何为数据库连接池
数据库连接池是一个容器 , 负责分配管理数据库连接 Connection
最大的作用是 : 重复使用 已经创建好的Connection 对象 , 而不是重复的创建和释放
最大空闲时间 : (maxIdTime参数)
数据库连接在被使用后 , 长时间没有被使用 , 只要超过预设的最大空闲时间 , 系统会自动释放这些链接以回收资源 .
如果没有释放连接 , 数据库资源会被占用 , 直到连接池耗尽 , 影响系统性能甚至引发故障
目前的主流数据库连接池
1. HikariCP
-
特点:HikariCP 是一个高性能的 JDBC 连接池,被广泛认为是目前最快的数据库连接池之一。它特别适用于高并发、大流量的系统。
-
优点:
- 极致的性能和低延迟。
- 支持数据库连接池的健康检查、回收和自动关闭。
- 与 Spring 和 Java EE 集成良好。
-
应用场景:适用于高性能要求的项目,如微服务架构、高并发的 web 应用。
2. C3P0
-
特点:C3P0 是一个经典的、开源的 JDBC 连接池。它提供了比较全面的功能,包括自动重试、连接验证、连接超时等。
-
优点:
- 稳定、成熟,支持多种数据库。
- 提供了良好的连接池管理和监控功能。
-
缺点:
- 性能相比 HikariCP 略逊色,尤其在高并发下。
-
应用场景:适用于中等规模的应用或在不需要极端性能优化的情况下。
3. Druid
-
特点:Druid 是阿里巴巴开源的数据库连接池,功能非常丰富,特别适合大规模分布式系统。除了基本的连接池管理外,Druid 还提供了数据库监控、SQL 性能分析、SQL 执行日志等功能。
-
优点:
- 提供全面的数据库监控功能,便于排查性能瓶颈。
- 支持连接池扩展和多种数据源的支持。
-
缺点:
- 配置较为复杂,性能上略逊色于 HikariCP。
-
应用场景:适用于大规模的企业级应用或需要复杂监控的系统。
JDBC搭配ORM
封装实体类
导入jar包
进入maven repo 获取 jar包 jar包
复制粘贴进入lib文件
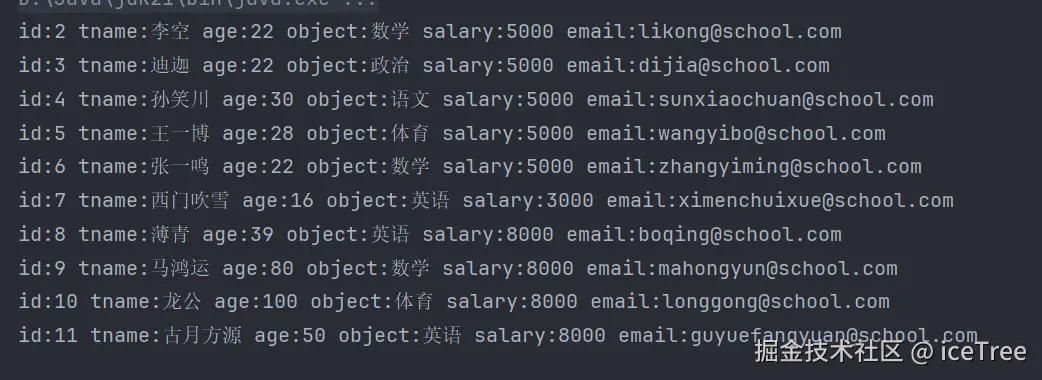
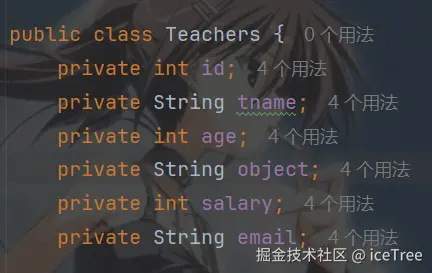
新建 com.zpero.advanced,pojo 包存储表对象
java
package com.zpero.advanced.pojo;
public class Teacher {
private int id;
private String tname;
private String object;
private int salary;
private String email;
//点击变量名 alt + enter 添加getter setter toString
}手动ORM
什么是ORM
ORM 将程序中的对象(类)与数据库中的表进行映射。例如,一个类的每个属性可以映射到数据库表的一列,类的每个实例可以映射到表中的一行。
在 com.zpero.advanced 包下创建 JDBCAdvanced 类文件
java
public class JDBCAdvanced {
@Test
public void testORM()throws Exception{
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata","root" , "123456");
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("select id ,tname,age,object,salary,email from teachers where id = ?");
ps.setInt(1,1);
ResultSet resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
Teacher teacher1 = null;
if(resultSet.next()){
teacher1 = new Teacher();
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String tname = resultSet.getString("tname");
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");
String object = resultSet.getString("object");
int salary = resultSet.getInt("salary");
String email = resultSet.getString("email");
teacher1.setId(id);
teacher1.setTname(tname);
teacher1.setAge(age);
teacher1.setObject(object);
teacher1.setSalary(salary);
teacher1.setEmail(email);
}
System.out.println(teacher1);
resultSet.close();
ps.close();
conn.close();
}
}测试多条数据
java
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("select id ,tname,age,object,salary,email from teacher where id > ?");
//在连接后面加入
List<Teacher> teacherList = new ArrayList<>();//alt + enter 导入Lsit容器
while(){
//...
teacherList.add(teacher1);
}
for(Teacher teacher : teacherList){
System.out.println(teacher);
}先将 teahcer1 对象创建后置空 , 就像 c++ 中的创建了对象的空指针 然后在循环中不断的 new 和 delete. java使用垃圾回收机制 在对象没有被引用后自动回收
结果正确
什么是主键回显
-
当 teachers 表的主键是 自增的 , 插入数据时 可以不用插入主键 或者把主键置空,
-
在执行完插入操作后, 只能得到受影响的行数 , 无法直接获取 新增的数据
-
在 不插入主键的情况下 执行插入操作 ,并把新增数据的主键 返回给
Java对象的 操作就是主键回显
简单来说就是 解决无法获取新增数据的主键信息的方法
java
@Test
public void testORMPriKey() throws Exception{
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata","root" , "123456");
String sql = "insert into teachers( tname,age,object,salary , email) values (?,?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher( 0,"伊藤诚" , 17,"体育" , 3000,"yitengcheng@school.com") ;
ps.setString(1 ,teacher1.getTname());
ps.setInt(2 ,teacher1.getAge());
ps.setString( 3,teacher1.getObject());
ps.setInt(4 ,teacher1.getSalary());
ps.setString(5 ,teacher1.getEmail());
ResultSet rs = null;
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
if (count>0){
System.out.println("success");
rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt(1);
teacher1.setId(id);
System.out.println(teacher1);
}
}else{
System.out.println("failed");
}
if (rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
ps.close();
conn.close();
}执行结果:
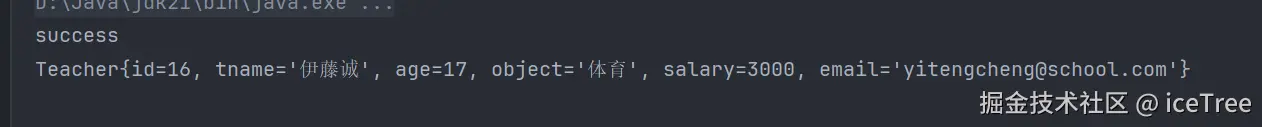
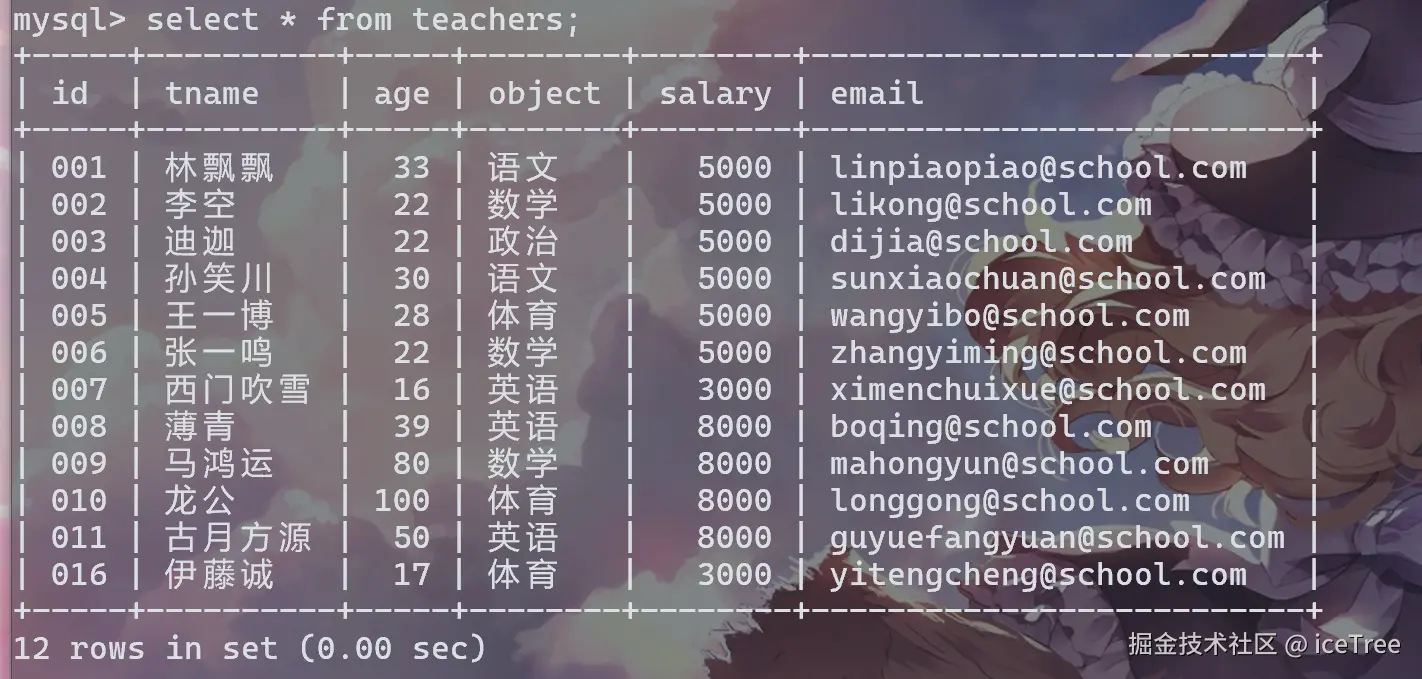
注意看 , 在博主多次增加删除同一条数据后 , 它的id 从11 突然 变成了16
auto_increment特性:
- 用来自动为每一行生成一个唯一的标识符
- 在删除数据后,自增字段的值默认并不会减小,而是会继续递增
大多数数据库设计时会让自增列保持增加的趋势
便于直观的看到 主键自增值 , 我们可以
查看auto_increment值
sql
select auto_increment from information_schema.tables where table_schema='mssqldata' and table_name='teachers';修改auto_increment值
sql
alter table mssqldata.teachers auto_increment = 1000;集成到代码中 JDBCOperation 类文件中添加
java
@Test
public void testAlterAutoIncrement() throws Exception {
Connection conn6 = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata",
"root",
"123456"
);
PreparedStatement ps6 = conn6.prepareStatement("alter table teachers auto_increment = ?");
int num = 255;
ps6.setInt(1, num);
int count = ps6.executeUpdate();
ps6.execute("FLUSH TABLES");
System.out.println("success alter auto increment into " + num);
String sql = "select auto_increment from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'mssqldata' and table_name='teachers'";
Statement ps7 = conn6.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = ps7.executeQuery(sql);
if (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1));
}
rs.close();
ps6.close();
ps7.close();
conn6.close();
}这段代码有点小瑕疵 , 即便是 刷新了数据库缓存 , 输出的 auto-increment 没有被刷新 , 查阅资料发现 可能是 MySQL 的小bug
java
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
Connection conn6 = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata",
"root",
"123456"
);
PreparedStatement ps6 = conn6.prepareStatement("delete from teachers where id > ?");
ps6.setInt(1, 11);
int count = ps6.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("deleted all data where id > 11");
ps6.close();
conn6.close();
}先运行testAlterAutoIncrement , 然后运行testORMPriKey , 会发现 :
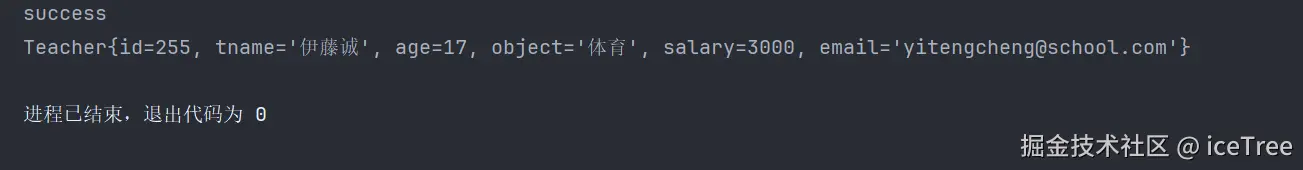
**auto-increment值已经变成我们所设置的 **
批量插入优化
-
在getConnection() url参数中加入
?rewriteBatchedStatements=true,允许把多个插入操作并入一条,避免多次使用数据库的交互 , 提高性能
-
insert操作必须 用Values , 语句后不要加
;方便语句合并 -
使用addBetch()方法,告诉JVM 这是批处理
-
调用executeBatch() 执行批处理
java
@Test
public void testBatchInsert() throws Exception{
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata?rewriteBatchedStatements=true","root" , "123456");
String sql = "insert into teachers( tname,age,object,salary , email) values (?,?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
ps.setString(1 , "tname"+i);
ps.setInt(2 , 20+i);
ps.setString( 3, "object"+i);
ps.setInt(4 , 3000+i);
ps.setString(5 , "email"+i);
ps.addBatch();
}
ps.executeBatch();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("time:"+(end-start));
ps.close();
conn.close();
}数据库连接池技术
通过上述的例子 , 可以发现 每次执行SQL语句,都必须获取新连接 , 释放connection,resultset , statement . 大量的创建销毁会浪费资源
连接池技术就是建立一个连接对象的Buffer , 通过配置实现数据库创建管理连接在用户和JDBC之间放一个数据库连接池 , 通过连接池得到 一个connection, 使用完后放回连接池
如果没有空闲连接且连接池中的连接数还未达到最大连接数,连接池会创建一个新的连接。
连接池通常还会配置连接的最大空闲时间(idleTimeout)和最大获取连接等待时间(connectionTimeout),防止连接过长时间占用而不释放
Druid使用
java
//推荐使用配置文件导入
@Test
public void druidSoft() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = DruidTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println( connection);
connection.close();
}创建resources目录
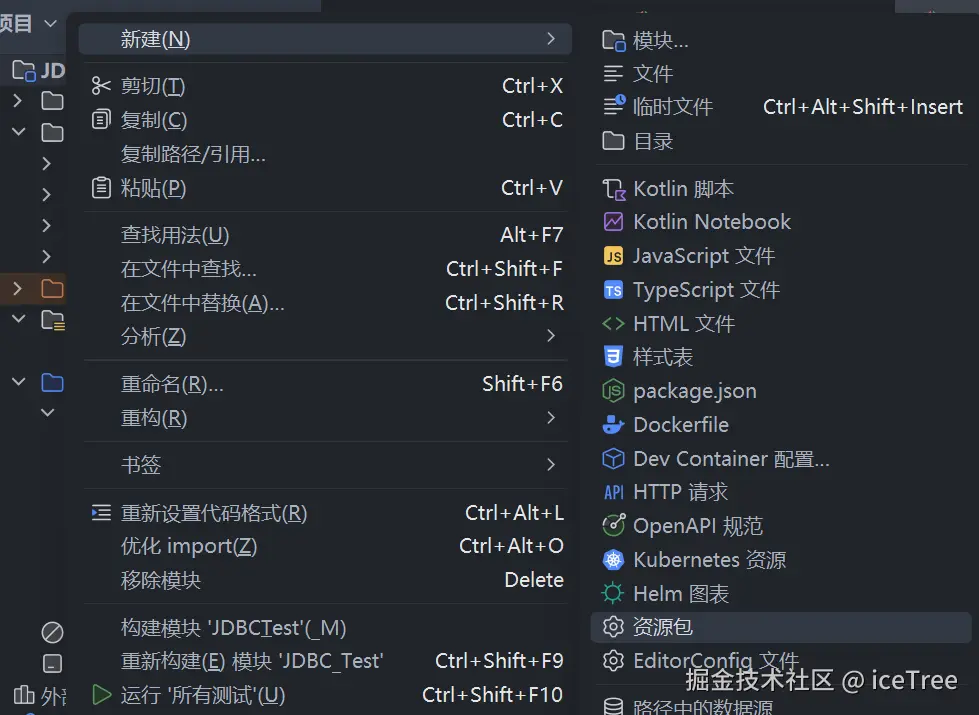
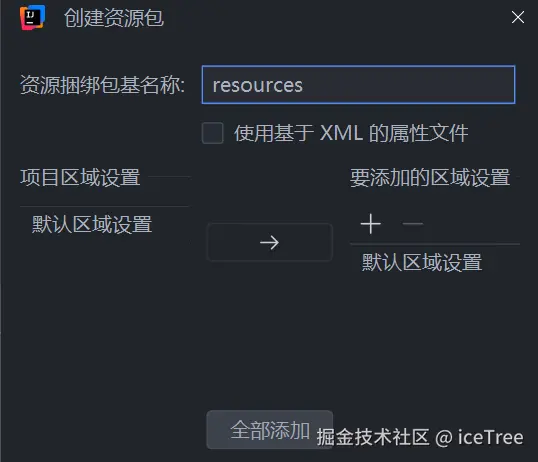
右键resources目录 , 创建 db.properties
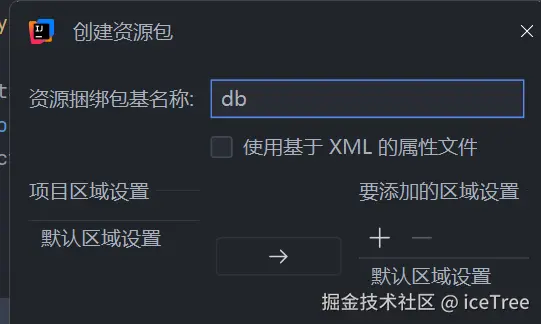
在db中输入
java
//url按自己情况而定
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata
username=root
password=123456
initialSize=10
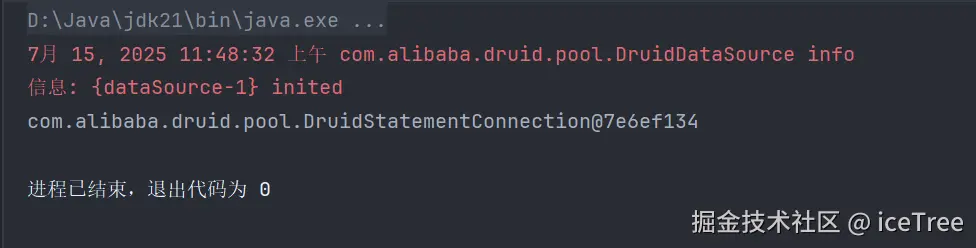
maxActive=20程序输出
HikariCP使用
导入jar包
mavenrope获取 jar包bundle jar包2jar
添加hikari.properties
tex
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata
username=root
password=123456
initialSize=10
maxActive=20
java
@Test
public void hikariHardCode() throws Exception {
HikariDataSource ds = new HikariDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mssqldata");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("123456");
ds.setMinimumIdle(10);
ds.setMaximumPoolSize(20);
Connection connection = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
@Test
public void hikariSoft() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream in = HikariTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("hikari.properties");
properties.load(in);
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig(properties);
HikariDataSource hikariDataSource = new HikariDataSource(config);
Connection connection = hikariDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}数据库连接池优化
Util封装连接池创建
java
public class JDBCUtil {
private static DataSource dataSource;
static{
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
return dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void release(Connection conn){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}使用Thread Local 优化
什么是ThreadLocal
- 同一个线程访问 数据库可能创建多个connection , 会很快耗尽连接池的连接数量 , 造成资源浪费
- 可以在同一个线程中共享同一个connection 从而保证
- 事务的一致性
- 避免重复get/close 连接
- 实现线程安全的数据库操作
java
//创建ThreadLocal对象
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
//...
//在getConnection方法try中
try {
//在threadLocal 获取连接
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
// threadLocal has no Connection, the First time to get Connection
if (connection == null) {
//get the first connection , store in threadLocal
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
threadLocal.set(connection); //store in threadLocal
}
return connection;
}
//...
//改造release方法
try {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if(connection != null){
//remove from threadLocal Connection Object that already stored
threadLocal.remove();
//return Connection Object to the connection pool
connection.close();
}为什么要在release方法中 从 threadlocal中获取连接?
我们从中得到共享Connection , 然后检查是否是null , 如果是null 说明 threadLocal中没有从连接池中得到connection , 也就不需要释放连接了
如果不是null,则需要把它从threadLocal中移除并归还给 连接池
验证:
java
@Test
public void testJDBCV2()throws Exception{
Connection connection1 = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
Connection connection2 = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
Connection connection3 = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection1);
System.out.println(connection2);
System.out.println(connection3);
JDBCUtilV2.release();
}使用DAO封装
DAO封装是将对数据库的增删改查封装到一个独立类里 ,使业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑 分离
比如说,我们封装了实体类Teachers
然后我们就可以针对实体类 定义接口类 TeacherDAO为什么要用接口类而不是直接定义一个实现类?
解耦 : 通过使用接口,可以减少代码的耦合度
如果要更换实现方式,只需要一个新的实现类,无需更改使用接口的地方
使用多态的便利性: 不同的实现类有不同的行为,但是对外提供的接口一样,可以处理不同类型的对象
允许使用多种设计模式
我们正是利用接口的隐藏具体实现只关注使用的目的实现代码分离解耦
javapublic interface TeachersDao { List<Teachers> selectAll(); Teachers selectTeacherId(Integer id); // add a new teacher record int insertTeacher(Teachers teacher); // update a teacher record int updateTeacher(Teachers teacher); //delete a teacher record int deleteTeacher(Teachers teacher); }之后我们可以添加实现类 重写接口
javapublic class TeachersDaoImpl extends BaseDao implements TeachersDao { @Override public List<Teachers> selectAll() { return List.of(); } @Override public Teachers selectTeacherId(Integer id) { return null; } @Override public int insertTeacher(Teachers teacher) { return 0; } @Override public int updateTeacher(Teachers teacher) { return 0; } @Override public int deleteTeacher(Teachers teacher) { return 0; }
使用DAO的优势
- 低耦合: 业务逻辑不需要直接操作 JDBC API
- 高复用 : 通用操作提取到BaseDao(在Dao中还可以把共用的代码提取出来,减少代码量)
- 易维护: 数据库变更只影响DAO,不影响上层逻辑
- 便于测试
使用BaseDao把通用的数据库操作封装起来,只需要写sql语句调用相应的执行方法就能执行相应的操作
目的是把sql语句和对数据库的创建执行过程分离,从而实现业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离
执行增删改
java
public int executeUpdate(String sql, Object... params) throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
if (params != null && params.length > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
}
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement.close();
JDBCUtilV2.release();
return count;
}执行查询
java
public <T> List<T> executeQuery(Class<T> clzz, String sql, Object... params) throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtilV2.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//Be Sure to check whether the params is null and whether the length
//of the params is 0 so that you can continued to iterate(遍历) the list of params
if(params != null && params.length > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
}
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//get meta-data(元数据) from ResultSet which contains column number and column name
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//create list to store objects
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
T t = clzz.newInstance();
//iterate over the columns of the current row,iterate serveral times
//to see how many columns there are
for (int i =1; i < metaData.getColumnCount(); i++) {
//get the values of the current column through the ResultSet
Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
//get the name of the current column through the ResultSetMetaData
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
//Get the field(字段) of the object to be encapsulated through the class object and fieldName
Field declaredField = clzz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
//break the encapsulation(封装) of private field
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(t,value);
}
list.add(t);
}
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
JDBCUtilV2.release();
return list;
}补充知识点:什么是反射?
Java 程序在运行的时候,可以"查看"和"操作"别的类或对象的内容。
- 获取类的结构
- 创建对象
- 访问私有属性(打破封装)
- 调用方法
主要依赖
java.lang.refelt包中的API常用类:
- Class 描述类的信息,反射的入口
- Field 表示字段
- Method 方法
- Constructor 构造器
- Modifier 解析修饰符(public private)
例子中的反射是得到当前列的值和字段,然后把值赋值给实体类相应字段
测试DAO封装 , 测试那一部分去掉注释即可
java
@Test
public void testTeacherDao() throws Exception {
TeachersDao teachersDao = new TeachersDaoImpl();
// //test selectAll
// List<Teachers> teacherList = teachersDao.selectAll();
// for(Teachers teacher : teacherList){
// System.out.println(teacher);
// }
// //test selectTeacherId
// Teachers teacher = teachersDao.selectTeacherId(1);
// System.out.println(teacher);
// //test insertTeacher
// Teachers teacher = new Teachers(0,"卫宫士郎",18,"弓道",5000,"EmiyaShirou@school.com");
// int result = teachersDao.insertTeacher(teacher);
// System.out.println(result);
// System.out.println(teacher);
// //test updateTeacher
// Teachers teacherDB = teachersDao.selectTeacherId(12);
// System.out.println(teacherDB);
// teacherDB.settName("卫宫士郎");
// int result = teachersDao.updateTeacher(teacherDB);
// System.out.println(result);
// System.out.println(teacherDB);
// //test deleteTeacher
// int count = teachersDao.deleteTeacher(12);
// System.out.println("deleted "+ count+ " teacher data");
}