前言
是看了这个大佬的视频后想进行一下自己的整理(流程只到了扁平化),如果有问题希望各位大佬能够给予指正。卷积神经网络(CNN)到底卷了啥?8分钟带你快速了解!_哔哩哔哩_bilibili![]() https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1MsrmY4Edi/?spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=7c3bfbf39d037fe80c97234396acc524
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1MsrmY4Edi/?spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=7c3bfbf39d037fe80c97234396acc524
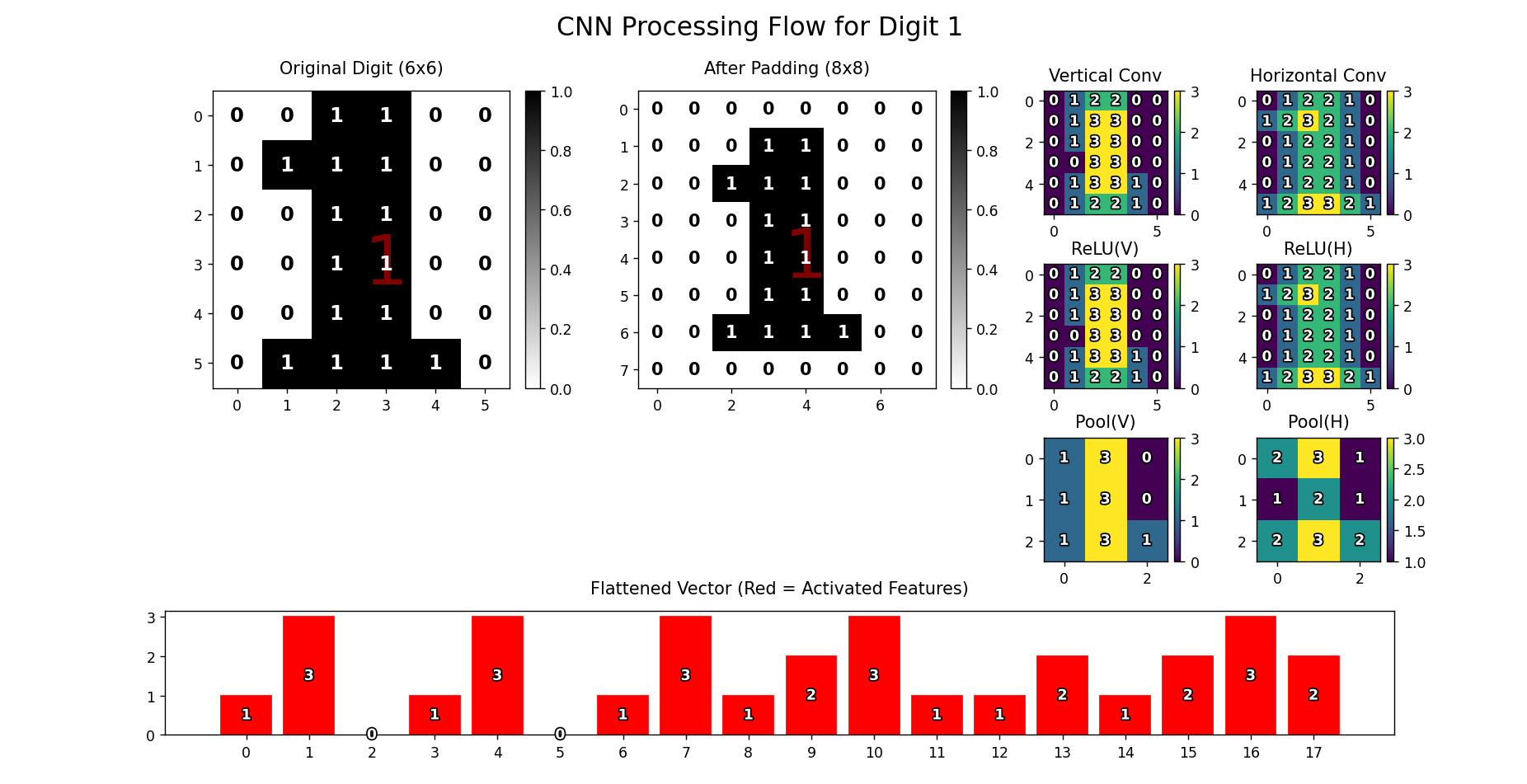
输入层
由于自己也不知道设置什么矩阵,就干脆让deepseek生成0~9的矩阵,每次随机使用一个数字来进行测试。
-
从预定义的
digit_templates中随机选择一个数字(0-9) -
将数字的6x6二进制矩阵转换为NumPy数组
关键变量: -
digit: 原始数字矩阵(6x6),值为0(黑)或1(白)
python
# 数字模板(6x6矩阵)
digit_templates = {
0: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
1: [[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
2: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]],
3: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
4: [[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]],
5: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
6: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
7: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
8: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
9: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]]
}
# 随机选择数字
random_digit = randint(0, 9)
digit = np.array(digit_templates[random_digit])Padding
将6*6的矩阵边界填充0扩展为8x8矩阵,防止丢失边缘信息。
numpy.pad()函数详解_numpy pad-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41862755/article/details/128336141
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41862755/article/details/128336141
-
在原始矩阵周围添加一圈0(
pad_width=1) -
将6x6矩阵扩展为8x8,防止卷积时边缘信息丢失
输出: -
padded: 填充后的矩阵(8x8)
python
padded = np.pad(digit, pad_width=1, mode='constant') # 边界填充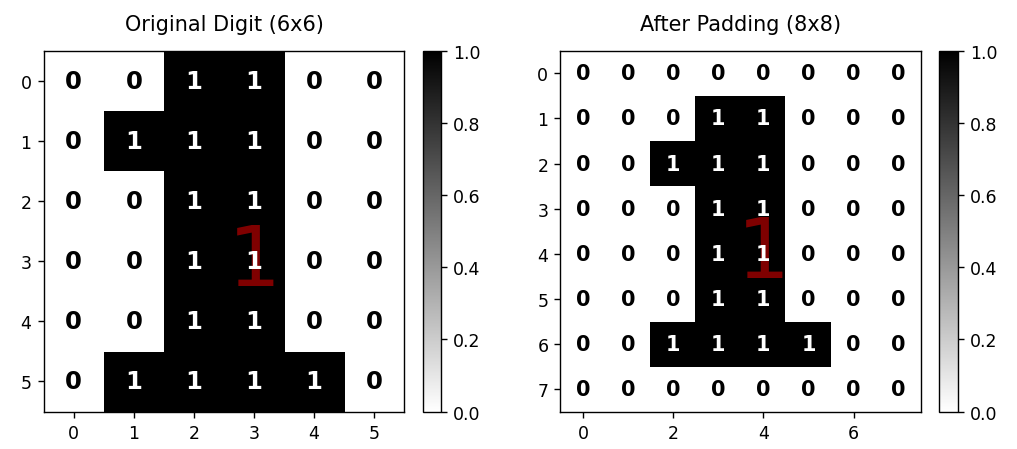
卷积
局部加权求和(对应相乘再相加),提取输入数据的局部特征,形成特征映射。
-
conv2d函数实现滑动窗口卷积运算 -
使用垂直核(
kernel_v)检测垂直边缘特征 -
使用水平核(
kernel_h)检测水平边缘特征
关键参数: -
kernel_v:[[0,1,0], [0,1,0], [0,1,0]](强化垂直线条) -
kernel_h:[[0,0,0], [1,1,1], [0,0,0]](强化水平线条)
输出: -
conv_v: 垂直卷积结果(6x6矩阵) -
conv_h: 水平卷积结果(6x6矩阵)
python
# 定义卷积核
kernel_v = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]]) # 垂直特征
kernel_h = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0]]) # 水平特征
def conv2d(image, kernel):
# 手动实现卷积运算
h, w = image.shape
k_h, k_w = kernel.shape
output = np.zeros((h - k_h + 1, w - k_w + 1))
for y in range(h - k_h + 1):
for x in range(w - k_w + 1):
output[y, x] = np.sum(image[y:y + k_h, x:x + k_w] * kernel)
return output.astype(int)
conv_v = conv2d(padded, kernel_v) # 垂直卷积
conv_h = conv2d(padded, kernel_h) # 水平卷积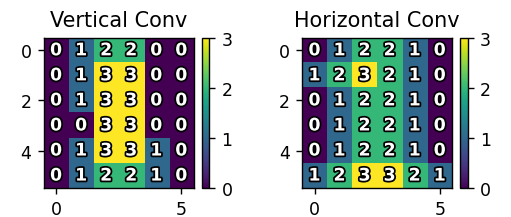
激活
这个视频中没有,然后代码中也没起作用,因为没有出现值为负数出现。激活函数可以进行 非线性变换,使网络能够学习复杂模式,可以进行特征过滤,保留有用特征,抑制噪声,可以优化训练,控制梯度流动,提高模型收敛速度。
-
对卷积结果应用ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)激活函数
-
保留正值,负值置为0(非线性变换)
输出: -
relu_v: 垂直特征激活结果(6x6) -
relu_h: 水平特征激活结果(6x6)
python
relu_v = np.maximum(0, conv_v) # ReLU激活
relu_h = np.maximum(0, conv_h)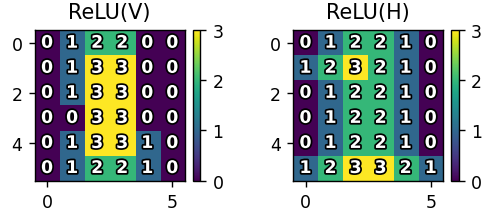
池化
池化能够进行信息压缩,用更少的参数表达关键特征,可以不变性增强,使模型对输入的小变化更鲁棒,可以计算效率,加速训练和推理过程。
-
maxpool2d函数实现2x2最大池化(步长=2) -
降低特征图维度,保留显著特征(保留2*2中的最大值)
输出: -
pool_v: 垂直特征池化结果(3x3) -
pool_h: 水平特征池化结果(3x3)
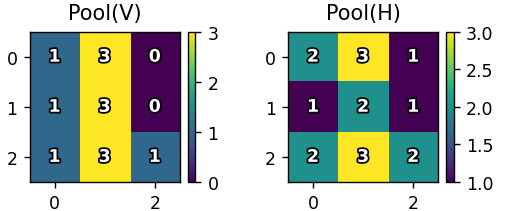
扁平化
扁平化可以结构转换,让多维特征转换成一维向量,可以信息整合,合并不同特征提取路径的结果,起到桥梁作用,连接特征提取层与分类决策层。
-
将池化后的3x3矩阵展平为一维向量(
flatten()) -
合并垂直和水平特征向量(最终18维向量)
输出: -
flattened: 合并后的特征向量(形状:(18,))
python
flattened = np.concatenate([pool_v.flatten(), pool_h.flatten()])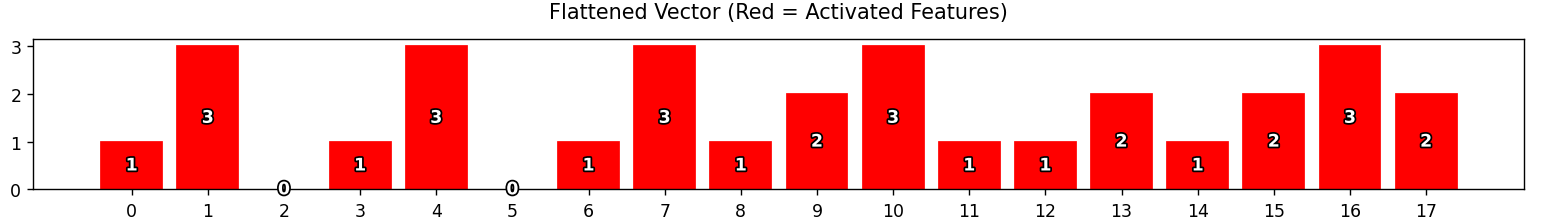
可视化
-
使用Matplotlib绘制处理流程各阶段的结果
-
关键可视化内容:
-
原始数字矩阵(标注0/1值)
-
卷积/激活/池化结果(热力图+数值标注)
-
扁平化向量(条形图,红色标记激活特征)
-
完整代码
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patheffects as path_effects
from random import randint
# 数字模板(6x6矩阵)
digit_templates = {
0: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
1: [[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
2: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]],
3: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
4: [[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]],
5: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
6: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
7: [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
8: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]],
9: [[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]]
}
# 随机选择数字
random_digit = randint(0, 9)
digit = np.array(digit_templates[random_digit])
# 定义卷积核
kernel_v = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0]]) # 垂直特征
kernel_h = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0]]) # 水平特征
def process_digit(digit):
# Padding
padded = np.pad(digit, pad_width=1, mode='constant')
# 卷积计算
def conv2d(image, kernel):
h, w = image.shape
k_h, k_w = kernel.shape
output = np.zeros((h - k_h + 1, w - k_w + 1))
for y in range(h - k_h + 1):
for x in range(w - k_w + 1):
output[y, x] = np.sum(image[y:y + k_h, x:x + k_w] * kernel)
return output.astype(int) # 转换为整型
conv_v = conv2d(padded, kernel_v)
conv_h = conv2d(padded, kernel_h)
# ReLU激活
relu_v = np.maximum(0, conv_v).astype(int) # 转换为整型
relu_h = np.maximum(0, conv_h).astype(int) # 转换为整型
# 最大池化
def maxpool2d(image, size=2):
h, w = image.shape
return np.array([[np.max(image[i:i + size, j:j + size])
for j in range(0, w, size)]
for i in range(0, h, size)]).astype(int) # 转换为整型
pool_v = maxpool2d(relu_v)
pool_h = maxpool2d(relu_h)
# 扁平化
flattened = np.concatenate([pool_v.flatten(), pool_h.flatten()]).astype(int) # 转换为整型
return {
'original': digit,
'padded': padded,
'conv_v': conv_v,
'conv_h': conv_h,
'relu_v': relu_v,
'relu_h': relu_h,
'pool_v': pool_v,
'pool_h': pool_h,
'flattened': flattened
}
def visualize_flow(results):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 12))
plt.suptitle(f'CNN Processing Flow for Digit {random_digit}', fontsize=18, y=0.97)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 6, hspace=0.4, wspace=0.3)
# 创建文本描边效果
text_effect = [path_effects.withStroke(linewidth=2, foreground='black')]
# 原始图像 - 显示阿拉伯数字
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(grid[0:2, 0:2])
img1 = ax1.imshow(results['original'], cmap='binary')
plt.colorbar(img1, ax=ax1, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
ax1.set_title("Original Digit (6x6)", pad=12)
ax1.text(3, 3, str(random_digit),
ha='center', va='center',
color='red', fontsize=48, alpha=0.5)
for y in range(results['original'].shape[0]):
for x in range(results['original'].shape[1]):
display_val = '1' if results['original'][y, x] > 0.5 else '0'
ax1.text(x, y, display_val,
ha='center', va='center',
color='white' if results['original'][y, x] > 0.5 else 'black',
fontsize=14, weight='bold')
# Padding后的图像 - 显示阿拉伯数字
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(grid[0:2, 2:4])
img2 = ax2.imshow(results['padded'], cmap='binary')
plt.colorbar(img2, ax=ax2, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
ax2.set_title("After Padding (8x8)", pad=12)
ax2.text(4, 4, str(random_digit),
ha='center', va='center',
color='red', fontsize=48, alpha=0.5)
for y in range(results['padded'].shape[0]):
for x in range(results['padded'].shape[1]):
display_val = '1' if results['padded'][y, x] > 0.5 else '0'
ax2.text(x, y, display_val,
ha='center', va='center',
color='white' if results['padded'][y, x] > 0.5 else 'black',
fontsize=12, weight='bold')
# 右侧图像的统一设置
right_plots = {
'conv_v': ('Vertical Conv', grid[0, 4]),
'conv_h': ('Horizontal Conv', grid[0, 5]),
'relu_v': ('ReLU(V)', grid[1, 4]),
'relu_h': ('ReLU(H)', grid[1, 5]),
'pool_v': ('Pool(V)', grid[2, 4]),
'pool_h': ('Pool(H)', grid[2, 5])
}
for key, (title, pos) in right_plots.items():
ax = fig.add_subplot(pos)
img = ax.imshow(results[key], cmap='viridis')
plt.colorbar(img, ax=ax, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
ax.set_title(title, pad=7)
for y in range(results[key].shape[0]):
for x in range(results[key].shape[1]):
ax.text(x, y, f"{results[key][y, x]:d}", # 使用整型格式
ha='center', va='center',
color='white',
fontsize=10, weight='bold',
path_effects=text_effect)
# 扁平化
ax9 = fig.add_subplot(grid[3, :])
bars = ax9.bar(range(len(results['flattened'])), results['flattened'])
for j, val in enumerate(results['flattened']):
if val > 0:
bars[j].set_color('red')
ax9.text(j, val / 2, f"{val:d}", # 使用整型格式
ha='center', va='center',
color='white',
weight='bold',
path_effects=text_effect)
ax9.set_xticks(range(len(results['flattened'])))
ax9.set_title("Flattened Vector (Red = Activated Features)", pad=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 执行流程
results = process_digit(digit)
print(f"Processing digit: {random_digit}")
print("Flattened vector:", results['flattened'])
visualize_flow(results)Processing digit: 1
Flattened vector: [1 3 0 1 3 0 1 3 1 2 3 1 1 2 1 2 3 2]