一位,但完全忽视效率也是不行的。下面是我为提升SoftGLImpl运行效率采取的一些措施。
高效的IntPtr GetProcAddress(string procName)
对应Windows的wglGetProcAddress和GetProcAddress,SoftGLImpl也要实现一个IntPtr GetProcAddress(string procName)函数供openGL程序员获取openGL函数指针。下面利用反射机制获取openGL全部函数指针并缓存之,避免了:
①使用笨重的Delegate委托;
②重复创建函数指针;
③way #2中千百次设置造成的冗长代码;
④更新openGL版本时遗忘了更新way #2中的缓存。
这里的"高效",包含着使用者高速(①②)、代码量低(③)、开发者省事(④)三个意思。
csharp
public unsafe partial class SoftGL {
// 缓存全部openGL函数指针
private static readonly Dictionary<string, IntPtr> procName2Address = new();
public static IntPtr GetProcAddress(string procName) {
if (SoftGL.procName2Address.TryGetValue(procName, out var address)) {
return address;
}
else { return IntPtr.Zero; }
}
static SoftGL() { // 在SoftGL加载时,初始化openGL函数指针的缓存dict
// way #1 - 利用反射机制
Type type = typeof(SoftGLImpl.SoftGL);
var methodInfos = type.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Static | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
foreach (var methodInfo in methodInfos) {
var procName = methodInfo.Name;
if (procName.StartsWith("gl")) { // SoftGL中以gl开头的static函数
var pointer = methodInfo.MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer();
procName2Address.Add(procName, pointer);
}
}
// way #2 - 一个一个设置
//var pglGenBuffers = (delegate* managed<GLsizei, GLuint[], void>)(&SoftGLImpl.SoftGL.glGenBuffers);
//procName2Address.Add("glGenBuffers", (IntPtr)pglGenBuffers);
//var pglDrawElements = (delegate* managed<GLenum, GLsizei, GLenum, IntPtr>)(&SoftGLImpl.SoftGL.glDrawElements);
//procName2Address.Add("glDrawElements", (IntPtr)pglDrawElements);
// other function pointers ...
}
}运用C#中的并行计算
pipeline中的某些环节可以用Parallel或ThreadPool施展并行计算,以提高软实现的运行效率。
例如,在渲染GL_TRIANGLES时,可以并行处理各个TRIANGLE。
csharp
private static unsafe ConcurrentBag<Fragment> LinearInterpolationTriangles(RenderContext context, int count, DrawElementsType type, IntPtr indices, GLVertexArrayObject vao, GLProgram program, GLBuffer indexBuffer, Dictionary<uint, VertexCodeBase> vertexID2Shader) {
var result = new System.Collections.Concurrent.ConcurrentBag<Fragment>();
byte[] indexData = indexBuffer.Data; int elementBytes = ByteLength(type);
int indexLength = indexData.Length / elementBytes;
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(indexData, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr pointer = pin.AddrOfPinnedObject();
ivec4 viewport = context.viewport; // ivec4(x, y, width, height)
count = (count - count % 3);
const int fromInclusive = 0; int toExclusive = count / 3;
int start = indices.ToInt32() / elementBytes;
int to2 = (indexLength - start) / 3;
if (to2 < toExclusive) { toExclusive = to2; }
Parallel.For(fromInclusive, toExclusive, t => {
int indexID = t * 3 + start;
var endpoints = new VertexCodeBase[3];
var fragCoords = stackalloc vec3[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
uint gl_VertexID = GetVertexID(pointer, type, indexID + i);
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(vertexID2Shader.ContainsKey(gl_VertexID));
var shaderObj = vertexID2Shader[gl_VertexID];
endpoints[i] = shaderObj;
vec4 gl_Position = shaderObj.gl_Position;
vec3 fragCoord = new vec3((gl_Position.x + 1) / 2.0f * viewport.z + viewport.x,
(gl_Position.y + 1) / 2.0f * viewport.w + viewport.y,
(gl_Position.z + 1) / 2.0f * (float)(context.depthRangeFar - context.depthRangeNear) + (float)context.depthRangeNear);
fragCoords[i] = fragCoord;
}
FindFragmentsInTriangle(
fragCoords[0], fragCoords[1], fragCoords[2],
endpoints[0], endpoints[1], endpoints[2], result);
});
pin.Free();
return result;
}其他可以并行计算的过程包括:
- 并行执行vertex shader。
- 在两个顶点之间进行线性插值。
- 并行执行fragment shader。
开源地址
开源地址在https://gitee.com/bitzhuwei/glTF2。github我已无法登陆了,它新要求的什么狗屁验证措施,让我很不安。我已经把github上我的所有项目都转移到gitee了。