1. localStorage 和 cookie 有什么区别?
| 维度 | localStorage | cookie |
|---|---|---|
| 容量 | ~5MB | ~4KB |
| 生命周期 | 永久(除非手动清除) | 可设置过期时间 |
| 是否随请求发送 | ❌ 不会 | ✅ 每次HTTP请求都带 |
| 作用域 | 同源 | 同源 + 可设 domain/path |
| API | setItem/getItem | document.cookie 字符串操作 |
「Q1: cookie 能被 XSS 窃取吗?」
A1: ✅ 能!除非加 HttpOnly 标志,这样 JS 无法读取,但 HTTP 请求仍携带。
👉安全底线!⚠️
「Q2: localStorage 有安全风险吗?」
A2: 有!XSS 攻击可直接读取 localStorage,所以敏感信息(如 Token)建议用 HttpOnly Cookie 存储。
「Q3: 如何实现跨标签页通信?」
A3: 用 localStorage 的 storage 事件:
js
window.addEventListener('storage', (e) => {
console.log(e.key, e.newValue); // 其他标签页修改时触发
});⚠️注意:当前页面修改不会触发!
2. CSS选择器有哪些?
分类如下(图示):
div"]:::item
B2["类选择器 .box"]:::item
B3["ID 选择器 #header"]:::item
B4["通配符 *"]:::item
%% 组合
C[" 组合"]:::category
C1["后代 .box p"]:::item
C2["子代 .box > p"]:::item
C3["相邻兄弟 .box + p"]:::item
C4["通用兄弟 .box ~ p"]:::item
%% 属性
D[" 属性"]:::category
D1["精确匹配 [type='text']"]:::item
D2["前缀匹配 [href^='https']"]:::item
%% 伪类 / 伪元素
E[" 伪类 / 伪元素"]:::category
E1["伪类 :hover :nth-child()"]:::item
E2["伪元素 ::before ::after"]:::item
%% ========== 3. 层级关系 ==========
CSS --> B
B --> B1
B --> B2
B --> B3
B --> B4
CSS --> C
C --> C1
C --> C2
C --> C3
C --> C4
CSS --> D
D --> D1
D --> D2
CSS --> E
E --> E1
E --> E2
%% ========== 4. 动效提示 ==========
%% 部署时可通过 CSS 实现:
%% .node:hover { transform: scale(1.03); transition: 0.2s; }⚠️权重计算易错?💥
选择器权重(优先级):
!important> 行内 > ID(100) > Class(10) > Tag(1)
「Q4: :nth-child(2n) 是什么意思?」
A4: 选偶数位置的子元素,等价于 :nth-child(even)。
「Q5: ::before 和 :before 区别?」
A5: ::before 是伪元素(生成新DOM节点),:before 是伪类(状态类)。双冒号是CSS3规范,防混淆。
3. 盒子模型,以及标准情况和IE下的区别
标准盒模型 vs IE盒模型:
ascii
标准模型(W3C)
+-----------------------+
| margin |
| +---------------+ |
| | border | |
| | +-------+ | |
| | | padding | |
| | | +---+ | | width = 内容宽度
| | | |内容| | |
| | | +---+ | |
| | +-------+ | |
| +---------------+ |
+-----------------------+
IE模型(怪异模式)
+-----------------------+
| margin |
| +---------------+ |
| | border | |
| | +-------+ | |
| | | padding | |
| | | +---+ | | width = 内容+padding+border
| | | |内容| | |
| | | +---+ | |
| | +-------+ | |
| +---------------+ |
+-----------------------+⚠️这差异让布局错位?🤯
解决:使用 box-sizing 统一:
css
* {
box-sizing: border-box; /* 推荐:开发更直观 */
}「Q6: 如何强制页面进入怪异模式?」
A6: 不写或写错 DOCTYPE,如 <html> 前有注释或空格。
「Q7: border-box 和 content-box 区别?」
A7:
content-box:width 只算内容(默认)border-box:width 包含 padding + border
4. 如何实现高度自适应?
常见场景与方案:
| 场景 | 方案 |
|---|---|
| 两栏布局(侧边栏+主内容) | flex 或 position: absolute |
| 全屏布局 | height: 100vh 或 flex: 1 |
| 圣杯/双飞翼 | flex + margin 负值(已淘汰) |
| 动态内容撑高 | min-height + overflow |
代码示例(flex 实现全屏自适应):
css
.app {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 100vh;
}
.header {
height: 60px;
}
.main {
flex: 1; /* 自动占满剩余空间 */
overflow-y: auto;
}
.footer {
height: 40px;
}「Q8: vh 和 % 有什么区别?」
A8:
vh:视口高度百分比%:相对父元素高度
👉父元素没设高时,% 失效!
「Q9: 如何监听高度变化?」
A9: 用 ResizeObserver:
js
new ResizeObserver(entries => {
console.log(entries[0].contentRect.height);
}).observe(document.body);5. prototype 和 proto 区别?
这是原型链的核心!图示:
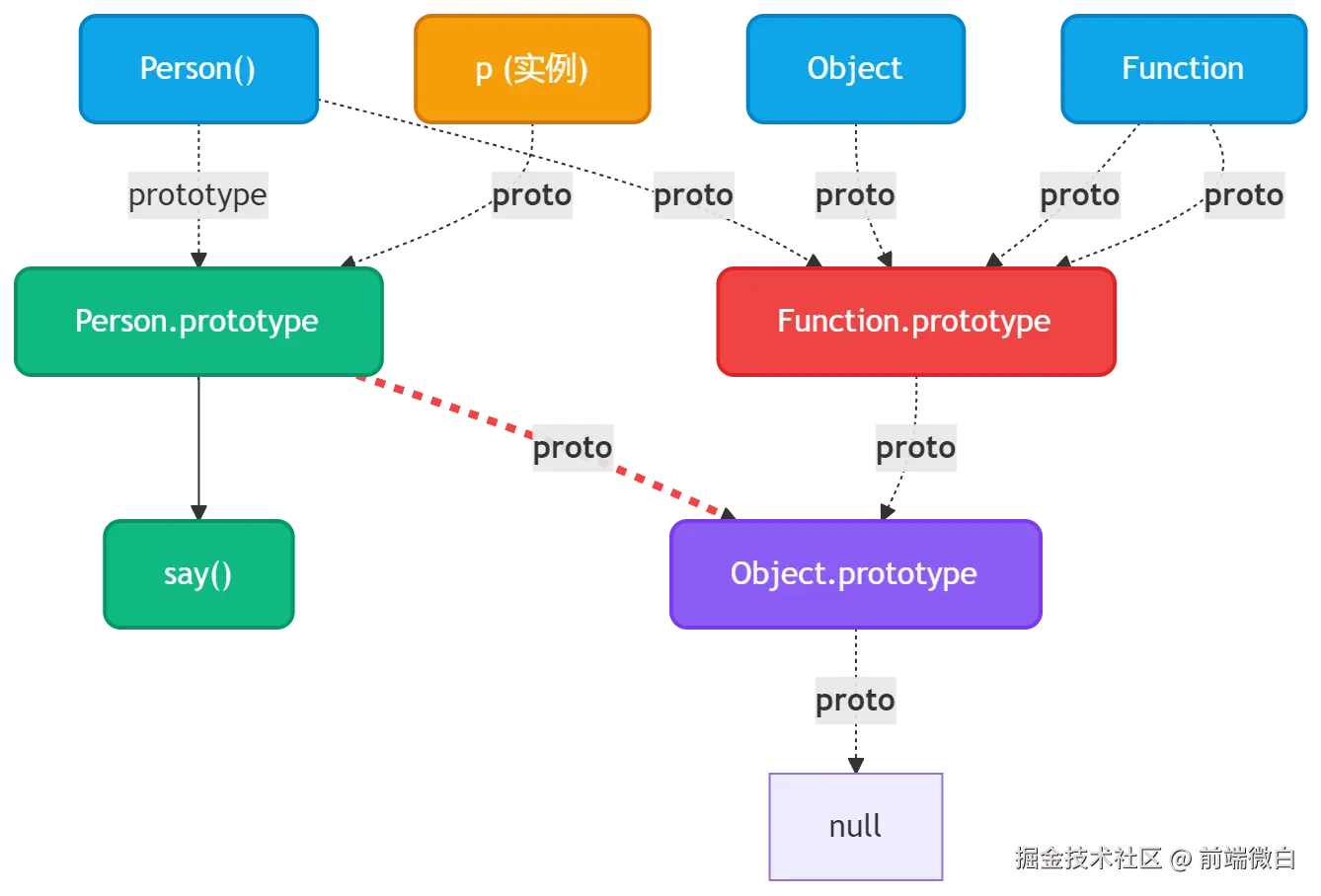
关系总结:
prototype:函数才有,是实例的原型对象__proto__:所有对象都有,指向其构造函数的prototype
「Q10: 所有对象的尽头是谁?」
A10: Object.prototype.__proto__ === null,原型链终点。
「Q11: 为什么函数有 prototype 而普通对象没有?」
A11: 因为 prototype 是"用来生成实例的模板",只有构造函数需要。
6. constructor 是什么?
constructor 是 prototype 上的一个属性,指向构造函数本身。
js
function Person() {}
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person) // true
const p = new Person()
console.log(p.constructor === Person) // true(通过__proto__链找到)⚠️易错点:重写 prototype 会丢失 constructor:
js
Person.prototype = {
say() {}
}
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person) // ❌ false修复:
js
Person.prototype.constructor = Person「Q12: constructor 能用来判断类型吗?」
A12: 不完全可靠!可被改写。推荐用 instanceof 或 Object.prototype.toString.call()。
7. new 是怎么实现的?
手写一个 myNew 函数,理解本质:
js
function myNew(Constructor, ...args) {
// 1. 创建空对象,继承构造函数的原型
const obj = Object.create(Constructor.prototype);
// 2. 绑定 this 并执行构造函数
const result = Constructor.apply(obj, args);
// 3. 返回对象(如果是引用类型则返回 result)
return result instanceof Object ? result : obj;
}
// 测试
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const p = myNew(Person, 'Tom');
console.log(p.name); // Tom// 注:Object.create 实现了 proto 链接
「Q13: 如果构造函数返回一个对象会怎样?」
A13: new 会忽略 this,返回该对象。若返回原始值,则仍返回 this。
「Q14: new 的4个步骤是什么?」
A14:
- 创建新对象
- 链接到原型
- 绑定 this
- 返回实例(或构造函数返回的对象)
8. promise 的精髓,以及优缺点
Promise 精髓:解决回调地狱,统一异步错误处理
核心状态机:
⚠️状态不可逆?👉继续看!
优点:
- 链式调用
.then().catch() - 错误冒泡,统一捕获
- 可组合:
Promise.all/race
缺点:
- 无法取消(ES2018 Cancelable Promise 提案)
- 中途不能中断链
- 错误需
.catch,否则静默失败
「Q15: Promise 构造函数里的错误怎么处理?」
A15: 用 try/catch 包裹 resolve/reject,或直接 reject(error)。
「Q16: 如何实现 Promise.finally?」
A16: 无论成功失败都执行:
js
Promise.prototype.finally = function (cb) {
return this.then(
value => Promise.resolve(cb()).then(() => value),
error => Promise.resolve(cb()).then(() => { throw error })
);
}