题⽬描述
操作给定的⼆叉树,将其变换为源⼆叉树的镜像。
⼆叉树的镜像定义:源⼆叉树
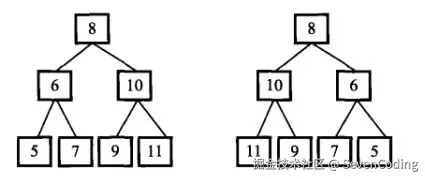
思路及解答
递归
采用后序遍历(左-右-根)的方式递归访问每个节点:
- 递归处理左子树
- 递归处理右子树
- 访问根节点并交换其左右子树
java
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
// 先递归处理子树
TreeNode left = mirrorTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = mirrorTree(root.right);
// 再交换左右子树
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}或者采用前序遍历(根-左-右)的方式递归访问每个节点:
- 访问根节点并交换其左右子树
- 递归处理左子树
- 递归处理右子树
java
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 交换左右子树
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
// 递归处理左右子树
mirrorTree(root.left);
mirrorTree(root.right);
return root;
}- 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点只被访问一次
- 空间复杂度:O(h),h为树的高度,递归栈空间消耗
迭代
利用队列实现广度优先搜索(BFS):
- 将根节点加入队列
- 取出队首节点并交换其左右子树
- 将非空的左右子节点加入队列
- 重复直到队列为空
java
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 交换左右子树
swap(node);
// 将子节点加入队列
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n),最坏情况下需要存储所有节点