一、概述
上一章了解了DispatcherServlet初始化的流程,着重讲了一个重点的初始化业务,本章节将重点讲解项目中的 controller 怎么跟url经行关联的。这一关键的业务流程都在 initHandlerMappings(context) 方法中完成的。
二、初始化处理器映射器-initHandlerMappings
initHandlerMappings初始化是SpringMVC中请求映射的核心链路,包括HandlerMapping的注入和HandlerMethod的注册。从Spring启动时加载HandlerMapping到解析请求路径找到相应的Controller方法,深入探讨了SpringMVC处理HTTP请求的内部机制。
java
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}从方法中我们可以看到,在这个过程中会先去Spring容器中查找是否存在自定义的HandlerMapping 的bean,存在则加入handlerMappings。如果没有则加载默认配置的HandlerMapping,默认的HandlerMapping实现类使用资源加载的方式。对应的实现类在配置文件 DispatcherServlet.properties 中,通过资源加载器,获取到默认HandlerMapping的类信息。
markup
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager可以看到系统默认加载的HandlerMapping 有 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RouterFunctionMapping。在日常的业务开发中,业务处理都是在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中的,所以重点看RequestMappingHandlerMapping的实例化过程即可。
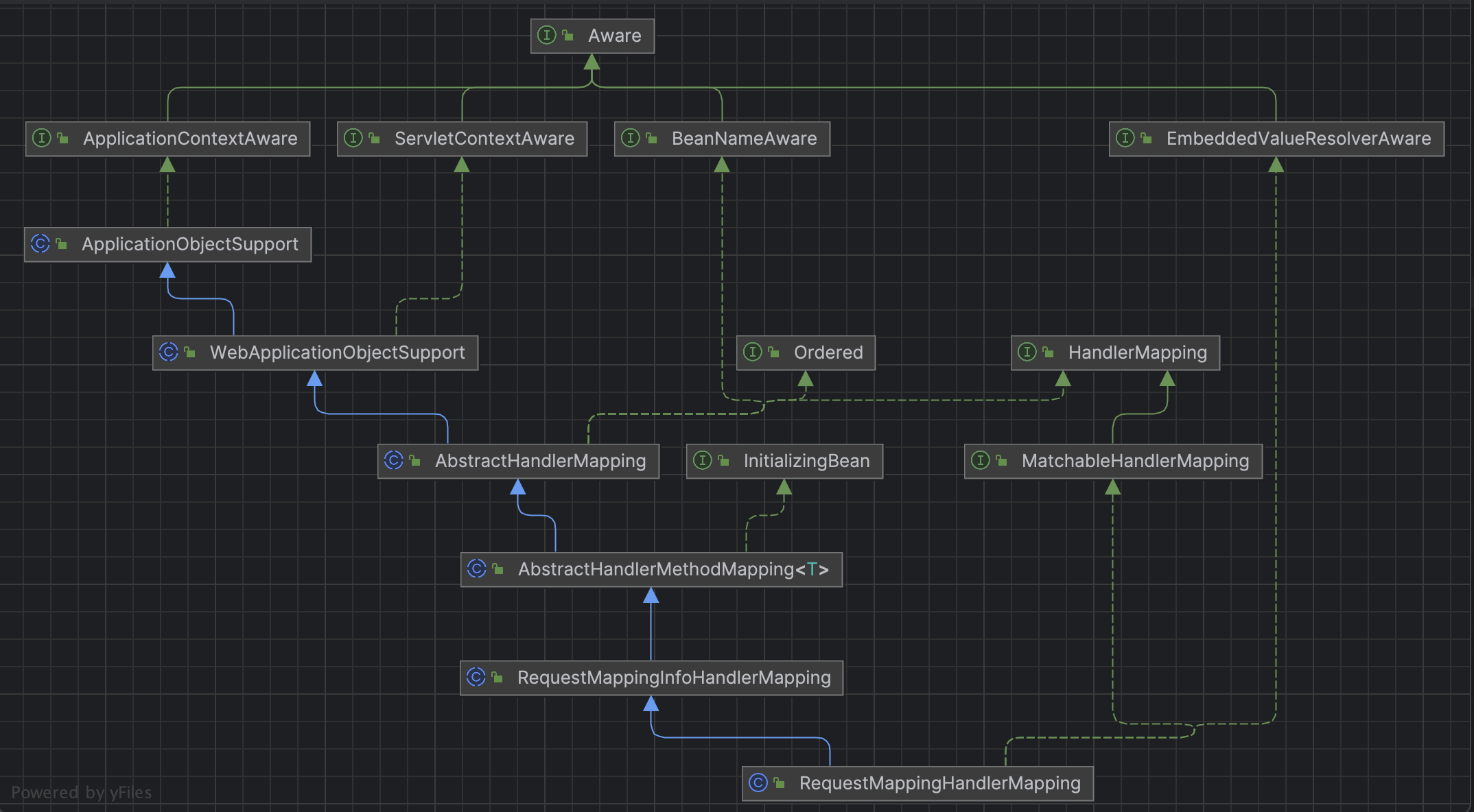
RequestMappingHandlerMapping继承 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping、AbstractHandlerMapping 而它们还要实现InitializingBean接口,所以RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象被容器创建之后,就会调用afterPropertiesSet()方法进行初始化。
java
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch());
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
if (getPatternParser() != null && this.defaultPatternParser &&
(this.useSuffixPatternMatch || this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch)) {
setPatternParser(null);
}
if (getPatternParser() != null) {
this.config.setPatternParser(getPatternParser());
Assert.isTrue(!this.useSuffixPatternMatch && !this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch,
"Suffix pattern matching not supported with PathPatternParser.");
}
else {
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
}
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}在容器创建完对象以后,调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping的 afterPropertiesSet方法,这里做了RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration的初始化,然后调用AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet方法。
java
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
/**
* Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods.
* @see #getCandidateBeanNames()
* @see #processCandidateBean
* @see #handlerMethodsInitialized
*/
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}这里开始遍历IOC容器中的bean,并经行下一步的处理。
java
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class);
}判断bean是否存在 Controller 注解,如果存在则对该bean进行处理。在此方法中开始遍历bean中的方法。
java
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String beanName ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}先判断方法上是否存在 RequestMapping注解如果存在则开始 创建RequestMappingInfo实例,将注解中的 url path 转成视图可识别的格式保存(并将controller 上的 path 值拼接上去),同时保存各类参数。
java
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
if (info.isEmptyMapping()) {
info = info.mutate().paths("", "/").options(this.config).build();
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class<?> clazz ?
getCustomTypeCondition(clazz) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}每个方法都会生成对应的 RequestMappingInfo,之后开始注册到MappingRegistry 对象中。
java
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
for (String path : directPaths) {
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
corsConfig.validateAllowPrivateNetwork();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping,
new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}在register方法中,先根据 对象及方法 创建HandlerMethod对象,再判断mapping是否已经存在,如果存在则抛出对应的错误。后续开始对mapping进行处理。
首先将路径映射到快速索引中,this.pathLookup,主要的作用是 通过path 快速找到对应的 RequestMappingInfo从而找到 对应的方法,
如:
"/api/getUser/info" -> getUserInfo() 方法。
同时支持 支持路径模式匹配
例如:
"/api/getUserByid/7234" 它可以匹配到
"/api/getUserByid/{id }" 或者 "/api/getUserByid/*" 等url。
pathLookup由于使用 MultiValueMap 结构,同一个路径模式可关联多个 RequestMappingInfo 对象
这对路径的动态参数匹配至关重要。
接下来是将注定nameLookup,nameLookup是一个映射,键(key)是处理器方法的名字(通常是方法名或用户指定的名称),值(value)是该名称对应的HandlerMethod列表。在RequestMapping 中设置类name 属性,则将name 作为key,如果没有设置则使用自定义策略生成对应的key,框架在获取不到指定策略时,将使用默认的策略生成 name 作为key,默认策略是 使用类名+"#" +方法名的 方式。
java
protected RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping() {
setHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(new RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy());
}
@Override
public String getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
if (mapping.getName() != null) {
return mapping.getName();
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String simpleTypeName = handlerMethod.getBeanType().getSimpleName();
for (int i = 0; i < simpleTypeName.length(); i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(simpleTypeName.charAt(i))) {
sb.append(simpleTypeName.charAt(i));
}
}
sb.append(SEPARATOR).append(handlerMethod.getMethod().getName());
return sb.toString();
}nameLookup 其主要作用是通过处理器方法名称快速查找对应的 HandlerMethod 对象。
接下来就是将跨域配置注册到this.corsLookup属性类中。
java
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
corsConfig.validateAllowPrivateNetwork();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}最后将 映射关系 添加在registry 中,将 RequestMappingInfo作为值,MappingRegistration对象作为value,用于存储所有控制器方法(HandlerMethod)与请求映射条件(如 URL 模式、HTTP 方法等)的绑定关系。为后续的执行流程提供映射表。
三、结尾
至此 url 与contrller类的映射主流程就基本完成,下一章节将介绍 adapter的初始化,及Springmvc的执行流程。在此过程中如存在纰漏或者错误,麻烦请支持,相互探讨相互学习。