一个项目足够复杂的话,所有代码如果都在一个页面中,那么,就会出现一个文件上万行代码的可能。vue 通过组件化的方式,将页面按照模块或功能进行拆分,方便团队合作和后期维护。组件化让项目开发如同搭积木一样简单,借用官方图示如下:
那么,组件化是如何实现的呢?
这还得从入口说起 ...
javascript
// main.js文件
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
const app = createApp(App);
app.mount('#app');例子中可以看出,通过import { createApp } from 'vue'的方式从vue中引入了方法createApp,并将App作为参数传入其中,最后,通过app.mount('#app')的方式将app挂载到#app上去。
举个例子:
js
// 子组件:Child.vue
<template>
<h5>这个是child组件</h5>
</template>
js
// 父组件:App.vue
<template>
<h3>这个是app组件</h3>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<script setup>
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
</script>一、const app = createApp(App)
js
const createApp = (...args) => {
// 创建app方法
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args);
// 从app中获取mount方法
const { mount } = app;
// 重写app.mount方法
app.mount = (containerOrSelector) => {
// ...
};
return app;
};createApp的主要逻辑可以分为获取app和重写app.mount
1、创建app
创建app需要通过const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)的方式,这里可以将流程分为两步,ensureRenderer和createApp。
(1)ensureRenderer
js
let renderer;
// 如果存在直接返回,如果不存在,才进行后续的操作,是一种单例模式的具体应用
function ensureRenderer() {
return renderer || (renderer = createRenderer(rendererOptions));
}
function createRenderer(options) {
return baseCreateRenderer(options);
}
function baseCreateRenderer(options, createHydrationFns) {
// ...
// 这里省略了render、patch、processElement、mountElement、mountChildren、unmount、move、unmountChildren、patchChildren等渲染需要的方法
return {
render,
hydrate,
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate),
};
}
function createAppAPI(render, hydrate) {
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
// ...
return app;
};
}baseCreateRenderer(options)的方式返回了一个包含createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate)的对象,其最终返回的是函数function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null){...}的执行结果。
所以const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)最终执行的就是createAppAPI内部返回的createApp函数。
需要注意的是,render作为参数传给了createAppAPI函数,是以闭包的形式被返回的app所持有。
继续看createApp的实现。
(2)createApp
js
function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
if (!isFunction(rootComponent)) {
rootComponent = Object.assign({}, rootComponent);
}
// 创建app执行环境
const context = createAppContext();
// 创建app
const app = (context.app = {
_uid: uid++,
_component: rootComponent,
_props: rootProps,
_container: null,
_context: context,
_instance: null,
version,
mount() {
// 与平台无关的mount方法
},
// 除了mount,还有use、mixin、component、directive等属性和方法
});
return app;
}
// 附:createAppContext的实现
function createAppContext() {
return {
app: null,
config: {
isNativeTag: NO,
performance: false,
globalProperties: {},
optionMergeStrategies: {},
errorHandler: undefined,
warnHandler: undefined,
compilerOptions: {},
},
mixins: [],
components: {},
directives: {},
provides: Object.create(null),
optionsCache: new WeakMap(),
propsCache: new WeakMap(),
emitsCache: new WeakMap(),
};
}如果rootComponent不是函数,通过rootComponent = Object.assign({}, rootComponent)的方式浅拷贝rootComponent,再通过createAppContext的方式返回一个app执行的环境。最终返回一个包含_uid、_component、_props、_container、_context、_instance、version和mount等属性的app对象,这里的mount与平台无关。
2、缓存mount
先通过const { mount } = app的方式将mount方法从app中拿出来缓存备用。
3、重写app.mount
然后通过app.mount = containerOrSelector) => {...}的方式对app.mount方法进行重写。
这样做的目的是,将与平台无关的mount进行缓存,然后在不同的平台中重写app.mout方法进行特定场景的处理。最终还是会执行到与平台无关的mount函数。
js
// 重写的app.mount
app.mount = (containerOrSelector) => {
// 处理字符串
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector);
if (!container) return;
const component = app._component;
// 这里主要处理无template和没有render选项的组件,将`container.innerHTML`作为`component`的`template`,作为后续编译的依据。
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
component.template = container.innerHTML;
}
if (container.nodeType === 1) {
container.textContent = "";
}
// 执行与平台无关的mount方法
const proxy = mount(container, false, resolveRootNamespace(container));
if (container instanceof Element) {
container.removeAttribute("v-cloak");
container.setAttribute("data-v-app", "");
}
return proxy;
};其中const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement);执行的就是前面缓存的mount。
直到这里,const app = createApp(App)就执行完成了。但是,挂载过程还未开始,接下来就需要开始mount的旅程了。
二、app.mount('#app')
当执行到入口文件的app.mount('#app')时,就会执行重写的方法app.mount。
这里先通过const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)的方式去将非 DOM 容器的字符串转换成 DOM 节点,内部使用了 DOM 操作的原生方法document.querySelector(container)。
再通过const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)的方式去调用与平台无关的mount方法,下面详细介绍mount相关的逻辑:
js
//执行通过const { mount } = app获取到的mount
function mount(rootContainer, isHydrate, namespace) {
const vnode = app._ceVNode || createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps);
if (isHydrate && hydrate) {
hydrate(vnode, rootContainer);
} else {
// 这里就是前面流程中闭包持有的render函数
render(vnode, rootContainer, namespace);
}
}1、生成vnode
这里通过const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps)的方式生成vnode,当前例子中会执行到以下逻辑:
js
// 将vnode的类型设置为
const shapeFlag = isString(type)
? 1
: isSuspense(type)
? 128
: isTeleport(type)
? 64
: isObject(type)
? 4
: isFunction(type)
? 2
: 0;
return createBaseVNode(
type,
props,
children,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
shapeFlag,
isBlockNode,
true
);
// 其中通过判断组件被编译后的 type,来确定`shapeFlag`,当前例子中其值为`4`,再继续看`createBaseVNode`:
function createBaseVNode(
type,
props = null,
children = null,
patchFlag = 0,
dynamicProps = null,
shapeFlag = type === Fragment ? 0 : 1,
isBlockNode = false,
needFullChildrenNormalization = false
) {
const vnode = {
__v_isVNode: true,
__v_skip: true,
type,
props,
key: props && normalizeKey(props),
ref: props && normalizeRef(props),
scopeId: currentScopeId,
slotScopeIds: null,
children,
component: null,
suspense: null,
ssContent: null,
ssFallback: null,
dirs: null,
transition: null,
el: null,
anchor: null,
target: null,
targetStart: null,
targetAnchor: null,
staticCount: 0,
shapeFlag,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
dynamicChildren: null,
appContext: null,
ctx: currentRenderingInstance,
};
// ...
return vnode;
}可以看出,当前的vnode就是一个由许多属性组成的对象,用来描述当前组件的主要信息,如同 DOM 树用来描述页面html一样。
紧接着会通过vnode.appContext = context的方式为vnode.context进行赋值。从文中刚开始可以看出,context是在createApp方法中通过context = createAppContext()的方式定义的,该方法中也为context.app进行了赋值。
生成vnode以后就会进行vnode的渲染逻辑,继续往下看。
2、vnode渲染
通过render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG):
js
const render = (vnode, container, namespace) => {
if (vnode == null) {
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true);
}
} else {
patch(
container._vnode || null,
vnode,
container,
null,
null,
null,
namespace
);
}
container._vnode = vnode;
};当前例子中vnode存在,所以会执行到patch的逻辑,其中有主要的逻辑如下:
js
if (shapeFlag & 6) {
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
);
}当前例子中首次渲染执行时shapeFlag为4,满足shapeFlag & 6为真值,所以会执行到processComponent:
js
const processComponent = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
) => {
n2.slotScopeIds = slotScopeIds;
if (n1 == null) {
if (n2.shapeFlag & 512) {
parentComponent.ctx.activate(n2, container, anchor, namespace, optimized);
} else {
mountComponent(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
optimized
);
}
} else {
updateComponent(n1, n2, optimized);
}
};当前例子中旧的节点vnode为null,并且n2.shapeFlag & 512为0,所以会执行到mountComponent的逻辑:
js
const mountComponent = (
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
optimized
) => {
// 创建组件实例
const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense
));
// 执行组件初始化逻辑,比如组件中的setup中的逻辑
setupComponent(instance, false, optimized);
// 执行渲染副作用函数
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
optimized
);
};以上有两个重要的逻辑,创建instance、setupComponent和调用setupRenderEffect。
(1)instance
在当前逻辑中,通过const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(initialVNode, parentComponent, parentSuspense))的方式创建子组件实例:
js
function createComponentInstance(vnode, parent, suspense) {
const type = vnode.type;
const appContext =
(parent ? parent.appContext : vnode.appContext) || emptyAppContext;
const instance = {
uid: uid++,
vnode,
type,
parent,
appContext,
root: null,
next: null,
subTree: null,
effect: null,
update: null,
job: null,
scope: new EffectScope(
true
/* detached */
),
render: null,
proxy: null,
// 还有很多其他属性
};
if (!!(process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production")) {
instance.ctx = createDevRenderContext(instance);
} else {
instance.ctx = { _: instance };
}
instance.root = parent ? parent.root : instance;
instance.emit = emit.bind(null, instance);
return instance;
}当前逻辑中通过const appContext = (parent ? parent.appContext : vnode.appContext) || emptyAppContext的方式去获取appContext,有父组件拿父组件的,无父组件拿当前vnode的,如果都找不到则使用默认的emptyAppContext。
在线上环境通过instance.ctx = { _: instance }的方式为instance定义ctx,其实就是它本身。
再通过instance.root = parent ? parent.root : instance的方式为instance定义根实例root。
(2)setupComponent
js
function setupComponent(instance, isSSR = false, optimized = false) {
isSSR && setInSSRSetupState(isSSR);
const { props, children } = instance.vnode;
const isStateful = isStatefulComponent(instance);
initProps(instance, props, isStateful, isSSR);
initSlots(instance, children, optimized || isSSR);
const setupResult = isStateful
? setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR)
: void 0;
isSSR && setInSSRSetupState(false);
return setupResult;
}这里会处理props和slots,当前例子中不涉及,暂时不介绍。
(3)setupRenderEffect
js
const setupRenderEffect = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
// 最后调用update()的时候,会执行到这里
};
// 实例化ReactiveEffect实例,进行调度
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(
componentUpdateFn,
() => queueJob(update),
instance.scope
));
const update = (instance.update = () => effect.run());
// 省略其他逻辑
update();
};通过new ReactiveEffect的方式创建ReactiveEffect实例,并赋值给instance.effect。通过const update = (instance.update = () => effect.run())的方式为instance.update赋值调用effect.run()的函数。最后,执行到update(),即componentUpdateFn。
componentUpdateFn函数中有两个重点:获取subTree和渲染subTree。
①subTree的获取
通过const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))的方式获取subTree。
renderComponentRoot中主要的逻辑为:
js
// 执行render函数
result = normalizeVNode(
render.call(
thisProxy,
proxyToUse,
renderCache,
!!(process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") ? shallowReadonly(props) : props,
setupState,
data,
ctx
)
);
// 此时的`render`函数为:
function render(_ctx, _cache, $props, $setup, $data, $options) {
return (
// 开启一个代码块(优化渲染性能)
(0, vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.openBlock)(),
// 创建一个 Fragment 元素块
(0, vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.createElementBlock)(
vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.Fragment,
null,
[
// 缓存检查:如果缓存中没有 h3 元素则创建
_cache[0] ||
(_cache[0] = (0, vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.createElementVNode)(
"h3",
null,
"这里是app组件",
-1 /* CACHED */ // 缓存标志
)),
// 渲染子组件
(0, vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.createVNode)(
$setup["Child"] // 从 setup 中获取 Child 组件
),
],
64 /* STABLE_FRAGMENT */ // 标志这是一个稳定的片段(不会重新排序的子节点)
)
);
}最终的执行结果为描述<h3>这个是app组件</h3>和<child></child>的vnode:
js
[
{
type: "h3",
children: "这个是app组件",
},
{
children: null,
type: {
render: function _sfc_render(_ctx, _cache) {
return _openBlock(), _createElementBlock("p", null, "这个是child组件");
},
},
},
];从结果中可以看出,第一个元素是普通的h3节点。第二个元素是有render函数的组件节点。
②subTree的patch
通过patch(null, subTree, container, anchor, instance, parentSuspense, isSVG)的方式渲染subTree。
在patch函数中,shapeFlag为17,shapeFlag & 1为真值1,所以会执行到processElement(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized)。
processElement中满足n1 == null,执行到mountElement(n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized)。
mountElement中shapeFlag & 16为真值16。会执行到mountChildren(vnode.children, el, null, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG && type !== 'foreignObject', slotScopeIds, optimized):
js
const mountChildren = (
children,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
start = 0
) => {
for (let i = start; i < children.length; i++) {
const child = (children[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(children[i])
: normalizeVNode(children[i]));
patch(
null,
child,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
);
}
};这里分别先看h3的渲染:
js
const mountElement = (
vnode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
) => {
// 根据tag创建dom
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(
vnode.type,
isSVG,
props && props.is,
props
);
// 根据vnode.children为text节点赋值
if (shapeFlag & 8 /* ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN */) {
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children);
}
// 将文本节点插入到父节点中
hostInsert(el, container, anchor);
};再看看child的渲染:
我们发现child是组件节点,然后会执行到patch中的processComponent(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized),最后执行到mountComponent逻辑。又回到了mountComponent,递归开始。
执行到const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))的方式获取subTree 后,简单看最终的执行结果为描述<child></child>的vnode:
js
{
type: 'p',
children: "这个是child组件"
}然后在子组件child的渲染过程中,会依然执行hostCreateElement、hostSetElementText和hostInsert的逻辑,最终将真实节点插入到父节点中。
执行完以后,跳出到上一级mountChildren逻辑中,将当前获取到的el通过hostInsert(el, container, anchor)的方式插入到父节点中,此时父节点中的节点为<div><h3>这个是app组件</h3><p>这个是child组件</p></div>。
页面渲染至此完成,简单总结如下:
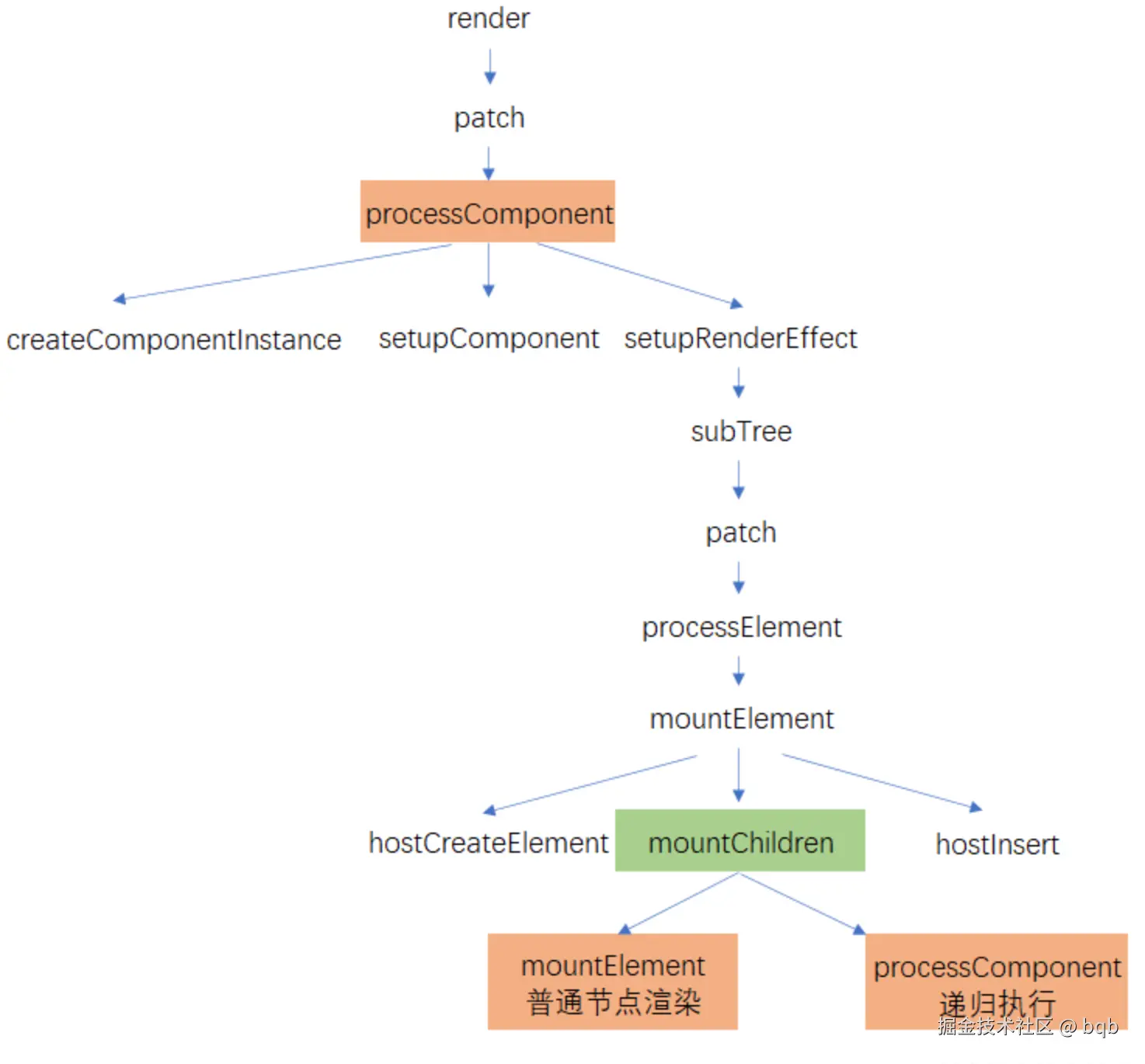
在mountElement的过程中,如果遇到mountChildren渲染过程子组件列表,普通节点会通过mountElement进行普通节点的创建和插入,组件节点会递归的执行processComponent将子组件树subTree的el插入到父节点中。这样,普通节点的el,子组件树中的el,都插入到了父节点中。依次类推,通过先子后父的方式,一层层的将节点插入到根节点中。
总结
vue组件树的渲染,是一个深度遍历的过程,从根节点开始寻找可创建真实节点的叶子节点,叶子节点完成真实节点的渲染后,再将其el交给父组件。依次类推,叶子节点将其el交给上一次中间组件,中间组件沿着树交给父级组件,最终会交给根组件。
纰漏之处在所难免,请批评指正。