利用Linux内核驱动开发,目前仅完成串口测试和摄像头测试
1、串口:以内核自带的串口驱动为基础,编写测试程序
uart.h
#ifndef __UART_H__
#define __UART_H__
#include <termios.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
// 打开串口设备并配置为115200波特率、8位数据位、无校验、1位停止位
int open_serial_port(const char *port);
// 写入数据到串口
int write_to_serial(int fd, const char *data, size_t length);
// 从串口读取数据
int read_from_serial(int fd, char *buffer, size_t buffer_size);
// 关闭串口设备
void close_serial_port(int fd);
#endif // TERMIOS_Huart.c
#include "uart.h"
int open_serial_port(const char *port) {
// 打开串口设备(阻塞模式)
int fd = open(port, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("Error opening serial port");
return -1;
}
// 获取当前串口配置
struct termios options;
if (tcgetattr(fd, &options) != 0) {
perror("tcgetattr failed");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
// 设置波特率为115200
cfsetispeed(&options, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&options, B115200);
// 配置数据位、停止位和校验位
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; // 清除数据位掩码
options.c_cflag |= CS8; // 8位数据位
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无校验位
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; // 1位停止位
// 启用接收和本地模式
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD);
// 设置原始输入模式(非规范模式)
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
// 禁用特殊输出处理
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
// 设置超时:立即返回(VMIN=0, VTIME=0)
//options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
//options.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
// 修改 c_cc 配置,启用阻塞读
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; // 至少读取1个字符才返回
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 10; // 等待超时:1秒(10 * 0.1秒)
// 应用配置
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &options) != 0) {
perror("tcsetattr failed");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
// 清空缓冲区
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
return fd;
}
int write_to_serial(int fd, const char *data, size_t length) {
ssize_t bytes_written = write(fd, data, length);
if (bytes_written < 0) {
perror("Error writing to serial port");
}
return bytes_written;
}
int read_from_serial(int fd, char *buffer, size_t buffer_size) {
ssize_t bytes_read = read(fd, buffer, buffer_size - 1);
if (bytes_read < 0) {
perror("Error reading from serial port");
return -1;
}
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
return bytes_read;
}
void close_serial_port(int fd) {
if (fd >= 0) {
close(fd);
}
}main.c
#include "uart.h"
int main(void)
{
int uartfd = 0;
int nret = 0;
char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};
uartfd = open_serial_port("/dev/ttymxc2");
if (-1 == uartfd)
{
printf("open_serial_port failed\n");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
write_to_serial(uartfd, "hello world", 11);
memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));
nret = read_from_serial(uartfd, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));
printf("nret = %d, tmpbuff = %s\n", nret, tmpbuff);
sleep(1);
}
close_serial_port(uartfd);
return 0;
}2、摄像头ov5640测试
一、修改设备树
1、 在i2c2下添加ov5640信息
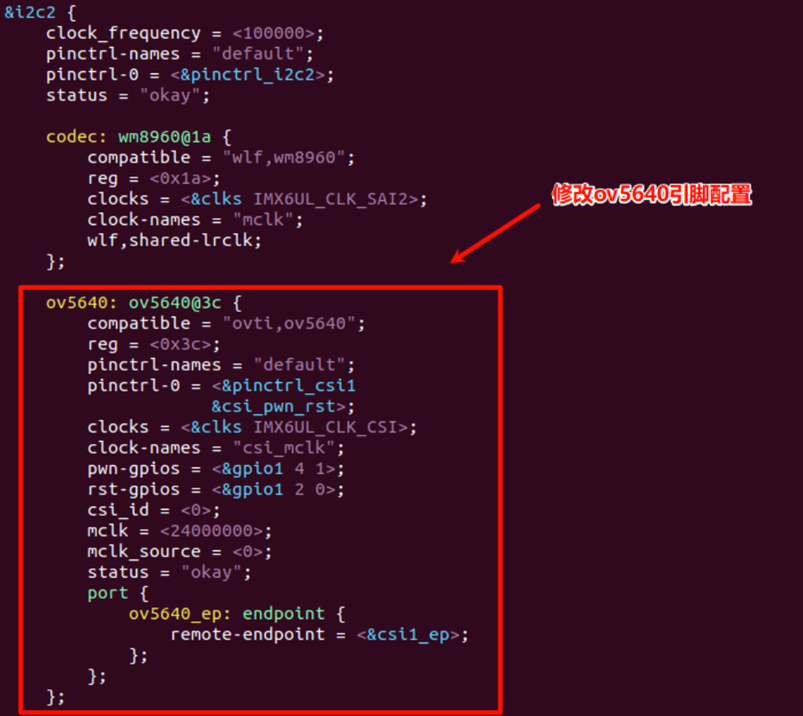
2、 设置pinctrl子系统中的摄像头复位引脚
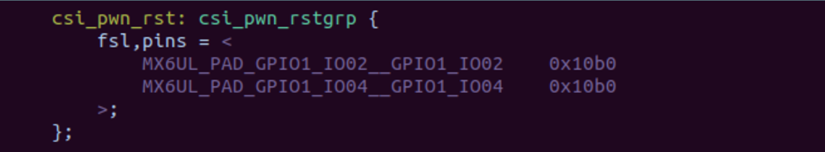
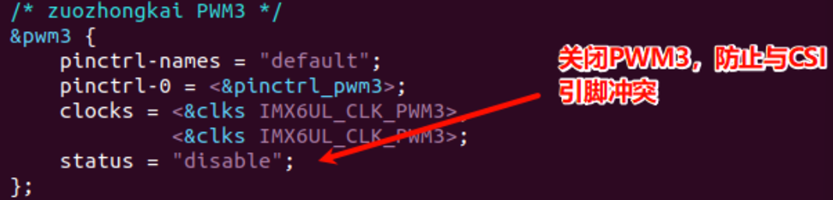
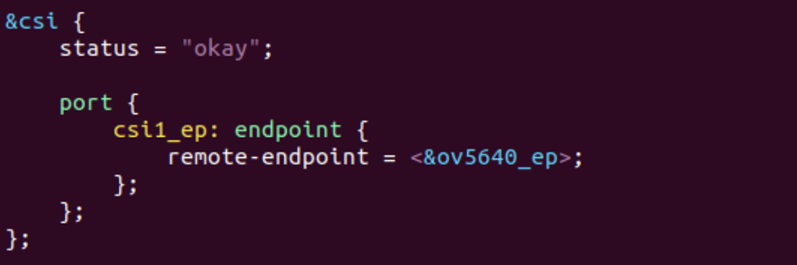
3、 开启CSI接口配置
二、修改内核加入ov5640相关驱动模块:
1、通过图形界面修改
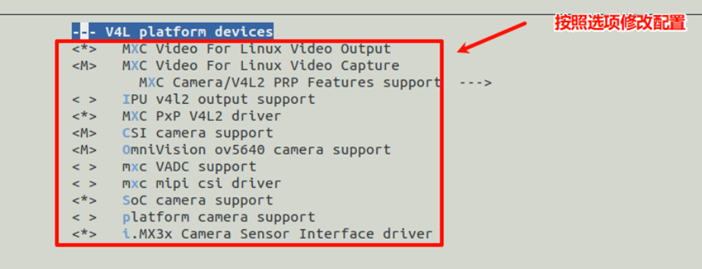
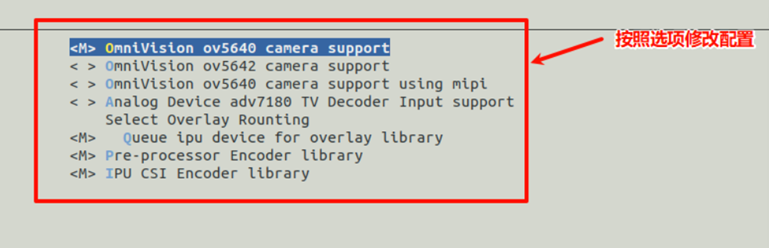
-
重新编译内核、设备树、驱动模块
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- zImage
make dtbs
make modules -
将设备树和内核镜像拷贝到tftp管理目录下
cp arch/arm/boot/dts/imx6ull-alientek-emmc.dtb ~/tftpboot
cp arch/arm/boot/zImage ~/tftpboot -
将所有的内核驱动模块安装到文件系统下
make INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/home/linux/nfs/rootfs modules_install
-
重新启动开发板,并插上ov5640摄像头
-
在开发板端加载摄像头内核驱动模块
cd /lib/modules/4.1.15 depmod -a
modprobe mx6s_capture.ko modprobe ov5640_camera.ko -
查看是否生成摄像头设备节点
ls /dev/video1。
三、编写测试文件测试摄像头功能