前端一次性将十万条数据都渲染到页面上,基本上100%会导致页面卡顿甚至无响应。
大量的DOM操作会极大的消耗浏览器的资源,所以在面试的时候千万不要说直接for循环渲染。
给大家几种优化方案:
虚拟滚动(Virtual Scrolling)
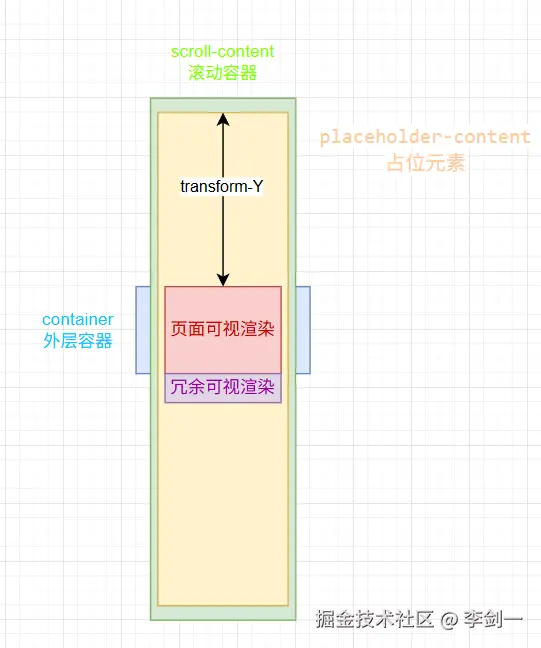
实现方案:通过只渲染视口内可见的数据项,而不是一次性渲染所有数据项,可以极大地减少DOM元素的数量,从而提升性能。
当用户滚动时,动态更新显示的数据项。实现这一功能的库包括react-window、react-virtualized、vue-virtual-scroll-list等。
实现思路:
- 只渲染可视区域内的数据项,通过监听滚动事件,动态计算当前应显示的数据范围。
- 利用占位的 padding 或 transform 来模拟滚动位置,保持滚动条高度正确。
代码实现
html
<div id="container" class="container"></div>
<style>
.container {
height: 100vh;
overflow-y: auto;
position: relative;
}
.scroll-content {
position: relative;
}
.item {
height: 50px; /* 每一项高度固定 */
line-height: 50px;
padding: 0 10px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #eee;
}
</style>
js
// 模拟 10 万条数据
const totalItems = 100000;
const itemHeight = 50; // 每条高度 50px
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight; // 可视区域高度
const visibleCount = Math.ceil(viewportHeight / itemHeight); // 视区内显示的条数
const buffer = 5; // 额外缓冲项,防止滚动过快白屏
const renderCount = visibleCount + buffer * 2; // 实际渲染数量
// DOM 元素
const container = document.getElementById('container');
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();
const content = document.createElement('div');
content.className = 'scroll-content';
container.appendChild(content);
// 创建占位元素(用于撑起滚动高度)
const placeholder = document.createElement('div');
placeholder.style.height = `${totalItems * itemHeight}px`;
placeholder.className = 'placeholder-content';
content.appendChild(placeholder);
// 渲染区域(实际显示的 item 容器)
const renderArea = document.createElement('div');
renderArea.style.position = 'absolute';
renderArea.style.top = '0';
renderArea.style.left = '0';
renderArea.style.width = '100%';
content.appendChild(renderArea);
// 初始渲染
function renderVisibleItems(startIndex) {
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + renderCount, totalItems);
renderArea.innerHTML = ''; // 清空
for (let i = startIndex - buffer; i < endIndex + buffer; i++) {
if (i >= 0 && i < totalItems) {
const item = document.createElement('div');
item.className = 'item';
item.textContent = `Item ${i}`;
renderArea.appendChild(item);
}
}
// 设置偏移,使内容出现在正确位置
renderArea.style.transform = `translateY(${startIndex * itemHeight}px)`;
}
// 滚动处理函数
function handleScroll() {
const scrollTop = container.scrollTop;
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
renderVisibleItems(startIndex);
}
// 初始化
renderVisibleItems(0);
container.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll, { passive: true });示意图
分页加载和懒加载
实现方案:分页加载和懒加载其实差不太多,通过将数据切片,分开渲染,减少一次性渲染数量,达到降低卡顿的效果。
当用户滚动,或点击分页器时,触发下一页或者是对应页的数据渲染。
实现思路:
- 每次只加载一页数据(如每页 50 条)。
- 用户点击"下一页"或滚动到底部时,加载下一页数据。
代码实现
js
// 无限滚动监听
let isLoading = false;
function handleScroll() {
if (isLoading || currentPage >= totalPages) return;
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight, clientHeight } = container;
// 距离底部 100px 时触发加载
if (scrollHeight - scrollTop - clientHeight < 100) {
loadMore();
}
}
async function loadMore() {
const nextPage = currentPage + 1;
if (nextPage > totalPages) return;
isLoading = true;
const result = await fetchPage(nextPage);
currentPage = nextPage;
// 追加数据
result.data.forEach((text) => {
const li = document.createElement('li');
li.className = 'item';
li.textContent = text;
listEl.appendChild(li);
});
isLoading = false;
}
// 监听滚动
const container = document.documentElement || document.body;
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
if (!isLoading && currentPage < totalPages) {
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight, clientHeight } = document.documentElement;
if (scrollHeight - scrollTop - clientHeight < 200) {
loadMore();
}
}
}, { passive: true });Ps: 这种存在一个弊端,假如后端数据不是一次性全部返回给前端,滚动过快可能会存在等待。
注意:懒加载的实现方案如果是在Vue/React中有两种实现方案:
- 通过v-if控制是否渲染
- 通过控数据分割控制渲染数据
Web Workers数据处理
实现方案:本质上也是将数据切割处理,但是处理方案不同。主要是通过将耗时的数据处理任务从主线程移到后台线程执行,从而避免阻塞UI线程,保证页面的响应性。
实现思路:
- 数据预处理:在Web Worker中进行数据过滤、排序、格式化等操作。
- 分批传输:将处理后的数据分批次发送回主线程,以减少一次性向DOM添加大量元素造成的性能瓶颈。
- 也可以再加上虚拟滚动进一步节省资源。
代码实现
js
// 主Js文件
const worker = new Worker('dataProcessor.js');
// 主线程代码
worker.postMessage({ action: 'processData', payload: largeDataSet }); // largeDataSet为大数据集
worker.onmessage = function(e) {
const { action, data } = e.data;
if (action === 'dataProcessed') {
// 使用处理后的数据更新DOM
renderData(data);
}
};
function renderData(data) {
// 渲染数据到页面的逻辑
const container = document.getElementById('dataContainer');
container.innerHTML = ''; // 清空容器
data.forEach(item => {
const div = document.createElement('div');
div.textContent = item;
container.appendChild(div);
});
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// dataProcessor.js
onmessage = function(e) {
const { action, payload } = e.data;
if (action === 'processData') {
// 假设payload是我们需要处理的数据集
let processedData = processData(payload); // 处理数据的函数
postMessage({ action: 'dataProcessed', data: processedData });
}
};
function processData(data) {
// 模拟复杂的数据处理,例如排序、过滤等
return data.sort((a, b) => a - b).slice(0, 50); // 返回前50条作为示例
}总结
海量数据渲染优先选择后端分页处理是最好的,毕竟海量数据通过接口传输比较慢,用户等待时间长。
并且数据尽量在后端完成全部的处理工作,最后交给前端只进行渲染,不再操作,尽可能节省浏览器资源。
如果非得选择一次性渲染全部数据,则虚拟滚动是比较好的方案。