设计目标
基于 Java 本地的缓存,而不是 Redis 的分布式缓存。它应该满足以下的设计:
- 设计一套 Cache API,派生不同的缓存实现。首先肯定是 key/value 的接口,然后带超时时间的控制
- 应该是线程安全的,使用
ConcurrentHashMap或LRULinkedHashMap - 实现类似 Redis 的超时控制,简单一点的可以自己删除过期的,复杂一点的用 Java 自带的线程池 Executors 去控制
- 缓存总数的容量限制,采用 LRU/LFU 淘汰机制
- 兼容 Spring Cache 体系,可以通过 Spring 的缓存注解施加到业务方法上
- 设计二级缓存,一级本地,二级 Redis
可见要考虑的事情话挺多的。为了避免目标一下子过于宏大,我们还是从简单的小例子开始。
简单的 Map 缓存
说起缓存自然便会想起 key/value 结构,------也不知道谁规定缓存就一定是 k/v 的,呵呵。那么我们很容易想到 Map 来做,又因为线程安全的缘故,我们选择了ConcurrentHashMap。
java
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class SimpleCache extends ConcurrentHashMap<String, SimpleCache.Item> {
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
private volatile boolean running = true;
/**
* 缓存项
*/
@Data
public static class Item {
String value;
int expireSeconds;
long addTime;
public Item(String value, int expireSeconds) {
this.value = value;
this.expireSeconds = expireSeconds;
addTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
/**
* 构造函数,初始化定时器
*
* @param scanIntervalSeconds 扫描间隔(秒)
*/
public SimpleCache(int scanIntervalSeconds) {
this.scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
startExpirationScanner(scanIntervalSeconds);
}
/**
* 默认构造函数,扫描间隔为 5 秒
*/
public SimpleCache() {
this(5);
}
/**
* 添加缓存项
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param expireSeconds 过期时间(秒)
*/
public void add(String key, String value, int expireSeconds) {
put(key, new Item(value, expireSeconds));
log.debug("Added item with key: {}, value: {}, expireSeconds: {}", key, value, expireSeconds);
}
/**
* 启动定时扫描任务,删除过期项
*
* @param scanIntervalSeconds 扫描间隔(秒)
*/
private void startExpirationScanner(int scanIntervalSeconds) {
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
if (running) {
try {
scanAndRemoveExpiredItems();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error during cache expiration scan", e);
}
}
}, scanIntervalSeconds, scanIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("Started cache expiration scanner with interval: {} seconds", scanIntervalSeconds);
}
/**
* 扫描并删除过期项
*/
private void scanAndRemoveExpiredItems() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
forEach((key, item) -> {
long elapsedSeconds = (currentTime - item.addTime) / 1000;
if (elapsedSeconds > item.expireSeconds) {
remove(key);
log.debug("Removed expired item with key: {}", key);
}
});
}
/**
* 优雅关闭定时器
*/
public void shutdown() {
running = false;
scheduler.shutdown();
try {
if (!scheduler.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
scheduler.shutdownNow();
log.warn("Scheduler did not terminate gracefully");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
scheduler.shutdownNow();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
log.warn("Interrupted during scheduler shutdown", e);
}
log.info("SimpleCache scheduler shut down");
}
}这个简单的缓存支持缓存过期的功能。它是通过线程池每隔五秒在后台扫描缓存,超时了就把缓存删掉。使用线程池的好处是简单直观,除了线程池还可以用BlockingQueue实现。
这个缓存存在的不足是没有缓存容量限制,如果一下子输入大量的缓存那么内存就会爆掉。
LRU 缓存
那我们限制缓存上限吧,给个maxCapacity最大容量。超过这个数就把缓存删掉。
java
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class BoundedCache<K, V> {
private final ConcurrentMap<K, V> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final int maxCapacity;
private final AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0);
public BoundedCache(int maxCapacity) {
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
public V get(K key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
V old = cache.put(key, value);
int currentSize = size.incrementAndGet();
// 如果是新增(不是替换),检查是否超限
if (old == null && currentSize > maxCapacity) {
// 简单策略:随机删除一个(实际可用 LRU/FIFO)
K firstKey = cache.keySet().iterator().next();
cache.remove(firstKey);
size.decrementAndGet();
}
return old;
}
public V remove(K key) {
V value = cache.remove(key);
if (value != null) {
size.decrementAndGet();
}
return value;
}
public int size() {
return size.get();
}
}该功能实现是实现了,可是没有考虑删除策略,是随机删除一个 _ ! ------这不太科学啊,而且~超时机制也没了(没线程删除,而是用 BlockingQueue 实现)。
好吧~我们先解决删除策略的问题,把 LRU 算法派生用场。
LRU =(Least Frequently Used,最不经常使用)
java
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 带锁的线程安全的 LRULinkedHashMap 简单实现
*
* @author <a href="https://blog.csdn.net/a921122/article/details/51992713">...</a>
*
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public class SimpleLRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -952299094512767664L;
/**
* 最大容量
*/
private final int maxCapacity;
private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 可重入锁
*/
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* 创建一个 LRUCache
*
* @param maxCapacity 最大容量
*/
public SimpleLRUCache(int maxCapacity) {
super(maxCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, true);
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return size() > maxCapacity;
}
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
try {
lock.lock();
return super.get(key);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 可以根据实际情况,考虑对不同的操作加锁
*/
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
try {
lock.lock();
return super.put(key, value);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}LRU 算法我之前介绍过。使用LinkedHashMap天然符合 LRU 这种的结构实现起来会比较简便。Spring 有内部的 LRU 也是这么做,只是它的 API 用法有点怪,需要传个什么回调函数进去,不如 k/v 方便。Spring 5 的 LRU 还是比较简单的,而新版本重新实现了却复杂很多。
带超时机制的 LRU 缓存
下面我们改用ConcurrentHashMap来实现 LRU:
- 存储
<K, V>数据 - 记录每个 key 的访问次数(frequency)
- 支持 get 和 put
- 超出容量时,淘汰 frequency 最小的 entry
- get 和 put 都算一次访问,频率 +1
接着我们需要对每个缓存条目添加时间戳信息,并在访问或插入时检查这些条目的存活时间。如果某个条目超过了设定的最大存活时间(TTL, Time To Live),则将其视为过期并从缓存中移除。
这里我们通过给CacheEntry增加一个lastAccessed字段来记录最后一次访问的时间,并在get和put方法中检查该条目是否已经过期。在淘汰过程中,首先检查候选者是否已过期,若过期则直接移除,否则继续保留。这种方式确保了即使在达到最大容量限制的情况下,也可以根据访问频率和过期时间有效管理缓存内容。
java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class LFUCache<K, V> {
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, CacheEntry<V>> cache;
private final TreeMap<Integer, LinkedHashSet<K>> freqToKeys;
private final int capacity;
private final long defaultTtlMillis; // 默认 TTL(毫秒),0 表示无默认
private final AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 后台清理相关
private final boolean enableExpiryCleanup;
private final long cleanupIntervalMs = 1000L;
private ScheduledExecutorService cleanupExecutor;
private final AtomicBoolean closed = new AtomicBoolean(false);
public LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL(int capacity) {
this(capacity, 0, false); // 无默认 TTL
}
public LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL(int capacity, long defaultTtlSeconds, boolean enableExpiryCleanup) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Capacity must be positive");
this.capacity = capacity;
this.defaultTtlMillis = defaultTtlSeconds * 1000L;
this.cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
this.freqToKeys = new TreeMap<>();
this.enableExpiryCleanup = enableExpiryCleanup;
if (enableExpiryCleanup) {
cleanupExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r, "LFU-Cache-Expiry-Cleaner");
t.setDaemon(true); // 守护线程
return t;
});
startExpiryCleanupTask();
}
}
/**
* 获取值,检查是否过期
*/
public V get(K key) {
CacheEntry<V> entry = cache.get(key);
if (entry == null || isExpired(entry)) {
// 如果过期,清理
if (entry != null) {
removeFromFreqMap(entry.frequency, key);
cache.remove(key);
size.decrementAndGet();
}
return null;
}
increaseFrequency(key, entry);
return entry.value;
}
/**
* put:使用默认 TTL(如果设置了)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (defaultTtlMillis > 0)
return put(key, value, (int) (defaultTtlMillis / 1000));
else
return put(key, value, 0); // 0 表示永不过期
}
/**
* put:指定 TTL(单位:秒)
* ttlSeconds = 0 表示永不过期
*/
public V put(K key, V value, int ttlSeconds) {
long expireTime = (ttlSeconds > 0) ? (System.currentTimeMillis() + ttlSeconds * 1000L) : Long.MAX_VALUE;
CacheEntry<V> oldEntry = cache.get(key);
if (oldEntry != null && !isExpired(oldEntry)) {
V oldValue = oldEntry.value;
oldEntry.value = value;
oldEntry.expireTime = expireTime;
increaseFrequency(key, oldEntry);
return oldValue;
}
// 处理新增
if (size.get() >= capacity)
evict(); // 淘汰一个条目
CacheEntry<V> newEntry = new CacheEntry<>(value, 1, expireTime);
cache.put(key, newEntry);
freqToKeys.computeIfAbsent(1, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>()).add(key);
size.incrementAndGet();
return null;
}
/**
* 检查是否过期
*/
private boolean isExpired(CacheEntry<V> entry) {
return System.currentTimeMillis() > entry.expireTime;
}
/**
* 增加频率
*/
private void increaseFrequency(K key, CacheEntry<V> entry) {
if (isExpired(entry)) { // 理论上不会到这里,但安全起见
evictEntry(key, entry);
return;
}
int oldFreq = entry.frequency;
int newFreq = oldFreq + 1;
entry.frequency = newFreq;
removeFromFreqMap(oldFreq, key);
freqToKeys.computeIfAbsent(newFreq, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>()).add(key);
}
/**
* 淘汰一个条目
* 优先淘汰已过期的条目,否则淘汰频率最低的
*/
private void evict() {
// 先尝试找一个过期的条目淘汰
for (Map.Entry<K, CacheEntry<V>> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
if (isExpired(entry.getValue())) {
evictEntry(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
return;
}
}
// 没有过期的,淘汰频率最低的(FIFO)
Integer minFreq = freqToKeys.firstKey();
LinkedHashSet<K> candidates = freqToKeys.get(minFreq);
K keyToEvict = candidates.iterator().next();
CacheEntry<V> entry = cache.get(keyToEvict);
evictEntry(keyToEvict, entry);
}
/**
* 统一淘汰逻辑
*/
private void evictEntry(K key, CacheEntry<V> entry) {
if (entry == null)
return;
removeFromFreqMap(entry.frequency, key);
cache.remove(key);
size.decrementAndGet();
}
/**
* 从 freqToKeys 中移除 key
*/
private void removeFromFreqMap(int freq, K key) {
LinkedHashSet<K> set = freqToKeys.get(freq);
if (set != null) {
set.remove(key);
if (set.isEmpty())
freqToKeys.remove(freq);
}
}
public int size() {
return size.get();
}
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
freqToKeys.clear();
size.set(0);
}
// 缓存条目
private static class CacheEntry<V> {
V value;
int frequency;
long expireTime; // 过期时间戳(毫秒)
public CacheEntry(V value, int frequency, long expireTime) {
this.value = value;
this.frequency = frequency;
this.expireTime = expireTime;
}
}
// ===================== 后台清理任务 =====================
private void startExpiryCleanupTask() {
cleanupExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
if (closed.get())
return;
try {
List<K> expiredKeys = new ArrayList<>();
// 扫描所有条目,收集过期的 key
for (Map.Entry<K, CacheEntry<V>> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
if (isExpired(entry.getValue()))
expiredKeys.add(entry.getKey());
}
// 批量清理
for (K key : expiredKeys)
evictEntry(key, cache.get(key));
} catch (Exception e) {
// 防止任务因异常退出
System.err.println("Expiry cleanup task error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}, cleanupIntervalMs, cleanupIntervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 关闭缓存,释放后台线程
*/
public void close() {
if (closed.compareAndSet(false, true) && enableExpiryCleanup) {
cleanupExecutor.shutdown();
try {
if (!cleanupExecutor.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
cleanupExecutor.shutdownNow();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cleanupExecutor.shutdownNow();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<String, String> cache = new LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<>(3);
//
// cache.put("A", "Apple", 2); // 2秒后过期
// cache.put("B", "Banana", 5); // 5秒后过期
// cache.put("C", "Cherry"); // 永不过期(使用默认或无 TTL)
//
// System.out.println(cache.get("A")); // Apple
// Thread.sleep(3000);
// System.out.println(cache.get("A")); // null(已过期)
//
// System.out.println(cache.get("B")); // Banana
// System.out.println(cache.get("C")); // Cherry
// 启用后台清理,每 500ms 扫描一次
LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<String, String> cache2 = new LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<>(100, 500, true);
cache2.put("A", "Apple", 2); // 2秒后过期
cache2.put("B", "Banana", 5); // 5秒后过期
System.out.println("1s后: " + cache2.get("A")); // Apple
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("3s后: " + cache2.get("A")); // null(后台或get时已清理)
// 关闭缓存,释放线程
cache2.close();
}
}另外还增加了定期清理的功能:添加一个后台线程或使用定时任务来定期扫描和清除过期条目。但这不是必须的,因为我们可以在每次访问时进行清理。好处是避免 get 时卡顿。当然增加线程也会带来一定的复杂(需要close()),于是我们通过构造参数开启/关闭(enableExpiryCleanup = true/false)是否允许打开后台线程清理。
- 大缓存建议启用:如果缓存条目多,建议启用后台清理
- 小缓存可关闭:条目少时,get 时清理就够了
- 如果使用了后台清理,请不要忘记调用
close():尤其是在应用关闭时,避免线程泄漏
至此,关于缓存的核心功能已经完成了:
- 设计一套 Cache API,派生不同的缓存实现。首先肯定是 key/value 的接口,然后带超时时间的控制
应该是线程安全的,使用ConcurrentHashMap或LRULinkedHashMap实现类似 Redis 的超时控制,简单一点的可以自己删除过期的,复杂一点的用 Java 自带的线程池 Executors 去控制缓存总数的容量限制,采用 LRU/LFU 淘汰机制- 兼容 Spring Cache 体系,可以通过 Spring 的缓存注解施加到业务方法上
- 设计二级缓存,一级本地,二级 Redis
剩下继续完成~
统一 Cache API
这个就简单了,声明一下Cache接口及其条目。
java
/**
* 缓存接口
*
* @param <K> 键类型
* @param <V> 值类型
*/
public interface Cache<K, V> {
/**
* 将对象加入到缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 对象
* @param timeout 过期时间,单位:毫秒, 0表示无限长
*/
void put(K key, V value, long timeout);
default void put(K key, V value, int timeout) {
put(key, value, timeout * 1000L);
}
default void put(K key, V value) {
put(key, value, 0);
}
/**
* 从缓存中获得对象
*
* @param key 键
* @return 键对应的对象
*/
V get(K key);
/**
* 根据指定的键获取相应的值,并将该值转换为指定的类型返回。
*
* @param key 键
* @param clz 指定的类
* @param <T> 期望的类型
* @return 转换后的值
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
default <T> T get(K key, Class<T> clz) {
V v = get(key);
return (T) v;
}
/**
* 从缓存中删除对象
*
* @param key 键
*/
void remove(K key);
}
/**
* 被缓存的数据
*
* @param <V> 缓存数据的类型
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CacheItem<V> {
/**
* 缓存值
*/
private V value;
/**
* 到期时间(毫秒)
*/
private long expire;
}这样,前面的LFUCache及其的内部类改写下。
java
package com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.smallredis.lfu;
import com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.smallredis.Cache;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* TODO TreeMap 和 LinkedHashSet 不是线程安全的,所以需要加锁或使用 ConcurrentSkipListMap
*
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public class LFUCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> {
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, LFUCacheItem<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final TreeMap<Integer, LinkedHashSet<K>> freqToKeys = new TreeMap<>();
// 替代 TreeMap<Integer, LinkedHashSet<K>>=new TreeMap<>();
// private final ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, KeySet> freqToKeys = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
private final int capacity;
private final long defaultTtlMillis; // 默认 TTL(毫秒),0 表示无默认
private final AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 后台清理相关
private final boolean enableExpiryCleanup;
private final long cleanupIntervalMs = 1000L;
private ScheduledExecutorService cleanupExecutor;
private final AtomicBoolean closed = new AtomicBoolean(false);
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this(capacity, 0, false); // 无默认 TTL
}
public LFUCache(int capacity, long defaultTtlSeconds, boolean enableExpiryCleanup) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Capacity must be positive");
this.capacity = capacity;
this.defaultTtlMillis = defaultTtlSeconds * 1000L;
this.enableExpiryCleanup = enableExpiryCleanup;
if (enableExpiryCleanup) {
cleanupExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r, "LFU-Cache-Expiry-Cleaner");
t.setDaemon(true); // 守护线程
return t;
});
startExpiryCleanupTask();
}
}
/**
* 获取值,检查是否过期
*/
@Override
public V get(K key) {
LFUCacheItem<V> entry = cache.get(key);
if (entry == null || isExpired(entry)) {
// 如果过期,清理
if (entry != null) {
removeFromFreqMap(entry.getFrequency(), key);
cache.remove(key);
size.decrementAndGet();
}
return null;
}
increaseFrequency(key, entry);
return entry.getValue();
}
/**
* put:使用默认 TTL(如果设置了)
*/
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (defaultTtlMillis > 0)
put(key, value, defaultTtlMillis);
else
put(key, value, 0); // 0 表示永不过期
}
@Override
public void put(K key, V value, long ttl) {
put(key, value, (int) (ttl / 1000));
}
/**
* put:指定 TTL(单位:秒)
* ttlSeconds = 0 表示永不过期
*/
@Override
public void put(K key, V value, int ttlSeconds) {
long expireTime = (ttlSeconds > 0) ? (System.currentTimeMillis() + ttlSeconds * 1000L) : Long.MAX_VALUE;
LFUCacheItem<V> oldEntry = cache.get(key);
if (oldEntry != null && !isExpired(oldEntry)) {
V oldValue = oldEntry.getValue();
oldEntry.setValue(value);
oldEntry.setExpire(expireTime);
increaseFrequency(key, oldEntry);
}
// 处理新增
if (size.get() >= capacity)
evict(); // 淘汰一个条目
LFUCacheItem<V> newEntry = new LFUCacheItem<>(value, 1, expireTime);
cache.put(key, newEntry);
freqToKeys.computeIfAbsent(1, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>()).add(key);
size.incrementAndGet();
}
/**
* 检查是否过期
*/
private boolean isExpired(LFUCacheItem<V> entry) {
return System.currentTimeMillis() > entry.getExpire();
}
/**
* 增加频率
*/
private void increaseFrequency(K key, LFUCacheItem<V> entry) {
if (isExpired(entry)) { // 理论上不会到这里,但安全起见
evictEntry(key, entry);
return;
}
int oldFreq = entry.getFrequency();
int newFreq = oldFreq + 1;
entry.setFrequency(newFreq);
removeFromFreqMap(oldFreq, key);
freqToKeys.computeIfAbsent(newFreq, k -> new LinkedHashSet<>()).add(key);
}
/**
* 淘汰一个条目
* 优先淘汰已过期的条目,否则淘汰频率最低的
*/
private void evict() {
// 先尝试找一个过期的条目淘汰
for (Map.Entry<K, LFUCacheItem<V>> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
if (isExpired(entry.getValue())) {
evictEntry(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
return;
}
}
// 没有过期的,淘汰频率最低的(FIFO)
Integer minFreq = freqToKeys.firstKey();
LinkedHashSet<K> candidates = freqToKeys.get(minFreq);
K keyToEvict = candidates.iterator().next();
LFUCacheItem<V> entry = cache.get(keyToEvict);
evictEntry(keyToEvict, entry);
}
/**
* 统一淘汰逻辑
*/
private void evictEntry(K key, LFUCacheItem<V> entry) {
removeFromFreqMap(entry.getFrequency(), key);
cache.remove(key);
size.decrementAndGet();
}
/**
* 从缓存中删除对象
*
* @param key 键
*/
public void remove(K key) {
LFUCacheItem<V> entry = cache.get(key);
if (entry != null)
evictEntry(key, entry);
}
/**
* 从 freqToKeys 中移除 key
*/
private void removeFromFreqMap(int freq, K key) {
LinkedHashSet<K> set = freqToKeys.get(freq);
if (set != null) {
set.remove(key);
if (set.isEmpty())
freqToKeys.remove(freq);
}
}
public int size() {
return size.get();
}
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
freqToKeys.clear();
size.set(0);
}
// ===================== 后台清理任务 =====================
private void startExpiryCleanupTask() {
cleanupExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
if (closed.get())
return;
try {
List<K> expiredKeys = new ArrayList<>();
// 扫描所有条目,收集过期的 key
for (Map.Entry<K, LFUCacheItem<V>> entry : cache.entrySet()) {
if (isExpired(entry.getValue()))
expiredKeys.add(entry.getKey());
}
// 批量清理
for (K key : expiredKeys)
evictEntry(key, cache.get(key));
} catch (Exception e) {
// 防止任务因异常退出
System.err.println("Expiry cleanup task error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}, cleanupIntervalMs, cleanupIntervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 关闭缓存,释放后台线程
*/
public void close() {
if (closed.compareAndSet(false, true) && enableExpiryCleanup) {
cleanupExecutor.shutdown();
try {
if (!cleanupExecutor.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
cleanupExecutor.shutdownNow();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cleanupExecutor.shutdownNow();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<String, String> cache = new LFUCacheWithPerEntryTTL<>(3);
//
// cache.put("A", "Apple", 2); // 2秒后过期
// cache.put("B", "Banana", 5); // 5秒后过期
// cache.put("C", "Cherry"); // 永不过期(使用默认或无 TTL)
//
// System.out.println(cache.get("A")); // Apple
// Thread.sleep(3000);
// System.out.println(cache.get("A")); // null(已过期)
//
// System.out.println(cache.get("B")); // Banana
// System.out.println(cache.get("C")); // Cherry
// 启用后台清理,每 500ms 扫描一次
LFUCache<String, String> cache2 = new LFUCache<>(100, 500, true);
cache2.put("A", "Apple", 2); // 2秒后过期
cache2.put("B", "Banana", 5); // 5秒后过期
System.out.println("1s后: " + cache2.get("A")); // Apple
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("3s后: " + cache2.get("A")); // null(后台或get时已清理)
// 关闭缓存,释放线程
cache2.close();
}
}
package com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.smallredis.lfu;
import com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.smallredis.CacheItem;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@Data
public class LFUCacheItem<V> extends CacheItem<V> {
private int frequency;
public LFUCacheItem(V value, int frequency, long expire) {
super(value, expire);
this.frequency = frequency;
}
}整合到 Spring Cache
Spring 3.1开始,引入了Spring Cache,即Spring缓存抽象。通过定义springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用注解简化开发过程。
- Cache接口:为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的 get put evict 各种操作集合。
- CacheManager:基于 name 管理一组 Cache,指定缓存的底层实现。例如 RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache 等,也实现我们自己的底层实现,比如当前的 LFUCache。
简单说,就是在业务层的方法上添加@Cacheable注解即可启用缓存,非常轻松的实现了缓存操作的处理,整体的实现效果是非常简单的,同时也避免影响其他数据层的缓存操作。每次执行该方法前会先去缓存中查有没有相同条件下,缓存的数据,有的话直接拿缓存的数据,没有的话执行方法,并将执行结果返回。
java
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class EmpService {
//编辑雇员
public Emp edit(Emp emp) {
return Emp.builder().build();
}
//根据id查询雇员信息
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "emp")
public Emp get(String eid) {
return Emp.builder().ename("Tom").build();
}
//根据名称查询雇员信息
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "emp")
public Emp getEname(String ename) {
return Emp.builder().ename("Jack").build();
}
}配置LfuSpringCacheManager:
java
import com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.lfu.springcache.LfuSpringCacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching//开启缓存
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ajaxjs.framework.cache")
public class Config {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
return new LfuSpringCacheManager(100); // LRU 容量为 100,可自行调整
}
}LfuSpringCacheManager和LfuSpringCache源码:
java
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class LfuSpringCacheManager implements CacheManager {
private final Map<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final int maxSize;
public LfuSpringCacheManager(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
return cacheMap.computeIfAbsent(name, n -> new LfuSpringCache(n, maxSize));
}
@Override
public Collection<String> getCacheNames() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(cacheMap.keySet());
}
}
import com.ajaxjs.framework.cache.lfu.LFUCache;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleValueWrapper;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class LfuSpringCache implements Cache {
private final String name;
private final LFUCache<String, Object> lfuCache;
public LfuSpringCache(String name, int maxSize) {
this.name = name;
this.lfuCache = new LFUCache<>(maxSize);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public Object getNativeCache() {
return lfuCache;
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {
Object value = lfuCache.get(key.toString());
System.out.println("LFU Cache: " + value);
return value != null ? new SimpleValueWrapper(value) : null;
}
@Override
public <T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type) {
Object value = lfuCache.get(key.toString());
if (type != null && type.isInstance(value))
return type.cast(value);
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
lfuCache.put(key.toString(), value);
}
@Override
public void evict(Object key) {
lfuCache.remove(key.toString());
}
@Override
public void clear() {
lfuCache.clear();
}
}运行测试:
java
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.cache.support.AbstractCacheManager;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = Config.class)
public class TestCache {
@Autowired
EmpService service;
@Test
void testGet() {
AbstractCacheManager l;
Emp emp1 = service.get("1");
log.info("[第一次查询],emp1:{}", emp1);
Emp emp2 = service.get("1");
log.info("[第二次查询],emp2:{}", emp2);
}
}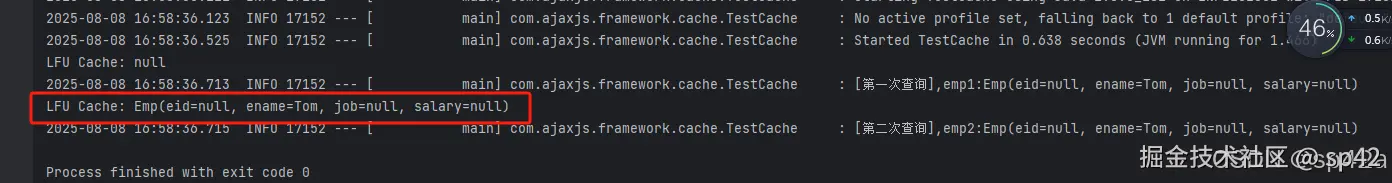 可见第二次执行的时候,命中了缓存。
可见第二次执行的时候,命中了缓存。
Spring Cache 还有其他强大的用法,这里就不展开介绍了。
二级缓存
这个实现起来比较复杂,另文再述。
源码
所有源码在 aj-framework:gitcode.com/lightweight...。