📖 前言
之前做项目时需要实现计时器功能,一直都在用 setTimeout 这种常规方式。但是在使用过程中发现,这种方式的计时有时候会不准确,特别是长时间运行后。后来了解到 用requestAnimationFrame 实现这个方案,测试后发现效果确实好很多。
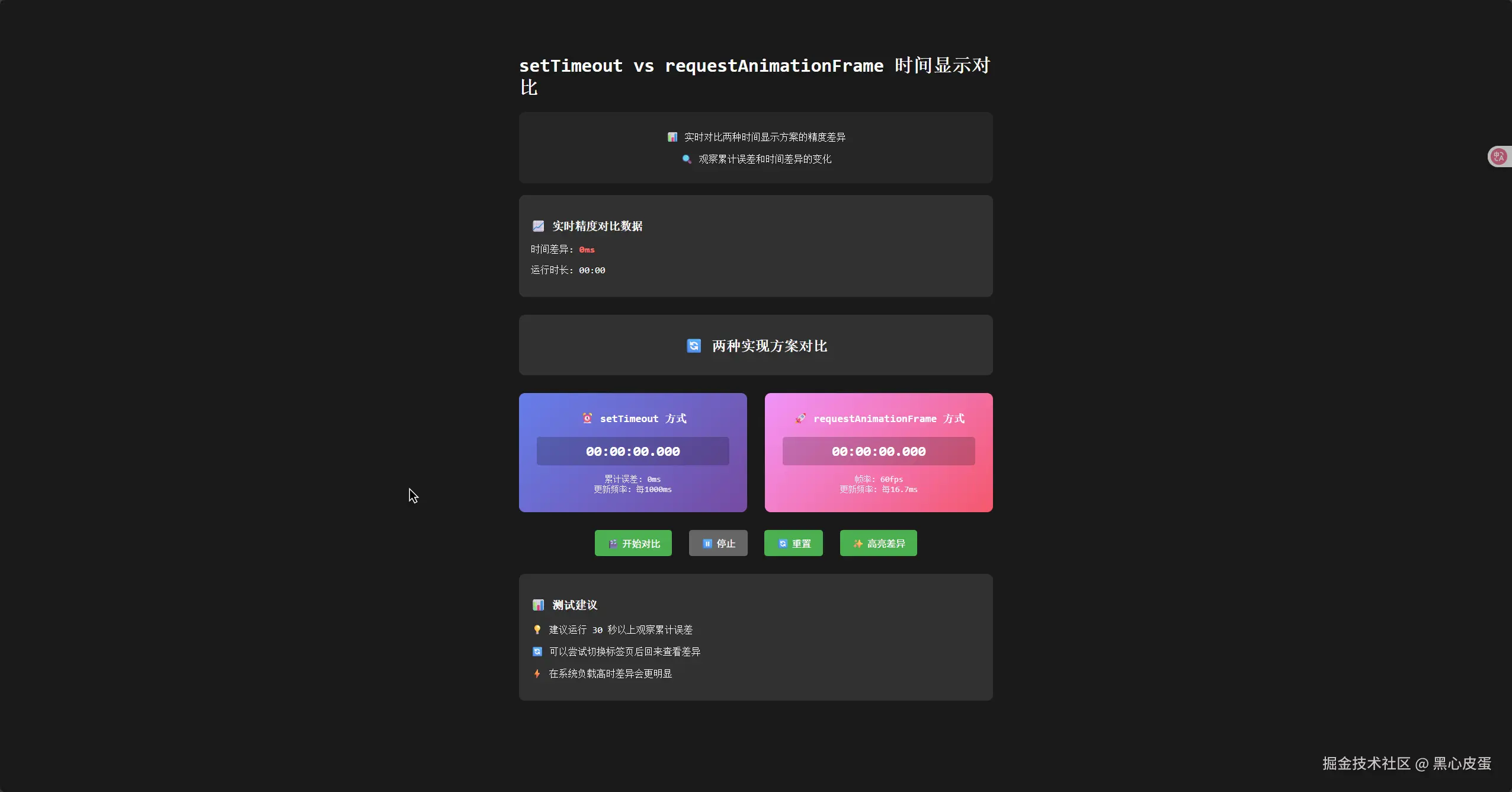
我让 ai 做了一个 demo 来对比两种方案的差异
⏰ setTimeout 实现计时器
最常见的实现方式是使用 setTimeout 递归调用:
javascript
// setTimeout 方式的的实现
let timerState = {
startTime: 0,
setTimeoutId: null
}
// 格式化时间显示
function formatTime(ms) {
const minutes = Math.floor(ms / 60000)
const seconds = Math.floor((ms % 60000) / 1000)
const milliseconds = Math.floor(ms % 1000)
return `${minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds
.toString()
.padStart(2, '0')}.${milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`
}
// setTimeout 计时循环
function setTimeoutLoop() {
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - timerState.startTime
document.getElementById('timer').textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
// 每1000ms更新一次
timerState.setTimeoutId = setTimeout(setTimeoutLoop, 1000)
}
// 开始计时
function startTimer() {
timerState.startTime = performance.now()
setTimeoutLoop()
}🚀 requestAnimationFrame 实现计时器
相比之下,requestAnimationFrame 的实现方式:
javascript
let rafState = {
startTime: 0,
rafId: null
}
// requestAnimationFrame 计时循环
function rafLoop() {
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - rafState.startTime
document.getElementById('timer').textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
// 请求下一帧
rafState.rafId = requestAnimationFrame(rafLoop)
}
// 开始计时
function startRAFTimer() {
rafState.startTime = performance.now()
rafLoop()
}这种方式提供了更平滑、更精确的计时效果。
📊 对比效果
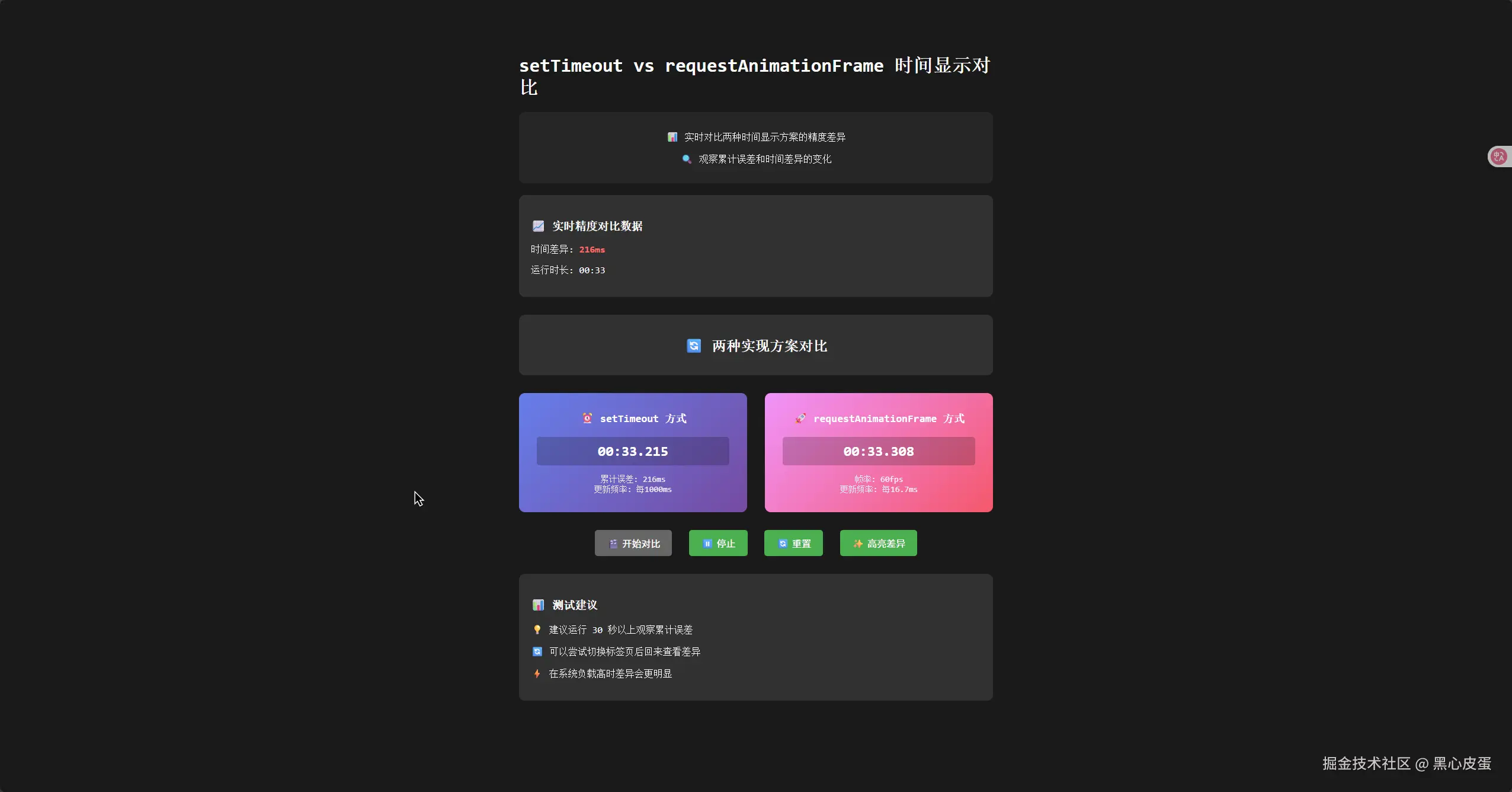
我做了一个对比测试,同时运行两种方式的计时器:
- setTimeout:运行 30 秒后,累计误差通常在 100-500ms 之间
- requestAnimationFrame:运行相同时间,误差基本保持在 10ms 以内
特别是在以下情况下,差异更加明显:
- 切换浏览器标签页后再回来
- 系统负载较高时
- 长时间运行(超过几分钟)
运行 3 分钟之后的差异

🤔 为什么会有这样的差异?
⚠️ setTimeout 的局限性
- 执行时机不精确
setTimeout(fn, 1000)只是告诉浏览器"至少 1000ms 后执行"- 实际执行时间受事件循环、其他任务影响
- 每次的小误差会累积,越来越不准确
- 浏览器优化策略
- 后台标签页会被限制到最小 1000ms 间隔
- 系统负载高时会延迟执行
- 移动设备上为了省电会进一步节流
✨ requestAnimationFrame 的优势
-
与显示器同步
- 根据显示器刷新率执行(通常 60fps)
- 每帧都会执行,提供连续平滑的更新
- 基于
performance.now()的高精度时间戳
-
浏览器原生优化
- 标签页不可见时自动暂停,节省资源
- 不会过度渲染,避免不必要的计算
- 更适合 UI 更新和动画场景
🎬 演示用的 DEMO 代码
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>setTimeout vs requestAnimationFrame 时间显示对比演示</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Monaco', 'Consolas', monospace;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 50px auto;
padding: 20px;
background: #1a1a1a;
color: #fff;
}
.container {
display: flex;
gap: 30px;
margin: 30px 0;
}
.timer-box {
flex: 1;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
.setTimeout-box {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #667eea 0%, #764ba2 100%);
}
.raf-box {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #f093fb 0%, #f5576c 100%);
}
.timer-title {
font-size: 18px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.timer-display {
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 15px 0;
padding: 10px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
border-radius: 5px;
}
.stats {
font-size: 14px;
margin-top: 15px;
opacity: 0.9;
}
.controls {
text-align: center;
margin: 30px 0;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
margin: 0 10px;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
background: #4caf50;
color: white;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
}
button:hover {
background: #45a049;
}
button:disabled {
background: #666;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
.accuracy-info {
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
margin: 20px 0;
}
.difference {
color: #ff6b6b;
font-weight: bold;
}
.description {
text-align: center;
margin: 20px 0;
padding: 15px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.05);
border-radius: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.method-title {
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 10px;
margin: 30px 0 20px 0;
text-align: center;
}
.highlight {
animation: pulse 2s infinite;
}
@keyframes pulse {
0% {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0 rgba(255, 107, 107, 0.7);
}
70% {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 10px rgba(255, 107, 107, 0);
}
100% {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0 rgba(255, 107, 107, 0);
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>setTimeout vs requestAnimationFrame 时间显示对比</h1>
<div class="description">
<p>📊 实时对比两种时间显示方案的精度差异</p>
<p>🔍 观察累计误差和时间差异的变化</p>
</div>
<div class="accuracy-info">
<h3>📈 实时精度对比数据</h3>
<div id="realTimeComparison">
<p>时间差异: <span class="difference" id="timeDifference">0ms</span></p>
<p>运行时长: <span id="runningTime">00:00</span></p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="method-title">
<h2>🔄 两种实现方案对比</h2>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="timer-box setTimeout-box">
<div class="timer-title">⏰ setTimeout 方式</div>
<div class="timer-display" id="setTimeoutTimer">00:00:00.000</div>
<div class="stats">
<div>累计误差: <span id="setTimeoutError">0</span>ms</div>
<div>更新频率: 每1000ms</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="timer-box raf-box">
<div class="timer-title">🚀 requestAnimationFrame 方式</div>
<div class="timer-display" id="rafTimer">00:00:00.000</div>
<div class="stats">
<div>帧率: <span id="rafFPS">60</span>fps</div>
<div>更新频率: 每16.7ms</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="controls">
<button id="startBtn">🎬 开始对比</button>
<button id="stopBtn" disabled>⏸️ 停止</button>
<button id="resetBtn">🔄 重置</button>
<button id="highlightBtn">✨ 高亮差异</button>
</div>
<div class="accuracy-info">
<h3>📊 测试建议</h3>
<div>
<p>💡 建议运行 30 秒以上观察累计误差</p>
<p>🔄 可以尝试切换标签页后回来查看差异</p>
<p>⚡ 在系统负载高时差异会更明显</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 全局状态管理
let timerState = {
isRunning: false,
startTime: 0,
setTimeoutId: null,
rafId: null,
setTimeoutError: 0,
globalStartTime: 0
}
// DOM元素引用
let elements = {}
// 初始化DOM元素引用
function initElements() {
elements = {
setTimeoutTimer: document.getElementById('setTimeoutTimer'),
rafTimer: document.getElementById('rafTimer'),
startBtn: document.getElementById('startBtn'),
stopBtn: document.getElementById('stopBtn'),
resetBtn: document.getElementById('resetBtn'),
highlightBtn: document.getElementById('highlightBtn'),
timeDifference: document.getElementById('timeDifference'),
setTimeoutErrorEl: document.getElementById('setTimeoutError'),
rafFPSEl: document.getElementById('rafFPS'),
runningTimeEl: document.getElementById('runningTime')
}
}
// 绑定按钮点击事件
function bindEvents() {
elements.startBtn.addEventListener('click', handleStart)
elements.stopBtn.addEventListener('click', handleStop)
elements.resetBtn.addEventListener('click', handleReset)
elements.highlightBtn.addEventListener('click', handleToggleHighlight)
}
// 格式化时间显示 (毫秒 -> MM:SS.sss)
function formatTime(ms) {
const totalMs = Math.floor(ms)
const totalSeconds = Math.floor(totalMs / 1000)
const minutes = Math.floor(totalSeconds / 60)
const seconds = totalSeconds % 60
const milliseconds = totalMs % 1000
return `${minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds
.toString()
.padStart(2, '0')}.${milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`
}
// setTimeout 方式的计时循环
function setTimeoutLoop() {
if (!timerState.isRunning) return
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - timerState.startTime
elements.setTimeoutTimer.textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
// 计算累计误差:实际经过时间 vs 期望时间(每秒整数倍)
const expectedTime = Math.floor(elapsed / 1000) * 1000
timerState.setTimeoutError = Math.abs(elapsed - expectedTime)
elements.setTimeoutErrorEl.textContent =
timerState.setTimeoutError.toFixed(0)
// 固定1000ms延迟,展示setTimeout的真实特性
timerState.setTimeoutId = setTimeout(setTimeoutLoop, 1000)
}
// requestAnimationFrame 方式的计时循环
function rafLoop() {
if (!timerState.isRunning) return
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - timerState.startTime
elements.rafTimer.textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
// 显示固定帧率60fps(简化代码)
elements.rafFPSEl.textContent = '60'
// 更新全局运行时间
const globalElapsed = now - timerState.globalStartTime
const totalSeconds = Math.floor(globalElapsed / 1000)
const minutes = Math.floor(totalSeconds / 60)
const seconds = totalSeconds % 60
elements.runningTimeEl.textContent = `${minutes
.toString()
.padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds.toString().padStart(2, '0')}`
// 显示与setTimeout的时间差异
elements.timeDifference.textContent =
timerState.setTimeoutError.toFixed(0) + 'ms'
// 请求下一帧动画
timerState.rafId = requestAnimationFrame(rafLoop)
}
// 开始计时处理函数
function handleStart() {
if (timerState.isRunning) return
timerState.isRunning = true
timerState.startTime = performance.now()
timerState.globalStartTime = performance.now()
// 更新按钮状态
elements.startBtn.disabled = true
elements.stopBtn.disabled = false
// 同时启动两种计时方式进行对比
setTimeoutLoop()
rafLoop()
}
// 停止计时处理函数
function handleStop() {
timerState.isRunning = false
// 清理setTimeout
if (timerState.setTimeoutId) {
clearTimeout(timerState.setTimeoutId)
timerState.setTimeoutId = null
}
// 清理requestAnimationFrame
if (timerState.rafId) {
cancelAnimationFrame(timerState.rafId)
timerState.rafId = null
}
// 更新按钮状态
elements.startBtn.disabled = false
elements.stopBtn.disabled = true
}
// 重置处理函数
function handleReset() {
handleStop()
// 重置显示内容
elements.setTimeoutTimer.textContent = '00:00:00.000'
elements.rafTimer.textContent = '00:00:00.000'
// 重置状态
timerState.setTimeoutError = 0
elements.setTimeoutErrorEl.textContent = '0'
elements.rafFPSEl.textContent = '60'
elements.timeDifference.textContent = '0ms'
elements.runningTimeEl.textContent = '00:00'
}
// 切换高亮效果处理函数
function handleToggleHighlight() {
const timerBoxes = document.querySelectorAll('.timer-box')
timerBoxes.forEach((box) => {
box.classList.toggle('highlight')
})
// 3秒后自动移除高亮
setTimeout(() => {
timerBoxes.forEach((box) => {
box.classList.remove('highlight')
})
}, 3000)
}
// 初始化应用
function initApp() {
initElements()
bindEvents()
handleReset() // 初始化状态
}
// 页面加载完成后自动初始化
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', initApp)
</script>
</body>
</html>🛠️ requestAnimationFrame 版计时工具
最后我基于requestAnimationFrame做了一个计时器工具
javascript
function createTimer(elementId, options = {}) {
const state = {
element: document.getElementById(elementId),
startTime: performance.now(),
animationId: null,
showMilliseconds: options.showMilliseconds || false
}
// 格式化时间显示
function formatTime(elapsed) {
const minutes = Math.floor(elapsed / 60000)
const seconds = Math.floor((elapsed % 60000) / 1000)
const milliseconds = Math.floor(elapsed % 1000)
let timeStr = `${minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds
.toString()
.padStart(2, '0')}`
if (state.showMilliseconds) {
timeStr += `.${milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`
}
return timeStr
}
// 更新时间显示
function update() {
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - state.startTime
state.element.textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
state.animationId = requestAnimationFrame(update)
}
// 立即开始
update()
return state.element
}
// 使用示例
const timer = createTimer('timer', {
showMilliseconds: true
})使用代码
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>计时器工具调用演示</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
max-width: 600px;
margin: 50px auto;
padding: 20px;
background: #f5f5f5;
}
.timer {
font-size: 48px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
background: #fff;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
margin: 20px 0;
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>计时器工具调用演示</h1>
<div id="timer" class="timer">00:00.000</div>
<script>
function createTimer(elementId, options = {}) {
const state = {
element: document.getElementById(elementId),
startTime: performance.now(),
animationId: null,
showMilliseconds: options.showMilliseconds || false
}
// 格式化时间显示
function formatTime(elapsed) {
const minutes = Math.floor(elapsed / 60000)
const seconds = Math.floor((elapsed % 60000) / 1000)
const milliseconds = Math.floor(elapsed % 1000)
let timeStr = `${minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds
.toString()
.padStart(2, '0')}`
if (state.showMilliseconds) {
timeStr += `.${milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`
}
return timeStr
}
// 更新时间显示
function update() {
const now = performance.now()
const elapsed = now - state.startTime
state.element.textContent = formatTime(elapsed)
state.animationId = requestAnimationFrame(update)
}
// 立即开始
update()
return state.element
}
// 调用计时器
const timer = createTimer('timer', {
showMilliseconds: true
})
</script>
</body>
</html>