一、背景
在基础设施即代码(IaC)实践中,经常需要基于表格数据批量创建云资源。本文介绍一种通过 Terraform 结合 Excel 表格数据批量创建资源的完整方案,适用于需要根据结构化表格数据快速生成标准化基础设施的场景。
二、核心思路
该方案通过 "数据转换 - 动态配置 - 模块化管理" 的流程实现实现批量资源创建,核心步骤包括:
- 数据提取与转换:将 Excel 表格数据转换为 Terraform 可直接解析的 JSON 格式
- 动态资源配置:利用 Terraform 的 for_each 循环,基于转换后的数据动态生成资源
- 模块化设计:将资源配置封装为 Terraform 模块,提升复用性和可维护性
- 校验与容错:在数据转换和资源创建过程中加入校验机制,确保配置合法性
三、实战步骤
3.1 准备 Excel 数据
以云服务器(CVM)配置为例,Excel 表格需包含资源创建的关键参数(可根据实际需求扩展):
| Instance Name | Instance Type | Image ID | Subnet ID | Security Groups | SystemDiskSize | Availability Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xuel-web-server-01 | SA5.MEDIUM2 | img-l8og963d | subnet-aosdz1ku | sg-1olrbu1b | 50 | ap-guangzhou-6 |
| xuel-app-server-01 | SA5.MEDIUM2 | img-l8og963d | subnet-aosdz1ku | sg-1olrbu1b | 50 | ap-guangzhou-6 |
| xuel-db-server-01 | SA5.MEDIUM2 | img-l8og963d | subnet-aosdz1ku | sg-1olrbu1b | 50 | ap-guangzhou-6 |
3.2 数据转换:Python 脚本处理 Excel
使用 Python 脚本将 Excel 数据转换为 Terraform 可识别的 JSON 格式,实现自动化数据处理。
脚本实现
python
import pandas as pd
import json
import os
import argparse
import traceback
def excel_to_terraform_vars(excel_file, output_file):
# 处理文件路径为绝对路径
excel_file = os.path.abspath(excel_file)
output_file = os.path.abspath(output_file)
# 校验输入文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(excel_file):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Excel文件不存在: {excel_file}")
# 识别文件类型(CSV或Excel)
file_extension = os.path.splitext(excel_file)[1].lower()
try:
if file_extension == '.csv':
# 读取CSV文件
df = pd.read_csv(
excel_file,
header=0,
names=['Instance Name', 'Instance Type', 'Image ID', 'Subnet ID',
'Security Groups', 'SystemDiskSize', 'Availability Zone']
)
else:
# 尝试多种引擎读取Excel文件
engines_to_try = ['openpyxl', 'xlrd', 'odf', 'pyxlsb']
df = None
for engine in engines_to_try:
try:
df = pd.read_excel(excel_file, engine=engine)
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"使用{engine}引擎读取失败: {e}")
if df is None:
raise ValueError(f"无法读取Excel文件 {excel_file},尝试了所有可用引擎")
# 校验必填列
required_columns = ['Instance Name', 'Instance Type', 'Image ID', 'Subnet ID',
'Security Groups', 'SystemDiskSize', 'Availability Zone']
missing_columns = [col for col in required_columns if col not in df.columns]
if missing_columns:
raise ValueError(f"缺少必填列: {missing_columns},可用列: {list(df.columns)}")
# 移除全为空的行
df = df.dropna(how='all')
resources = {}
for index, row in df.iterrows():
# 跳过无效行(标题行、分隔行或空行)
if (pd.isna(row['Instance Name']) or
row['Instance Name'] in ['---', ''] or
row['Instance Name'].startswith(('---', '|'))):
continue
# 校验系统盘大小(必须为数字)
try:
system_disk_size = int(row['SystemDiskSize'])
except (ValueError, TypeError):
print(f"跳过无效行(系统盘大小非数字): {row['SystemDiskSize']}")
continue
# 组装资源数据
instance_name = row['Instance Name']
resources[instance_name] = {
'instance_type': str(row['Instance Type']).strip(),
'image_id': str(row['Image ID']).strip(),
'subnet_id': str(row['Subnet ID']).strip(),
'security_groups': [sg.strip() for sg in str(row['Security Groups']).split(',') if sg.strip()],
'system_disk_size': system_disk_size,
'availability_zone': str(row['Availability Zone']).strip()
}
# 确保输出目录存在
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(output_file), exist_ok=True)
# 写入JSON文件
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(resources, f, indent=2)
print(f"数据转换完成: {excel_file} -> {output_file}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理失败: {e}")
raise
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Excel转Terraform变量工具')
parser.add_argument('excel_file', help='输入Excel/CSV文件路径')
parser.add_argument('--output', default=None, help='输出tfvars.json文件路径')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 自动生成输出文件名(默认与输入文件同路径,后缀为.tfvars.json)
output_file = args.output or f"{os.path.splitext(args.excel_file)[0]}.tfvars.json"
excel_to_terraform_vars(args.excel_file, output_file)环境准备
安装依赖包:
arduino
pip install pandas openpyxl xlrd # openpyxl支持xlsx,xlrd支持xls执行转换
bash
# 转换CSV文件(Excel文件同理)
python excel_to_tfvars.py resources.csv --output resources.tfvars.json转换结果(resources.tfvars.json)
json
{
"xuel-web-server-01": {
"instance_type": "SA5.MEDIUM2",
"image_id": "img-l8og963d",
"subnet_id": "subnet-aosdz1ku",
"security_groups": ["sg-1olrbu1b"],
"system_disk_size": 50,
"availability_zone": "ap-guangzhou-6"
},
"xuel-app-server-01": {
"instance_type": "SA5.MEDIUM2",
"image_id": "img-l8og963d",
"subnet_id": "subnet-aosdz1ku",
"security_groups": ["sg-1olrbu1b"],
"system_disk_size": 50,
"availability_zone": "ap-guangzhou-6"
},
"xuel-db-server-01": {
"instance_type": "SA5.MEDIUM2",
"image_id": "img-l8og963d",
"subnet_id": "subnet-aosdz1ku",
"security_groups": ["sg-1olrbu1b"],
"system_disk_size": 50,
"availability_zone": "ap-guangzhou-6"
}
}3.3 Terraform 配置实现
目录结构
bash
.
├── modules/ # 资源模块目录
│ └── instance/ # 云服务器实例模块
│ ├── main.tf # 资源定义
│ ├── variables.tf # 模块变量
│ └── outputs.tf # 模块输出
├── main.tf # 主配置(调用模块)
├── providers.tf # 云厂商配置
└── resources.tfvars.json # 转换后的资源数据关键配置文件
- providers.tf(云厂商配置)
ini
terraform {
required_providers {
tencentcloud = {
source = "tencentcloudstack/tencentcloud"
version = "~> 1.81.0"
}
}
}
provider "tencentcloud" {
# 可通过环境变量配置:TENCENTCLOUD_SECRET_ID、TENCENTCLOUD_SECRET_KEY
# secret_id = "your-secret-id"
# secret_key = "your-secret-key"
region = "ap-guangzhou" # 地域
}- modules/instance/ variables.tf(模块变量定义)
ini
variable "instance_name" {
description = "实例名称"
type = string
}
variable "instance_type" {
description = "实例类型"
type = string
}
variable "image_id" {
description = "镜像ID"
type = string
}
variable "subnet_id" {
description = "子网ID"
type = string
}
variable "security_groups" {
description = "安全组ID列表"
type = list(string)
}
variable "system_disk_size" {
description = "系统盘大小(GB)"
type = number
default = 50
}
variable "availability_zone" {
description = "可用区"
type = string
}- modules/instance/ main.tf(资源定义)
ini
resource "tencentcloud_instance" "this" {
instance_name = var.instance_name
instance_type = var.instance_type
image_id = var.image_id
subnet_id = var.subnet_id
security_groups = var.security_groups
availability_zone = var.availability_zone
# 系统盘配置
system_disk_size = var.system_disk_size
system_disk_type = "CLOUD_PREMIUM" # 高性能云硬盘
# 其他可选配置(根据需求添加)
# internet_charge_type = "TRAFFIC_POSTPAID_BY_HOUR"
# internet_max_bandwidth_out = 100
}- modules/instance/ outputs.tf(模块输出)
ini
output "instance_id" {
description = "实例ID"
value = tencentcloud_instance.this.id
}
output "public_ip" {
description = "公网IP"
value = tencentcloud_instance.this.public_ip
}
output "private_ip" {
description = "内网IP"
value = tencentcloud_instance.this.private_ip
}- main.tf(主配置,批量创建资源)
ini
# 读取JSON数据
locals {
instances = jsondecode(file("${path.module}/resources.tfvars.json"))
}
# 循环调用模块创建实例
module "instances" {
source = "./modules/instance"
for_each = local.instances
# 传递变量(与JSON字段对应)
instance_name = each.key
instance_type = each.value.instance_type
image_id = each.value.image_id
subnet_id = each.value.subnet_id
security_groups = each.value.security_groups
system_disk_size = each.value.system_disk_size
availability_zone = each.value.availability_zone
}
# 全局输出所有实例信息
output "all_instances" {
description = "所有实例信息"
value = {
for name, instance in module.instances :
name => {
id = instance.instance_id
public_ip = instance.public_ip
private_ip = instance.private_ip
}
}
}3.4 执行 Terraform 命令
- 初始化工作目录
csharp
terraform init # 下载Provider和模块- 预览资源创建计划
bash
terraform plan # 检查配置并预览将要创建的资源- 执行资源创建
bash
terraform apply # 确认后输入yes执行创建- 查看输出结果
bash
terraform output # 显示所有实例的ID和IP信息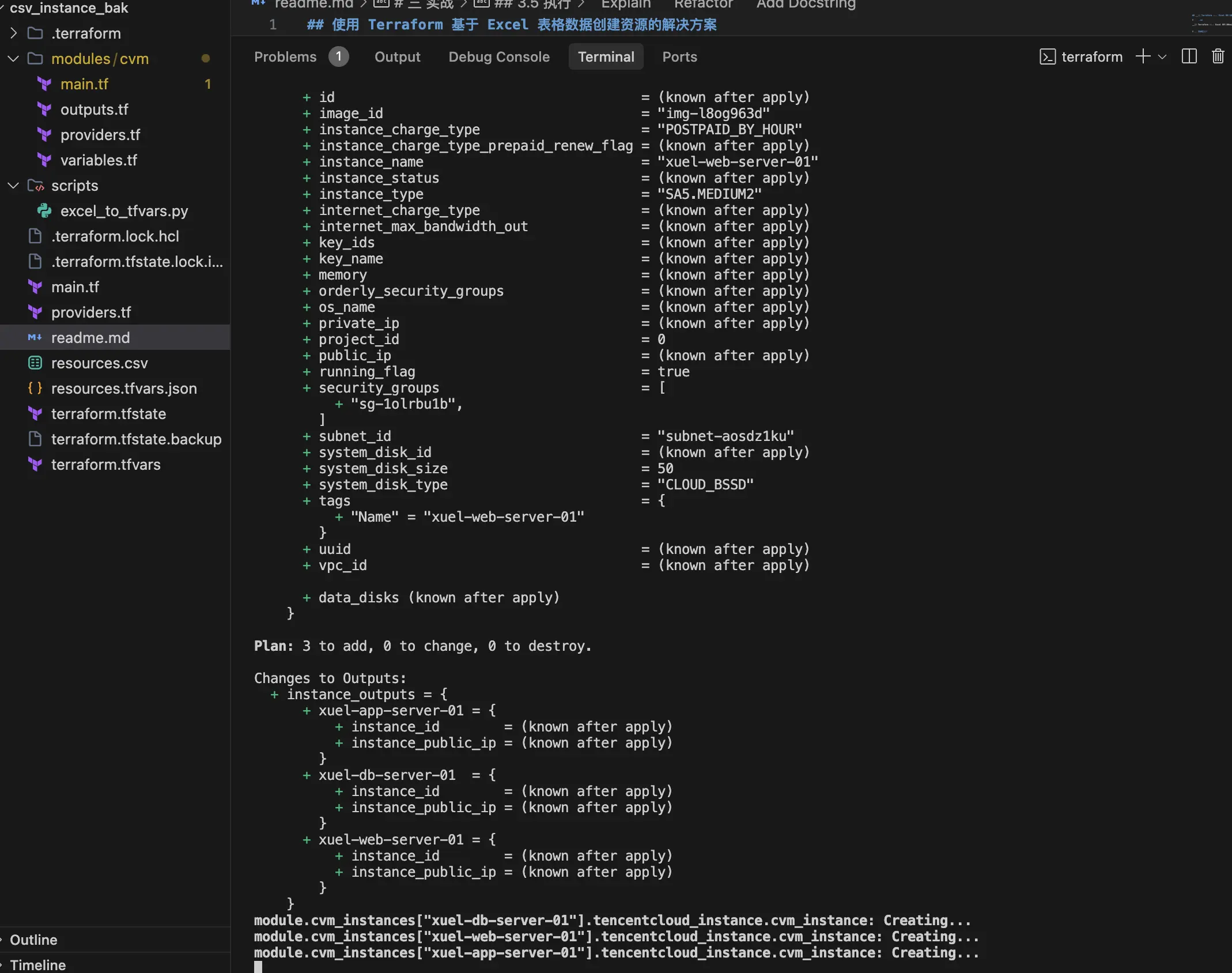
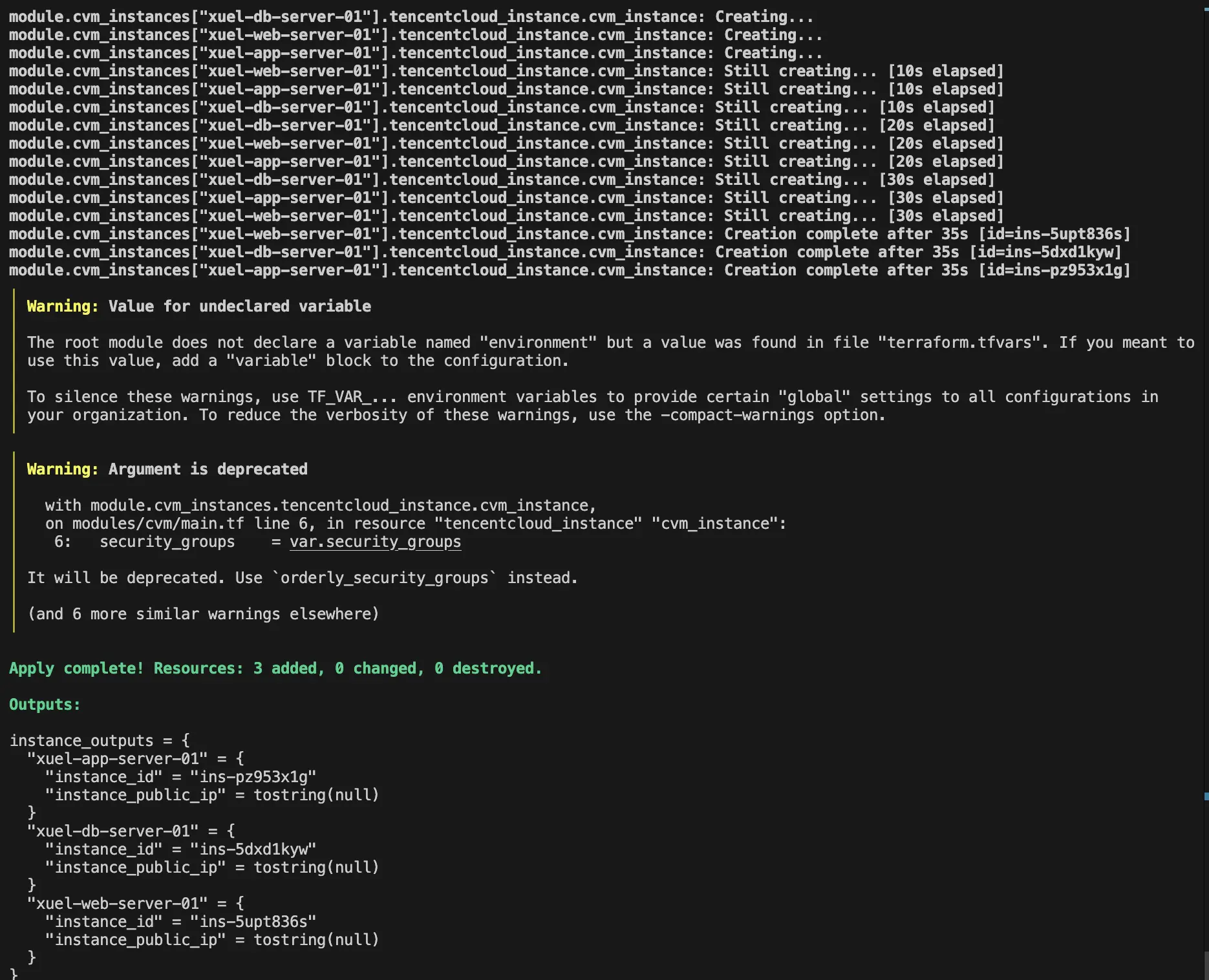
四、方案总结
本方案通过 "Excel 表格→Python 转换→Terraform 批量创建" 的流程,实现了基于表格数据的标准化资源部署,核心优势包括:
- 高效批量操作:避免手动编写重复的资源配置,通过表格批量管理资源参数
- 可扩展性强:支持扩展 Excel 字段(如磁盘类型、网络带宽等),只需同步更新脚本和 Terraform 模块
- 标准化配置:通过模块确保资源配置的一致性,降低人为配置错误风险
五、注意事项
- 权限配置:确保 Terraform 已配置云厂商 API 密钥(如腾讯云的TENCENTCLOUD_SECRET_ID和TENCENTCLOUD_SECRET_KEY)
- 参数校验:生产环境中建议增强 Python 脚本的校验逻辑(如实例类型合法性、可用区匹配性等)
- 版本兼容:注意 Terraform Provider 版本与云厂商 API 的兼容性
- 敏感信息:避免在 Excel 或 JSON 中存储敏感信息(如密钥),建议通过 Terraform 变量或环境变量注入
- 备份策略:重要表格数据建议版本化管理(如纳入 Git),便于追溯配置变更
六、扩展方案
除 Python 转换外,Terraform 官方提供csvdecode函数可直接解析 CSV 文件(无需 Python 脚本),示例:
ini
locals {
# 直接解析CSV文件
instances = csvdecode(file("${path.module}/resources.csv"))
}
# 后续使用方式与JSON方案一致选择哪种方式取决于需求:
- 简单场景(纯 CSV、无复杂校验):优先使用csvdecode
- 复杂场景(Excel 格式、需数据清洗 / 校验):使用 Python 脚本方案