上一章介绍了 React 中初次渲染和
setState创建更新到触发调度的流程。这章会从上一章最后提到的scheduleUpdateOnFiber方法开始详细分析 React 中的调度过程。
scheduleUpdateOnFiber
调度更新的入口函数,比如 setState 使组件状态发生变化后,React 会通过 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 将更新任务加入调度系统,最终触发更新流程。
简化后的源码如下,有三个核心步骤。
ts
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
): FiberRoot | null {
const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane);
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime);
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
return root;
}markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot
为 Fiber 树上的节点记录更新。
ts
function markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(
sourceFiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
): FiberRoot | null {
sourceFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(sourceFiber.lanes, lane);
let alternate = sourceFiber.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, lane);
}
let node = sourceFiber;
let parent = sourceFiber.return;
while (parent !== null) {
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);
alternate = parent.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.childLanes = mergeLanes(alternate.childLanes, lane);
}
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
const root: FiberRoot = node.stateNode;
return root;
} else {
return null;
}
}参数:
-
sourceFiber:更新对应的 Fiber 节点。 -
lane:更新的优先级。
核心流程:
- 将当前更新的优先级 lane 通过位运算 合并到当前更新的 Fiber 节点的
fiber.lanes属性上。即,记录 Fiber 节点自身的更新优先级。
ts
export function mergeLanes(a: Lanes | Lane, b: Lanes | Lane): Lanes {
return a | b;
}-
通过
fiber.return属性从当前 Fiber 节点向上遍历父节点,直到 RootFiber(RootFiber.parent === null),并沿途将当前更新的 lane 合并到每个父节点的childLanes属性上。即,一个节点更新优先级变化,它的父节点的childLanes会随之变化。 -
最后从
RootFiber.stateNode获取 FiberRoot(之前有讲过FiberRoot和RootFiber的关系),并返回 FiberRoot 供后续调度使用。
此处对
fiber.lanes和沿途父节点parent.childLanes的标记,用于记录 Fiber 树上的各个节点是否需要更新。
markRootUpdated
在 FiberRoot 上标记此次更新的优先级和优先级对应的时间戳。
ts
export function markRootUpdated(
root: FiberRoot,
updateLane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
) {
root.pendingLanes |= updateLane;
if (updateLane !== IdleLane) {
root.suspendedLanes = NoLanes;
root.pingedLanes = NoLanes;
}
const eventTimes = root.eventTimes;
const index = laneToIndex(updateLane);
eventTimes[index] = eventTime;
}参数:
-
root:上一步返回的 FiberRoot。 -
updateLane:更新的优先级。 -
eventTime:更新任务的时间戳。
核心流程:
1. 更新 FiberRoot.pendingLanes
把当前更新的 lane 合并到 FiberRoot.pendingLanes 中。FiberRoot.pendingLanes 属性之前有讲过,表示当前所有待处理的更新。
2. 清除挂起状态任务
如果当前更新不是低优先级更新(这里可以回顾 Scheduler 的优先级,此处判断 lane !== IdleLane),则清除 suspendedLanes 挂起状态的任务 和 pingedLanes 恢复状态的任务。因为要重新开始新一轮调度了。
3. 更新 eventTimes
FiberRoot 上的 eventTimes 属性是一个长度为 31 位的数组,每个索引记录一个 lane 优先级最近一次事件发生的时间戳。这恰好对应 Lane 模型是一个 31位的位掩码表示最多 31 种更新优先级。
ts
root.eventTimes = [
1670000000000,
0,
1670000001234,
...
]laneToIndex 用于获取 lane 值在 eventTimes 数组中对应的索引,比如 updateLane 为 0b000000000000000000010000,即 lane 12,laneToIndex(updateLane) 会返回数字 12。
然后将此次更新任务的 eventTime 时间戳存到 eventTimes 数组对应的 lane 索引中。
这样做的目的是:记录某个 lane 优先级的更新是何时发生的,在之后的调度中,用于判断是否已经「等待太久」,需要抢占或提升优先级。
ensureRootIsScheduled
React 中的"调度总管",每次创建更新后,决定是否要进入调度、以何种方式(同步/异步)调度。
精简后的源码如下:
ts
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root, currentTime) {
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime);
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes);
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
return;
}
const newCallbackPriority = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes);
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
if (
existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority
) {
return;
}
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
let newCallbackNode;
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
scheduleSyncCallback(() => performSyncWorkOnRoot(root));
scheduleMicrotask(() => flushSyncCallbacks());
newCallbackNode = null;
} else {
let schedulerPriorityLevel;
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
case DiscreteEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = ImmediateSchedulerPriority;
break;
case ContinuousEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = UserBlockingSchedulerPriority;
break;
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
case IdleEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = IdleSchedulerPriority;
break;
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
}
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}参数:
-
root:FiberRoot。 -
currentTime:当前时间戳。
核心逻辑:
markStarvedLanesAsExpired 处理饥饿问题
在调度过程中,某些任务可能因为高优任务插队而长期不能执行,产生「饥饿问题」,这个方法把等待时间太久的 lanes 标记为过期,强制尽快执行。
ts
export function markStarvedLanesAsExpired(
root: FiberRoot,
currentTime: number,
): void {
const pendingLanes = root.pendingLanes;
const suspendedLanes = root.suspendedLanes;
const pingedLanes = root.pingedLanes;
const expirationTimes = root.expirationTimes;
let lanes = pendingLanes;
while (lanes > 0) {
const index = pickArbitraryLaneIndex(lanes);
const lane = 1 << index;
const expirationTime = expirationTimes[index];
if (expirationTime === NoTimestamp) {
if (
(lane & suspendedLanes) === NoLanes ||
(lane & pingedLanes) !== NoLanes
) {
expirationTimes[index] = computeExpirationTime(lane, currentTime);
}
} else if (expirationTime <= currentTime) {
root.expiredLanes |= lane;
}
lanes &= ~lane;
}
}1. 从 FiberRoot 上获取 pendingLanes、expirationTimes
pendingLanes:当前所有待处理任务优先级的集合。
expirationTimes:一个 31 位的数组,类似前面提到的 eventTimes,记录每个 lane 的过期时间。
2. 遍历 pendingLanes 集合
pickArbitraryLaneIndex 方法找到 lanes 中第一个 1 所在的 index。比如:
ts
lanes = 0b00010110; // 有第 1、2、4 位任务在等待
index = pickArbitraryLaneIndex(lanes); // 返回 1const lane = 1 << index 根据 index 还原 lane 值。比如:
ts
lane = 1 << 1 = 0b00000010;中间经过一系列处理,最后 lanes &= ~lane,去掉刚刚处理过的 lane 值,再开始下一轮循环。
比如第一轮循环 lanes 为 0b00010110,处理的 lane 为 0b00000010,进入下一轮循环的 lanes 为 0b00010100。
3. 每一轮循环的处理
通过本轮要处理的 lane 值对应的 index ,从 root.expirationTimes 上获取这个 lane 的过期时间。
如果这个 lane 没有设置过期时间,就计算一个过期时间,存放在 root.expirationTimes 中。
如果这个 lane 设置了过期时间,检查是否过期。如果已过期,则将当前 lane 值添加到 root.expiredLanes 上,表示这个 lane 在下一轮调度中会以同步模式渲染,不可中断(后续在 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 中判断),避免任务饥饿问题。
getNextLanes 挑选调度目标
从 root.pendingLanes 中挑出一批 Lane(任务),优先级最高、不被挂起的,作为调度的目标。
ts
export function getNextLanes(root: FiberRoot, wipLanes: Lanes): Lanes {
const pendingLanes = root.pendingLanes;
if (pendingLanes === NoLanes) {
return NoLanes;
}
let nextLanes = NoLanes;
const suspendedLanes = root.suspendedLanes;
const pingedLanes = root.pingedLanes;
const nonIdlePendingLanes = pendingLanes & NonIdleLanes;
if (nonIdlePendingLanes !== NoLanes) {
const nonIdleUnblockedLanes = nonIdlePendingLanes & ~suspendedLanes;
if (nonIdleUnblockedLanes !== NoLanes) {
nextLanes = getHighestPriorityLanes(nonIdleUnblockedLanes);
} else {
const nonIdlePingedLanes = nonIdlePendingLanes & pingedLanes;
if (nonIdlePingedLanes !== NoLanes) {
nextLanes = getHighestPriorityLanes(nonIdlePingedLanes);
}
}
} else {
const unblockedLanes = pendingLanes & ~suspendedLanes;
if (unblockedLanes !== NoLanes) {
nextLanes = getHighestPriorityLanes(unblockedLanes);
} else {
if (pingedLanes !== NoLanes) {
nextLanes = getHighestPriorityLanes(pingedLanes);
}
}
}
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
return NoLanes;
}
if (
wipLanes !== NoLanes &&
wipLanes !== nextLanes &&
(wipLanes & suspendedLanes) === NoLanes
) {
const nextLane = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes);
const wipLane = getHighestPriorityLane(wipLanes);
if (
nextLane >= wipLane ||
(nextLane === DefaultLane && (wipLane & TransitionLanes) !== NoLanes)
) {
return wipLanes;
}
}
return nextLanes;
}参数:
-
root:FiberRoot。 -
wipLanes:当前正在进行渲染中的 lanes,用于避重新进入已在进行中的任务,导致的重复调度。
ts
root === workInProgressRoot
? workInProgressRootRenderLanes
: NoLanes逻辑:
-
获取所有待处理的任务,没有则直接返回
NoLanes。 -
优先调度非 Idle 任务(低优空闲任务),从非
IdleLanes中找:
- 非 suspense 任务(挂起任务)中优先级最高的。
- 找不到,则找从 suspense 状态被恢复的任务(pinged)。
- 从
IdleLanes中找:
- 非 suspense 任务(挂起任务)中优先级最高的。
- 找不到,则找从 suspense 状态被恢复的任务(pinged)。
-
依然找不到,返回
NoLanes。 -
避免打断正在 render 中的任务(
wipLanes):如果下一批 lanes 完全被当前正在执行的任务包含,那就返回wipLanes继续当前的工作,目的是减少 render 被打断造成的浪费。 -
最终返回找到的
nextLanes。
没有要执行的任务则取消之前设置的调度任务
existingCallbackNode 是指 当前已经在调度器中注册的任务 ,它来自 FiberRoot.callbackNode,用来跟踪该 FiberRoot 上已经设置的调度任务。
React 在某次 getNextLanes() 的结果是 NoLanes,意味着当前 Fiber 树中没有任何更新需要处理,那就可以取消之前设置的调度任务。
getHighestPriorityLane
从一组 lanes 中,找出优先级最高的那个 lane。
ts
export function getHighestPriorityLane(lanes: Lanes): Lane {
return lanes & -lanes;
}核心就是一行位运算,返回最低位 1 的那个 lane(位越低,优先级越高)。
新旧任务优先级相同跳过调度
ts
// 如果已有 callback,且优先级不变,不需要重新调度
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
if (existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority) {
return;
}比较「旧的任务」和「新的任务」的优先级,如果两者相同,则 return 跳过调度,复用之前的 callback 即可。
新旧任务优先级不同则取消旧任务
ts
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}根据优先级决定以同步或异步方式调度任务
newCallbackPriority 是 getHighestPriorityLane() 返回的当前 root.pendingLanes 上最高优先级的 lane。
同步调度
如果最高优先级的 lane 是 SyncLane 则同步执行。
ts
scheduleSyncCallback(() => performSyncWorkOnRoot(root));
scheduleMicrotask(() => flushSyncCallbacks());异步调度
否则走 Scheduler 调度系统进行异步调度。
先把 React 的 lane 优先级转为 Scheduler 优先级,这两个优先级之前有介绍过:Scheduler 优先级和事件优先级。
然后调用 scheduleCallback,传入 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 作为回调,后面会详细讲它们的实现。
ts
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);缓存当前调度任务和它的优先级
ts
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;newCallbackNode 为当前调度任务,newCallbackPriority 为当前 root.pendingLanes 上最高优先级,也是当前调度任务的优先级。
缓存它们的作用是:下次 ensureRootIsScheduled() 执行时可以比较新旧任务优先级,优先级相同则跳过调度,否则取消旧任务重新调度。
同步调度流程
ts
scheduleSyncCallback(() => performSyncWorkOnRoot(root));
scheduleMicrotask(() => flushSyncCallbacks());scheduleSyncCallback
将回调(performSyncWorkOnRoot())放入同步队列 syncQueue 中。
ts
let syncQueue = null;
export function scheduleSyncCallback(callback) {
if (syncQueue === null) {
syncQueue = [callback];
} else {
syncQueue.push(callback);
}
}scheduleMicrotask
一个跨平台封装,queueMicrotask -> Promise -> setTimeout 逐步降级,用于在当前调用栈执行完之后,安排一个微任务,在本轮事件循环尾部尽快执行。此处安排执行 flushSyncCallbacks()。
ts
export const scheduleMicrotask =
typeof queueMicrotask === 'function'
? queueMicrotask
: typeof Promise !== 'undefined'
? (callback) => Promise.resolve(null).then(callback)
: setTimeout;同步任务不直接执行,而是用微任务包一层的原因:
- 避免嵌套执行引发不一致或死循环 比如在
render里调用flushSync(),需要先等当前逻辑结束。- 收集多个
flushSyncCallbacks()在微任务中统一批量处理,避免多次重渲染。
flushSyncCallbacks
遍历 syncQueue ,其中每一项是一个 callback,逐个执行。即,执行 performSyncWorkOnRoot()。
ts
export function flushSyncCallbacks() {
if (syncQueue !== null) {
const queue = syncQueue;
syncQueue = null;
for (let i = 0; i < queue.length; i++) {
const callback = queue[i];
callback(); // 执行传入的 performSyncWorkOnRoot(root)
}
}
}performSyncWorkOnRoot
其中调用 renderRootSync + commitRoot,renderRootSync 过程不可中断。
ts
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
renderRootSync(root);
commitRoot(root);
}异步调度流程
ts
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);scheduleCallback
位于 Scheduler 包中,用于将一个任务调度到合适的优先级队列中,在浏览器空闲时间立即执行或延迟到指定时间后执行。
ts
function scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
var currentTime = getCurrentTime();
var startTime;
if (typeof options === 'object' && options !== null) {
var delay = options.delay;
if (typeof delay === 'number' && delay > 0) {
startTime = currentTime + delay;
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
var timeout;
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
timeout = IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
timeout = USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case IdlePriority:
timeout = IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case LowPriority:
timeout = LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case NormalPriority:
default:
timeout = NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
}
var expirationTime = startTime + timeout;
var newTask = {
id: taskIdCounter++,
callback,
priorityLevel,
startTime,
expirationTime,
sortIndex: -1,
};
if (enableProfiling) {
newTask.isQueued = false;
}
if (startTime > currentTime) {
newTask.sortIndex = startTime;
push(timerQueue, newTask);
if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {
if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {
cancelHostTimeout();
} else {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;
}
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
}
} else {
newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime;
push(taskQueue, newTask);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(newTask, currentTime);
newTask.isQueued = true;
}
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}
}
return newTask;
}参数:
priorityLevel:任务的 scheduler 优先级。callback:要调度执行的任务函数,这里是performConcurrentWorkOnRoot。options: 可选对象,包含delay(延迟时间)字段。
核心流程:
确定任务开始时间
currentTime 为当前时间戳,根据参数中是否传了 delay 分为普通任务和延时任务:
-
普通任务:
startTime=currentTime -
延时任务:
startTime=currentTime+delay
即,普通任务立即开始,延时任务延时开始。
可以通过
startTime和currentTime比较得到任务是否为延时任务。
根据优先级确定任务过期时间
根据任务优先级,映射到不同的 timeout:
ts
IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = -1
USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 250
NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 5000
LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 10000
IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = MAX_INT过期时间 expirationTime = startTime + timeout,这是任务最晚必须执行的时间。
构建任务对象
任务对象中各个字段的含义如下:
id:全局递增 ID。callback:要调度执行的任务函数,performConcurrentWorkOnRoot()。priorityLevel:任务优先级startTime:任务开始时间。expirationTime:任务过期时间。sortIndex:排序字段。
将任务对象加入合适的任务队列
Scheduler 中有两个任务队列:taskQueue 和 timerQueue,都是用最小堆的数据结构存储。
taskQueue:普通任务队列,按照expirationTime任务过期时间排序,过期时间越早则越靠前。timerQueue:延时任务队列,按照startTime任务开始时间排序,开始时间越早则越靠前。
延时任务
如果 startTime > currentTime 即延时任务。
-
标记任务对象的
sortIndex为startTime。 -
push 到
timerQueue延时任务队列。 -
如果此时
taskQueue中没有任务,且当前任务是延时任务队列中最早的任务,则调用requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime)。
requestHostTimeout
通过 setTimeout 延迟到当前任务设定的时间再执行 callback,即 handleTimeout。
ts
function requestHostTimeout(callback, ms) {
taskTimeoutID = localSetTimeout(() => {
callback(getCurrentTime());
}, ms);
}advanceTimers
handleTimeout 中先执行 advanceTimers。它的作用是把 timerQueue 中所有到达 startTime 的任务移动到 taskQueue 准备执行。
ts
function advanceTimers(currentTime) {
let timer = peek(timerQueue);
while (timer !== null) {
if (timer.callback === null) {
pop(timerQueue);
} else if (timer.startTime <= currentTime) {
pop(timerQueue);
timer.sortIndex = timer.expirationTime;
push(taskQueue, timer);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(timer, currentTime);
timer.isQueued = true;
}
} else {
return;
}
timer = peek(timerQueue);
}
}-
循环从
timerQueue中取堆顶。 -
如果任务对象上的
callback属性为null,表示该任务被取消(外部代码调用了cancelCallback),就从timerQueue中移除它,不需要放到taskQueue。 -
如果任务对象的延迟时间到了,就从
timerQueue中弹出,设置sortIndex为expirationTime(因为在taskQueue中要按这个字段排序),然后 push 到taskQueue准备执行。
handleTimeout
ts
function handleTimeout(currentTime) {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = false;
advanceTimers(currentTime);
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {
if (peek(taskQueue) !== null) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
}
}
}-
调用
advanceTimers把timerQueue中所有到达startTime的任务移动到taskQueue准备执行。 -
taskQueue中有任务可执行,调用requestHostCallback(flushWork)在浏览器空闲时立即执行。 -
taskQueue中没有任务可执行,但timerQueue中有延时任务等待,就取最早的延时任务,继续通过requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime)延时到特定的时间再放入taskQueue执行。
也就是说,
timerQueue中的任务不会直接执行,都是到期以后移动到taskQueue中被执行的。
普通任务
不满足 startTime > currentTime 则为普通任务:
-
标记任务对象的
sortIndex为expirationTime。 -
push 到
taskQueue普通任务队列。 -
调用
requestHostCallback(flushWork)在浏览器空闲时立即执行。
requestHostCallback
注册宏任务,在浏览器事件循环的下一个空闲时间执行。
ts
function requestHostCallback(callback) {
scheduledHostCallback = callback;
if (!isMessageLoopRunning) {
isMessageLoopRunning = true;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
}
}
ts
let schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline;
if (typeof localSetImmediate === 'function') {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetImmediate(performWorkUntilDeadline);
};
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined') {
const channel = new MessageChannel();
const port = channel.port2;
channel.port1.onmessage = performWorkUntilDeadline;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
port.postMessage(null);
};
} else {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetTimeout(performWorkUntilDeadline, 0);
};
}-
保存传入的
flushWork到scheduledHostCallback后续使用。 -
isMessageLoopRunning避免重复注册。 -
通过
setImmediate->MessageChannel->setTimeout逐步降级,将performWorkUntilDeadline注册到浏览器事件循环的宏任务中,在主线程空闲的时候执行。
performWorkUntilDeadline
在主线程空闲时调用 flushWork ,以及判断 taskQueue 中是否还有任务并再次开启调度。
ts
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {
const currentTime = getCurrentTime();
startTime = currentTime;
const hasTimeRemaining = true;
let hasMoreWork = true;
try {
hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime);
} finally {
if (hasMoreWork) {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
scheduledHostCallback = null;
}
}
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
}
needsPaint = false;
};-
调用
scheduledHostCallback即flushWork(前面将它保存在了这个变量上)。 -
flushWork返回hasMoreWork为true则表示taskQueue中还有可执行的任务,则调用schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline再次调度,在浏览器事件循环的下一个空闲时间执行;否则停止调度。
flushWork
内部实现简化一下,其实就是调用 workLoop。
workLoop
在主线程空闲时间,从 taskQueue 中取任务,真正执行。
ts
function workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
let currentTime = initialTime;
advanceTimers(currentTime);
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
while (currentTask !== null) {
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
break;
}
const callback = currentTask.callback;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = null;
currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;
const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
} else {
if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {
pop(taskQueue);
}
}
advanceTimers(currentTime);
} else {
pop(taskQueue);
}
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
}
if (currentTask !== null) {
return true;
} else {
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
return false;
}
}1. 调用 advanceTimers 把 timerQueue 中所有到期的任务推到 taskQueue 准备执行
2. 进入一个可中断的 while 循环
从 taskQueue 堆顶取一个任务对象进入循环。
3. 检查是否需要中断(React 时间切片的关键)
React 源码系列的第一篇文章(这里)就有讲过时间切片的思想,即把一个大任务拆成多个小任务,分散在多个帧中完成。每个帧中时间到了,就把执行权交还给浏览器,下次浏览器空闲时间再继续执行。
浏览器流畅的用户体验为 60 FPS,则一帧需要控制在 1000ms / 60 ≈ 16ms 内,这 16ms 中需要留足够的时间给浏览器,剩余时间留给 React 执行。React 团队根据经验值,给默认的时间片设置为 5ms,超过这个时间就会中断,把主线程控制权交还给浏览器,下一个时间片再执行。
来看这里中断的判断,需要同时满足 2 个条件:
- 当前任务还没过期(
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime) - 时间片用完,即
shouldYieldToHost为true。
4. 执行任务回调
不中断则从任务对象 task.callback 上获取任务函数并执行,即执行 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot。
如果返回一个 continuationCallback 函数,表示任务未执行完成,将其赋值回 task.callback 上,下一个 while 循环继续执行。
否则将当前任务对象从 taskQueue 中移除,下次循环从剩余的 taskQueue 中取堆顶执行。
5. 准备下一轮循环
再次把 timerQueue 中所有到期的任务推到 taskQueue,然后从 taskQueue 堆顶取一个任务对象进入下一轮循环。
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
其中调用 renderRootConcurrent + commitRoot,renderRootConcurrent 过程可中断。
ts
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
const lanes = getNextLanes(root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes);
if (lanes === NoLanes) {
return null;
}
const shouldTimeSlice = !includesExpiredLane(root, lanes) &&
const exitStatus = shouldTimeSlice
? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes)
: renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (exitStatus !== RootInProgress) {
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
}
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}1. 判断是否要进行可中断的渲染
前面提到,root.expiredLanes 上记录了已经过期的更新任务对应的 lane 集合。这里通过 includesExpiredLane 比较要执行的 lanes 和 root.expiredLanes。如果要执行的任务已过期,则后续只能不可中断渲染(renderRootSync),否则可以进入可中断渲染流程。
2. 调用 renderRootConcurrent 可中断渲染
看下简化后的源码:
ts
function renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes) {
prepareFreshStack(root, lanes);
do {
try {
workLoopConcurrent();
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
if (workInProgress !== null) {
return RootInProgress;
} else {
workInProgressRoot = null;
workInProgressRootRenderLanes = NoLanes;
return workInProgressRootExitStatus;
}
}
ts
function workLoopConcurrent() {
while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}workLoopConcurrent 中可以通过 shouldYield 中断。
中断时如果 workInProgress 不为 null,即这个任务还未完成,renderRootConcurrent 就返回 RootInProgress。
3. 任务已完成调用 commitRoot
renderRootConcurrent 返回的不是 RootInProgress,则该任务已完成,调用 finishConcurrentRender,其中调用 commitRoot。
4. 任务未完成返回 continuationCallback 函数
renderRootConcurrent 返回 RootInProgress,则该任务未完成,返回 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 本身,即前面提到的 continuationCallback 函数,调度系统会在下一个时间片继续执行。
异步调度的整体流程图如下:
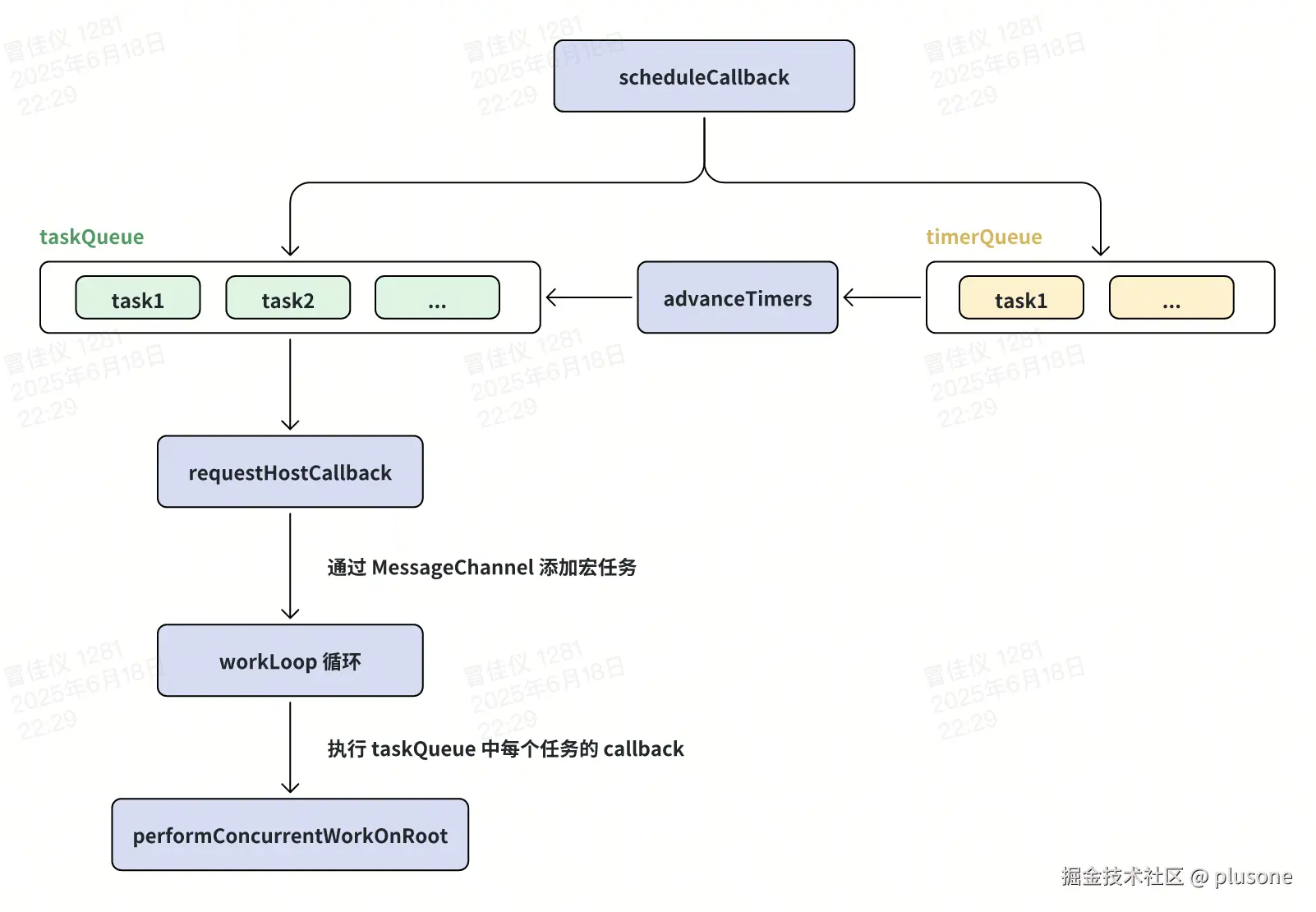
总结
本文分析了 React 中的核心调度流程,其中有几个核心点:
1. 时间切片 + 可中断
通过 MessageChannel 添加宏任务,实现异步任务在浏览器空闲时间执行。
执行任务的 while 循环中 shouldYield 控制中断,实现到达时间片就将控制权交还给浏览器。
可中断的节点有:
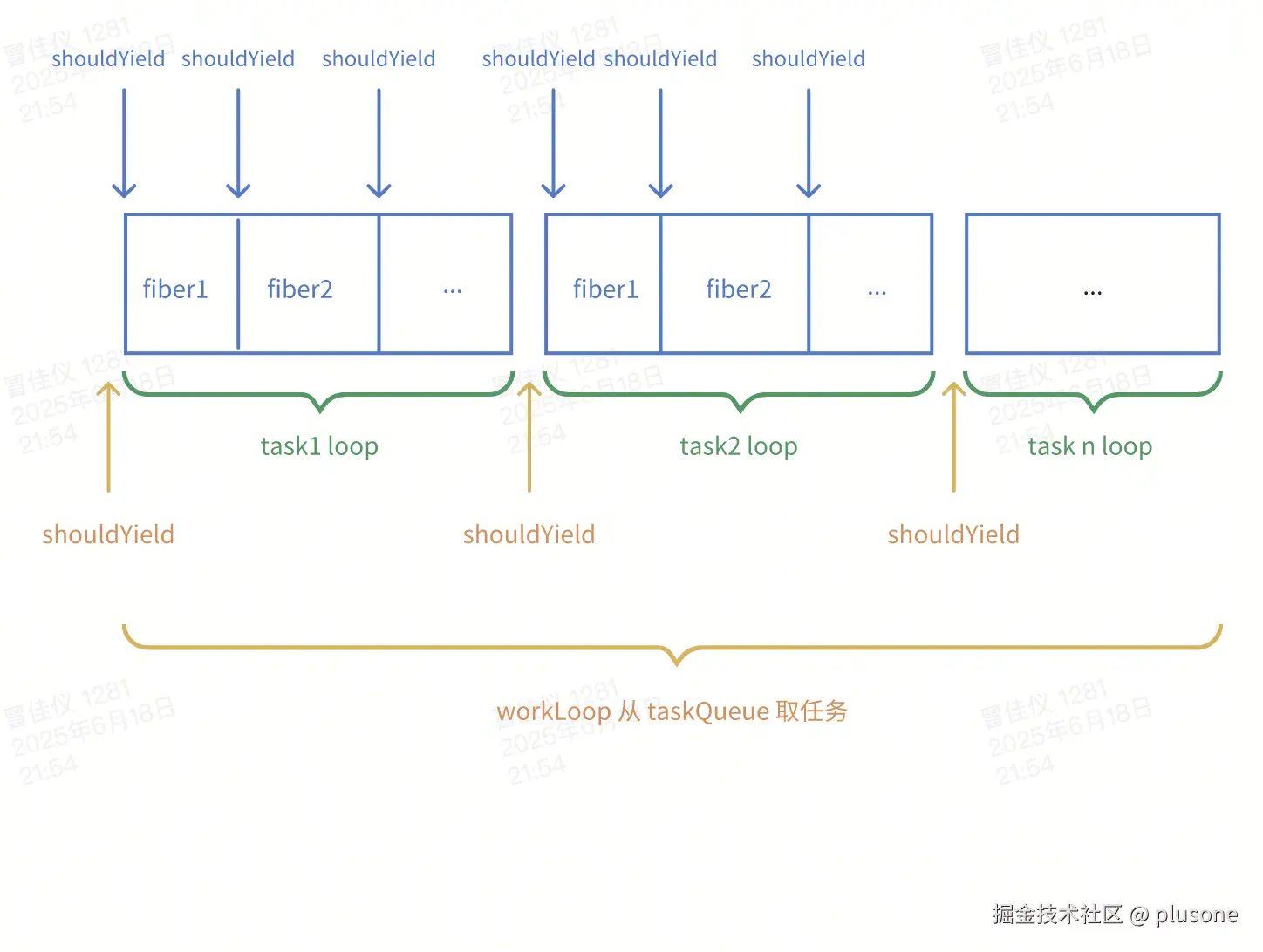
- 从
taskQueue中每次取任务开始执行前。 - 每个任务的
renderRoot中对单个 Fiber 节点的更新前。
2. 基于优先级的调度
优先级的概念贯穿整个调度过程。基于优先级可以实现:
-
每次都挑选最高优先级进行调度。
-
新旧任务优先级相同则复用之前的调度。
-
根据优先级确定同步/异步调度。
-
异步调度时,
taskQueue队列中任务的排序与任务开始时间和任务优先级相关,越早越先执行。 -
shouldYield中断后,如果有新的高优任务进来,下一帧中会优先执行,即高优任务打断低优任务。