记录选中的城市
在上篇博文中,我们已经成功完成了展示天气的功能。但我们并没有对选中的城市进行保存,所以每当退出应用重进时,还需要重新搜索并选择城市。为此,我们现在就来实现记录选中城市的功能。
Dao 层
因为要存储的数据是单个的地点信息,不属于复杂的关系型数据,所以我们使用 SharedPreferences 来存储选中的城市即可。
在 data/dao 包下创建 PlaceDao 单例类。
kotlin
import androidx.core.content.edit
object PlaceDao {
// 用于序列化和反序列化 Place 对象
private val gson = Gson()
// SharedPreferences 文件的名称
private const val PREFERENCES_NAME = "sunny_weather"
// 存储 Place 对象的键
private const val KEY_PLACE = "place"
/**
* 将 Place 对象保存到 SharedPreferences
*/
suspend fun savePlace(place: Place) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
sharedPreferences().edit {
// 将 Place 对象转换为 JSON 字符串后存储
putString(KEY_PLACE, gson.toJson(place))
}
}
/**
* 从 SharedPreferences 中读取已保存的 Place 对象
*/
suspend fun getSavedPlace(): Place? = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
val placeJson = sharedPreferences().getString(KEY_PLACE, null)
placeJson?.let {
try {
// 将 JSON 字符串反序列化为 Place 对象
gson.fromJson(it, Place::class.java)
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
null
}
}
}
/**
* 检查是否已有地点信息被保存
*/
suspend fun isPlaceSaved() = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
sharedPreferences().contains(KEY_PLACE)
}
/**
* 获取 SharedPreferences 的实例
*/
private fun sharedPreferences() =
SunnyWeatherApplication.context.getSharedPreferences(PREFERENCES_NAME, Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
}在 PlaceDao 中,我们封装了存储、读取数据的接口。由于 SharedPreferences 的读写是文件 IO 操作,可能会阻塞主线程(数据量大或系统繁忙时)。所以我们将这些方法声明为挂起函数,并通过使用 withContext(Dispatchers.IO) 函数,确保它们在 IO 线程池中执行。
仓库层
在 Repository 中封装上述接口,作为数据来源的统一入口。
kotlin
object Repository {
...
/**
* 保存地点信息
*/
suspend fun savePlace(place: Place) = PlaceDao.savePlace(place)
/**
* 获取已保存的地点信息
*/
suspend fun getSavedPlace() = PlaceDao.getSavedPlace()
/**
* 检查是否已保存地点信息
*/
suspend fun isPlaceSaved() = PlaceDao.isPlaceSaved()
}ViewModel
这几个接口的业务逻辑和 PlaceViewModel 相关,所以我们需要在 PlaceViewModel 再做一层封装。
kotlin
class PlaceViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
private val _savedPlace = MutableLiveData<Place?>()
val savedPlace: LiveData<Place?> = _savedPlace
/**
* 从仓库层获取已保存的地点信息
*/
fun getSavedPlace() {
viewModelScope.launch {
val place = Repository.getSavedPlace()
_savedPlace.value = place
}
}
/**
* 保存选中的地点信息
*/
fun savePlace(place: Place) {
viewModelScope.launch {
Repository.savePlace(place)
_savedPlace.value = place
}
}
}实现功能
在 PlaceFragment 中增加列表项的点击逻辑,并在 Fragment 创建时检查是否已有记录。
kotlin
class PlaceFragment : Fragment() {
// ...
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
// 实现自动跳转
checkSavedPlace()
// 设置 RecyclerView 和 Adapter
binding.recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(activity)
adapter = PlaceAdapter { place ->
// 存储选中的城市
viewModel.savePlace(place)
// 跳转到天气详情页
navigateToWeather(place)
}
binding.recyclerView.adapter = adapter
// ...
}
/**
* 检查是否有已保存的城市记录
*/
private fun checkSavedPlace() {
// 触发 ViewModel 加载已保存的地点数据
viewModel.getSavedPlace()
viewModel.savedPlace.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { place ->
// 如果有城市被保存过
if (place != null) {
// 直接跳转到天气详情页
navigateToWeather(place)
}
}
}
/**
* 跳转到 WeatherActivity
*/
private fun navigateToWeather(place: Place) {
val intent = Intent(requireActivity(), WeatherActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra("key_place", place)
}
startActivity(intent)
// 结束当前 Activity,防止用户返回
requireActivity().finish()
}
// ...
}这里我们进行了几处修改:
-
在点击列表项跳转到
WeatherActivity之前,调用了PlaceViewModel的savePlace()方法存储了选中的城市。 -
封装了跳转到
WeatherActivity的逻辑到navigateToWeather方法中。 -
然后在
onViewCreated方法中,我们调用了checkSavedPlace()方法检查是否已有存储的城市数据,如果有,就会直接跳转到WeatherActivity,而无需用户每次都搜索并选择城市。
现在,当已选择某个城市后,下次再次进入应用时,会直接跳转到天气页,并展示该城市的天气信息。
手动刷新天气和切换城市
现在,你会发现有个很严重的bug。那就是当你选择一个城市后,就无法再回到搜索页搜索并查看其他城市的天气了。
所以,现在我们来完成切换城市以及手动刷新城市的功能。
手动刷新天气
我们通过下拉刷新来完成天气信息的刷新。
修改 activity_weather.xml 布局文件,在最外面套上一层 SwipeRefreshLayout,这样就可以进行下拉刷新了。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/swipeRefreshLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView
android:id="@+id/weatherLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:overScrollMode="never"
android:scrollbars="none"
android:visibility="visible">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<include
android:id="@+id/nowLayout"
layout="@layout/now" />
<include
android:id="@+id/forecastLayout"
layout="@layout/forecast" />
<include
android:id="@+id/lifeIndexLayout"
layout="@layout/life_index" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>
</androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout>在 WeatherActivity 中添加下拉刷新的逻辑。
kotlin
class WeatherActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// ...
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
// 观察 weatherLiveData 的数据变化
viewModel.weatherLiveData.observe(this) { result ->
val weather = result.getOrNull()
if (weather != null) {
// 如果成功获取到天气,则显示天气信息
showWeatherInfo(weather)
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "无法成功获取天气信息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
result.exceptionOrNull()?.printStackTrace()
}
// 结束下拉刷新动画
binding.swipeRefreshLayout.isRefreshing = false
}
// 触发首次数据加载
currentPlace?.let {
refreshWeather()
} ?: run {
Toast.makeText(this, "获取地点信息失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
finish()
}
// 设置下拉刷新监听器
binding.swipeRefreshLayout.setOnRefreshListener {
refreshWeather()
}
}
/**
* 刷新天气信息
*/
private fun refreshWeather() {
// 显示下拉刷新进度条
binding.swipeRefreshLayout.isRefreshing = true
currentPlace?.let {
// 发起刷新
viewModel.refreshWeather(it.copy())
}
}
// ...
}此次修改中,我们将首次数据的逻辑放到了 refreshWeather() 方法中,并添加了显示下拉进度条的逻辑。通过 setOnRefreshListener() 给 SwipeRefreshLayout 设置了监听器,每当用户下拉时,就会调用 refreshWeather() 方法。最后,我们在 weatherLiveData 的观察者中,无论请求成功或失败,都要隐藏刷新进度条。
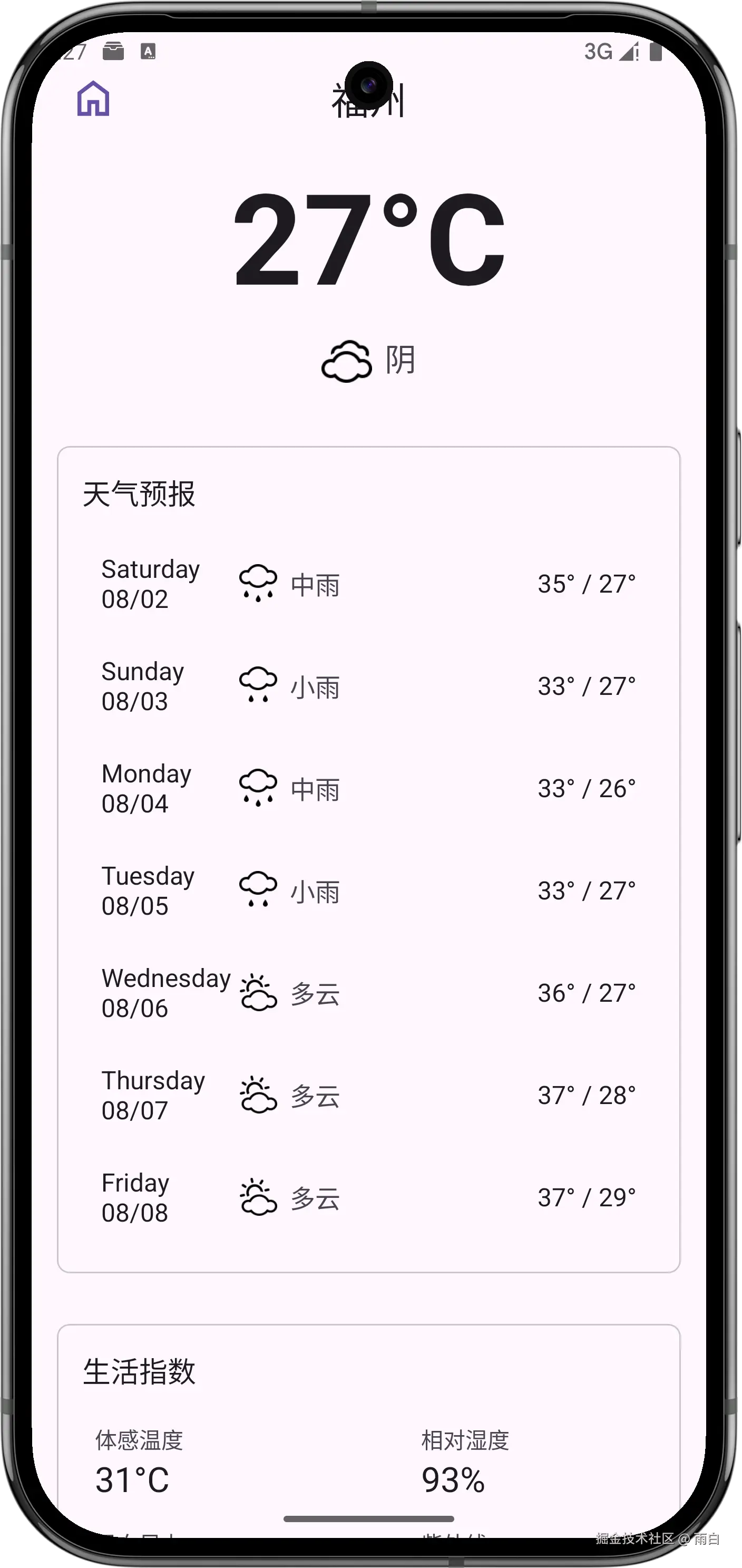
现在,手动刷新天气的功能就完成了。
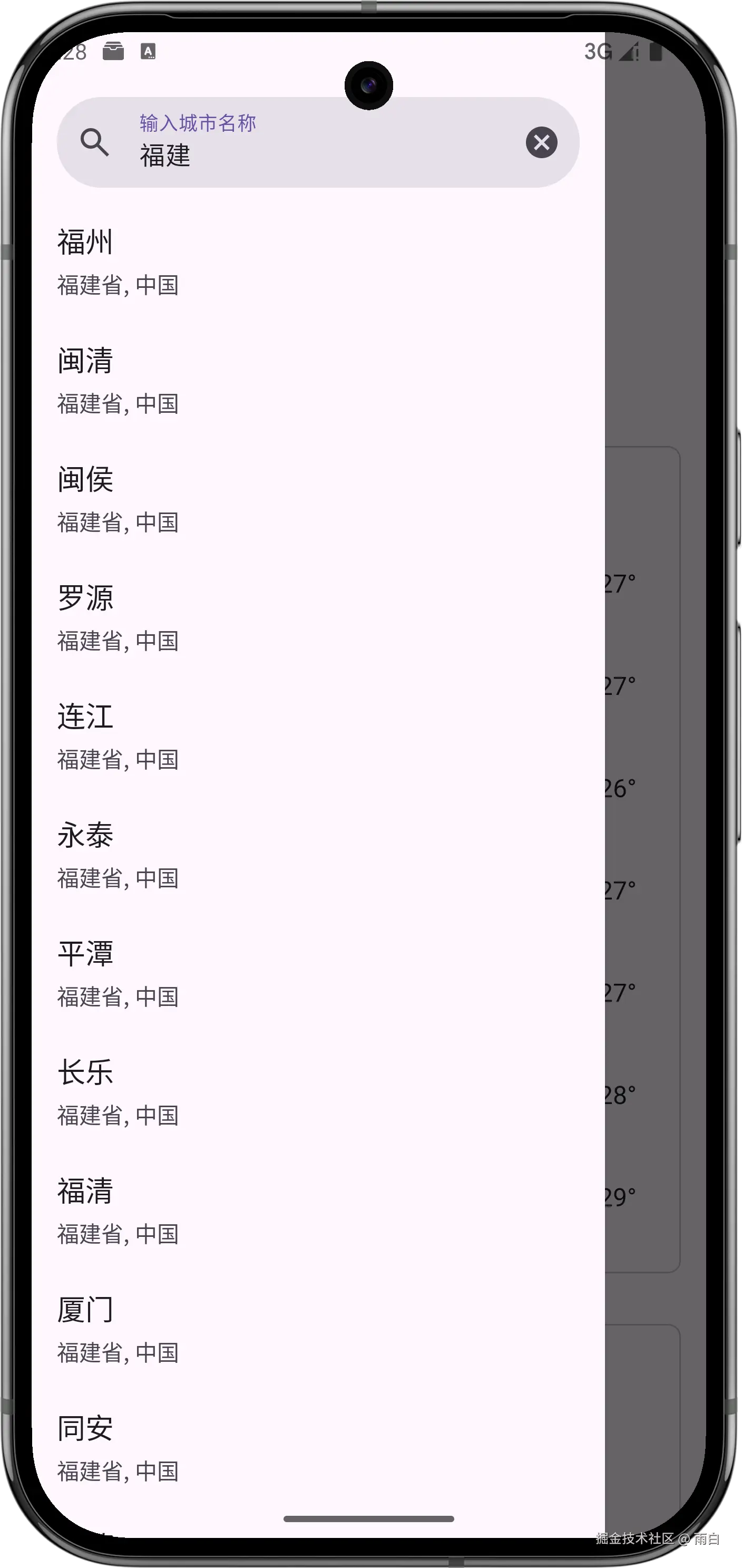
切换城市
切换城市功能需要搜索全球城市的数据,对此,我们可以复用之前的 PlaceFragment。只需在天气页的布局中引入即可。
为了不遮挡天气页,我们将其放入到滑动菜单(DrawerLayout)中。
首先在 now.xml 布局文件中添加一个用于打开滑动菜单的按钮。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button
android:id="@+id/navBtn"
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:background="@drawable/ic_home"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@id/placeName"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/placeName"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@id/placeName" />
...
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>其中的图标,你可以在 res/drawable-xxhdpi 下创建 ic_home.xml 文件。
xml
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="24dp"
android:height="24dp"
android:viewportWidth="960"
android:viewportHeight="960"
android:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal">
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/white"
android:pathData="M240,760L360,760L360,520L600,520L600,760L720,760L720,400L480,220L240,400L240,760ZM160,840L160,360L480,120L800,360L800,840L520,840L520,600L440,600L440,840L160,840ZM480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490L480,490Z"/>
</vector>或是从 Google Fonts 获取。
在 activity_weather.xml 布局中加入滑动菜单和承载 PlaceFragment 的容器。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/drawerLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout
android:id="@+id/swipeRefreshLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView
android:id="@+id/weatherLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:overScrollMode="never"
android:scrollbars="none"
android:visibility="visible">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<include
android:id="@+id/nowLayout"
layout="@layout/now" />
<include
android:id="@+id/forecastLayout"
layout="@layout/forecast" />
<include
android:id="@+id/lifeIndexLayout"
layout="@layout/life_index" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>
</androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
android:background="?attr/colorSurface"
android:clickable="true"
android:focusable="true">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/placeFragment"
android:name="com.sunnyweather.android.ui.place.PlaceFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp" />
</FrameLayout>
</androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout>接着,在 WeatherActivity 中增加滑动菜单的逻辑。
kotlin
// 在 WeatherActivity.kt 的 onCreate 方法中
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
binding.nowLayout.navBtn.setOnClickListener {
// 打开滑动菜单
binding.drawerLayout.openDrawer(GravityCompat.START)
}
binding.drawerLayout.addDrawerListener(object : DrawerLayout.DrawerListener {
override fun onDrawerStateChanged(newState: Int) {}
override fun onDrawerSlide(drawerView: View, slideOffset: Float) {}
override fun onDrawerOpened(drawerView: View) {}
// 抽屉关闭时的回调
override fun onDrawerClosed(drawerView: View) {
val manager = getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE)
as InputMethodManager
// 隐藏软键盘
manager.hideSoftInputFromWindow(
drawerView.windowToken,
InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS
)
}
})
}另外,之前我们在 PlaceFragment 进行了一个判断:如果当前已有选中的城市,就跳转到 WeatherActivity。但此时我们将 PlaceFragment 嵌入到了 WeatherActivity,这段逻辑会造成无限循环跳转。
为此,我们来对 PlaceFragment 进行修改。
kotlin
// PlaceFragment.kt
private fun checkSavedPlace() {
viewModel.getSavedPlace()
viewModel.savedPlace.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { place ->
// 新增条件:只有当前宿主是 MainActivity 时,才执行自动跳转
if (place != null && activity is MainActivity) { // <-修改点
navigateToWeather(place)
}
}
}我们再来修改选中城市列表项的逻辑。之前是点击后直接跳转到 WeatherActivity,但现在如果 PlaceFragment 被嵌入到了 WeatherActivity 中,就无需跳转,只要请求城市的天气信息即可。
kotlin
// PlaceFragment.kt
// 获取与宿主 Activity 共享的 WeatherViewModel 实例
private val sharedWeatherViewModel: WeatherViewModel by activityViewModels()
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
adapter = PlaceAdapter { place ->
// 存储选中的城市
viewModel.savePlace(place)
if (activity is WeatherActivity) {
val activity = requireActivity() as WeatherActivity
// 关闭抽屉
activity.closeDrawer()
// 刷新天气信息
sharedWeatherViewModel.refreshWeather(place)
} else {
// 执行跳转逻辑
navigateToWeather(place)
}
}
// ...
}使用
activityViewModels()方法委托需要添加依赖:
kotlin// app/build.gradle.kts implementation("androidx.fragment:fragment-ktx:1.8.8")
其中,我们需要在 WeatherActivity 中创建 closeDrawer() 公有方法,用于关闭抽屉。
kotlin
// 公共方法,用于让 Fragment 请求关闭抽屉
fun closeDrawer() {
binding.drawerLayout.closeDrawers()
}由于当前天气页地点的数据来源不止一种,可能由 Intent 传入,也可能是用户在抽屉中选择的。为此,我们让 WeatherViewModel 持有"当前地点"这个状态。
kotlin
class WeatherViewModel : ViewModel() {
// ...
// 用于触发天气刷新
private val _currentPlace = MutableLiveData<Place>()
val currentPlace: LiveData<Place> = _currentPlace
val weatherLiveData = _currentPlace.switchMap { location ->
Repository.refreshWeather(location.id, DEFAULT_QUERY_DAYS)
}
/**
* 为指定地点加载天气
*/
fun refreshWeather(place: Place) {
_currentPlace.value = place
}
}删除 WeatherActivity 中的 currentPlace 变量。
kotlin
class WeatherActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// ...
// 从Intent传入的Place对象
// private var currentPlace: Place? = null 不再需要了
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
// 从 Intent 中获取初始地点信息
val initialPlace = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU) {
intent.getParcelableExtra("key_place", Place::class.java)
} else {
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
intent.getParcelableExtra("key_place")
}
// 触发首次数据加载
if (initialPlace != null) {
viewModel.refreshWeather(initialPlace)
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "获取地点信息失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
finish()
return
}
viewModel.currentPlace.observe(this) { place ->
//更新地点名称
binding.nowLayout.placeName.text = place.name
}
}
/**
* 将 Weather 对象的数据填充到界面上
*/
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun showWeatherInfo(weather: Weather) {
// binding.nowLayout.placeName.text = currentPlace?.name 删除这一行
// ...
}
/**
* 刷新天气信息
*/
private fun refreshWeather() {
binding.swipeRefreshLayout.isRefreshing = true
// 发起刷新
viewModel.currentPlace.value?.let { viewModel.refreshWeather(it) }
}
}现在切换城市的功能就完成了。
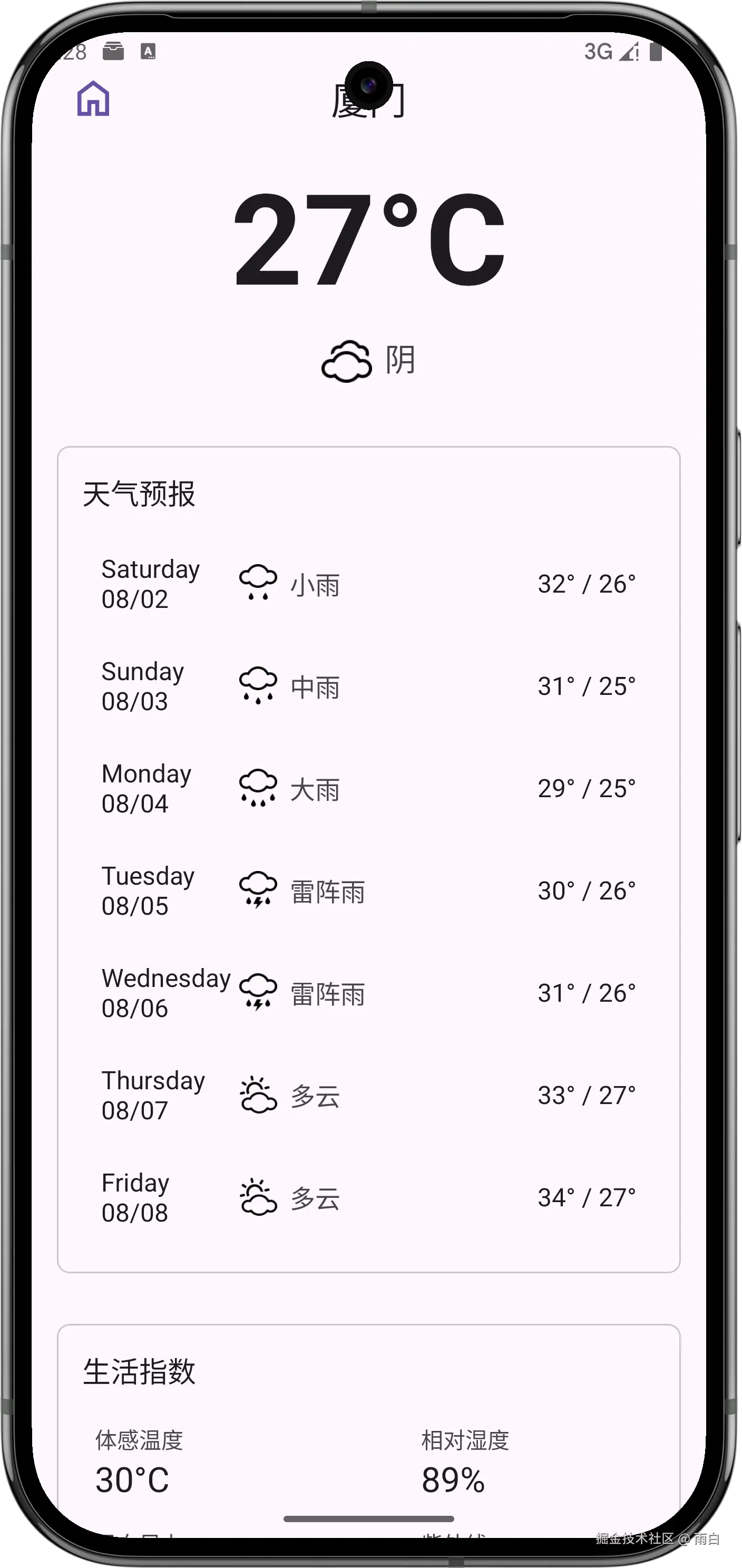
生成正式签名的APK文件
之前我们都是通过 Android Studio 来将应用安装到手机的。Android Studio 实际上会将代码打包成 APK 文件(应用程序的安装包),再将这个文件传到手机上进行安装。
但 Android 系统要求只有签名后的 APK 文件才能安装,而这一步 Android Studio 自动帮我们完成了:使用了默认的 keystore 文件帮我们签名。
不过在开发阶段这样做可以,要正式发布应用的话,就需要使用正式的 keystore 文件进行签名。我们来看看如何生成带有正式签名的 APK 文件。
使用 Android Studio 生成
点击导航菜单中的 Build->Generate Signed Bundle/APK。
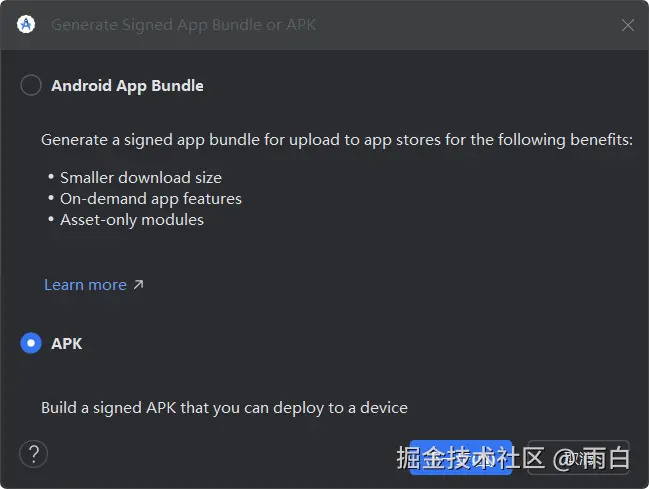
选择 APK 即可,因为 Android App Bundle 是用于上架 Google 商店的,虽说可以减少 App 安装包体积,但无法直接安装到手机上。
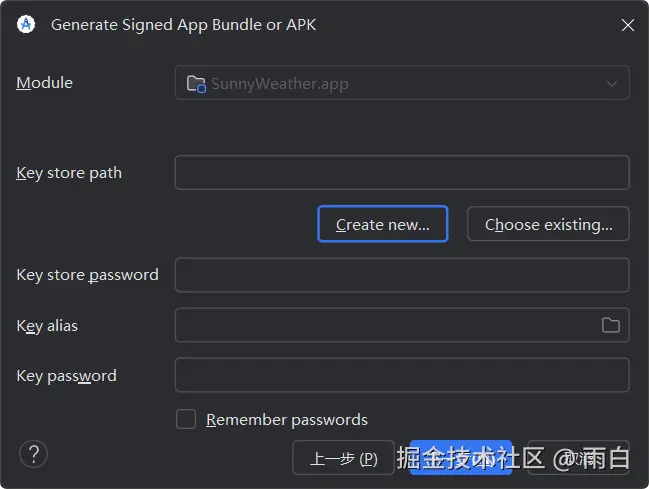
因为我们还没有 keyStore 文件,点击 Create New 按钮创建一个。
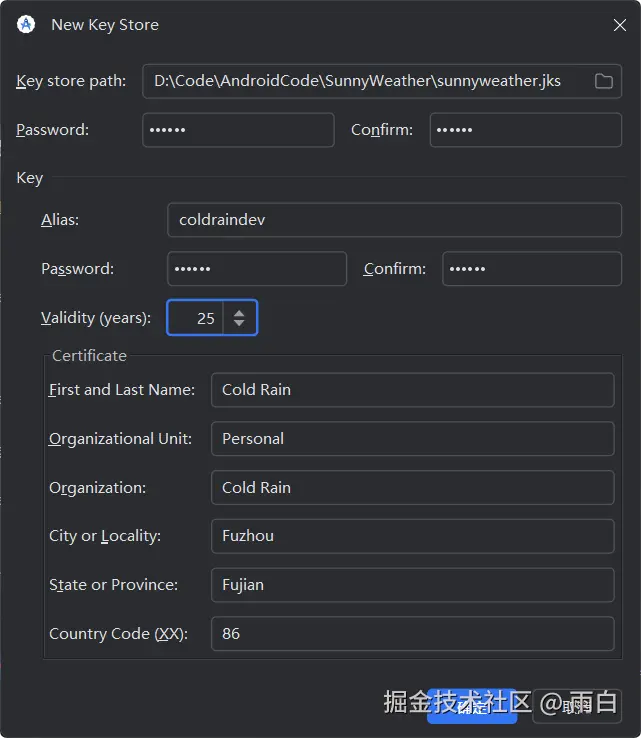
尽量填写即可,然后点击确定。
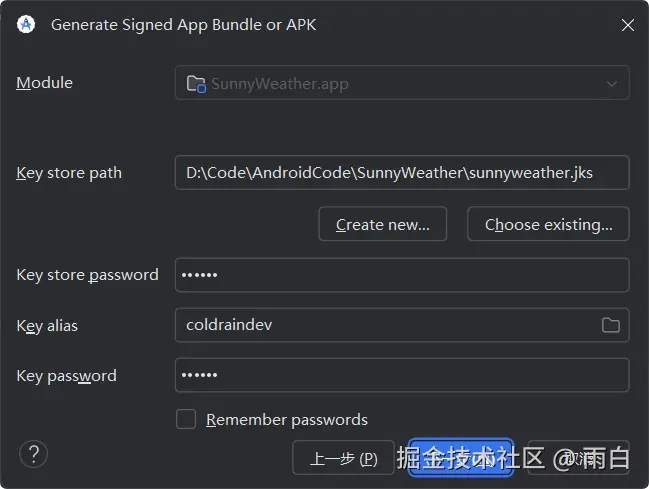
点击下一步,构建类型选择 release。
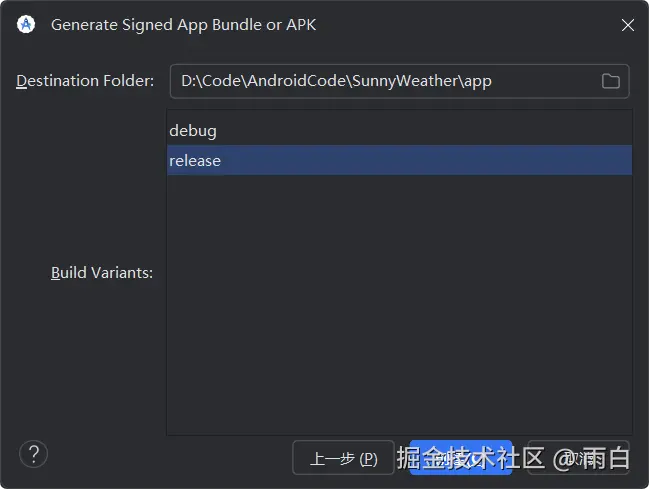
点击创建,过一会,APK 文件就会生成。你可以将这个文件发给别人,别人可以直接安装到手机上。
使用 Gradle 生成
我们还可以使用 Gradle 生成 APK 文件,在 app/build.gradle.kts 文件中添加如下内容:
kotlin
android {
// 签名配置
signingConfigs {
// 创建签名配置
create("config") {
storeFile = file("D:\Code\AndroidCode\SunnyWeather\sunnyweather.jks")
storePassword = "123456"
keyAlias = "coldraindev"
keyPassword = "123456"
}
}
// 构建类型配置
buildTypes {
// 对 release 构建类型进行配置
release {
// 是否启用代码混淆和压缩
isMinifyEnabled = false
// 指定混淆规则文件
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro"
)
// 使用上面创建的签名配置
signingConfig = signingConfigs.getByName("config")
}
}
}然后点击右侧的 Gradle,再点击执行 Gradle 任务按钮,输入 gradlew assembleRelease 命令即可。
当命令执行完成后,已签名的 APK 文件会自动生成在 app/build/outputs/apk/release/ 目录下。
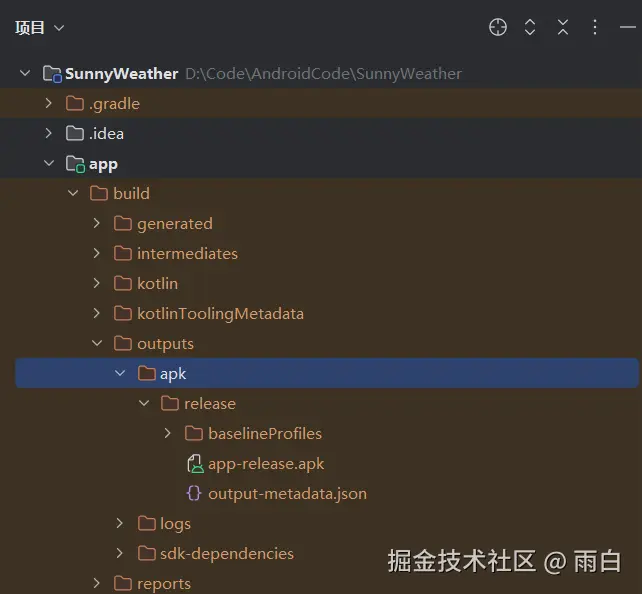
最后注意:签名配置相关信息不要硬编码 在 build.gradle.kts 文件中,应该将这些敏感信息放在项目根路径的 local.properties 文件中,然后在 build.gradle.kts 中读取。
像这样:
Properties
# local.properties 这个文件通常不会上传到代码仓库
KEYSTORE_FILE=D:\Code\AndroidCode\SunnyWeather\sunnyweather.jks
KEY_ALIAS=coldraindev
KEY_PASSWORD=123456
STORE_PASSWORD=123456
kotlin
// app/build.gradle.kts
val localProperties = Properties().apply {
val localPropertiesFile = rootProject.file("local.properties")
if (localPropertiesFile.exists()) {
load(FileInputStream(localPropertiesFile))
}
}
// 签名配置
signingConfigs {
create("config") {
storeFile = file(localProperties.getProperty("KEYSTORE_FILE"))
storePassword = localProperties.getProperty("STORE_PASSWORD")
keyAlias = localProperties.getProperty("KEY_ALIAS")
keyPassword = localProperties.getProperty("KEY_PASSWORD")
}
}这样一来,在 Git 中直接查看 build.gradle.kts 文件,是无法看到 keystore 文件的各种信息的,只有在本地的local.properties 文件中才能看到,也就避免了 keystore 文件信息泄露的问题。