题目列表
-
- 相交链表 简单难度 leetcode链接
-
- 反转链表 简单难度 leetcode链接
-
- 回文链表 简单难度 leetcode链接
-
- 环形链表 简单难度 leetcode链接
-
- 环形链表II 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- 合并两个有序链表 简单难度 leetcode链接
-
- 两数相加 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- 删除链表的倒数第N个结点 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- 两两交换链表中的节点 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- K个一组翻转链表 困难难度 leetcode链接
-
- 随机链表的复制 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- 排序链表 中等难度 leetcode链接
-
- 合并K个升序链表 困难难度 leetcode链接
-
- LRU缓存 中等难度 leetcode链接
题目
(1)相交链表
题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
示例 1:
输入: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 **输出:**Intersected at '8'
示例 2:
输入: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 **输出:**Intersected at '2'
示例 3:
输入: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 **输出:**No intersection
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dis = self.getLength(headA) - self.getLength(headB)# 通过移动较长的链表,使两链表长度相等
if dis > 0:
headA = self.moveForward(headA, dis)
else:
headB = self.moveForward(headB, abs(dis))# 将两个头向前移动,直到它们相交
while headA and headB:
if headA == headB:
return headA
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None
def getLength(self, head: ListNode) -> int:
length = 0
while head:
length += 1
head = head.next
return length
def moveForward(self, head: ListNode, steps: int) -> ListNode:
while steps > 0:
head = head.next
steps -= 1
return head
(2)反转链表
题目
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入: head = [] 输出:[]
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
cur = head
pre = None
while cur:
temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre(3)回文链表
题目
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入: head = [1,2,2,1] **输出:**true
示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2] **输出:**false
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# 思路:寻找中间节点+反转链表
# 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度(节点个数)。
# 空间复杂度:O(1)。
# 876. 链表的中间结点
def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# 206. 反转链表
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
pre, cur = None, head
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = nxt
return pre
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
mid = self.middleNode(head)
head2 = self.reverseList(mid)
while head2:
if head.val != head2.val: # 不是回文链表
return False
head = head.next
head2 = head2.next
return True(4)环形链表
题目
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意: pos 不作为参数进行传递。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果 链表 中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出: true **解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出: true **解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入: head = [1], pos = -1 输出: false **解释:**链表中没有环。
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
# 采用快慢指针:当链表中不存在环时,快指针将先于慢指针到达链表尾部,链表中每个节点至多被访问两次。当链表中存在环时,每一轮移动后,快慢指针的距离将减小一。而初始距离为环的长度,因此至多移动N轮。
# 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是链表中的节点数。
# 空间复杂度:O(1)。我们只使用了两个指针的额外空间。
if not head or not head.next:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while slow != fast:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return False
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return True(5)环形链表II
题目
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null 。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始 )。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意: pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改链表。
示例 1:
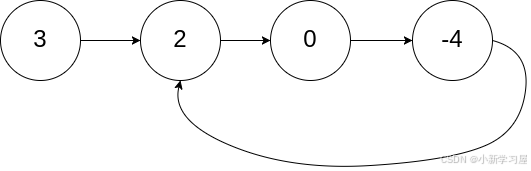
输入: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出: 返回索引为 1 的链表节点 **解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
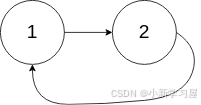
输入: head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出: 返回索引为 0 的链表节点 **解释:**链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入: head = [1], pos = -1 输出: 返回 null **解释:**链表中没有环。
提示:
-
链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 10(4)]内 -
-10(5) <= Node.val <= 10(5) -
pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# If there is a cycle, the slow and fast pointers will eventually meet
if slow == fast:
# Move one of the pointers back to the start of the list
slow = head
while slow != fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
# If there is no cycle, return None
return None(6)合并两个有序链表
题目
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入: l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入: l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 迭代实现
# 时间复杂度:O(n+m),其中n和m分别为两个链表的长度。因为每次循环迭代中,l1和l2只有一个元素会被放进合并链表中, 因此while循环的次数不会超过两个链表的长度之和。所有其他操作的时间复杂度都是常数级别的,因此总的时间复杂度为O(n+m)。
# 空间复杂度:O(1)。我们只需要常数的空间存放若干变量。
prehead = ListNode()
prev = prehead
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
prev.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
prev.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
prev = prev.next
# 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 if l1 is not None else l2
return prehead.next(7)两数相加
题目
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
输入: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出: [7,0,8] **解释:**342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
-
每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 -
0 <= Node.val <= 9 -
题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为l1长度和l2长度的最大值。
# 空间复杂度:O(1)。返回值不计入。
cur = dummy = ListNode() # 哨兵节点
carry = 0 # 进位
while l1 or l2 or carry: # 有一个不是空节点,或者还有进位,就继续迭代
if l1:
carry += l1.val # 节点值和进位加在一起
l1 = l1.next # 下一个节点
if l2:
carry += l2.val # 节点值和进位加在一起
l2 = l2.next # 下一个节点
cur.next = ListNode(carry % 10) # 每个节点保存一个数位
carry //= 10 # 新的进位
cur = cur.next # 下一个节点
return dummy.next # 哨兵节点的下一个节点就是头节点 (8)删除链表的倒数第N个结点
题目
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
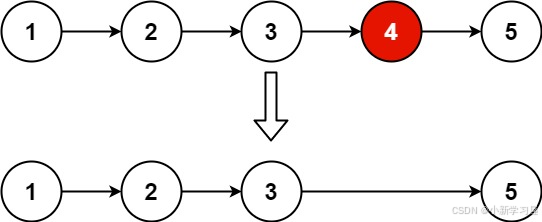
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入: head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入: head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode()# 创建两个指针,慢指针和快指针,并将它们初始化为虚拟节点
dummy_head.next = head
slow = fast = dummy_head
# 快指针比慢指针快 n+1 步
for i in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
# 移动两个指针,直到快速指针到达链表的末尾
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
# 通过更新第 (n-1) 个节点的 next 指针删除第 n 个节点
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy_head.next(9)两两交换链表中的节点
题目
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
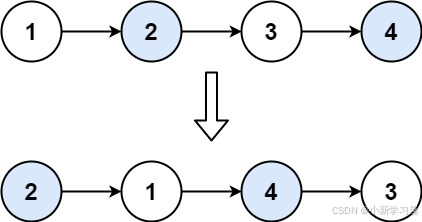
输入: head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入: head = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入: head = [1] 输出:[1]
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode()
dummy_head.next = head
current = dummy_head
# 必须有cur的下一个和下下个才能交换,否则说明已经交换结束了
while current.next and current.next.next:
temp = current.next # 防止节点修改
temp1 = current.next.next.next
current.next = current.next.next
current.next.next = temp
temp.next = temp1
current = current.next.next
return dummy_head.next(10)K个一组翻转链表
题目
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例1:
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
-
链表中的节点数目为
n -
1 <= k <= n <= 5000 -
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为链表的长度。head指针会停留在节点上,每次停留需要进行一次 O(k) 的翻转操作。
# 空间复杂度:O(1),我们只需要建立常数个变量
# 翻转一个子链表,并且返回新的头与尾
def reverse(self, head: ListNode, tail: ListNode):
prev = tail.next
p = head
while prev != tail:
nex = p.next
p.next = prev
prev = p
p = nex
return tail, head
def reverseKGroup(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
hair = ListNode(0)
hair.next = head
pre = hair
while head:
tail = pre
# 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 k
for i in range(k):
tail = tail.next
if not tail:
return hair.next
nex = tail.next
head, tail = self.reverse(head, tail)
# 把子链表重新接回原链表
pre.next = head
tail.next = nex
pre = tail
head = tail.next
return hair.next(11)随机链表的复制
题目
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝 。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
-
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。 -
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
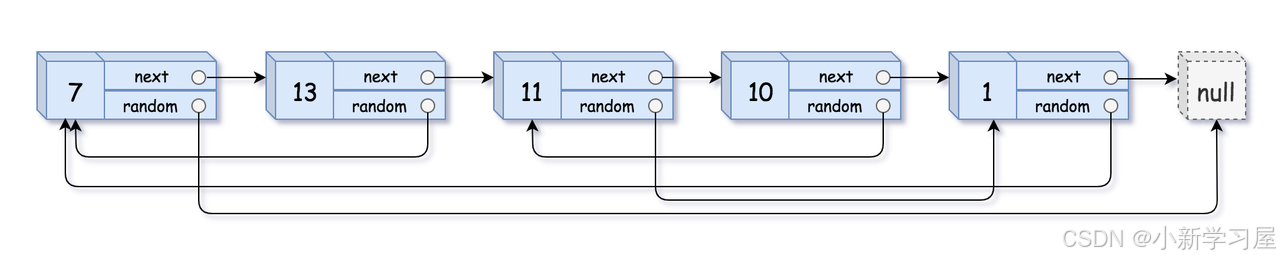
输入: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
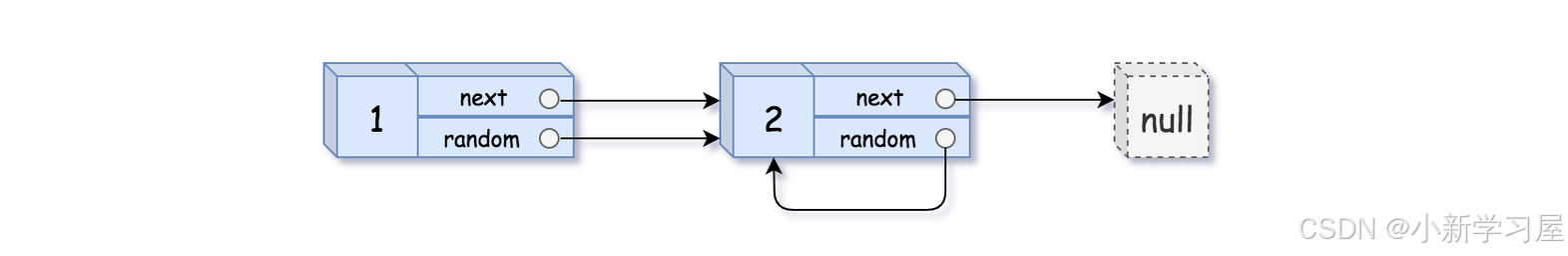
输入: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
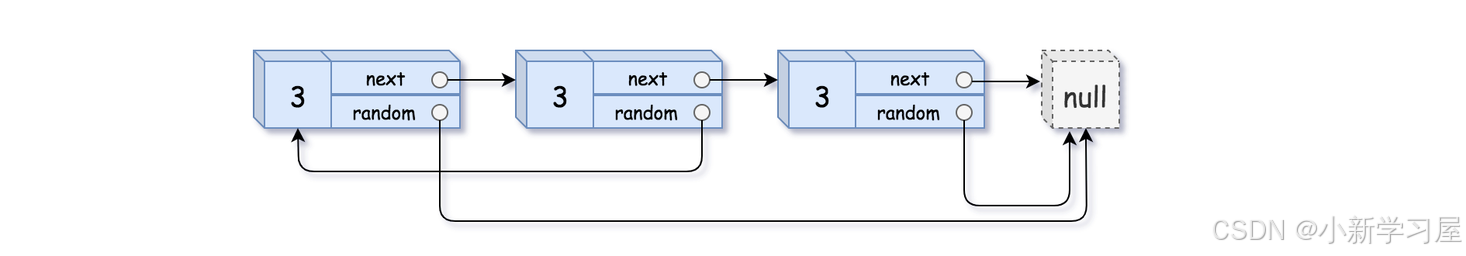
输入: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
-
0 <= n <= 1000 -
-10(4) <= Node.val <= 10(4) -
Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
思路
python
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not head: return
cur = head
# 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while cur:
tmp = Node(cur.val)
tmp.next = cur.next
cur.next = tmp
cur = tmp.next
# 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head
while cur:
if cur.random:
cur.next.random = cur.random.next
cur = cur.next.next
# 3. 拆分两链表
cur = res = head.next
pre = head
while cur.next:
pre.next = pre.next.next
cur.next = cur.next.next
pre = pre.next
cur = cur.next
pre.next = None # 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res # 返回新链表头节点
#链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solutions/2361362/138-fu-zhi-dai-sui-ji-zhi-zhen-de-lian-b-6jeo/(12)排序链表
题目
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入: head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
-
链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5 * 10(4)]内 -
-10(5) <= Node.val <= 10(5)
思路
python
class Solution:
# 按照归并排序,自低向上完成排序
# 时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中 n 是链表长度。
# 空间复杂度:O(1)。
# 获取链表长度
def getListLength(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> int:
length = 0
while head:
length += 1
head = head.next
return length
# 分割链表
# 如果链表长度 <= size,不做任何操作,返回空节点
# 如果链表长度 > size,把链表的前 size 个节点分割出来(断开连接),并返回剩余链表的头节点
def splitList(self, head: Optional[ListNode], size: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 先找到 next_head 的前一个节点
cur = head
for _ in range(size - 1):
if cur is None:
break
cur = cur.next
# 如果链表长度 <= size
if cur is None or cur.next is None:
return None # 不做任何操作,返回空节点
next_head = cur.next
cur.next = None # 断开 next_head 的前一个节点和 next_head 的连接
return next_head
# 21. 合并两个有序链表(双指针)
# 返回合并后的链表的头节点和尾节点
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
cur = dummy = ListNode() # 用哨兵节点简化代码逻辑
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val < list2.val:
cur.next = list1 # 把 list1 加到新链表中
list1 = list1.next
else: # 注:相等的情况加哪个节点都是可以的
cur.next = list2 # 把 list2 加到新链表中
list2 = list2.next
cur = cur.next
cur.next = list1 or list2 # 拼接剩余链表
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
# 循环结束后,cur 是合并后的链表的尾节点
return dummy.next, cur
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
length = self.getListLength(head) # 获取链表长度
dummy = ListNode(next=head) # 用哨兵节点简化代码逻辑
step = 1 # 步长(参与合并的链表长度)
while step < length:
new_list_tail = dummy # 新链表的末尾
cur = dummy.next # 每轮循环的起始节点
while cur:
# 从 cur 开始,分割出两段长为 step 的链表,头节点分别为 head1 和 head2
head1 = cur
head2 = self.splitList(head1, step)
cur = self.splitList(head2, step) # 下一轮循环的起始节点
# 合并两段长为 step 的链表
head, tail = self.mergeTwoLists(head1, head2)
# 合并后的头节点 head,插到 new_list_tail 的后面
new_list_tail.next = head
new_list_tail = tail # tail 现在是新链表的末尾
step *= 2
return dummy.next
#链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-list/solutions/2993518/liang-chong-fang-fa-fen-zhi-die-dai-mo-k-caei/(13)合并K个升序链表
题目
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入: lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] **解释:**链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入: lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入: lists = [[]] 输出:[]
提示:
-
k == lists.length -
0 <= k <= 10^4 -
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500 -
-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4 -
lists[i]按 升序 排列 -
lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
思路
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# 时间复杂度为NlogK(N是所有链表中元素的总数,K是链表数量)
# 空间复杂度为logK
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
if len(lists) <= 2:
return self.mergeTwoLists(lists)
def splitLists(lists):
idx = len(lists) // 2
return lists[:idx], lists[idx:]
a, b = splitLists(lists)
a_merge = self.mergeKLists(a)
b_merge = self.mergeKLists(b)
return self.mergeTwoLists([a_merge, b_merge])
def mergeTwoLists(self, lists):
if not lists: return None
if len(lists)==1: return lists[0]
head1, head2 = lists
head = dump = ListNode(0)
while head1 and head2:
if head1.val < head2.val:
head.next = head1
head1 = head1.next
else:
head.next = head2
head2 = head2.next
head = head.next
head.next = head1 if head1 else head2
return dump.next(14)LRU缓存
题目
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
-
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存 -
int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。 -
void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4] 解释 LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3 lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
-
1 <= capacity <= 3000 -
0 <= key <= 10000 -
0 <= value <= 10(5) -
最多调用
2 * 10(5)次get和put
思路
python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, key=None, value=None):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
self.capacity = capacity
self.hashmap = {}
# 新建两个节点 head 和 tail
self.head = ListNode()
self.tail = ListNode()
# 初始化链表为 head <-> tail
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
# 因为get与put操作都可能需要将双向链表中的某个节点移到末尾,所以定义一个方法
def move_node_to_tail(self, key):
# 先将哈希表key指向的节点拎出来,为了简洁起名node
# hashmap[key] hashmap[key]
# | |
# V --> V
# prev <-> node <-> next pre <-> next ... node
node = self.hashmap[key]
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
# 之后将node插入到尾节点前
# hashmap[key] hashmap[key]
# | |
# V --> V
# prev <-> tail ... node prev <-> node <-> tail
node.prev = self.tail.prev
node.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev.next = node
self.tail.prev = node
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key in self.hashmap:
# 如果已经在链表中了久把它移到末尾(变成最新访问的)
self.move_node_to_tail(key)
res = self.hashmap.get(key, -1)
if res == -1:
return res
else:
return res.value
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key in self.hashmap:
# 如果key本身已经在哈希表中了就不需要在链表中加入新的节点
# 但是需要更新字典该值对应节点的value
self.hashmap[key].value = value
# 之后将该节点移到末尾
self.move_node_to_tail(key)
else:
if len(self.hashmap) == self.capacity:
# 去掉哈希表对应项
self.hashmap.pop(self.head.next.key)
# 去掉最久没有被访问过的节点,即头节点之后的节点
self.head.next = self.head.next.next
self.head.next.prev = self.head
# 如果不在的话就插入到尾节点前
new = ListNode(key, value)
self.hashmap[key] = new
new.prev = self.tail.prev
new.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev.next = new
self.tail.prev = new
# 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/solutions/7583/shu-ju-jie-gou-fen-xi-python-ha-xi-shuang-xiang-li/结尾
亲爱的读者朋友:感谢您在繁忙中驻足阅读本期内容!您的到来是对我们最大的支持❤️
正如古语所言:"当局者迷,旁观者清"。您独到的见解与客观评价,恰似一盏明灯💡,能帮助我们照亮内容盲区,让未来的创作更加贴近您的需求。
若此文给您带来启发或收获,不妨通过以下方式为彼此搭建一座桥梁: ✨ 点击右上角【点赞】图标,让好内容被更多人看见 ✨ 滑动屏幕【收藏】本篇,便于随时查阅回味 ✨ 在评论区留下您的真知灼见,让我们共同碰撞思维的火花
我始终秉持匠心精神,以键盘为犁铧深耕知识沃土💻,用每一次敲击传递专业价值,不断优化内容呈现形式,力求为您打造沉浸式的阅读盛宴📚。
有任何疑问或建议?评论区就是我们的连心桥!您的每一条留言我都将认真研读,并在24小时内回复解答📝。
愿我们携手同行,在知识的雨林中茁壮成长🌳,共享思想绽放的甘甜果实。下期相遇时,期待看到您智慧的评论与闪亮的点赞身影✨!
万分感谢🙏🙏您的点赞👍👍、收藏⭐🌟、评论💬🗯️、关注❤️💚
自我介绍:一线互联网大厂资深算法研发(工作6年+),4年以上招聘面试官经验(一二面面试官,面试候选人400+),深谙岗位专业知识、技能雷达图,已累计辅导15+求职者顺利入职大中型互联网公司。熟练掌握大模型、NLP、搜索、推荐、数据挖掘算法和优化,提供面试辅导、专业知识入门到进阶辅导等定制化需求等服务,助力您顺利完成学习和求职之旅(有需要者可私信联系)
友友们,自己的知乎账号为**"快乐星球"**,定期更新技术文章,敬请关注!