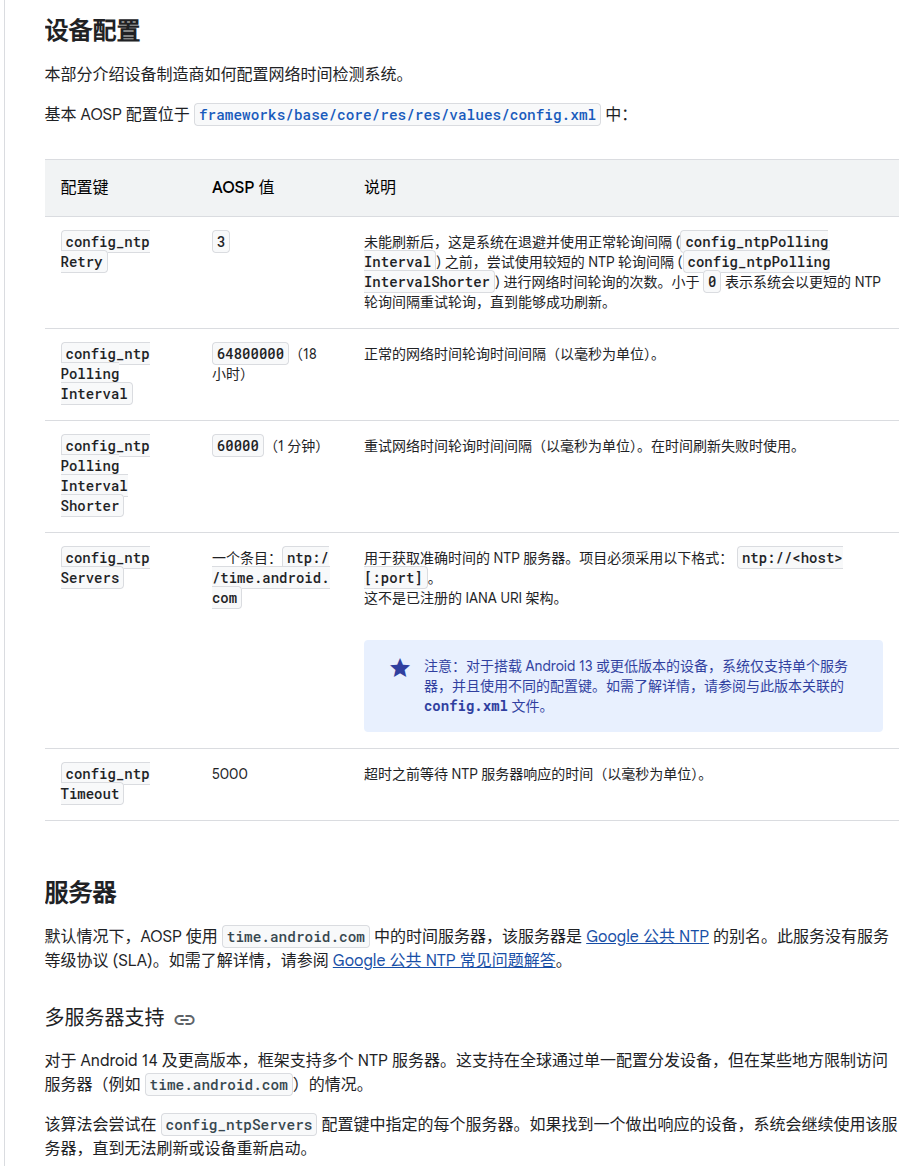
Android 手机的 NTP 时间同步(网络时间同步)主要依赖网络,但系统时间来源还包括其他方式,整体时间校准机制是多种来源的结合。具体可分为以下几类:
1. 网络 NTP 同步(最主要方式)
这是 Android 设备获取时间的核心方式,通过访问 NTP 服务器实现:
- 原理 :设备连接 Wi-Fi 或移动数据(蜂窝网络)时,会定期向预设的 NTP 服务器(如
time.android.com、厂商自定义服务器等)发送请求,获取标准时间并校准本地时间。 - 特点:依赖网络连接,精度通常在毫秒到秒级,是日常使用中最主要的时间来源。
2. GPS/位置服务(辅助时间来源)
GPS 不仅提供位置信息,也会同步时间:
- 原理:GPS 卫星内置高精度原子钟,设备接收 GPS 信号时,会同时获取卫星的精确时间(UTC 时间),并结合时区信息转换为本地时间。
- 特点 :
- 精度极高(毫秒级),不受网络限制,户外定位时自动同步。
- 通常作为网络同步的补充,尤其在网络不稳定或无网络时提供时间参考。
- 部分设备在开启"位置服务"后,会优先使用 GPS 时间校准系统时间。
3. 移动网络(蜂窝网络)时间
部分运营商的移动网络(如 4G/5G)会通过信令传递时间信息:
- 原理:设备接入蜂窝网络时,可能从基站获取时间(类似 NTP 的简化机制),尤其在早期 2G/3G 网络中更常见。
- 特点:精度较低(通常秒级),依赖运营商网络配置,现代设备更多以 NTP 同步为主。
4. 本地保存的时间(离线临时使用)
设备断电或重启时,会依赖内置的 RTC(实时时钟)芯片维持基本时间:
- 原理:RTC 芯片由设备内置电池供电,即使主电源关闭也能运行,保存最近同步的时间。
- 特点:精度低(可能每天偏差几秒到几分钟),仅作为离线时的临时时间来源,联网后会立即通过 NTP 或 GPS 校准。
总的来说, Android 手机的时间来源是多方式协同的:
- 主要来源:网络 NTP 同步(最常用,依赖网络)。
- 辅助来源:GPS 时间(高精度,依赖定位信号)、蜂窝网络时间(运营商提供)。
- fallback 机制:本地 RTC 时钟(离线时临时使用)。
系统会根据网络状态、定位信号强度等自动选择最优时间来源,确保时间准确性。例如:联网时优先用 NTP,户外定位时结合 GPS 校准,离线时依赖 RTC 并在联网后修正偏差。
NTP 服务:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/NetworkTimeUpdateService.java
java
public NetworkTimeUpdateService(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mTime = NtpTrustedTime.getInstance(context);
mAlarmManager = mContext.getSystemService(AlarmManager.class);
mTimeDetector = mContext.getSystemService(TimeDetector.class);
mCM = mContext.getSystemService(ConnectivityManager.class);
Intent pollIntent = new Intent(ACTION_POLL, null);
// Broadcast alarms sent by system are immutable
mPendingPollIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(mContext, POLL_REQUEST, pollIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE);
mPollingIntervalMs = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_ntpPollingInterval);
mPollingIntervalShorterMs = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_ntpPollingIntervalShorter);
mTryAgainTimesMax = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_ntpRetry);
mWakeLock = context.getSystemService(PowerManager.class).newWakeLock(
PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, TAG);
}
private void onPollNetworkTimeUnderWakeLock(int event) {
long currentElapsedRealtimeMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
// Force an NTP fix when outdated
NtpTrustedTime.TimeResult cachedNtpResult = mTime.getCachedTimeResult();
if (cachedNtpResult == null || cachedNtpResult.getAgeMillis(currentElapsedRealtimeMillis)
>= mPollingIntervalMs) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "Stale NTP fix; forcing refresh");
boolean isSuccessful = mTime.forceRefresh();
if (isSuccessful) {
mTryAgainCounter = 0;
} else {
String logMsg = "forceRefresh() returned false: cachedNtpResult=" + cachedNtpResult
+ ", currentElapsedRealtimeMillis=" + currentElapsedRealtimeMillis;
if (DBG) {
Log.d(TAG, logMsg);
}
mLocalLog.log(logMsg);
}
cachedNtpResult = mTime.getCachedTimeResult();
}
//....
}frameworks/base/core/java/android/util/NtpTrustedTime.java
java
@GuardedBy("this")
private NtpConnectionInfo getNtpConnectionInfo() {
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
final Resources res = mContext.getResources();
final String hostname;
if (mHostnameForTests != null) {
hostname = mHostnameForTests;
} else {
String serverGlobalSetting =
Settings.Global.getString(resolver, Settings.Global.NTP_SERVER);
if (serverGlobalSetting != null) {
hostname = serverGlobalSetting;
} else {
hostname = res.getString(com.android.internal.R.string.config_ntpServer);
}
}
final Integer port;
if (mPortForTests != null) {
port = mPortForTests;
} else {
port = SntpClient.STANDARD_NTP_PORT;
}
final int timeoutMillis;
if (mTimeoutForTests != null) {
timeoutMillis = (int) mTimeoutForTests.toMillis();
} else {
int defaultTimeoutMillis =
res.getInteger(com.android.internal.R.integer.config_ntpTimeout);
timeoutMillis = Settings.Global.getInt(
resolver, Settings.Global.NTP_TIMEOUT, defaultTimeoutMillis);
}
return TextUtils.isEmpty(hostname) ? null :
new NtpConnectionInfo(hostname, port, timeoutMillis);
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)
public boolean forceRefresh() {
synchronized (this) {
NtpConnectionInfo connectionInfo = getNtpConnectionInfo();
if (connectionInfo == null) {
// missing server config, so no NTP time available
if (LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "forceRefresh: invalid server config");
return false;
}
ConnectivityManager connectivityManager = mConnectivityManagerSupplier.get();
if (connectivityManager == null) {
if (LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "forceRefresh: no ConnectivityManager");
return false;
}
final Network network = connectivityManager.getActiveNetwork();
final NetworkInfo ni = connectivityManager.getNetworkInfo(network);
// This connectivity check is to avoid performing a DNS lookup for the time server on a
// unconnected network. There are races to obtain time in Android when connectivity
// changes, which means that forceRefresh() can be called by various components before
// the network is actually available. This led in the past to DNS lookup failures being
// cached (~2 seconds) thereby preventing the device successfully making an NTP request
// when connectivity had actually been established.
// A side effect of check is that tests that run a fake NTP server on the device itself
// will only be able to use it if the active network is connected, even though loopback
// addresses are actually reachable.
if (ni == null || !ni.isConnected()) {
if (LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "forceRefresh: no connectivity");
return false;
}
if (LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "forceRefresh() from cache miss");
final SntpClient client = new SntpClient();
final String serverName = connectionInfo.getServer();
final int port = connectionInfo.getPort();
final int timeoutMillis = connectionInfo.getTimeoutMillis();
if (client.requestTime(serverName, port, timeoutMillis, network)) {
long ntpCertainty = client.getRoundTripTime() / 2;
mTimeResult = new TimeResult(
client.getNtpTime(), client.getNtpTimeReference(), ntpCertainty);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}系统默认采用android的NTP服务器:
frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml
xml
<string translatable="false" name="config_ntpServer">2.android.pool.ntp.org</string>frameworks/base/core/java/android/provider/Settings.java
java
/** Preferred NTP server. {@hide} */
public static final String NTP_SERVER = "ntp_server";通常, 系统没有提供可视界面供用户设置NTP服务器的接口. 可以通过adb命令来设置:
bash
# 设置NTP服务器
adb shell settings put global "ntp_server" "ntp.aliyun.com"
# 关闭 和 打开 自动时间同步
adb shell settings put global "auto_time" 0
adb shell settings put global "auto_time" 1实际测试发现, AOSP中默认的NTP服务器地址, 经常是访问不上的, 所以, 可以考虑更换为aliyun的ntp服务器;
测试过程:
- 关闭自动设置时间(auto_time)
- 更改当前系统时间为任意非准确时间
- 关闭网络/有SIM卡可以拔出来
- 重启系统, 清除NTP缓存数据, 否则, 系统会从缓存的NTP数据来更新当前系统时间
- 启动后时间是错误的, 打开WIFI, 打开自动设置时间, 正常情况下系统时间成功更新
适用性
- 国内的手机厂商大部分采用的是自定义的NTP服务端
- 某些厂商的设备(比如Oculus Quest 系列)在国内水土不服, 建议修改为国内的服务器
- 某些特定的行业需要自主的NTP服务器.