目录
一.Ansible简介
什么是Ansible?
-
ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于python开发,集合了很多的运维工具(puppet、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
-
ansible是基于paramiko开发的,并且基于模块化 工作,它本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架,ansible不需要在远程主机上安装client/agents,因为它们是基于ssh来和远程主机通讯的。ansible目前已经被红帽官方收购,是自动化运维工具认可度最高的。
-
更加详细的资源参考官方文档,如右是Ansible的官方网站:Ansible Documentation
Ansible的特点
-
部署简单,只需要在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无需做任何操作;
-
默认使用SSH协议对设备进行管理;
-
有大量的常规运维操作模块,可实现日常绝大部分的操作;
-
配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强;
-
支持API以及自定义模块,可以通过Python轻松扩展;
-
通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理;
-
轻量级、无需在客户端安装agent,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可;
-
提供一个功能强大、操作性强的web管理界面和REST API接口------AWX平台。
Ansible的架构
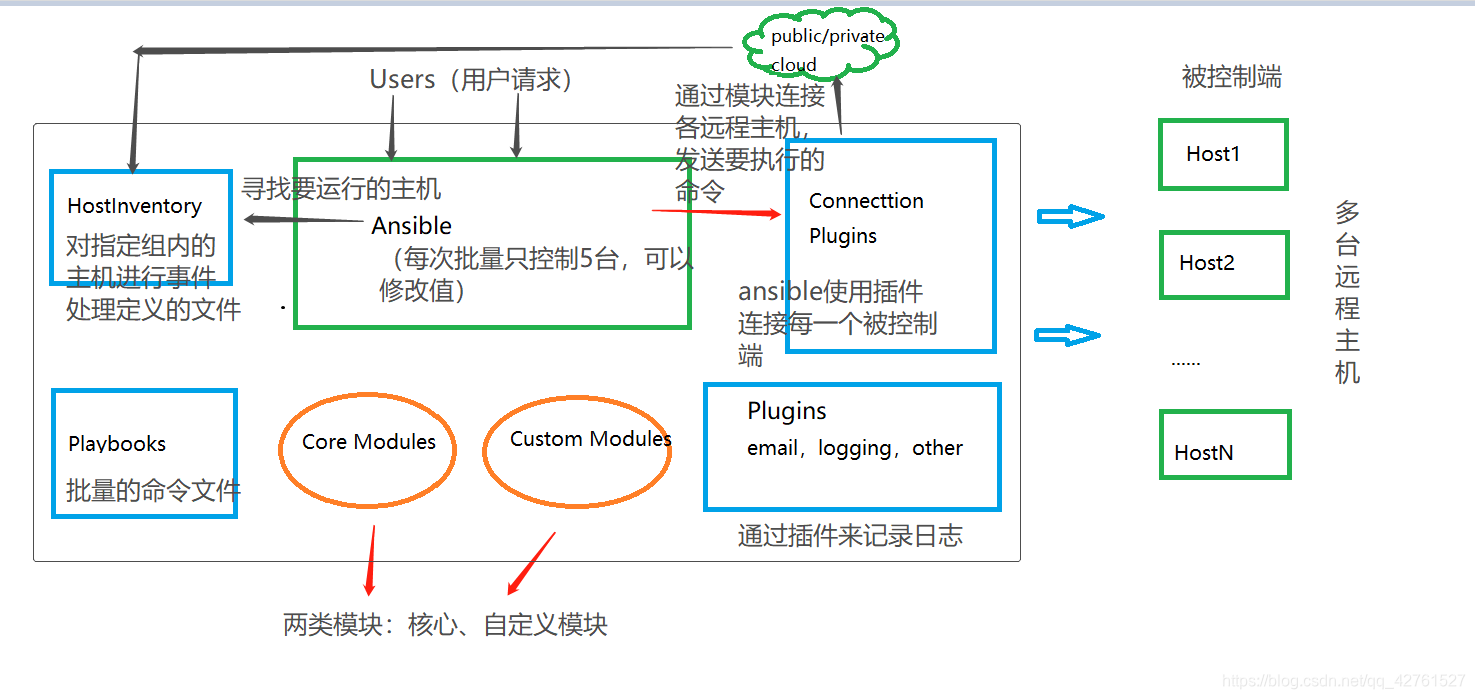
-
Ansible:Ansible的核心程序
-
HostInventory:记录有Ansible管理的主机信息,包括端口、密码、IP地址等
-
Playbooks:"剧本"YAML格式的文件,多个任务定义在一个文件中,定义主机需要调用哪些模块来完成的功能。
-
CoreModules:核心模块,主要操作是通过调用核心模块来完成管理任务
-
CustomModules:自定义模块,完成核心模块无法完成的功能,支持多种语言。
-
ConnectionPlugins:连接插件,Ansible和Host通信使用
二.Ansible任务执行解析
ansible任务执行模式
-
ansible系统由控制主机被管节点的操作方式可以分为两类,即adhoc和playbook
-
ad-hoc模式(点对点模式)
使用单个模块,支持批量执行单条命令。ad-hoc命令是一种可以快速输入的命令,而且不需要保存起来的命令。就相当于bash中的一句话shell
- playbook模式(剧本模式)
剧本模式是Ansible的主要管理方式,也是Ansible功能强大的关键所在。playbook通过多个task(任务)集合完成一类功能,比如web服务的安装部署、数据库服务的批量备份等。可以简单地把playbook理解为通过组合多条ad-hoc操作的配置文件
ansible执行流程
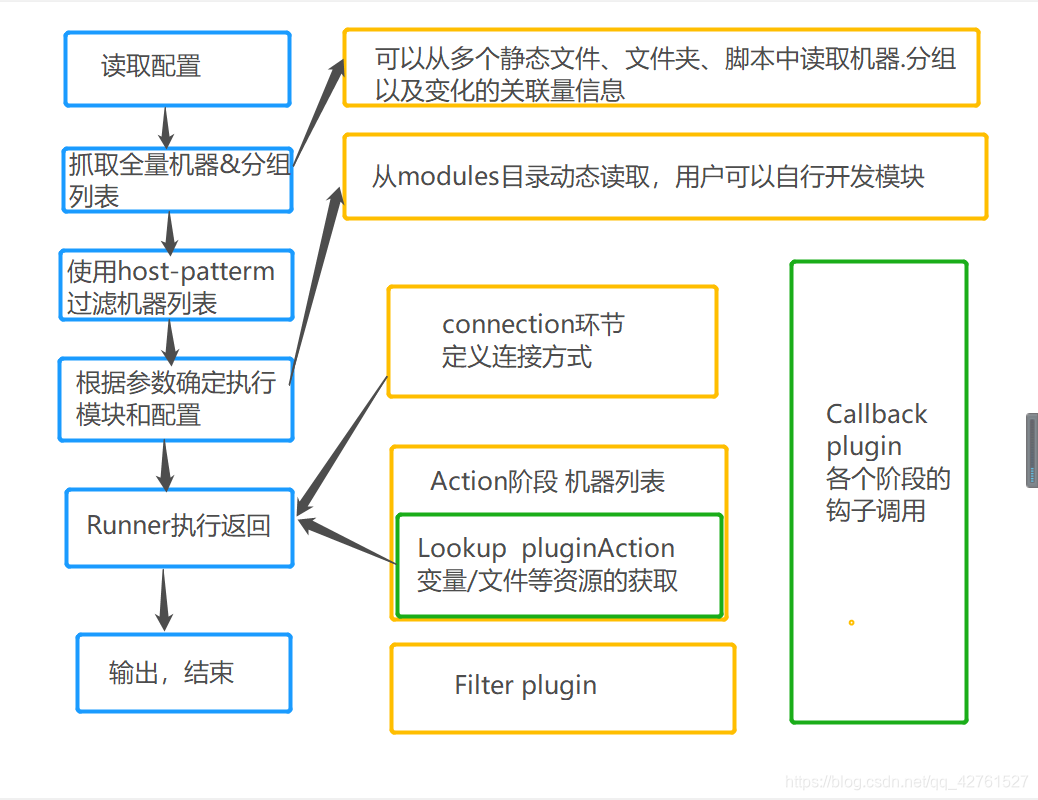
- 简单理解就是Ansible在运行时,首先读取ansible.cfg中的配置,根据规则获取Inventory中的管理主机列表,并行的在这些主机中执行配置的任务,最后等待执行返回结果。
ansible命令执行过程(背会)
-
加载自己的配置文件,默认为/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg;
-
查找对应的主机配置文件,找到要执行的主机或者组;
-
加载自己对应的模块文件,如command;
-
通过ansible将模块或者命令生成对应的py文件(python脚本),并且将该文件传输到远程服务器;
-
对应执行用户的家目录.ansible/tmp/xxx/xxx.py文件;
-
给文件添加执行权限;
-
执行并且返回结果;
-
删除临时的py文件, sleep 0退出;
三.Ansible配置解析
ansible的安装方式
- ansible安装常用两种方式,yum安装和pip程序安装。
使用pip(python的包管理模块)安装
-
首先,我们需要安装python-pip包,安装完成之后,则直接使用pip命令来安装我们的包,具体操作过程如下:
yum install python-pip
pip install ansible
使用yum安装
-
yum安装是我们比较熟悉的安装方式。我们需要先安装一个epel-release包,然后再安装ansible即可。
yum install epel-release -y
yum install ansible -y
ansible的程序结构(yum安装为例)
-
配置文件目录:/etc/ansible/
-
执行文件目录:/usr/bin/
-
Lib库依赖目录:/usr/lib/pyhtonX.X/site-packages/ansible/
-
Help文档目录:/usr/share/doc/ansible-X.X.X/
-
Man文档目录:/usr/share/man/man1/
ansible的配置文件查找顺序(背会)
- ansible与我们其他的服务在这一点上又很大的不同,这里的配置文件查找是从多个地方找的,顺序如下:
1.检查环境变量 ANSIBLE_CONFIG 指向的路径文件(export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg);
- ~/.ansible.cfg,检查当前目录下的ansible.cfg配置文件;
3./etc/ansible.cfg检查etc目录的配置文件。
ansible的配置文件
-
ansible的配置文件路径是/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg,ansible许多参数,下面我们列出一些常见的参数:
inventory = /etc/ansible/hoste #这个参数表示资源清单inventory文件的位置
library = /usr/share/ansible #指向存放ansible模块的目录,支持多个目录方式,只要用冒号(:)隔开就行。fbrks = 5 #并发连接数,默认为5
sudo_user = root #设置默认执行命令的用户 ,2.14版本中是:become_user=root
remote_port = 22 #指定连接被管理节点的端口,默认为22端口,为安全考虑,建议修改
host_key_checking = False #设置是否检查SSH主机的密钥,值为True/False,关闭后第一次连接不会提示配置实例
timeout = 60 #设置SSH连接的超时时间,单位为秒
log_path = /var/log/ansible.cfg #指定一个存储ansible日志的文件(默认不记录日志)
ansible的主机清单
-
在配置文件中,我们提到了资源清单,这个清单就是主机清单,里面保存的是一些ansible需要连接管理的主机列表。
-
如下是ansible主机清单的定义方式:
2.定义一个主机组(组名)把地址或者主机名加进去
[mysql_test]
192.168.115.101
192.168.115.102
192.168.115.103 -
需要注意的是,这里的组成员可以使用通配符来匹配,这样对于一些标准化管理就比较方便。我们可以根据实际情况来配置我们的主机列表,具体的操作如下:
vi /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
192.168.115.109
192.168.115.110
四.Ansible常用命令
[root@ansible bin]# ls /usr/bin/| grep ansible
ansible
ansible-community
ansible-config
ansible-connection
ansible-console
ansible-doc
ansible-galaxy
ansible-inventory
ansible-playbook
ansible-pull
ansible-vaultansible命令集解释
-
/usr/bin/ansible,Ansible AD-Hoc临时命令执行工具,常用于临时命令的执行
-
/usr/bin/ansible-doc,Ansible模块功能查看工具(document)
-
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy,下载上传优秀的代码或者Roles模块的官网平台,基于网络的
-
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook,Ansible定制自动化的任务集编排工具
-
/usr/bin/ansible-pull,Ansible远程执行命令的工具,拉取配置而非推送配置(使用较少,海量机器时使用,对运维架构能力要求高)
-
/usr/bin/ansible-vault,Ansible文件加密工具
-
/usr/bin/ansible-console,Ansible基于Linux Consoble界面可与用户交互的命令执行工具
-
ansible-community:
-
含义:
- "ansible-community" 严格来说不是一个命令。Ansible 是一个自动化工具,Ansible 社区(Ansible-community)是围绕 Ansible 项目的一个开源社区。这个社区主要负责维护和开发 Ansible 相关的内容,包括模块、插件、角色等。社区成员通过贡献代码、提交问题、参与讨论等方式来改进 Ansible 生态。
-
用法:
-
作为用户,你可以在社区网站(Ansible Galaxy)上查找其他人共享的 Ansible 角色。例如,如果你要部署一个 Web 服务器,你可以搜索像 "nginx-ansible-role" 这样的角色。下载并使用这些角色可以极大地简化你的 Ansible 配置过程。
-
你也可以参与社区讨论,在社区论坛或者 Ansible 官方的 GitHub 仓库(https://github.com/ansible/ansible)中提交问题或者功能请求。如果你是开发者,还可以贡献自己编写的 Ansible 模块或角色,帮助完善 Ansible 的功能。
-
-
-
ansible-config:-
含义:
ansible-config命令用于查看和管理 Ansible 的配置。Ansible 的配置文件控制着 Ansible 的行为,例如它会指定 Inventory 文件(用于定义主机列表和主机组)的位置、连接类型(SSH 等)、模块搜索路径等诸多设置。
-
用法:
-
查看配置选项:
- 运行
ansible-config view可以查看 Ansible 的当前配置。它会显示配置文件中的所有设置,包括默认设置和用户自定义设置。例如,它会显示inventory选项的值,该值指向 Ansible 用于确定受管主机的文件或脚本路径。
- 运行
-
列出配置文件搜索路径:
- 使用
ansible-config list命令可以列出 Ansible 在启动时查找配置文件的路径顺序。Ansible 会按照一定的顺序查找配置文件,通常会先查找当前目录下的ansible.cfg,然后是用户主目录下的~/.ansible.cfg,最后是系统默认的配置文件路径(如/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg)。这有助于你了解 Ansible 从哪里读取配置信息。
- 使用
-
检查配置文件中的特定选项:
- 可以使用
ansible-config dump-- only-changed命令来只显示用户修改过的配置选项。这在你有一个复杂的 Ansible 配置环境,并且只想查看与默认设置不同的部分时非常有用。例如,如果你在ansible.cfg文件中修改了remote_user选项,运行此命令就会只显示remote_user相关的配置内容。
- 可以使用
-
-
-
ansible-inventory:
-
含义
ansible-inventory是 Ansible 的一个重要组件,用于管理 Ansible 的主机清单。主机清单定义了 Ansible 将要管理的目标主机,包括主机的 IP 地址、主机名、所属的组等信息。它就像是 Ansible 的 "目标地图",告诉 Ansible 需要在哪些主机上执行任务。
-
用法
-
查看主机清单内容
-
基本的查看命令是
ansible-inventory --list。这个命令会以 JSON 格式(默认)输出主机清单中的所有信息。例如,你可以看到主机组的构成,每个主机组中有哪些主机,以及主机的一些变量(如果定义了的话)。假设你有一个简单的主机清单文件,内容如下:
inventory.ini [web_servers] web1.example.com web2.example.com [db_servers] db1.example.com -
当你运行
ansible-inventory --list时,它会输出类似这样的内容(为了简洁,省略了部分细节):
{ "web_servers": { "hosts": ["web1.example.com", "web2.example.com"], "vars": {} }, "db_servers": { "hosts": ["db1.example.com"], "vars": {} } }
-
-
以特定格式输出主机清单
-
除了 JSON 格式,你还可以使用
--yaml选项以 YAML 格式输出,即
ansible-inventory --list --yamlYAML 格式对于人类阅读可能更友好一些。继续以上面的主机清单为例,YAML 格式输出可能如下:
web_servers: hosts: -web1.example.com -web2.example.com vars: {} db_servers: hosts: -db1.example.com vars: {}
-
-
检查主机是否在清单中
- 可以使用
ansible-inventory --host <hostname>命令来检查特定主机是否在主机清单中,并查看该主机的相关变量。例如,ansible-inventory --host web1.example.com会输出该主机所属的组以及其变量(如果有)。如果主机不在清单中,会显示相应的提示信息。
- 可以使用
-
使用动态主机清单脚本
- Ansible 也支持动态主机清单。你可以编写一个脚本来动态生成主机清单内容,例如从一个数据库或者云服务提供商的 API 获取主机信息。假设你有一个名为
dynamic_inventory.py的动态主机清单脚本,你可以通过ansible-inventory-- inventory <path_to_script>来使用它。这样,每次 Ansible 运行任务时,都会先执行这个脚本获取最新的主机清单信息。
- Ansible 也支持动态主机清单。你可以编写一个脚本来动态生成主机清单内容,例如从一个数据库或者云服务提供商的 API 获取主机信息。假设你有一个名为
-
较为常用的是/usr/bin/ansible和/usr/bin/ansible-playbook
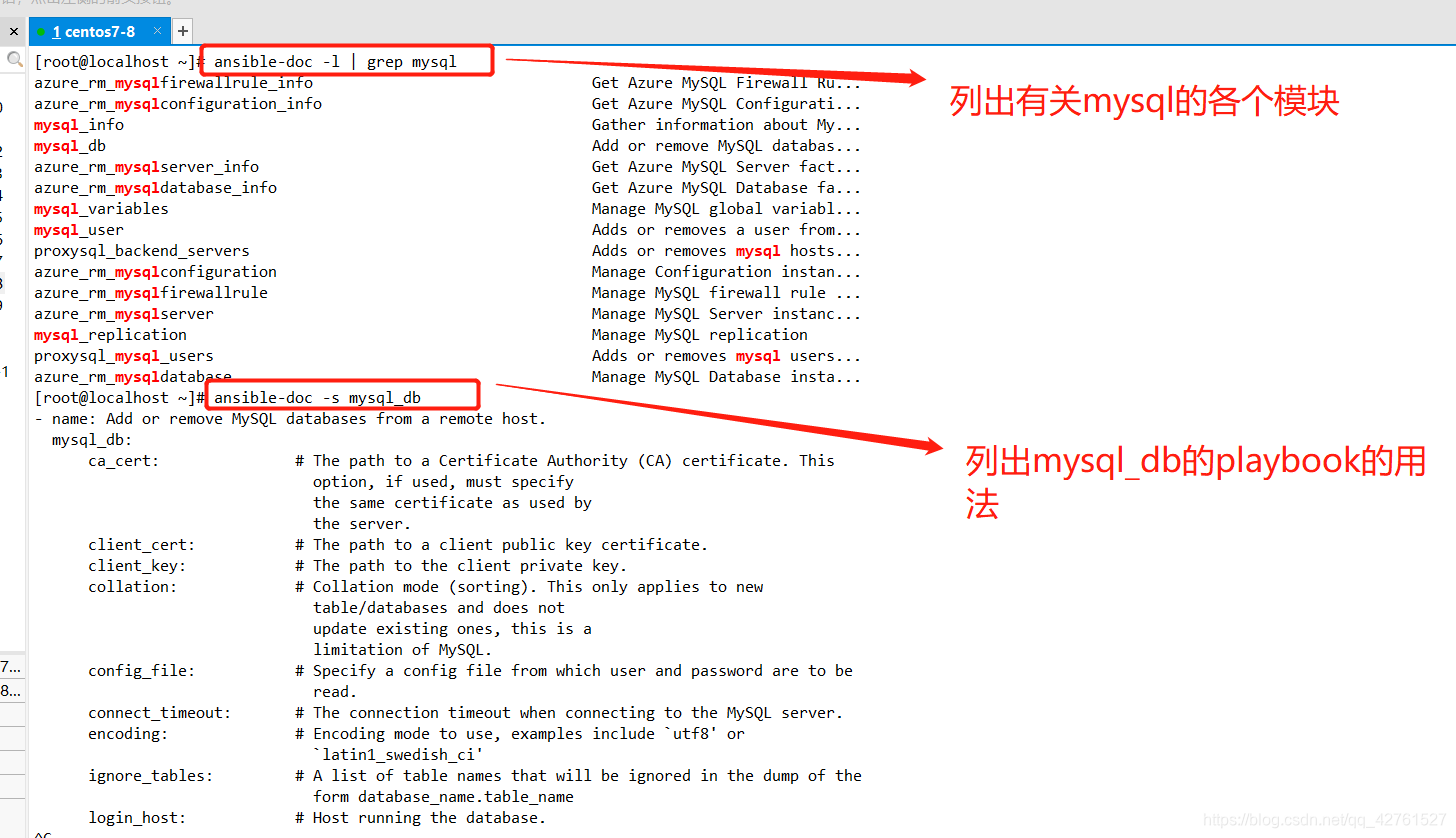
ansible-doc命令
-
ansible-doc命令常用于获取模板块信息及其适用帮助,一般用法如下:
ansible-doc -l ##获取全部模块信息
ansible-doc -s MOD_NAME #获取指定模块的使用帮助 -
ansible-doc的全部用法:
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc
usage: ansible-doc [-h] [--version] [-v] [-M MODULE_PATH]
...
optional arguments:
--metadata-dump For internal testing only Dump json metadata for
all plugins.
--playbook-dir BASEDIR
Since this tool does not use playbooks, use this as a
substitute playbook directory.This sets the relative
path for many features including roles/ group_vars/
etc.
--version show program's version number, config file location,
configured module search path, module location,
executable location and exit
-F, --list_files Show plugin names and their source files without
summaries (implies --list)##-M,指定模块的路径
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path MODULE_PATH
prepend colon-separated path(s) to module library (def
ault=~/.ansible/plugins/modules:/usr/share/ansible/plu
gins/modules)
##-h,显示命令参数API文档
-h, --help show this help message and exit##输出为json格式
-j, --json Change output into json format.
##-l,列出可用模块
-l, --list List available plugins##-s,显示剧本指定模块的用法
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified plugin(s)
ansible命令
-
ansible命令的具体格式如下
ansible <host-pattern> <-f forks> [-m module_name] [-a args]
-
如下
#使用ansible -h来查看帮助
-a,MODULE_ARGS #模块的参数,如果执行默认COMMAND的模块,即是命令参数,如:"date","pwd"。
-k,--ask-pass #ask for SSH password。登录密码,提示输入SSH密码而不是假设基于密钥的验证
--ask-pass #ask for SSH。su切换密码
-K,--ask-sudo-pass #ask for sudo password。提示密码使用sudo,sudo表示提权操作
--ask-vault-pass #ask for vault password。 假设我们设定了加密的密码,则用该选项进行访问
-B SECONDS #后台超时时间
-C #模拟运行环境并且进行预运行,可以进行查错测试
-c CONNECTION #连接类型使用
-f FORKS #并行任务数,默认为5
-i INVENTORY #指定主机清单的路径,默认为/etc/ansible/hosts
--list-hosts #查看有哪些主机组
-m MODULE_NAME #执行模块的名字,默认使用command模块,所以如果只执行单一命令可以不用 -m 参数
-o #压缩输出,尝试讲所有结果在一行输出,一般针对收集工具使用
-S #用su命令
-R SU_USER #指定su的用户,默认为root用户
-s #用sudo的命令
-U SUDO_USERSUDO #指定sudo到哪个用户,默认为root用户
-T TIMEOUT #指定ssh默认超时时间,默认为10s,也可以在配置文件中修改
-u REMOTE_USER #远程用户,默认为root用户
-v #查看详细信息,同时支持 -vvv,-vvvv可以查看更加详细的信息
ansible配置公私钥
-
上面已经提到ansible是基于ssh协议实现管理主机的,所以ansible配置公私钥的方式与ssh协议的方式相同,具体操作步骤如下:
1.生产私钥
ssh-keygen
2.向被管理主机分发私钥
ssh-copy-id root@192.168.115.109
ssh-copy-id root@192.168.115.110
五.部署ansible管理集群
实验环境
|---------|--------------------|----------------------|
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 安装包 |
| ansible | 192.168.115.108/24 | epel-release、ansible |
| node1 | 192.168.115.109/24 | - |
| node2 | 192.168.115.110/24 | - |
实验步骤
-
安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname ansible
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@ansible ~]# yum install epel-release -y
[root@ansible ~]# yum install ansible -y -
添加主机清单
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible ansible]# ls
ansible.cfg hosts roles
[root@ansible ansible]# vi hosts[web] ##添加到最后一行
192.168.115.109
192.168.115.110 -
配置公私钥
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:LPYTI56Y4SDp+SC6GkYrMoXCx1PhftoIvs3AM6iwtc4 root@localhost.localdomain
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| . . |
| o |
|.o. o . |
|=oo=..+.S |
|+oBoo*== o |
|BB.+oo.o |
|Oo.B . |
|BoEo o |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.115.109
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.115.109 (192.168.115.109)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:nryK+/NCYC3BMKWWs5x2gbYTOXHh1XQfrA1hIak57bQ.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:b4:f5:03:a7:f0:2c:48:5e:c8:26:b0:eb:c2:c3:37:45.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.115.109's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.115.109'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.115.110
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.115.110 (192.168.115.110)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Nc4WQ6E4MwaQD/67ALzZ36hjNRigxQSUiDa2ZP5ZT+o.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:f7:33:08:60:92:d5:99:2c:9e:fe:47:5a:63:c8:e5:a8.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.115.110's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.115.110'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
全程是只需要,在ansible上面操作就行!!!
六.Ansible常用模块
主机连通性测试
-
使用下列命令对主机清单中的资源进行连通性测试,出现下列信息说明主机处于连通状态
#ansible 主机清单组名 -m(指定模块名字)
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible web -m ping
192.168.115.110 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.115.109 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
command模块
-
command模块可以直接在远程主机上执行命令,并且结果返回打印出来,举例如下:
##-m 指定执行模块
##-a 指定命令执行
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m command -a 'date'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 05月 09日 星期六 23:47:12 CST
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 05月 09日 星期六 23:47:12 CST
[root@ansible ~]# -
命令模块接受命令名称,后面是空格分隔的列表参数。给定的命令将在所有选定的节点上执行,它不会通过shell进行处理,比如$HOME和操作如"<",">","| ", " ; " ," & " (需要使用 shell模块实现这些功能)。注意,command模块不支持 | 管道命令。
-
下面是command模块常用的几个命令:
-
chdir:在执行命令之前,先切换到该目录
-
execurable:切换shell来执行命令,需要使用命令的绝对路径
- free_form:要执行的Linux指令,一般使用Ansible的-a参数代替
- creates:一个文件名,当这个文件存在,则该命令不执行,可以用来做判断
- removes:一个文件名,这个文件不存在,则该命令不执行
-
-
以下是这些命令的效果
##使用chdir切换到/etc/init.d目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m command -a 'chdir=/etc/init.d/ ls'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
functions
netconsole
network
README
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
functions
netconsole
network
README
[root@ansible ~]###使用removes,如果/demo/1.txt存在,就执行cat /demo/1.txt
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m command -a 'removes=/demo/1.txt cat /demo/1.txt'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
123456
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
hello##使用creates命令,如果/demo/1.txt存在,就不执行cat /demo/1.txt
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m command -a 'creates=/demo/1.txt cat /demo/1.txt'
192.168.115.109 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
skipped, since /demo/1.txt exists
192.168.115.110 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
skipped, since /demo/1.txt exists
[root@ansible ~]#
shell模块
-
shell模块可以在远程主机上调用shell解释器运行命令,支持shell的各种功能,例如管道等
-
只要是shell命令都可以在通过这个模块在远程主机里面运行
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'cat /etc/passwd | grep zhangsan'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
zhangsan:x:1000:1000:zhangsan:/home/zhangsan:/bin/bash
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
zhangsan:x:1000:1000:zhangsan:/home/zhangsan:/bin/bash
[root@ansible ~]#
由于command不支持 管道符,所以它只会支持cat /etc/passwd命令
copy模块
-
这个模块用于将文件复制到远程主机上,同时支持给定的内容生成文件和修改权限等
-
copy模块的相关选项如下:
-
src:被复制到远程主机的本地文件。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,则会递归复制,用法类似于"rsync"。
-
content:用于替换"src",可以直接指定文件的值。
- dest:必选项,将源文件复制到远程主机的绝对路径。
- backup:当文件内容发生改变之后,在覆盖之前,把源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息
- directory_mode:递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限。
- force:当目标主机包含该文件,但是内容不同时,设定为"yes",表示强制覆盖;设定为"no"表示目标主机的目标位置不存在该文件才复制。默认为"yes"
-
others:所有的file模块中的选项可以在这里使用
-
mode:设置文件权限
-
-
实例如下:复制文件
##将本机上的/demo目录下的3.txt文件,复制到两台主机上的/demo目录下
[root@ansible demo]# ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/demo/3.txt dest=/demo/'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "4258ace817f2bab84ea0000994ef1c5e8af846a6",
"dest": "/demo/3.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "dc0f773ded25b9d58df84db7aa32f469",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589042627.02-39109-97783002427527/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "4258ace817f2bab84ea0000994ef1c5e8af846a6",
"dest": "/demo/3.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "dc0f773ded25b9d58df84db7aa32f469",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589042626.95-39110-67128953762580/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@ansible demo]# -
给定内容生成文件,并且制定权限
##生成内容为"are you ok?"名为leijun的文件,并且设置权限的777
[root@ansible demo]# ansible web -m copy -a 'content="are you ok?" dest=/demo/leijun mode=777'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "268b5f3043df32453de96b4ada31359fd272cdf1",
"dest": "/demo/leijun",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "9a631734b0ff69c17ddc29ad6630e5ca",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589042810.58-39188-12173260144729/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "268b5f3043df32453de96b4ada31359fd272cdf1",
"dest": "/demo/leijun",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "9a631734b0ff69c17ddc29ad6630e5ca",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589042810.56-39186-85881390315107/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[root@ansible demo]###我们在两台主机上查看文件以及权限
[root@ansible demo]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ls -l /demo/'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 16
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:25 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:23 2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:43 3.txt
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:46 leijun
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 7 5月 10 00:20 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:43 3.txt
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:46 leijun
[root@ansible demo]# -
备份源文件,并且覆盖源文件
##创建新的内容覆盖原文件,并且备份
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m copy -a 'content="I AM FINE!!" backup=yes dest=/demo/leijun mode=777'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"backup_file": "/demo/leijun.38452.2020-05-10@00:52:24~",
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"dest": "/demo/leijun",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "83e50cab85cd9c3c97653bba92bd4f3c",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589043141.62-39340-178866206619671/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"backup_file": "/demo/leijun.40723.2020-05-10@00:52:24~",
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"dest": "/demo/leijun",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "83e50cab85cd9c3c97653bba92bd4f3c",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1589043141.62-39342-73367933698642/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}###查看被控主机的文件状态
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ls -l /demo/'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 20
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:25 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:23 2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:43 3.txt
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:52 leijun
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:46 leijun.40723.2020-05-10@00:52:24~
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 16
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 7 5月 10 00:20 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6 5月 10 00:43 3.txt
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:52 leijun
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 00:46 leijun.38452.2020-05-10@00:52:24~
[root@ansible ~]#
file模块
-
file模块主要用于设置文件的属性,比如创建文件、创建连接文件、删除文件等,如下为常见的命令:
-
force:需要两种情况下强制创建软连接,一种是源文件不存在,但是之后会建立的情况下;另外一种是目标软链接已存在,需要取消之前的软链接,然后创建新的,有两个选项:yes|no。
-
path:指定创建路径
-
-
group:定义文件/目录的属组。后面可以加上mode:定义文件/目录的权限。
-
owner:定义文件/目录的属主,后面必须加上path:定义文件/目录的路径。
-
recurse:递归设置文件的属性,只对目录有效,后面跟上src:被链接的源文件路径,只应用于state=link的情况
-
dest:被链接到的路径,只应用于state=link的情况
-
mode:指定权限。
-
state:状态,有如下选项:
-
directory:如果目录不存在,就创建目录
-
file:即使文件不存在,也不会被创建;已经存在的文件可以修改文件的属性。
-
link:创建软链接
-
hard:创建硬链接
-
touch:如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新的文件,如果文件或者目录已经存在,则更新其最后修改时间
-
absent:删除目录、文件或者取消链接文件
-
-
创建目录,实例如下:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m file -a 'path=/opt/app state=directory'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/opt/app",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/opt/app",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ls -l /opt/'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
[root@ansible ~]# -
创建链接文件,实例如下:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m file -a 'path=/opt/abc src=/demo/1.txt state=link'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/abc",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/demo/1.txt",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/abc",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 11,
"src": "/demo/1.txt",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ls -l /opt'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 01:22 abc -> /demo/1.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 5月 10 01:22 abc -> /demo/1.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
[root@ansible ~]# -
删除文件如下所示:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m file -a 'path=/opt/abc state=absent'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/opt/abc",
"state": "absent"
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/opt/abc",
"state": "absent"
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'ls -l /opt'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 5月 10 01:18 app
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
[root@ansible ~]#
fetch模块
-
fetch模块用于从远程某个主机获取(复制)文件到本地来
-
dest:用来存储文件的目录。
-
src:在远程拉取的文件,并且是一个file,不能是目录
-
-
具体实例如下:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m fetch -a 'src=/demo/leijun dest=/mnt'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"dest": "/mnt/192.168.115.110/demo/leijun",
"md5sum": "83e50cab85cd9c3c97653bba92bd4f3c",
"remote_checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"dest": "/mnt/192.168.115.109/demo/leijun",
"md5sum": "83e50cab85cd9c3c97653bba92bd4f3c",
"remote_checksum": "fc01c3f0eb6a707879d64649b22b31f710ebede5",
"remote_md5sum": null
}
[root@ansible ~]# ls /mnt
192.168.115.109 192.168.115.110
[root@ansible ~]# ls /mnt/192.168.115.110/
demo
[root@ansible ~]# ls /mnt/192.168.115.110/demo/
leijun
[root@ansible ~]#
cron模块
-
cron模块用于管理crontab计划性任务的,它的语法和crontab中的语法一致
-
day=:日应该运行的工作( 1-31, *, */2, ) -
hour=:小时 ( 0-23, *, */2, ) -
minute=:分钟( 0-59, *, */2, ) -
month=:月( 1-12, *, /2, ) -
weekday=: 周 ( 0-6 for Sunday-Saturday,, ) -
job=:指明运行的命令是什么 -
name=:定时任务描述 -
reboot:任务在重启时运行,不建议使用,建议使用special_time -
special_time:特殊的时间范围,参数:reboot(重启时),annually(每年),monthly(每月),weekly(每周),daily(每天),hourly(每小时) -
state:指定状态-
present表示添加定时任务,也是默认设置,
-
absent表示删除定时任务
-
-
user:以哪个用户的身份执行
-
-
添加计划性任务如下,实例如下:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m cron -a 'name="ifconfig every 5 min" minute=*/5 job="/sbin/ifconfig"'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"ifconfig every 5 min"
]
}
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"ifconfig every 5 min"
]
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: ifconfig every 5 min
*/5 * * * * /sbin/ifconfig
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: ifconfig every 5 min
*/5 * * * * /sbin/ifconfig
[root@ansible ~]# -
删除计划性任务,比如我们计划任务添加错误,则可以执行以下命令删除计划任务
##首先查看一下,已有的计划性任务
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: ifconfig every 5 min
*/5 * * * * /sbin/ifconfig
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: ifconfig every 5 min
*/5 * * * * /sbin/ifconfig##准备删除计划性任务
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m cron -a 'name="ifconfig every 5 min" minute=*/5 job="/sbin/ifconfig" state=absent'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'crontab -l'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@ansible ~]#
yum模块
-
yum模块主要用于软件的安装,它的选项如下
- name= :所安装的软件包的名称
-
state= :
-
present--》安装
-
latest--》安装最新的
-
absent--》卸载软件
-
-
update_cache :强制更新yum的缓存
-
conf_file :指定远程yum安装时所依赖的配置文件(安装本地已有的包)。
-
disable_pgp_check :是否禁止GPG checking,只用于present 或者 latest。
-
disablerepo :临时禁止使用yum库。只用于安装或者更新时。
-
enablerepo :临时使用的yum库。只用于安装或者更新时。
-
如下演示安装 tree软件包
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m yum -a 'name=tree state=present'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"tree"
]
},
"msg": "warning: /var/cache/yum/x86_64/7/base/packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY\nImporting GPG key 0xF4A80EB5:\n Userid : "CentOS-7 Key (CentOS 7 Official Signing Key) security@centos.org"\n Fingerprint: 6341 ab27 53d7 8a78 a7c2 7bb1 24c6 a8a7 f4a8 0eb5\n Package : centos-release-7-4.1708.el7.centos.x86_64 (@anaconda)\n From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7\n",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks\nLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile\n * base: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\n * extras: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\n * updates: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\nResolving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package tree.x86_64 0:1.6.0-10.el7 will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n tree x86_64 1.6.0-10.el7 base 46 k\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package\n\nTotal download size: 46 k\nInstalled size: 87 k\nDownloading packages:\nPublic key for tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm is not installed\nRetrieving key from file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7\nRunning transaction check\nRunning transaction test\nTransaction test succeeded\nRunning transaction\n Installing : tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n Verifying : tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n tree.x86_64 0:1.6.0-10.el7 \n\nComplete!\n"
]
}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"tree"
]
},
"msg": "warning: /var/cache/yum/x86_64/7/base/packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY\nImporting GPG key 0xF4A80EB5:\n Userid : "CentOS-7 Key (CentOS 7 Official Signing Key) security@centos.org"\n Fingerprint: 6341 ab27 53d7 8a78 a7c2 7bb1 24c6 a8a7 f4a8 0eb5\n Package : centos-release-7-4.1708.el7.centos.x86_64 (@anaconda)\n From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7\n",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks\nLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile\n * base: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn\n * extras: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn\n * updates: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn\nResolving Dependencies\n--> Running transaction check\n---> Package tree.x86_64 0:1.6.0-10.el7 will be installed\n--> Finished Dependency Resolution\n\nDependencies Resolved\n\n================================================================================\n Package Arch Version Repository Size\n================================================================================\nInstalling:\n tree x86_64 1.6.0-10.el7 base 46 k\n\nTransaction Summary\n================================================================================\nInstall 1 Package\n\nTotal download size: 46 k\nInstalled size: 87 k\nDownloading packages:\nPublic key for tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm is not installed\nRetrieving key from file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7\nRunning transaction check\nRunning transaction test\nTransaction test succeeded\nRunning transaction\n Installing : tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n Verifying : tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64 1/1 \n\nInstalled:\n tree.x86_64 0:1.6.0-10.el7 \n\nComplete!\n"
]
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'rpm -q tree'
[WARNING]: Consider using the yum, dnf or zypper module rather than running 'rpm'. If
you need to use command because yum, dnf or zypper is insufficient you can add 'warn:
false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in ansible.cfg to get rid of
this message.
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64
[root@ansible ~]#
service模块
-
service模块用于服务程序的管理,它的主要选项如下:
- arguments:命令行提供额外的参数
-
enabled:设置开机自启;true | false
-
name:服务名称
-
runlevel:开机启动的级别,一般不用指定。
-
sleep:在重启服务的过程中,是否等待。如在服务关闭以后等待2秒在启动。(定义在剧本当中)
-
state:有四种状态分别为
-
started(启动服务)
-
stopped(停止服务)
-
restarted(重启服务)
-
reloaded(重载服务)
-
-
开启httpd服务并且设置开启自启
##httpd服务必须自行安装httpd软件包
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=present'##检查80端口有没有开启
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'netstat -natp | grep 80'
192.168.115.110 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
192.168.115.109 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code##开启httpd服务并且设置开机自启
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=true'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
"status": {
"ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveState": "inactive",
"After": "remote-fs.target system.slice tmp.mount basic.target -.mount systemd-journald.socket network.target nss-lookup.target",
"AllowIsolate": "no",
"AmbientCapabilities": "0",
"AssertResult": "no",
"AssertTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"Before": "shutdown.target",
"BlockIOAccounting": "no",
"BlockIOWeight": "18446744073709551615",
"CPUAccounting": "no",
"CPUQuotaPerSecUSec": "infinity",
"CPUSchedulingPolicy": "0",
"CPUSchedulingPriority": "0",
"CPUSchedulingResetOnFork": "no",
"CPUShares": "18446744073709551615",
"CanIsolate": "no",
"CanReload": "yes",
"CanStart": "yes",
"CanStop": "yes",
"CapabilityBoundingSet": "18446744073709551615",
"ConditionResult": "no",
"ConditionTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"Conflicts": "shutdown.target",
"ControlPID": "0",
"DefaultDependencies": "yes",
"Delegate": "no",
"Description": "The Apache HTTP Server",
"DevicePolicy": "auto",
"Documentation": "man:httpd(8) man:apachectl(8)",
"EnvironmentFile": "/etc/sysconfig/httpd (ignore_errors=no)",
"ExecMainCode": "0",
"ExecMainExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ExecMainPID": "0",
"ExecMainStartTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ExecMainStatus": "0",
"ExecReload": "{ path=/usr/sbin/httpd ; argv[]=/usr/sbin/httpd OPTIONS -k graceful ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }", "ExecStart": "{ path=/usr/sbin/httpd ; argv[]=/usr/sbin/httpd OPTIONS -DFOREGROUND ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }",
"ExecStop": "{ path=/bin/kill ; argv[]=/bin/kill -WINCH {MAINPID} ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }", "FailureAction": "none", "FileDescriptorStoreMax": "0", "FragmentPath": "/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service", "GuessMainPID": "yes", "IOScheduling": "0", "Id": "httpd.service", "IgnoreOnIsolate": "no", "IgnoreOnSnapshot": "no", "IgnoreSIGPIPE": "yes", "InactiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0", "InactiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0", "JobTimeoutAction": "none", "JobTimeoutUSec": "0", "KillMode": "control-group", "KillSignal": "18", "LimitAS": "18446744073709551615", "LimitCORE": "18446744073709551615", "LimitCPU": "18446744073709551615", "LimitDATA": "18446744073709551615", "LimitFSIZE": "18446744073709551615", "LimitLOCKS": "18446744073709551615", "LimitMEMLOCK": "65536", "LimitMSGQUEUE": "819200", "LimitNICE": "0", "LimitNOFILE": "4096", "LimitNPROC": "3789", "LimitRSS": "18446744073709551615", "LimitRTPRIO": "0", "LimitRTTIME": "18446744073709551615", "LimitSIGPENDING": "3789", "LimitSTACK": "18446744073709551615", "LoadState": "loaded", "MainPID": "0", "MemoryAccounting": "no", "MemoryCurrent": "18446744073709551615", "MemoryLimit": "18446744073709551615", "MountFlags": "0", "Names": "httpd.service", "NeedDaemonReload": "no", "Nice": "0", "NoNewPrivileges": "no", "NonBlocking": "no", "NotifyAccess": "main", "OOMScoreAdjust": "0", "OnFailureJobMode": "replace", "PermissionsStartOnly": "no", "PrivateDevices": "no", "PrivateNetwork": "no", "PrivateTmp": "yes", "ProtectHome": "no", "ProtectSystem": "no", "RefuseManualStart": "no", "RefuseManualStop": "no", "RemainAfterExit": "no", "Requires": "basic.target -.mount", "RequiresMountsFor": "/var/tmp", "Restart": "no", "RestartUSec": "100ms", "Result": "success", "RootDirectoryStartOnly": "no", "RuntimeDirectoryMode": "0755", "SameProcessGroup": "no", "SecureBits": "0", "SendSIGHUP": "no", "SendSIGKILL": "yes", "Slice": "system.slice", "StandardError": "inherit", "StandardInput": "null", "StandardOutput": "journal", "StartLimitAction": "none", "StartLimitBurst": "5", "StartLimitInterval": "10000000", "StartupBlockIOWeight": "18446744073709551615", "StartupCPUShares": "18446744073709551615", "StatusErrno": "0", "StopWhenUnneeded": "no", "SubState": "dead", "SyslogLevelPrefix": "yes", "SyslogPriority": "30", "SystemCallErrorNumber": "0", "TTYReset": "no", "TTYVHangup": "no", "TTYVTDisallocate": "no", "TasksAccounting": "no", "TasksCurrent": "18446744073709551615", "TasksMax": "18446744073709551615", "TimeoutStartUSec": "1min 30s", "TimeoutStopUSec": "1min 30s", "TimerSlackNSec": "50000", "Transient": "no", "Type": "notify", "UMask": "0022", "UnitFilePreset": "disabled", "UnitFileState": "disabled", "Wants": "system.slice", "WatchdogTimestampMonotonic": "0", "WatchdogUSec": "0" } } 192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => { "ansible_facts": { "discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed": true, "enabled": true, "name": "httpd", "state": "started", "status": { "ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0", "ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0", "ActiveState": "inactive", "After": "tmp.mount network.target systemd-journald.socket nss-lookup.target remote-fs.target basic.target system.slice -.mount", "AllowIsolate": "no", "AmbientCapabilities": "0", "AssertResult": "no", "AssertTimestampMonotonic": "0", "Before": "shutdown.target", "BlockIOAccounting": "no", "BlockIOWeight": "18446744073709551615", "CPUAccounting": "no", "CPUQuotaPerSecUSec": "infinity", "CPUSchedulingPolicy": "0", "CPUSchedulingPriority": "0", "CPUSchedulingResetOnFork": "no", "CPUShares": "18446744073709551615", "CanIsolate": "no", "CanReload": "yes", "CanStart": "yes", "CanStop": "yes", "CapabilityBoundingSet": "18446744073709551615", "ConditionResult": "no", "ConditionTimestampMonotonic": "0", "Conflicts": "shutdown.target", "ControlPID": "0", "DefaultDependencies": "yes", "Delegate": "no", "Description": "The Apache HTTP Server", "DevicePolicy": "auto", "Documentation": "man:httpd(8) man:apachectl(8)", "EnvironmentFile": "/etc/sysconfig/httpd (ignore_errors=no)", "ExecMainCode": "0", "ExecMainExitTimestampMonotonic": "0", "ExecMainPID": "0", "ExecMainStartTimestampMonotonic": "0", "ExecMainStatus": "0", "ExecReload": "{ path=/usr/sbin/httpd ; argv[]=/usr/sbin/httpd OPTIONS -k graceful ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }",
"ExecStart": "{ path=/usr/sbin/httpd ; argv[]=/usr/sbin/httpd OPTIONS -DFOREGROUND ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }", "ExecStop": "{ path=/bin/kill ; argv[]=/bin/kill -WINCH {MAINPID} ; ignore_errors=no ; start_time=[n/a] ; stop_time=[n/a] ; pid=0 ; code=(null) ; status=0/0 }",
"FailureAction": "none",
"FileDescriptorStoreMax": "0",
"FragmentPath": "/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service",
"GuessMainPID": "yes",
"IOScheduling": "0",
"Id": "httpd.service",
"IgnoreOnIsolate": "no",
"IgnoreOnSnapshot": "no",
"IgnoreSIGPIPE": "yes",
"InactiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"InactiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"JobTimeoutAction": "none",
"JobTimeoutUSec": "0",
"KillMode": "control-group",
"KillSignal": "18",
"LimitAS": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitCORE": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitCPU": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitDATA": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitFSIZE": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitLOCKS": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitMEMLOCK": "65536",
"LimitMSGQUEUE": "819200",
"LimitNICE": "0",
"LimitNOFILE": "4096",
"LimitNPROC": "3789",
"LimitRSS": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitRTPRIO": "0",
"LimitRTTIME": "18446744073709551615",
"LimitSIGPENDING": "3789",
"LimitSTACK": "18446744073709551615",
"LoadState": "loaded",
"MainPID": "0",
"MemoryAccounting": "no",
"MemoryCurrent": "18446744073709551615",
"MemoryLimit": "18446744073709551615",
"MountFlags": "0",
"Names": "httpd.service",
"NeedDaemonReload": "no",
"Nice": "0",
"NoNewPrivileges": "no",
"NonBlocking": "no",
"NotifyAccess": "main",
"OOMScoreAdjust": "0",
"OnFailureJobMode": "replace",
"PermissionsStartOnly": "no",
"PrivateDevices": "no",
"PrivateNetwork": "no",
"PrivateTmp": "yes",
"ProtectHome": "no",
"ProtectSystem": "no",
"RefuseManualStart": "no",
"RefuseManualStop": "no",
"RemainAfterExit": "no",
"Requires": "-.mount basic.target",
"RequiresMountsFor": "/var/tmp",
"Restart": "no",
"RestartUSec": "100ms",
"Result": "success",
"RootDirectoryStartOnly": "no",
"RuntimeDirectoryMode": "0755",
"SameProcessGroup": "no",
"SecureBits": "0",
"SendSIGHUP": "no",
"SendSIGKILL": "yes",
"Slice": "system.slice",
"StandardError": "inherit",
"StandardInput": "null",
"StandardOutput": "journal",
"StartLimitAction": "none",
"StartLimitBurst": "5",
"StartLimitInterval": "10000000",
"StartupBlockIOWeight": "18446744073709551615",
"StartupCPUShares": "18446744073709551615",
"StatusErrno": "0",
"StopWhenUnneeded": "no",
"SubState": "dead",
"SyslogLevelPrefix": "yes",
"SyslogPriority": "30",
"SystemCallErrorNumber": "0",
"TTYReset": "no",
"TTYVHangup": "no",
"TTYVTDisallocate": "no",
"TasksAccounting": "no",
"TasksCurrent": "18446744073709551615",
"TasksMax": "18446744073709551615",
"TimeoutStartUSec": "1min 30s",
"TimeoutStopUSec": "1min 30s",
"TimerSlackNSec": "50000",
"Transient": "no",
"Type": "notify",
"UMask": "0022",
"UnitFilePreset": "disabled",
"UnitFileState": "disabled",
"Wants": "system.slice",
"WatchdogTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"WatchdogUSec": "0"
}
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'netstat -natp | grep 80'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3459/httpd
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3492/httpd
[root@ansible ~]# -
通过service模块关闭httpd服务
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'netstat -natp | grep 80'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3492/httpd
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3459/httpd
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped'
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "stopped",
"status": {
...}}
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "stopped",
"status": {
...
}
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'netstat -natp | grep 80'
192.168.115.110 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
192.168.115.109 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
[root@ansible ~]#
user模块
-
user模块主要用来管理用户账号,它的主要选项如下所示:
- comment :用户的描述信息
-
createhome:是否创建家目录
-
force:在使用state=absent时,行为于userdel --force一致
-
group:指定基本组
-
groups:指定附加组
-
home:指定用户家目录
-
move_home:如果设置为home=时,试图将用户主目录移动到指定的目录
-
name:指定用户名
-
non_unique:该选项允许改变非唯一的用户ID值
-
password:指定用户密码,使用密文密码
-
remove:在使用state=absent时,行为是与userdel --remove一致
-
shell:指定默认的shell
-
state:设置账号状态,不指定为默认创建,指定值为absent表示删除
-
system:当创建一个用户,设置这个用户是系统用户。这个设置不能更改现有的用户
-
uid:指定用户的uid
-
添加用户并且指定用户的uid和密码
[root@localhost ~]# openssl passwd -1 "123"
[root@ansible ~]# ansible testpc -m user -a "name=zhangs password=$1$YQ95Kwoj$zl3/WhADN52TxlYT3bJ4W0"
192.168.115.112 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"append": false,
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"group": 1003,
"home": "/home/zhangs",
"move_home": false,
"name": "zhangs",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"uid": 1003
}
192.168.115.114 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"append": false,
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"group": 1003,
"home": "/home/zhangs",
"move_home": false,
"name": "zhangs",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"uid": 1003
}
192.168.115.113 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"append": false,
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"group": 1003,
"home": "/home/zhangs",
"move_home": false,
"name": "zhangs",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"uid": 1003
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible testpc -m shell -a "tail -1 /etc/shadow"
192.168.115.112 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
zhangs:1YQ95Kwojzl3/WhADN52TxlYT3bJ4W0:19795:0:99999:7::: 192.168.115.113 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> zhangs:1YQ95Kwojzl3/WhADN52TxlYT3bJ4W0:19795:0:99999:7:::
192.168.115.114 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
zhangs:1YQ95Kwoj$zl3/WhADN52TxlYT3bJ4W0:19795:0:99999:7:::
-
删除用户
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m user -a 'name=lisi state=absent'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "lisi",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "lisi",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'cat /etc/passwd | grep lisi'
192.168.115.109 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
192.168.115.110 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
[root@ansible ~]#
group模块
-
group模块主要用于添加或者删除组,常用选项如下所示:
- gid= 设置组的GID号
-
name= 指定组的名称
-
state= 指定组的状态,默认为创建,设置值为absent为删除
-
system= 设置值为yes,表示创建为系统组
-
实例命令如下
#创建组
ansible web -m group -a 'name=lisi gid=33333'
#查看已经创建的组
ansible web -m shell -a 'cat /etc/group | grep 33333'##删除组
ansible web -m group -a 'name=lisi state=absent'
script模块
-
script模块用于将本机的脚本在被管理端的机器上运行。该模块直接指定脚本的路径即可
-
现在本机写一个脚本文件
[root@ansible ~]# chmod +x demo.sh
[root@ansible ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg 模板 图片 下载 桌面
demo.sh 公共 视频 文档 音乐
[root@ansible ~]# cat demo.sh
#/bin/bash
df -hT
[root@ansible ~]# -
运行这个脚本于被管理端
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m script -a '/root/demo.sh'
192.168.115.109 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.115.109 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.115.109 closed."
],
"stdout": "文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点\r\n/dev/sda2 xfs 20G 3.3G 17G 17% /\r\ndevtmpfs devtmpfs 474M 0 474M 0% /dev\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /dev/shm\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 7.2M 482M 2% /run\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup\r\n/dev/sda3 xfs 10G 33M 10G 1% /home\r\n/dev/sda1 xfs 8.0G 158M 7.9G 2% /boot\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0\r\n",
"stdout_lines": [
"文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点",
"/dev/sda2 xfs 20G 3.3G 17G 17% /",
"devtmpfs devtmpfs 474M 0 474M 0% /dev",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /dev/shm",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 7.2M 482M 2% /run",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup",
"/dev/sda3 xfs 10G 33M 10G 1% /home",
"/dev/sda1 xfs 8.0G 158M 7.9G 2% /boot",
"tmpfs tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42",
"tmpfs tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0"
]
}
192.168.115.110 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.115.110 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.115.110 closed."
],
"stdout": "文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点\r\n/dev/sda2 xfs 20G 4.3G 16G 22% /\r\ndevtmpfs devtmpfs 474M 0 474M 0% /dev\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /dev/shm\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 7.2M 482M 2% /run\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup\r\n/dev/sda3 xfs 10G 33M 10G 1% /home\r\n/dev/sda1 xfs 8.0G 158M 7.9G 2% /boot\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42\r\ntmpfs tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0\r\n",
"stdout_lines": [
"文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点",
"/dev/sda2 xfs 20G 4.3G 16G 22% /",
"devtmpfs devtmpfs 474M 0 474M 0% /dev",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /dev/shm",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 7.2M 482M 2% /run",
"tmpfs tmpfs 489M 0 489M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup",
"/dev/sda3 xfs 10G 33M 10G 1% /home",
"/dev/sda1 xfs 8.0G 158M 7.9G 2% /boot",
"tmpfs tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42",
"tmpfs tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0"
]
}
[root@ansible ~]#
setup模块
-
setup模块主要用于收集信息,是通过调用facts组件来实现的,facts组件时Ansible用于采集被管理机器设备信息的一个功能。我们可以使用setup模块查看机器的所有facts信息,可以使用filter来查看指定信息。整个facts信息被包装在一个JSON格式的数据文件中,ansible_facts是最上层的值。
-
facts就是变量,内建变量。每个主机的各种信息,cpu个数,内存的大小等。会存在facts中的某个变量中,调用后返回很多对应主机的信息,在后面的操作中可以根据不同的信息来做不同的操作。比如redhat系列用yum安装,而debian系列用apt安装软件
-
查看信息实例,查看被管理主机的内存
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m setup -a 'filter="mem"'
192.168.115.109 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memfree_mb": 177,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 603,
"used": 373
},
"real": {
"free": 177,
"total": 976,
"used": 799
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 2045,
"total": 2045,
"used": 0
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": 976,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
192.168.115.110 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memfree_mb": 180,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 594,
"used": 382
},
"real": {
"free": 180,
"total": 976,
"used": 796
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 2045,
"total": 2045,
"used": 0
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": 976,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
[root@ansible ~]# -
setup模块还有一个很好的功能就是保存我们筛选出来的信息到我们的主机上,同时,文件名是被管理主机的IP地址,方便检测那台主机出现问题。
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m setup -a 'filter="mem"' --tree /tmp/facts
192.168.115.110 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memfree_mb": 181,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 596,
"used": 380
},
"real": {
"free": 181,
"total": 976,
"used": 795
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 2045,
"total": 2045,
"used": 0
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": 976,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
192.168.115.109 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memfree_mb": 177,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 604,
"used": 372
},
"real": {
"free": 177,
"total": 976,
"used": 799
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 2045,
"total": 2045,
"used": 0
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": 976,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
[root@ansible ~]# ls /tmp/facts/
192.168.115.109 192.168.115.110
[root@ansible ~]# cat /tmp/facts/192.168.115.109
{"ansible_facts": {"ansible_memfree_mb": 177, "ansible_memory_mb": {"nocache": {"free": 604, "used": 372}, "real": {"free": 177, "total": 976, "used": 799}, "swap": {"cached": 0, "free": 2045, "total": 2045, "used": 0}}, "ansible_memtotal_mb": 976, "discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false}
[root@ansible ~]#