前言
智能体必须能够与外界交互,我们此处介绍tool_calls(function_calling)的方式。
大模型本身是不能调用任何工具的,但是当我们给大模型增加一些工具的描述时,大模型会根据用户的问题来确认是不是需要外部工具,如果需要调用外部工具的话,就会把需要调用的工具名字和具体参数作为一个AIMessage的tool_calls参数返回给应用程序,应用程序收到后,需要自行执行相应的任务,并把任务结果告诉大模型,这个过程称之为tool_call。
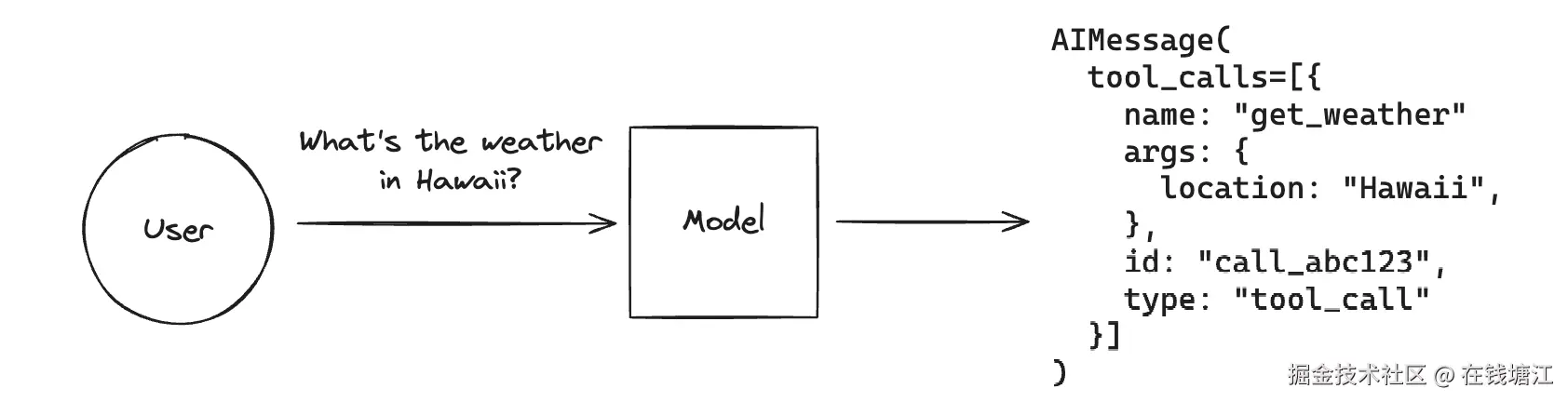
具体流程如下 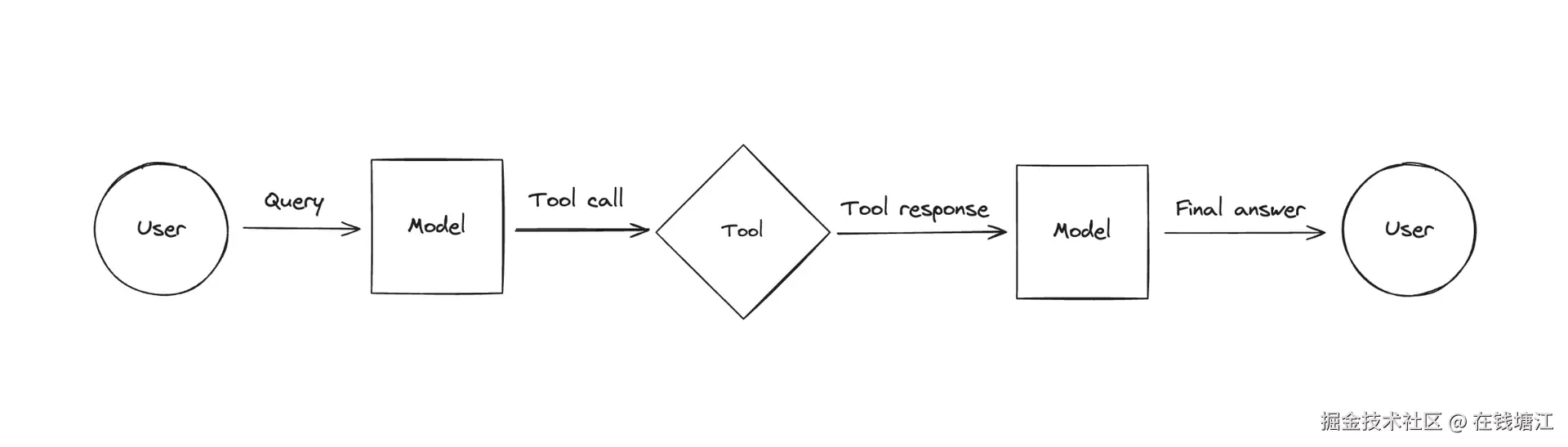
环境
见前文
查询天气的示例
我们给大模型配置了查询天气的工具,当我们询问某地区的天气时,看下大模型是怎么处理的
步骤
- 加载环境变量
- 定义工具和工具节点
- 创建大模型并绑定工具
- 定义工作流
- 大模型调用节点,需要处理返回的AI消息中的tool_calls
- tool_calls交给工具节点处理,然把结果返回
- 用户输入并询问大模型
- 输出结果
python
# 调用工具
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END, MessageGraph, MessagesState
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
#1. 加载环境变量
load_dotenv()
base_url = os.getenv("BASE_URL")
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
model_name = "qwen-plus"
#2. 定义工具和工具节点
# Define a tool to get the weather for a city
@tool
def get_weather(location: str):
"""Fetch the current weather for a specific location."""
weather_data = {
"San Francisco": "Its 60 degrees and foggy.",
"New York": "Its 90 degrees and sunny.",
"London": "Its 70 degrees and cloudy.",
"上海": "晴天 20摄氏度",
"北京": "大雨 10摄氏度",
}
return weather_data.get(location, "无法获取当地天气状况")
# 错误传播出来
tool_node = ToolNode([get_weather], handle_tool_errors=False)
#3. 创建大模型并绑定工具
model = ChatOpenAI(
base_url=base_url, api_key=openai_api_key, model=model_name
).bind_tools([get_weather])
# 4. 定义工作流
def call_llm(state: MessagesState):
messages = state["messages"]
response = model.invoke(messages[-1].content)
# 是否 toolcall
if response.tool_calls:
tool_result = tool_node.invoke({"messages": [response]})
tool_message = tool_result["messages"][-1].content
response.content += f"\nTool Result:{tool_message}"
return {"messages": [response]}
workflow = StateGraph(MessagesState)
workflow.add_node("call_llm", call_llm)
workflow.add_edge(START, "call_llm")
workflow.add_edge("call_llm", END)
app = workflow.compile()
# 持续对话
def interact_with_agent():
while True:
# 5. 用户输入并询问大模型
user_input = input("You: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["exit", "quit", "q"]:
print("结束对话")
break
input_message = {"messages": [("human", user_input)]}
for chunk in app.stream(input_message, stream_mode="values"):
# 6. 输出结果
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
interact_with_agent()输出结果
bash
You: London 天气如何
================================ Human Message =================================
London 天气如何
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Result:Its 70 degrees and cloudy.
Tool Calls:
get_weather (call_1b89d3f1afe94be3bfc020)
Call ID: call_1b89d3f1afe94be3bfc020
Args:
location: London
You: 上海天气怎么样
================================ Human Message =================================
上海天气怎么样
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Result:晴天 20摄氏度
Tool Calls:
get_weather (call_f05384e466f84037b4cb81)
Call ID: call_f05384e466f84037b4cb81
Args:
location: 上海
You: 北京天气呢
================================ Human Message =================================
北京天气呢
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Result:大雨 10摄氏度
Tool Calls:
get_weather (call_00cae603cea84dacb4cfaf)
Call ID: call_00cae603cea84dacb4cfaf
Args:
location: 北京
You: exit
结束对话ToolCall 的原理模拟示例
上面的示例是大模型直接返回的tool_calls参数,我们也可以直接模拟这一行为,用于演示原理或者测试我们自己 的工具。
下面我们将创建一个获取用户信息的工具,然后创建一个带tool_calls的AIMessage,来调用工具节点
步骤
- 加载环境
- 定义工具和工具节点
- 定义AiMessage
- 调用工具节点
- 输出结果
python
# 调用工具
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END, MessageGraph, MessagesState
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
# 1. 加载环境
load_dotenv()
base_url = os.getenv("BASE_URL")
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
model_name = "qwen-plus"
# 2. 定义工具和工具节点
# Define a tool to get the weather for a city
@tool
def get_user_profile(user_id: str):
"""通过user_id获取用户信息"""
weather_data = {
"101": {"name": "爱丽丝", "年龄": 30, "location": "纽约"},
"102": {"name": "Bob", "age": 25, "location": "旧金山"},
}
return weather_data.get(user_id, "没有此用户")
# 工具节点
# handle_tool_errors 错误传播出来
tool_node = ToolNode([get_user_profile], handle_tool_errors=False)
# 3. 定义AiMessage
message_with_tool_call = AIMessage(
content="",
tool_calls=[
{
"name": "get_user_profile",
"args": {"user_id": "101"},
"id": "tool_call_id",
"type": "tool_call",
}
],
)
#
state = {"messages": [message_with_tool_call]}
# 4. 调用工具节点
# 直接把消息交给工具节点调用
result = tool_node.invoke(state)
# 5. 输出结果
print(result)输出结果
rust
{'messages': [ToolMessage(content='{"name": "爱丽丝", "年龄": 30, "location": "纽约"}', name='get_user_profile', tool_call_id='tool_call_id')]}