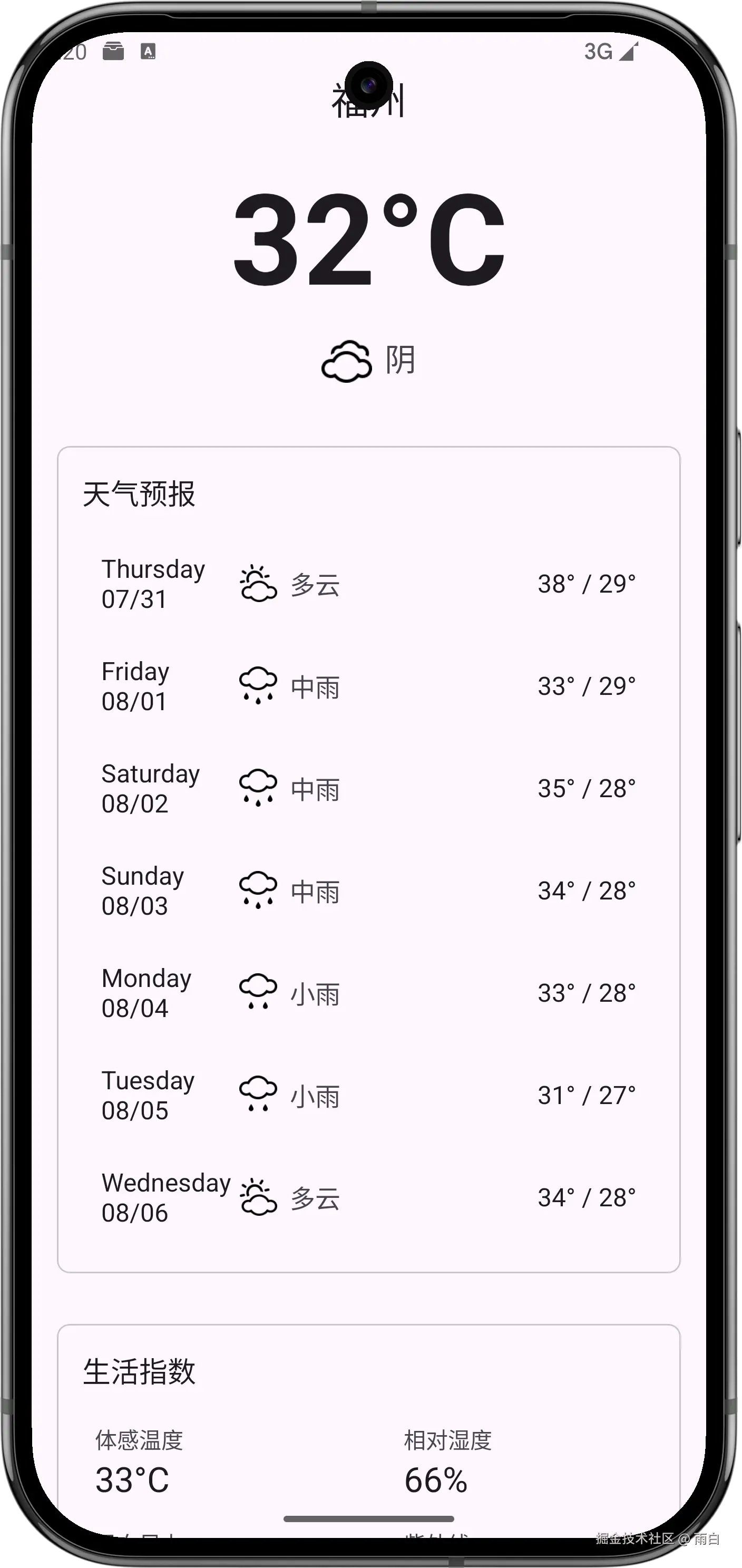
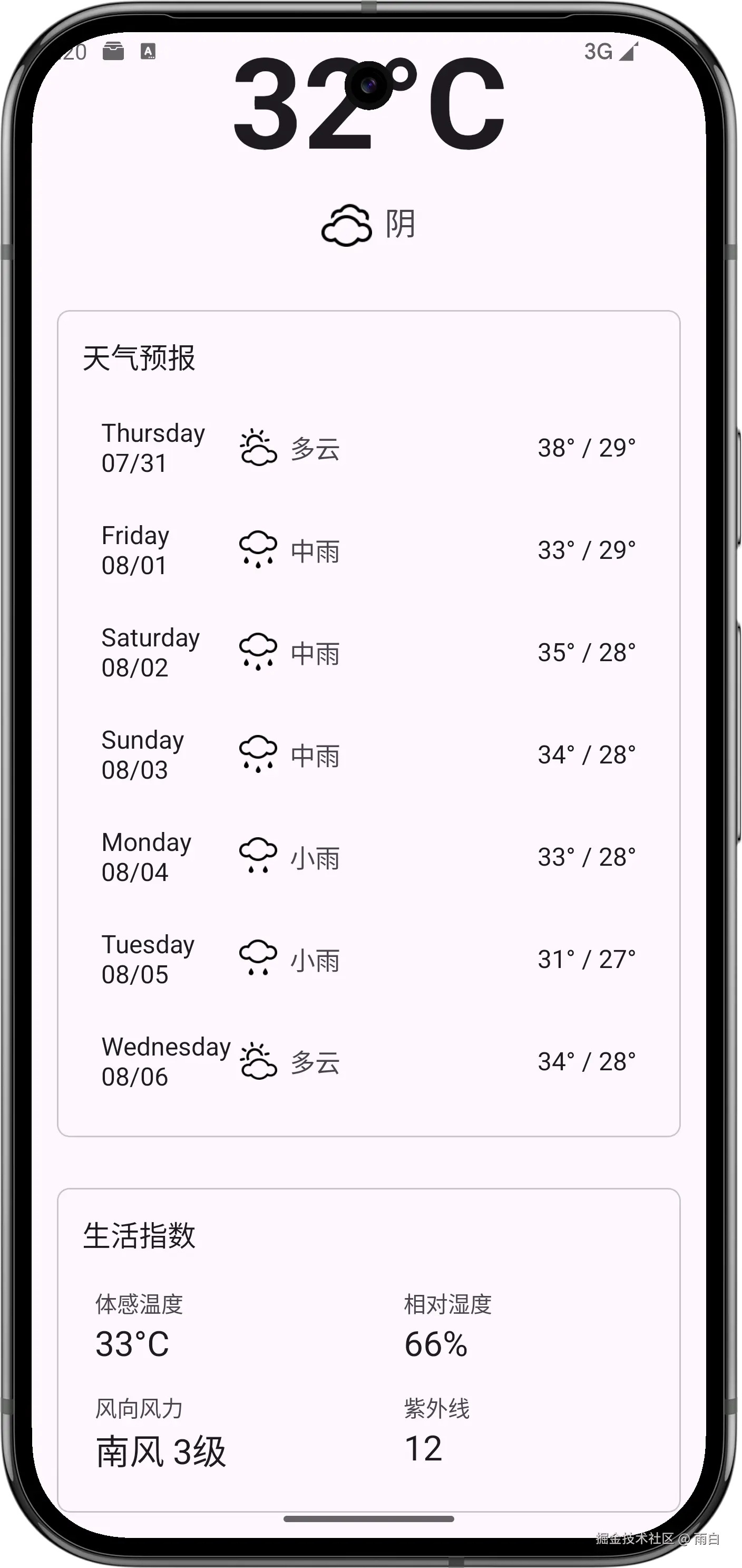
现在,我们就来完成一个天气预报 App,给它起名为 SunnyWeather。
功能需求及技术可行性分析
在开始写代码之前,我们先对程序进行需求分析。我们认为 SunnyWeather 至少应该具备以下功能:
-
可以搜索全球大多数国家的各个城市数据。
-
可以查看全球大多数城市的天气信息。
-
可以自由切换城市,查看其他城市的天气。
-
可以手动刷新实时天气。
分析完需求后,接下来进行技术可行性分析。
毋庸置疑,目前最大的难题是,我们如何才能获取到全球大多数国家的城市数据?以及如何才能得到每个城市的天气信息?对此,我们的解决方案是:使用和风天气提供的服务器接口。
和风天气的介绍以及用法,我就不详细解释了。官方文档很详尽,你可以查看官方文档,也可以看视频教程。
确定技术可行后,我们就可以开始了。
搭建 MVVM 项目架构
创建 Empty Views Activity 项目,项目命名为 SunnyWeather,包名命名为 com.sunnyweather.android。
项目创建好后,我们来搭建 MVVM 架构。
Jetpack的架构组件很多都是专门为了MVVM架构设计的。
那什么是 MVVM 架构呢?
MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)是一种高级项目架构模式,目前被广泛应用于 Android 程序设计领域,与之类似的架构还有 MVP、MVC、MVI 等。
简单来说,MVVM 架构可以将程序结构主要分为三部分:
-
Model: 数据模型部分。 -
View: 界面展示部分。 -
ViewModel: 数据模型和界面展示连接的桥梁。有了它,即可实现业务逻辑和界面展示分离的程序结构设计。
当然,优秀的项目架构还会包含仓库、数据源。
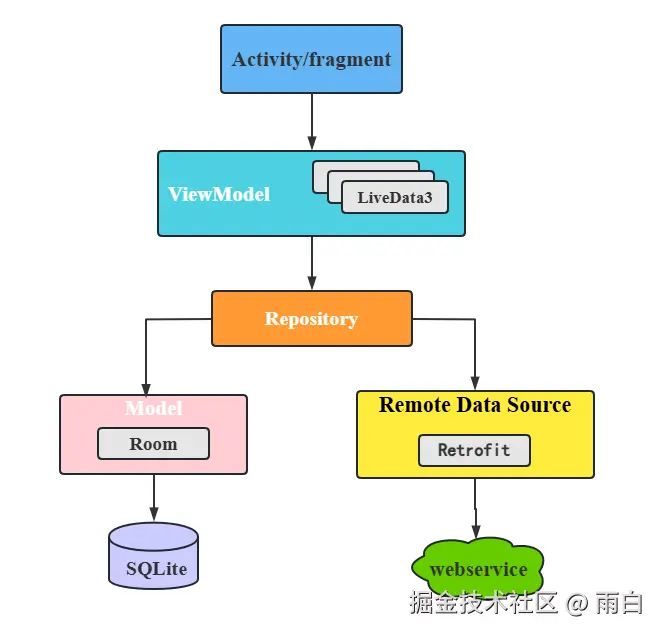
其中,Activity/Fragment 是与界面相关的,ViewModel 用于持有与界面相关的数据,并提供接口给界面调用、和 Repository 通信,Repository 会判断请求的数据是从本地数据源还是网络数据源中获取,返回获取到的数据。
本地数据源使用 Room、SharedPreferences 等持久化技术实现,而网络数据源通常使用 Retrofit 访问 WebService 接口来实现。
注意,图中的箭头都是"单向"的。也就是说 Activity/Fragment 可以持有 ViewModel 的引用,但 ViewModel 却不能持有 Fragment/Activity 的引用。另外,引用不能跨层持有,比如 Activity/Fragment 不能持有 Repository 的引用。
现在,我们就创建项目的包结构:
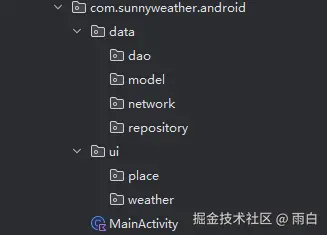
data 包用于存放数据源相关的代码,ui 包用于存放用户界面层相关的代码。
data 包下的 dao、model、network 以及 repository 子包,分别用于存放数据访问对象、对象模型、网络层代码以及仓库。而 ui 包下的 place 和 weather 子包,分别对应了两个页面。
接着,我们引入将会用到的依赖库,开启视图绑定以便安全访问视图,以及启用序列化插件,这样能通过 Intent 传递对象。在 build.gradle.kts (:app) 文件中添加如下内容:
kotlin
// app/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
// 序列化插件,用于 @Parcelize 注解
id("kotlin-parcelize")
}
android {
buildFeatures {
// 启用视图绑定 (ViewBinding)
viewBinding = true
}
// ...
}
dependencies {
// RecyclerView 列表控件
implementation("androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.4.0")
// LiveData 以及 ViewModel KTX 扩展库
implementation("androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-livedata-ktx:2.9.2")
implementation("androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.9.2")
// 下拉刷新控件
implementation("androidx.swiperefreshlayout:swiperefreshlayout:1.1.0")
// Retrofit 和 Gson 转换器
implementation("com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.11.0")
implementation("com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.11.0")
// Kotlin 协程核心库和 Android 扩展
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.8.1")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.9.0")
// OkHttp 日志拦截器,方便调试
implementation("com.squareup.okhttp3:logging-interceptor:4.9.3")
// JWT 签名库 (EdDSA)
implementation("net.i2p.crypto:eddsa:0.3.0")
}最后,将会用到的图标资源,导入到 res/drawable-xxhdpi 目录中。
你也可以从和风天气图标官网获取。
这些准备工作完成后,就正式进入到 SunnyWeather 的开发中。
搜索全球城市数据
我们想要查看天气信息,我们先得获取到一个地区的经纬度坐标。所以,我们先来实现全球城市数据信息的搜索功能。先从逻辑层开始实现。
实现逻辑层代码
Application 类
在 MVVM 这种分层架构中,一般从 ViewModel 开始就不会直接持有 Context。为了方便地获取 Context,我们可以通过自定义 Application 类来实现。
在 com.sunnyweather.android 包下创建 SunnyWeatherApplication 类。
kotlin
class SunnyWeatherApplication : Application() {
companion object {
// 使用 @SuppressLint 忽略静态Context可能引起的内存泄漏警告
// 因为我们存储的是 applicationContext,它的生命周期和应用一致
@SuppressLint("StaticFieldLeak")
lateinit var context: Context
private set
}
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
// 获取全局的 applicationContext
context = applicationContext
}
}注意:在大型项目中通常不会直接暴露一个静态
Context,因为这样会破坏封装和代码可测试性,而是会使用依赖注入(Dependency Injection)框架(如Hilt)来管理Context等依赖。当前项目为了便捷、简洁,所以就直接这样了。
然后在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中指定它。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:name=".SunnyWeatherApplication" ... >
</application>
</manifest>数据模型
然后按照架构示意图,自底向上一步步实现。先根据城市搜索接口返回的 JSON 格式数据定义数据模型,在 data/model 包下新建 Place.kt 文件。
kotlin
import kotlinx.parcelize.Parcelize
/**
* 城市搜索API的返回体数据模型
* @param code 状态码
* @param places 包含的地点列表
*/
data class PlaceResponse(
@SerializedName("code") val code: String,
@SerializedName("location") val places: List<Place>,
)
/**
* 单个地点的数据模型
*/
@Parcelize
data class Place(
@SerializedName("name") val name: String,
@SerializedName("id") val id: String,
@SerializedName("lat") val lat: String,
@SerializedName("lon") val lon: String,
@SerializedName("adm2") val district: String,
@SerializedName("adm1") val province: String,
@SerializedName("country") val country: String,
@SerializedName("tz") val timezone: String,
@SerializedName("utcOffset") val utcOffset: String,
@SerializedName("isDst") val isDst: String,
@SerializedName("type") val type: String,
@SerializedName("rank") val rank: String,
@SerializedName("fxLink") val fxLink: String,
) : Parcelable在上述数据模型中,我们使用了 @Parcelize 注解,让 Place 对象实现了 Parcelable 接口,使其能够通过 Intent 进行传递。
使用了 @SerializedName 注解,建立了 JSON 字段名与 Kotlin 属性名的映射关系。这样解决了 JSON 字段名不符合 Kotlin 命名规范的问题,并且让我们可以在代码中使用更具有描述性的属性名(如 adm2 映射为 district),增强代码可读性。
网络层
首先,定义一个用于访问城市搜索接口的 Retrofit 接口,在 data/network 包下创建 PlaceService 接口。
kotlin
interface PlaceService {
/**
* 搜索城市数据
* @param query 搜索关键字
* @param number 返回结果的数量
* @return 返回地点列表的响应体
*/
@GET("geo/v2/city/lookup")
suspend fun searchPlaces(
@Query("location") query: String,
@Query("number") number: Int = 20
): PlaceResponse
}每当我们调用 searchPlaces 方法时,Retrofit 会自动发起 GET 请求,去访问 @GET 注解配置的地址。其中,location 参数值是需要动态指定的,我们通过 @Query 注解来完成。当请求成功后,Retrofit 会将服务器返回的 JSON 数据自动解析成 PlaceResponse 对象。
为了能够使用 PlaceService 接口,我们需要创建一个 Retrofit 构建器。在 data/network 包下创建 ServiceCreator 单例类。
kotlin
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit
object ServiceCreator {
// 基础请求路径
private const val BASE_URL = "YOUR_API_HOST"
// 创建 OkHttpClient 实例
private val httpClient = OkHttpClient.Builder().apply {
// 设置连接和读取超时时间
connectTimeout(6, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
readTimeout(6, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// 添加日志拦截器
val loggingInterceptor = HttpLoggingInterceptor().apply {
level = HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY
}
addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
}.build()
// 构建 Retrofit 实例
private val retrofit = Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.client(httpClient) // 设置自定义的 OkHttpClient
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()) // 设置JSON解析库
.build()
/**
* 创建 Service 接口的实例
*/
fun <T> create(serviceClass: Class<T>): T = retrofit.create(serviceClass)
/**
* 内联泛型实化方法,简化 create 方法的调用
*/
inline fun <reified T> create(): T = create(T::class.java)
}另外,关于身份认证,我们选择 JWT(JSON Web Token) 这种方式。为此,我们需要在每一次 Retrofit 请求的请求头中加上 Authorization: Bearer your_token。
首先,在 com.sunnyweather.android/utils 包下创建 JwtGenerator 工具类,用于获取 Token 值。
kotlin
import android.util.Base64
/**
* JWT 生成器
* 使用 EdDSA (Ed25519) 算法进行签名。
*/
object JwtGenerator {
private val PRIVATE_KEY_STRING = """
YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY
""".trim()
private const val KEY_ID = "YOU_KEY_ID"
private const val PROJECT_ID = "YOUR_PROJECT_ID"
// JWT 有效期,单位:秒
private const val TOKEN_VALIDITY_SECONDS = 900L
// 时钟偏差容忍期,用于兼容客户端与服务器之间微小的时间差
private const val TOKEN_GRACE_PERIOD_SECONDS = 30L
private data class JwtHeader(val alg: String = "EdDSA", val kid: String)
private data class JwtPayload(val sub: String, val iat: Long, val exp: Long)
/**
* 生成最终的JWT字符串
*/
suspend fun generateJwt(): String = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
val privateKey = parsePrivateKey(PRIVATE_KEY_STRING)
val gson = Gson()
val headerJson = gson.toJson(JwtHeader(kid = KEY_ID))
val currentTimeSeconds = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000
// 签发时间
val iat = currentTimeSeconds - TOKEN_GRACE_PERIOD_SECONDS
// 过期时间
val exp = iat + TOKEN_VALIDITY_SECONDS
val payloadJson = gson.toJson(JwtPayload(sub = PROJECT_ID, iat = iat, exp = exp))
val headerEncoded = base64UrlEncode(headerJson)
val payloadEncoded = base64UrlEncode(payloadJson)
val dataToSign = "$headerEncoded.$payloadEncoded"
// 使用 EdDSA 算法对数据进行签名
val spec = EdDSANamedCurveTable.getByName(EdDSANamedCurveTable.ED_25519)
val signer = EdDSAEngine(MessageDigest.getInstance(spec.hashAlgorithm))
signer.initSign(privateKey)
signer.update(dataToSign.toByteArray(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
val signatureBytes = signer.sign()
val signatureEncoded = base64UrlEncode(signatureBytes)
"$dataToSign.$signatureEncoded"
}
/**
* 解析 PEM 格式的私钥字符串。
*/
private fun parsePrivateKey(pem: String): PrivateKey {
val cleanKey = pem
.replace("-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replace("-----END PRIVATE KEY-----", "")
.replace("\\s".toRegex(), "")
val privateKeyBytes = Base64.decode(cleanKey, Base64.DEFAULT)
val keySpec = PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes)
return EdDSAPrivateKey(keySpec)
}
/**
* 执行 Base64Url 编码
*/
private fun base64UrlEncode(data: String): String {
return base64UrlEncode(data.toByteArray(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
}
/**
* 执行 Base64Url 编码
*/
private fun base64UrlEncode(data: ByteArray): String {
// 使用 URL_SAFE, NO_PADDING, NO_WRAP 标志
return Base64.encodeToString(data, Base64.URL_SAFE or Base64.NO_PADDING or Base64.NO_WRAP)
}
}其次,在 data/network 包下创建 OkHttp 拦截器,完成在请求头中加上 Token。
kotlin
import okhttp3.Response
class AuthInterceptor : Interceptor {
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
// 使用 runBlocking 桥接同步的 intercept 方法和异步的 generateJwt 方法
// 它会阻塞当前线程直到 token 生成完毕
val token = runBlocking {
JwtGenerator.generateJwt()
}
// 获取原始的请求
val originalRequest = chain.request()
// 构建新的请求,并添加 Authorization 请求头
val newRequest = originalRequest.newBuilder()
.header("Authorization", "Bearer $token")
.build()
// 继续执行请求链
return chain.proceed(newRequest)
}
}最后,我们需要在创建 OkHttpClient 实例时,加上这个 AuthInterceptor 拦截器,这样发出的每个网络请求才会自动携带认证信息。
kotlin
// 在 ServiceCreator.kt 中
private val httpClient = OkHttpClient.Builder().apply {
// 添加认证拦截器
addInterceptor(AuthInterceptor())
// 添加日志拦截器
// ...
}.build()网络数据源访问入口
再定义一个统一的网络数据源访问入口,对所有网络请求的 API 进行封装。在 data/network 包下新建一个 SunnyWeatherNetwork 单例类。
kotlin
object SunnyWeatherNetwork {
// 创建 PlaceService 接口的动态代理对象
private val placeService = ServiceCreator.create<PlaceService>()
/**
* 统一的搜索城市数据入口
*/
suspend fun searchPlaces(query: String) = placeService.searchPlaces(query)
}仓库层
仓库层有点像数据获取与缓存的中间层,在本地没有缓冲数据的情况下,就去网络层获取,否则,直接将缓存数据返回。不过,对于搜索城市的请求,我们每次都发起网络请求去获取即可。
在 data/repository 包下创建 Repository 单例类。
kotlin
object Repository {
// 搜索地点信息
fun searchPlaces(query: String): LiveData<Result<List<Place>>> =
// liveData 是一个协程构建器,可以创建 LiveData 对象
liveData(Dispatchers.IO) { // 运行在 IO 线程
val result = try {
val placeResponse = SunnyWeatherNetwork.searchPlaces(query)
if (placeResponse.code == "200") {
// 如果请求成功,使用 Result.success 包装数据
val places = placeResponse.places
Result.success(places)
} else {
// 如果返回错误,使用 Result.failure 包装异常
Result.failure(RuntimeException("response status is ${placeResponse.code}"))
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
// 包装异常
Result.failure(e)
}
// emit() 用于发射最终结果,通知 LiveData 更新数据
emit(result)
}
}为了将仓库层获取的数据以响应式的方式传递给 ViewModel,我们选择返回一个 LiveData 对象。
这里我们用到了 liveData() 函数,它能帮我们自动创建并返回一个 LiveData 对象。并且它的代码块中还提供了挂起函数的上下文,让我们可以在其中调用挂起函数,就比如 SunnyWeatherNetwork.searchPlaces()。
在 liveData() 的代码块中,我们使用了 try-catch 捕获异常,并判断网络请求是否成功。最后将成功的数据或是失败的异常包装到 Kotlin 内置的 Result 对象中,通过 emit() 方法将这个 Result 对象发射出去。
emit 方法是 liveData 中专门提供、用于发射数据的挂起函数。它的作用是设定 LiveData 的值,并通知该
LiveData对象的观察者数据发生了变化。
ViewModel 层
最后,来定义 ViewModel 层。它通常和 Activity 或 Fragment 一一对应,在 ui/place 包下创建 PlaceViewModel。
kotlin
class PlaceViewModel : ViewModel() {
// 触发器
private val searchLiveData = MutableLiveData<String>()
// 当 searchLiveData 的值变化时,会自动调用 Repository.searchPlaces 并将返回的 LiveData 切换给 placeLiveData
val placeLiveData = searchLiveData.switchMap { query ->
Repository.searchPlaces(query)
}
/**
* 搜索方法,通过调用此方法来触发搜索
*/
fun searchPlaces(query: String) {
searchLiveData.value = query
}
}现在,我们就具有搜索全球城市数据的能力,接下来实现 UI 层。
实现 UI 层代码
城市搜索页布局
在 res/layout 目录下创建 fragment_place.xml 布局文件。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="?attr/colorSurface">
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/searchPlaceLayout"
style="@style/Widget.Material3.TextInputLayout.FilledBox"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"
android:hint="输入城市名称"
app:boxBackgroundColor="?attr/colorSurfaceContainerHighest"
app:boxCornerRadiusBottomEnd="28dp"
app:boxCornerRadiusBottomStart="28dp"
app:boxCornerRadiusTopEnd="28dp"
app:boxCornerRadiusTopStart="28dp"
app:boxStrokeWidth="0dp"
app:boxStrokeWidthFocused="0dp"
app:endIconMode="clear_text"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:startIconDrawable="@drawable/ic_search">
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputEditText
android:id="@+id/searchPlaceEdit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:imeOptions="actionSearch"
android:inputType="text"
android:singleLine="true" />
</com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout>
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
android:visibility="gone"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/searchPlaceLayout"
tools:visibility="visible" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/emptyStateLayout"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:visibility="visible"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/searchPlaceLayout"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.4">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:alpha="0.5"
android:src="@drawable/ic_search_empty"
app:tint="?attr/colorOnSurfaceVariant" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="开始搜索城市"
android:textColor="?attr/colorOnSurfaceVariant"
android:textSize="16sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
城市列表子项布局
创建一个 item_place.xml 布局文件。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="?attr/selectableItemBackground"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingStart="16dp"
android:paddingTop="12dp"
android:paddingEnd="16dp"
android:paddingBottom="12dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_place_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="18sp"
tools:text="福州" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_place_address"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="4dp"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary"
android:textSize="14sp"
tools:text="福州, 福建省, 中国" />
</LinearLayout>
列表适配器
在 ui/place 包下为 RecyclerView 创建 PlaceAdapter。
kotlin
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.ListAdapter
class PlaceAdapter(
private val onItemClick: (Place) -> Unit,
) : ListAdapter<Place, PlaceAdapter.ViewHolder>(PlaceDiffCallback()) {
// ViewHolder 负责持有和管理单个列表项的视图
inner class ViewHolder(private val binding: ItemPlaceBinding) :
RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
fun bind(place: Place) {
// 绑定地名和详细地址
binding.tvPlaceName.text = place.name
binding.tvPlaceAddress.text = "${place.province}, ${place.country}"
// 设置点击事件
itemView.setOnClickListener {
onItemClick(place)
}
}
}
// 创建 ViewHolder
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
val binding =
ItemPlaceBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false)
return ViewHolder(binding)
}
// 绑定数据到 ViewHolder
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
holder.bind(getItem(position))
}
}
/**
* DiffUtil.ItemCallback 用于计算列表差异
*/
class PlaceDiffCallback : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Place>() {
// 判断是否是同一个Item
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Place, newItem: Place): Boolean {
return oldItem.id == newItem.id
}
// 判断Item的内容是否相同
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Place, newItem: Place): Boolean {
return oldItem == newItem
}
}Fragment
在 ui/place 包下创建 PlaceFragment,并继承自 Fragment。
kotlin
class PlaceFragment : Fragment() {
private val viewModel by lazy { ViewModelProvider(this)[PlaceViewModel::class.java] }
private var _binding: FragmentPlaceBinding? = null
private val binding get() = _binding!!
private lateinit var adapter: PlaceAdapter
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?,
): View {
_binding = FragmentPlaceBinding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
return binding.root
}
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
// 设置 RecyclerView
binding.recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(activity)
adapter = PlaceAdapter {}
binding.recyclerView.adapter = adapter
// 监听搜索框的文本变化
binding.searchPlaceEdit.addTextChangedListener { editable ->
val content = editable.toString()
if (content.isNotEmpty()) {
viewModel.searchPlaces(content)
} else {
// 如果输入框为空,则清空列表并显示空状态
binding.recyclerView.visibility = View.GONE
binding.emptyStateLayout.visibility = View.VISIBLE
adapter.submitList(emptyList()) // 使用 submitList 清空列表
}
}
// 观察 ViewModel 中的数据变化
viewModel.placeLiveData.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { result ->
val places = result.getOrNull()
if (places != null) {
// 如果有数据,显示列表,隐藏空状态
binding.recyclerView.visibility = View.VISIBLE
binding.emptyStateLayout.visibility = View.GONE
adapter.submitList(places) // 使用 submitList 提交新数据
} else {
// 如果返回错误,显示Toast
Toast.makeText(activity, "未能查询到任何地点", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
result.exceptionOrNull()?.printStackTrace()
}
}
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
}最后,将当前 Fragment 添加到 Activity,使其显示在界面中。
activity_main.xml 文件中的代码:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/placeFragment"
android:name="com.sunnyweather.android.ui.place.PlaceFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</FrameLayout>别忘了在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中加上网络权限声明:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
...
</manifest>至此,城市搜索功能就完成了。
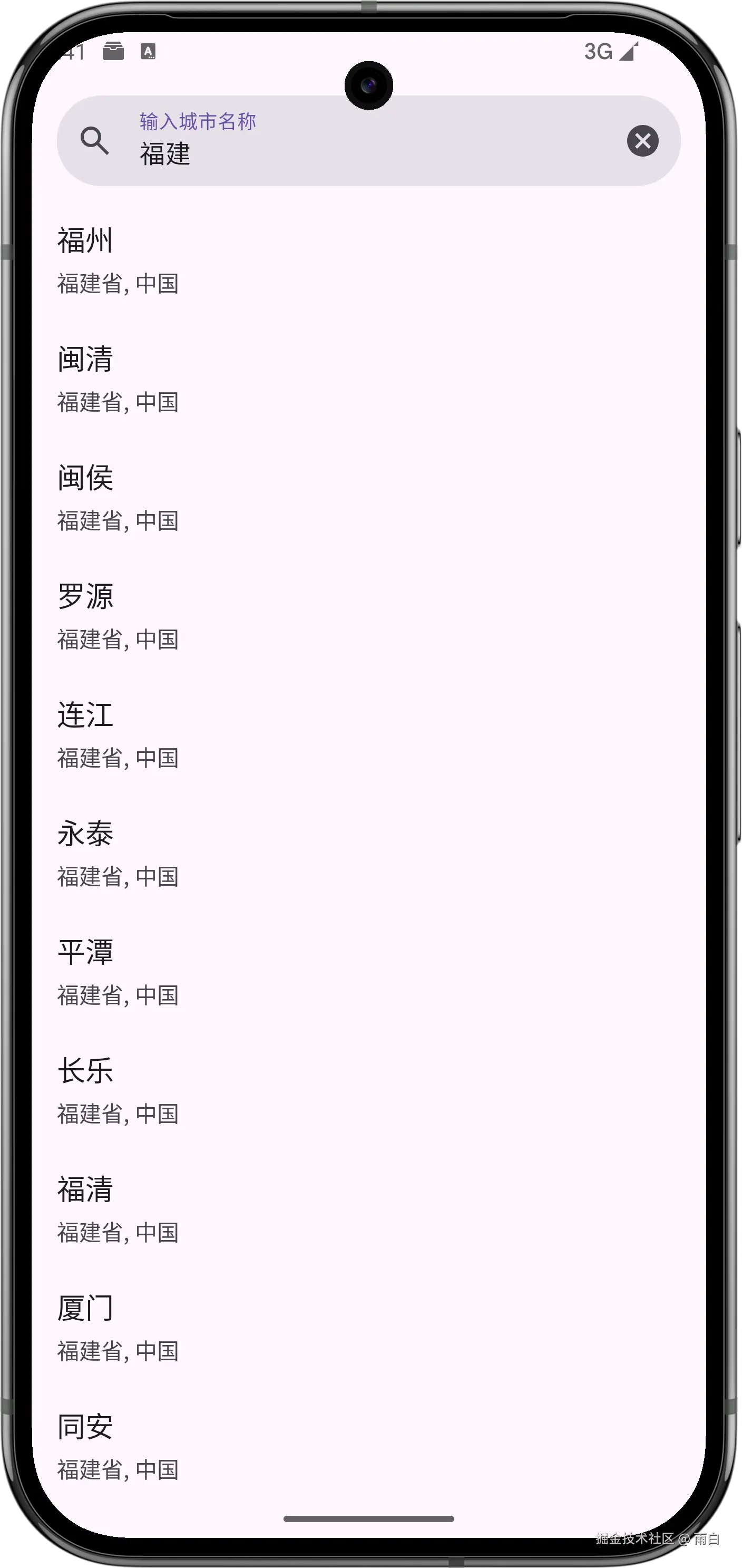
虽然现在我们只在界面中显示了相关城市的名称、行政区、国家,但其实我们也拿到了请求天气所需的城市经纬度信息。待会我们就会利用这些信息,来完成查询并显示天气的功能。
显示天气信息
现在,我们来完成显示详细天气信息的功能。
实现逻辑层代码
数据模型
根据实时天气接口返回的数据和每日天气预报接口返回的数据,我们需要定义相应的数据模型。
在 data/model 包下创建 Weather.kt 文件。
kotlin
/**
* 实时天气API返回的数据模型
*/
data class RealtimeResponse(
@SerializedName("code") val code: String,
@SerializedName("now") val now: Now,
) {
data class Now(
@SerializedName("temp") val temperature: String,
@SerializedName("feelsLike") val feelsLike: String,
@SerializedName("icon") val icon: String,
@SerializedName("text") val weatherText: String,
@SerializedName("windDir") val windDirection: String,
@SerializedName("windScale") val windScale: String,
@SerializedName("humidity") val humidity: String,
@SerializedName("pressure") val pressure: String,
)
}
/**
* 每日天气API返回的数据模型
*/
data class DailyResponse(
@SerializedName("code") val code: String,
@SerializedName("daily") val dailyForecasts: List<DailyForecast>,
) {
data class DailyForecast(
@SerializedName("fxDate") val forecastDate: String,
@SerializedName("sunrise") val sunrise: String?,
@SerializedName("sunset") val sunset: String?,
@SerializedName("tempMax") val maxTemperature: String,
@SerializedName("tempMin") val minTemperature: String,
@SerializedName("iconDay") val iconDay: String,
@SerializedName("textDay") val textDay: String,
@SerializedName("uvIndex") val uvIndex: String,
)
}
/**
* 封装实时天气和未来天气的数据
*/
data class Weather(
val realtime: RealtimeResponse.Now,
val daily: List<DailyResponse.DailyForecast>,
)网络层
接下来,定义访问天气信息API的 Retrofit 接口,在 data/network 包下创建 WeatherService 接口。
kotlin
interface WeatherService {
/**
* 获取实时天气信息
*/
@GET("v7/weather/now")
suspend fun getRealtimeWeather(
@Query("location") locationId: String, // 地点经纬度
): RealtimeResponse
/**
* 获取未来几天的天气信息
*/
@GET("v7/weather/{days}")
suspend fun getDailyWeather(
@Path("days") days: String, // 预报的天数
@Query("location") locationId: String,
): DailyResponse
}其中,我们使用了 @Path 注解来动态向请求地址中传入预报天数。
然后,依旧在 SunnyWeatherNetwork 中对 WeatherService 接口进行封装。
kotlin
object SunnyWeatherNetwork {
...
// 创建 WeatherService 接口的动态代理对象
private val weatherService = ServiceCreator.create<WeatherService>()
suspend fun getRealtimeWeather(locationId: String) =
weatherService.getRealtimeWeather(locationId)
suspend fun getDailyWeather(days: String, locationId: String) =
weatherService.getDailyWeather(days, locationId)
}仓库层
在 Repository 类中,添加刷新天气信息的方法 refreshWeather()。
kotlin
object Repository {
...
// 刷新天气信息
fun refreshWeather(locationId: String, days: String): LiveData<Result<Weather>> =
liveData(Dispatchers.IO) {
val result = try {
// coroutineScope 函数用于创建协程作用域,因为 async 函数需要在协程作用域中才能调用
coroutineScope {
// 启动子协程来获取实时天气
val deferredRealtime = async {
SunnyWeatherNetwork.getRealtimeWeather(locationId)
}
// 启动另一个子协程来获取每日天气
val deferredDaily = async {
SunnyWeatherNetwork.getDailyWeather(days, locationId)
}
// 使用 await() 方法等待两个请求的结果返回,总耗时取决于最慢的那个请求
val realtimeResponse = deferredRealtime.await()
val dailyResponse = deferredDaily.await()
if (realtimeResponse.code == "200" && dailyResponse.code == "200") {
val weather = Weather(realtimeResponse.now, dailyResponse.dailyForecasts)
Result.success(weather)
} else {
Result.failure(
RuntimeException(
"realtime response code is ${realtimeResponse.code}, " +
"daily response code is ${dailyResponse.code}"
)
)
}
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
Result.failure(e)
}
emit(result)
}
}对于实时天气和未来天气是两个独立的的网络请求,没有先后顺序。所以,我们使用了 coroutineScope 和 async 函数让它们并发执行,以提高执行效率。
定义 ViewModel 层
在 ui/weather 包下创建 WeatherViewModel。
kotlin
class WeatherViewModel : ViewModel() {
companion object {
// 默认请求天数
const val DEFAULT_QUERY_DAYS = "7d"
}
// 用于触发天气刷新
private val locationLiveData = MutableLiveData<Place>()
val weatherLiveData = locationLiveData.switchMap { location ->
Repository.refreshWeather(location.id, DEFAULT_QUERY_DAYS)
}
/**
* 刷新天气
*/
fun refreshWeather(place: Place) {
if (locationLiveData.value == place) {
return
}
locationLiveData.value = place
}
}实现 UI 层代码
创建用于显示天气信息的 WeatherActivity。在 ui/weather 包下创建 WeatherActivity,布局名默认为 activity_weather.xml。
天气主布局
activity_weather.xml 布局中的代码如下:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/weatherLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:overScrollMode="never"
android:scrollbars="none"
android:visibility="invisible">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<include
android:id="@+id/nowLayout"
layout="@layout/now" />
<include
android:id="@+id/forecastLayout"
layout="@layout/forecast" />
<include
android:id="@+id/lifeIndexLayout"
layout="@layout/life_index" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>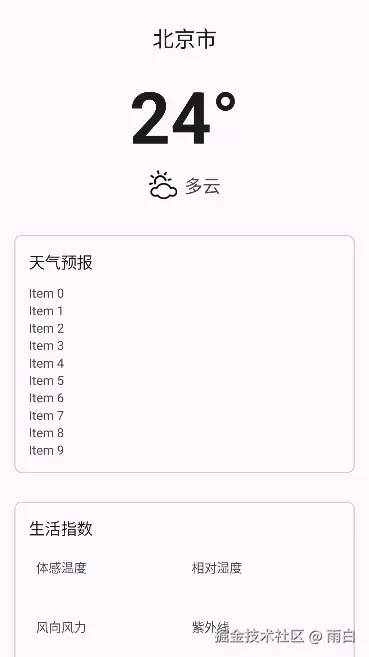
当前天气信息布局
创建 now.xml 作为当前天气信息的布局。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="24dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/placeName"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="24sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
tools:text="北京市" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/currentTemp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="80sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/placeName"
tools:text="24°" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/skyLayout"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/currentTemp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/nowIcon"
android:layout_width="32dp"
android:layout_height="32dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
tools:src="@drawable/ic_weather_101" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/currentSky"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary"
android:textSize="20sp"
tools:text="多云" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
未来天气信息布局
创建 forecast.xml 作为未来天气信息的布局。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="8dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="天气预报"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/forecastRecyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="12dp" />
</LinearLayout>
</com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView>
未来天气信息子项布局
创建 item_forecast.xml。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="12dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dateInfo"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="16sp"
tools:text="周三 7/24" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/skyIcon"
android:layout_width="24dp"
android:layout_height="24dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
tools:src="@drawable/ic_weather_100" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/skyInfo"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary"
android:textSize="16sp"
tools:text="晴" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/temperatureInfo"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:gravity="end"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="16sp"
tools:text="26° / 18°" />
</LinearLayout>
适配器
在 ui/weather 包下创建 ForecastAdapter。
kotlin
import android.icu.text.SimpleDateFormat
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.ListAdapter
class ForecastAdapter :
ListAdapter<DailyResponse.DailyForecast, ForecastAdapter.ViewHolder>(ForecastDiffCallback()) {
inner class ViewHolder(private val binding: ItemForecastBinding) :
RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
fun bind(forecast: DailyResponse.DailyForecast) {
// 绑定数据到视图
binding.apply {
dateInfo.text = formatForecastDate(forecast.forecastDate)
skyInfo.text = forecast.textDay
temperatureInfo.text = "${forecast.maxTemperature}° / ${forecast.minTemperature}°"
// 动态加载天气图标
val context = itemView.context
val iconResourceId = context.resources.getIdentifier(
"ic_weather_${forecast.iconDay}",
"drawable",
context.packageName
)
if (iconResourceId != 0) {
skyIcon.setImageResource(iconResourceId)
}
}
}
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
val binding =
ItemForecastBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false)
return ViewHolder(binding)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
holder.bind(getItem(position))
}
/**
* 用于格式化日期
*/
private fun formatForecastDate(inputDate: String): String {
return try {
val inputFormat = SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd", Locale.getDefault())
val date = inputFormat.parse(inputDate)
val outputFormat = SimpleDateFormat("EEEE MM/dd", Locale.getDefault())
outputFormat.format(date!!)
} catch (e: Exception) {
inputDate
}
}
}
class ForecastDiffCallback : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<DailyResponse.DailyForecast>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(
oldItem: DailyResponse.DailyForecast,
newItem: DailyResponse.DailyForecast,
): Boolean {
return oldItem.forecastDate == newItem.forecastDate
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(
oldItem: DailyResponse.DailyForecast,
newItem: DailyResponse.DailyForecast,
): Boolean {
return oldItem == newItem
}
}生活指数布局
创建 life_index.xml 生活指数布局。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="8dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="生活指数"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="12dp"
android:columnCount="2">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="体感温度"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/feelsLikeText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="相对湿度"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/humidityText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="风向风力"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/windText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_columnWeight="1"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="紫外线"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorSecondary" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/uvText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="?android:attr/textColorPrimary"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</GridLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView>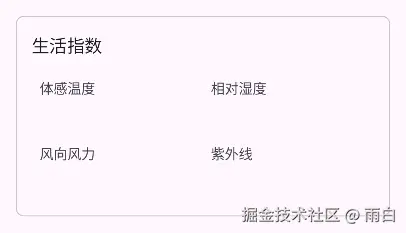
WeatherActivity
最后,来到 WeatherActivity 中请求天气数据并展示到界面中。
kotlin
class WeatherActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val viewModel by lazy { ViewModelProvider(this)[WeatherViewModel::class.java] }
private lateinit var binding: ActivityWeatherBinding
private lateinit var forecastAdapter: ForecastAdapter
// 从Intent传入的Place对象
private var currentPlace: Place? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityWeatherBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(binding.root)
// 初始化 Adapter 和 RecyclerView
forecastAdapter = ForecastAdapter()
binding.forecastLayout.forecastRecyclerView.apply {
layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this@WeatherActivity)
adapter = forecastAdapter
}
// 从 Intent 中获取地点信息
currentPlace = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU) {
intent.getParcelableExtra("key_place", Place::class.java)
} else {
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
intent.getParcelableExtra("key_place")
}
// 观察 LiveData 数据变化
viewModel.weatherLiveData.observe(this) { result ->
val weather = result.getOrNull()
if (weather != null) {
showWeatherInfo(weather) // 如果成功,则显示天气信息
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "无法成功获取天气信息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
result.exceptionOrNull()?.printStackTrace()
}
}
// 触发首次数据加载
currentPlace?.let {
viewModel.refreshWeather(it)
} ?: run {
Toast.makeText(this, "获取地点信息失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
finish()
}
}
/**
* 将 Weather 对象的数据填充到界面上
*/
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun showWeatherInfo(weather: Weather) {
// 填充 now.xml 布局
binding.nowLayout.placeName.text = currentPlace?.name
val realtime = weather.realtime
binding.nowLayout.currentTemp.text = "${realtime.temperature}°C"
binding.nowLayout.currentSky.text = realtime.weatherText
// 动态加载当前天气图标
val realtimeIconResId =
resources.getIdentifier("ic_weather_${realtime.icon}", "drawable", packageName)
if (realtimeIconResId != 0) {
binding.nowLayout.nowIcon.setImageResource(realtimeIconResId)
}
// 填充 forecast.xml 布局,使用 submitList 更新 RecyclerView
forecastAdapter.submitList(weather.daily)
// 填充 life_index.xml 布局
val lifeIndex = weather.daily[0] // 生活指数数据取自当天
binding.lifeIndexLayout.feelsLikeText.text = "${realtime.feelsLike}°C"
binding.lifeIndexLayout.humidityText.text = "${realtime.humidity}%"
binding.lifeIndexLayout.windText.text = "${realtime.windDirection} ${realtime.windScale}级"
binding.lifeIndexLayout.uvText.text = lifeIndex.uvIndex
// 让天气信息主布局可见
binding.weatherLayout.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
}实现页面跳转
在 PlaceFragment 中添加列表项的点击回调逻辑,以便能够从城市搜索页跳转到天气页。
kotlin
class PlaceFragment : Fragment() {
...
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
binding.recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(activity)
adapter = PlaceAdapter { place ->
val intent = Intent(activity, WeatherActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra("key_place", place) // 将选中的 Place 对象传递给天气页面
}
startActivity(intent)
activity?.finish()
}
binding.recyclerView.adapter = adapter
...
}
...
}现在运行程序,点击搜索结果后,就能跳转并显示天气信息了。