mongo插入单条文档insert()
cpp
> db.user.insert({
... "name": "alice",
... "age": 28
... });
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
>MongoDB插入文档代码调用链如下:
- mongo/db/commands/write_commands/write_commands.cpp的CmdInsert类
- mongo/db/commands/write_commands/write_commands.cpp的runImpl
- mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的performInserts
- mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的insertBatchAndHandleErrors
- mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的insertDocuments
- mongo/db/catalog/collection_impl.cpp的insertDocuments
- mongo/db/catalog/collection_impl.cpp的_insertDocuments
- mongo/db/storage/wiredtiger/wiredtiger_record_store.cpp的insertRecords
- mongo/db/storage/wiredtiger/wiredtiger_record_store.cpp的_insertRecords
mongo/db/commands/write_commands/write_commands.cpp的CmdInsert代码如下:
cpp
class CmdInsert final : public WriteCommand {
public:
CmdInsert() : WriteCommand("insert") {}
private:
class Invocation final : public InvocationBase {
public:
Invocation(const WriteCommand* cmd, const OpMsgRequest& request)
: InvocationBase(cmd, request), _batch(InsertOp::parse(request)) {}
private:
NamespaceString ns() const override {
return _batch.getNamespace();
}
...
void runImpl(OperationContext* opCtx, BSONObjBuilder& result) const override {
auto reply = performInserts(opCtx, _batch);
serializeReply(opCtx,
ReplyStyle::kNotUpdate,
!_batch.getWriteCommandBase().getOrdered(),
_batch.getDocuments().size(),
std::move(reply),
&result);
}
write_ops::Insert _batch;
};
std::unique_ptr<CommandInvocation> parse(OperationContext*,
const OpMsgRequest& request) override {
return std::make_unique<Invocation>(this, request);
}
...
std::string help() const final {
return "insert documents";
}
} cmdInsert;mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的方法performInserts代码:
1、获取系统阈值, maxBatchSize = internalInsertMaxBatchSize.load()默认64,batch一次最多插入64个文档; maxBatchBytes = write_ops::insertVectorMaxBytes默认256,batch一次最多插入N个文档大小小于256KB。
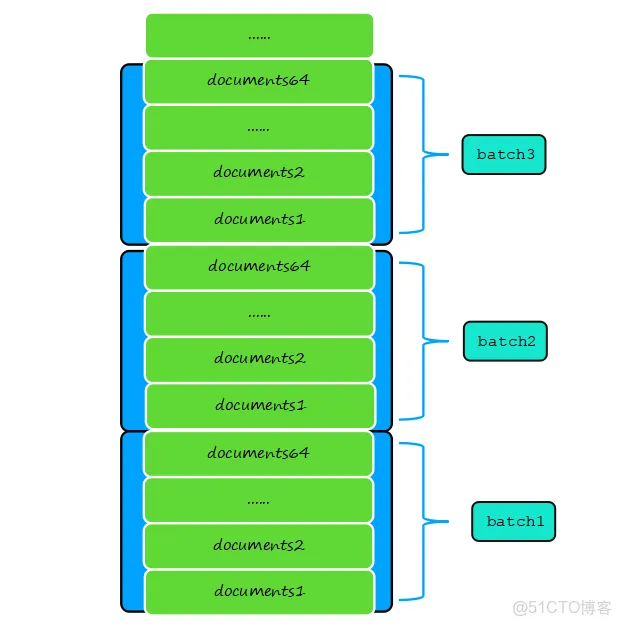
2、循环wholeOp.getDocuments()文档集合,将遍历文档放入batch中,fixDocumentForInsert验证每个文档参数合法性,重要是系统字段_id生成。
3、循环wholeOp.getDocuments()文档集合,将遍历文档放入batch中,batch满足两个阀值其中一个就insertBatchAndHandleErrors插入到数据库中。
cpp
WriteResult performInserts(OperationContext* opCtx,
const write_ops::Insert& wholeOp,
bool fromMigrate) {
// Insert performs its own retries, so we should only be within a WriteUnitOfWork when run in a
// transaction.
auto txnParticipant = TransactionParticipant::get(opCtx);
invariant(!opCtx->lockState()->inAWriteUnitOfWork() ||
(txnParticipant && opCtx->inMultiDocumentTransaction()));
auto& curOp = *CurOp::get(opCtx);
ON_BLOCK_EXIT([&] {
// This is the only part of finishCurOp we need to do for inserts because they reuse the
// top-level curOp. The rest is handled by the top-level entrypoint.
curOp.done();
Top::get(opCtx->getServiceContext())
.record(opCtx,
wholeOp.getNamespace().ns(),
LogicalOp::opInsert,
Top::LockType::WriteLocked,
durationCount<Microseconds>(curOp.elapsedTimeExcludingPauses()),
curOp.isCommand(),
curOp.getReadWriteType());
});
{
stdx::lock_guard<Client> lk(*opCtx->getClient());
curOp.setNS_inlock(wholeOp.getNamespace().ns());
curOp.setLogicalOp_inlock(LogicalOp::opInsert);
curOp.ensureStarted();
curOp.debug().additiveMetrics.ninserted = 0;
}
uassertStatusOK(userAllowedWriteNS(wholeOp.getNamespace()));
DisableDocumentValidationIfTrue docValidationDisabler(
opCtx, wholeOp.getWriteCommandBase().getBypassDocumentValidation());
LastOpFixer lastOpFixer(opCtx, wholeOp.getNamespace());
WriteResult out;
out.results.reserve(wholeOp.getDocuments().size());
bool containsRetry = false;
ON_BLOCK_EXIT([&] { updateRetryStats(opCtx, containsRetry); });
size_t stmtIdIndex = 0;
size_t bytesInBatch = 0;
std::vector<InsertStatement> batch;
const size_t maxBatchSize = internalInsertMaxBatchSize.load();
const size_t maxBatchBytes = write_ops::insertVectorMaxBytes;
batch.reserve(std::min(wholeOp.getDocuments().size(), maxBatchSize));
std::cout << "conca " << "maxBatchSize:"<<maxBatchSize<<std::endl;
std::cout << "conca " << "maxBatchBytes:"<<maxBatchBytes<< std::endl;
for (auto&& doc : wholeOp.getDocuments()) {
const bool isLastDoc = (&doc == &wholeOp.getDocuments().back());
auto fixedDoc = fixDocumentForInsert(opCtx->getServiceContext(), doc);
if (!fixedDoc.isOK()) {
// Handled after we insert anything in the batch to be sure we report errors in the
// correct order. In an ordered insert, if one of the docs ahead of us fails, we should
// behave as-if we never got to this document.
} else {
const auto stmtId = getStmtIdForWriteOp(opCtx, wholeOp, stmtIdIndex++);
if (opCtx->getTxnNumber()) {
if (!opCtx->inMultiDocumentTransaction() &&
txnParticipant.checkStatementExecutedNoOplogEntryFetch(stmtId)) {
containsRetry = true;
RetryableWritesStats::get(opCtx)->incrementRetriedStatementsCount();
out.results.emplace_back(makeWriteResultForInsertOrDeleteRetry());
continue;
}
}
BSONObj toInsert = fixedDoc.getValue().isEmpty() ? doc : std::move(fixedDoc.getValue());
batch.emplace_back(stmtId, toInsert);
bytesInBatch += batch.back().doc.objsize();
if (!isLastDoc && batch.size() < maxBatchSize && bytesInBatch < maxBatchBytes)
continue; // Add more to batch before inserting.
}
bool canContinue =
insertBatchAndHandleErrors(opCtx, wholeOp, batch, &lastOpFixer, &out, fromMigrate);
batch.clear(); // We won't need the current batch any more.
bytesInBatch = 0;
if (canContinue && !fixedDoc.isOK()) {
globalOpCounters.gotInsert();
ServerWriteConcernMetrics::get(opCtx)->recordWriteConcernForInsert(
opCtx->getWriteConcern());
try {
uassertStatusOK(fixedDoc.getStatus());
MONGO_UNREACHABLE;
} catch (const DBException& ex) {
canContinue = handleError(
opCtx, ex, wholeOp.getNamespace(), wholeOp.getWriteCommandBase(), &out);
}
}
if (!canContinue)
break;
}
return out;
}其中fixDocumentForInsert方法验证参数,如果_id没有值,则MongoDB生成系统字符串对象ObjectId,具体代码是 b.appendOID("_id", nullptr, true)。
MongoDB的ObjectId介绍:
- 插入一条数据系统都会自动插入一个_id键,键值不可以重复,它可以是任何类型的,也可以手动的插入,默认情况下它的数据类型是ObjectId,由于MongoDB在设计之初就是用作分布式数据库,所以使用ObjectId可以避免不同数据库中_id的重复(如果使用自增的方式在分布式系统中就会出现重复的_id的值)。
- objectId使用12字节的存储空间,每个字节可以存储两个十六进制数字,所以一共可以存储24个十六进制数字组成的字符串,在这24个字符串中,前8位表示时间戳,接下来6位是一个机器码,接下来4位表示进程id,最后6位表示计数器。示意图如下:
其中包括4-byte Unix 时间戳,3-byte 机器 ID,2-byte 进程 ID,3-byte 计数器(初始化随机)。
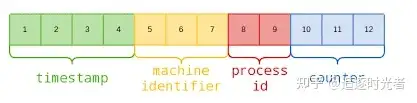
601e2b6b aa203c c89f 2d31aa
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
时间戳 机器码 进程id 计数器
mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的方法insertBatchAndHandleErrors。一批数据通过分批拆分存入多个batch后,调用insertBatchAndHandleErrors()接口来完成单个batch的数据写入。整个batch数据写入可以在一个transaction事务完成,也可以一条数据一个事务来完成写入,具体核心代码实现如下:
cpp
bool insertBatchAndHandleErrors(OperationContext* opCtx,
const write_ops::Insert& wholeOp,
std::vector<InsertStatement>& batch,
LastOpFixer* lastOpFixer,
WriteResult* out,
bool fromMigrate) {
if (batch.empty())
return true;
auto& curOp = *CurOp::get(opCtx);
CurOpFailpointHelpers::waitWhileFailPointEnabled(
&hangDuringBatchInsert,
opCtx,
"hangDuringBatchInsert",
[&wholeOp]() {
log() << "batch insert - hangDuringBatchInsert fail point enabled for namespace "
<< wholeOp.getNamespace()
<< ". Blocking "
"until fail point is disabled.";
},
true, // Check for interrupt periodically.
wholeOp.getNamespace());
if (MONGO_unlikely(failAllInserts.shouldFail())) {
uasserted(ErrorCodes::InternalError, "failAllInserts failpoint active!");
}
boost::optional<AutoGetCollection> collection;
auto acquireCollection = [&] {
while (true) {
collection.emplace(
opCtx,
wholeOp.getNamespace(),
fixLockModeForSystemDotViewsChanges(wholeOp.getNamespace(), MODE_IX));
if (collection->getCollection())
break;
collection.reset(); // unlock.
makeCollection(opCtx, wholeOp.getNamespace());
}
curOp.raiseDbProfileLevel(collection->getDb()->getProfilingLevel());
assertCanWrite_inlock(opCtx, wholeOp.getNamespace(), collection->getCollection());
CurOpFailpointHelpers::waitWhileFailPointEnabled(
&hangWithLockDuringBatchInsert, opCtx, "hangWithLockDuringBatchInsert");
};
try {
acquireCollection();
auto txnParticipant = TransactionParticipant::get(opCtx);
auto inTxn = txnParticipant && opCtx->inMultiDocumentTransaction();
LOG(1) << "conca collection->getCollection()->isCapped();"<<collection->getCollection()->isCapped();
LOG(1) << "conca batch.size();"<<batch.size();
if (!collection->getCollection()->isCapped() && !inTxn && batch.size() > 1) {
// First try doing it all together. If all goes well, this is all we need to do.
// See Collection::_insertDocuments for why we do all capped inserts one-at-a-time.
lastOpFixer->startingOp();
insertDocuments(
opCtx, collection->getCollection(), batch.begin(), batch.end(), fromMigrate);
lastOpFixer->finishedOpSuccessfully();
globalOpCounters.gotInserts(batch.size());
ServerWriteConcernMetrics::get(opCtx)->recordWriteConcernForInserts(
opCtx->getWriteConcern(), batch.size());
SingleWriteResult result;
result.setN(1);
std::fill_n(std::back_inserter(out->results), batch.size(), std::move(result));
curOp.debug().additiveMetrics.incrementNinserted(batch.size());
return true;
}
} catch (const DBException&) {
// Ignore this failure and behave as if we never tried to do the combined batch
// insert. The loop below will handle reporting any non-transient errors.
collection.reset();
}
LOG(1) << "conca Try to insert the batch one-at-a-time;";
// Try to insert the batch one-at-a-time. This path is executed for singular batches,
// multi-statement transactions, capped collections, and if we failed all-at-once inserting.
for (auto it = batch.begin(); it != batch.end(); ++it) {
globalOpCounters.gotInsert();
ServerWriteConcernMetrics::get(opCtx)->recordWriteConcernForInsert(
opCtx->getWriteConcern());
try {
LOG(1) << "conca writeConflictRetry;";
writeConflictRetry(opCtx, "insert", wholeOp.getNamespace().ns(), [&] {
try {
if (!collection)
acquireCollection();
// Transactions are not allowed to operate on capped collections.
uassertStatusOK(
checkIfTransactionOnCappedColl(opCtx, collection->getCollection()));
lastOpFixer->startingOp();
insertDocuments(opCtx, collection->getCollection(), it, it + 1, fromMigrate);
lastOpFixer->finishedOpSuccessfully();
SingleWriteResult result;
result.setN(1);
out->results.emplace_back(std::move(result));
curOp.debug().additiveMetrics.incrementNinserted(1);
} catch (...) {
// Release the lock following any error if we are not in multi-statement
// transaction. Among other things, this ensures that we don't sleep in the WCE
// retry loop with the lock held.
// If we are in multi-statement transaction and under a WUOW, we will
// not actually release the lock.
collection.reset();
throw;
}
});
} catch (const DBException& ex) {
bool canContinue =
handleError(opCtx, ex, wholeOp.getNamespace(), wholeOp.getWriteCommandBase(), out);
if (!canContinue) {
// Failed in ordered batch, or in a transaction, or from some unrecoverable error.
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}一批batch数据(假设64条)写入过程,如果不是capped固定集合,则这64条数据首先放入一个transaction事务中完成写入,writeConflictRetry里面会执行{}中的函数体。如果写入异常,判断canContinue =handleError()是否继续一个事务一条数据写入。
mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp中的方法insertDocuments把单条文档插入,核心代码如下:WriteUnitOfWork wuow(opCtx)事务开始;把数组begin到end之间的所有doc文档数据放入该事务中insertDocuments;wuow.commit()事务提交。
cpp
void insertDocuments(OperationContext* opCtx,
Collection* collection,
std::vector<InsertStatement>::iterator begin,
std::vector<InsertStatement>::iterator end,
bool fromMigrate) {
WriteUnitOfWork wuow(opCtx);
...
LOG(1) << "conca collection->insertDocuments" ;
uassertStatusOK(
collection->insertDocuments(opCtx, begin, end, &CurOp::get(opCtx)->debug(), fromMigrate));
wuow.commit();
}上面从mongo/db/ops/write_ops_exec.cpp数据库层转移到集合层,调用的是集合插入文档方法collection->insertDocuments。
mongo/db/catalog/collection_impl.cpp的方法insertDocuments
cpp
Status CollectionImpl::insertDocuments(OperationContext* opCtx,
const std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator begin,
const std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator end,
OpDebug* opDebug,
bool fromMigrate) {
LOG(1) << "conca CollectionImpl::insertDocuments" ;
auto status = checkFailCollectionInsertsFailPoint(_ns, (begin != end ? begin->doc : BSONObj()));
if (!status.isOK()) {
return status;
}
// Should really be done in the collection object at creation and updated on index create.
const bool hasIdIndex = _indexCatalog->findIdIndex(opCtx);
for (auto it = begin; it != end; it++) {
if (hasIdIndex && it->doc["_id"].eoo()) {
return Status(ErrorCodes::InternalError,
str::stream()
<< "Collection::insertDocument got document without _id for ns:"
<< _ns);
}
auto status = checkValidation(opCtx, it->doc);
if (!status.isOK())
return status;
}
const SnapshotId sid = opCtx->recoveryUnit()->getSnapshotId();
status = _insertDocuments(opCtx, begin, end, opDebug);
if (!status.isOK()) {
return status;
}
invariant(sid == opCtx->recoveryUnit()->getSnapshotId());
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->onInserts(
opCtx, ns(), uuid(), begin, end, fromMigrate);
opCtx->recoveryUnit()->onCommit(
[this](boost::optional<Timestamp>) { notifyCappedWaitersIfNeeded(); });
hangAfterCollectionInserts.executeIf(
[&](const BSONObj& data) {
const auto& firstIdElem = data["first_id"];
std::string whenFirst;
if (firstIdElem) {
whenFirst += " when first _id is ";
whenFirst += firstIdElem.str();
}
log() << "hangAfterCollectionInserts fail point enabled for " << _ns << whenFirst
<< ". Blocking until fail point is disabled.";
hangAfterCollectionInserts.pauseWhileSet(opCtx);
},
[&](const BSONObj& data) {
const auto& collElem = data["collectionNS"];
const auto& firstIdElem = data["first_id"];
// If the failpoint specifies no collection or matches the existing one, hang.
return (!collElem || _ns.ns() == collElem.str()) &&
(!firstIdElem ||
(begin != end && firstIdElem.type() == mongo::String &&
begin->doc["_id"].str() == firstIdElem.str()));
});
return Status::OK();
}mongo/db/catalog/collection_impl.cpp的方法_insertDocuments
cpp
Status CollectionImpl::_insertDocuments(OperationContext* opCtx,
const std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator begin,
const std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator end,
OpDebug* opDebug) {
dassert(opCtx->lockState()->isCollectionLockedForMode(ns(), MODE_IX));
const size_t count = std::distance(begin, end);
if (isCapped() && _indexCatalog->haveAnyIndexes() && count > 1) {
// We require that inserts to indexed capped collections be done one-at-a-time to avoid the
// possibility that a later document causes an earlier document to be deleted before it can
// be indexed.
// TODO SERVER-21512 It would be better to handle this here by just doing single inserts.
return {ErrorCodes::OperationCannotBeBatched,
"Can't batch inserts into indexed capped collections"};
}
if (_needCappedLock) {
// X-lock the metadata resource for this capped collection until the end of the WUOW. This
// prevents the primary from executing with more concurrency than secondaries.
// See SERVER-21646.
Lock::ResourceLock heldUntilEndOfWUOW{
opCtx->lockState(), ResourceId(RESOURCE_METADATA, _ns.ns()), MODE_X};
}
std::vector<Record> records;
records.reserve(count);
std::vector<Timestamp> timestamps;
timestamps.reserve(count);
for (auto it = begin; it != end; it++) {
records.emplace_back(Record{RecordId(), RecordData(it->doc.objdata(), it->doc.objsize())});
timestamps.emplace_back(it->oplogSlot.getTimestamp());
}
LOG(1) << "conca CollectionImpl::insertDocuments _recordStore->insertRecords" ;
Status status = _recordStore->insertRecords(opCtx, &records, timestamps);
if (!status.isOK())
return status;
std::vector<BsonRecord> bsonRecords;
bsonRecords.reserve(count);
int recordIndex = 0;
for (auto it = begin; it != end; it++) {
RecordId loc = records[recordIndex++].id;
invariant(RecordId::min() < loc);
invariant(loc < RecordId::max());
BsonRecord bsonRecord = {loc, Timestamp(it->oplogSlot.getTimestamp()), &(it->doc)};
bsonRecords.push_back(bsonRecord);
}
LOG(1) << "conca CollectionImpl::insertDocuments __indexCatalog->indexRecords" ;
int64_t keysInserted;
status = _indexCatalog->indexRecords(opCtx, bsonRecords, &keysInserted);
if (opDebug) {
opDebug->additiveMetrics.incrementKeysInserted(keysInserted);
}
return status;
}RecordStore> _recordStore是抽象类, _recordStore->insertRecords()不同的存储引擎有各自的实现类,MongoDB默认的存储引擎是wiredtiger,后面会重点分析wiredtiger_record_store.cpp插入文档记录逻辑。
_recordStore->insertRecords()插入文档之后调用_indexCatalog->indexRecords继续插入索引key,_recordStore->insertRecords()后面单独分析索引插入过程。
mongo/db/storage/mobile/mobile_record_store.cpp移动存储引擎是 MongoDB 为嵌入式设备设计的轻量级存储引擎,特点是资源占用少、依赖简单。
mongo/db/storage/wiredtiger/wiredtiger_record_store.cpp,WiredTiger是MongoDB 的默认存储引擎,提供高性能、高并发和完整的事务支持,insertRecords插入代码:
cpp
Status WiredTigerRecordStore::insertRecords(OperationContext* opCtx,
std::vector<Record>* records,
const std::vector<Timestamp>& timestamps) {
return _insertRecords(opCtx, records->data(), timestamps.data(), records->size());
}
Status WiredTigerRecordStore::_insertRecords(OperationContext* opCtx,
Record* records,
const Timestamp* timestamps,
size_t nRecords) {
dassert(opCtx->lockState()->isWriteLocked());
// We are kind of cheating on capped collections since we write all of them at once ....
// Simplest way out would be to just block vector writes for everything except oplog ?
int64_t totalLength = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < nRecords; i++)
totalLength += records[i].data.size();
// caller will retry one element at a time
if (_isCapped && totalLength > _cappedMaxSize)
return Status(ErrorCodes::BadValue, "object to insert exceeds cappedMaxSize");
LOG(1) << "conca WiredTigerRecordStore::insertRecords _uri:" << _uri;
LOG(1) << "conca WiredTigerRecordStore::insertRecords _tableId:" << _tableId;
WiredTigerCursor curwrap(_uri, _tableId, true, opCtx);
curwrap.assertInActiveTxn();
WT_CURSOR* c = curwrap.get();
invariant(c);
RecordId highestId = RecordId();
dassert(nRecords != 0);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nRecords; i++) {
auto& record = records[i];
if (_isOplog) {
StatusWith<RecordId> status =
oploghack::extractKey(record.data.data(), record.data.size());
if (!status.isOK())
return status.getStatus();
record.id = status.getValue();
} else {
record.id = _nextId(opCtx);
}
dassert(record.id > highestId);
highestId = record.id;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < nRecords; i++) {
auto& record = records[i];
Timestamp ts;
if (timestamps[i].isNull() && _isOplog) {
// If the timestamp is 0, that probably means someone inserted a document directly
// into the oplog. In this case, use the RecordId as the timestamp, since they are
// one and the same. Setting this transaction to be unordered will trigger a journal
// flush. Because these are direct writes into the oplog, the machinery to trigger a
// journal flush is bypassed. A followup oplog read will require a fresh visibility
// value to make progress.
ts = Timestamp(record.id.repr());
opCtx->recoveryUnit()->setOrderedCommit(false);
} else {
ts = timestamps[i];
}
if (!ts.isNull()) {
LOG(4) << "inserting record with timestamp " << ts;
fassert(39001, opCtx->recoveryUnit()->setTimestamp(ts));
}
setKey(c, record.id);
WiredTigerItem value(record.data.data(), record.data.size());
c->set_value(c, value.Get());
int ret = WT_OP_CHECK(c->insert(c));
if (ret)
return wtRCToStatus(ret, "WiredTigerRecordStore::insertRecord");
}
_changeNumRecords(opCtx, nRecords);
_increaseDataSize(opCtx, totalLength);
if (_oplogStones) {
_oplogStones->updateCurrentStoneAfterInsertOnCommit(
opCtx, totalLength, highestId, nRecords);
} else {
_cappedDeleteAsNeeded(opCtx, highestId);
}
return Status::OK();
}WiredTigerCursor curwrap(_uri, _tableId, true, opCtx);WT_CURSOR* c = curwrap.get();获取WiredTiger引擎游标;
record.id = _nextId(opCtx);设置记录系统隐藏字段recordId,数值类型,自增,唯一不变;
setKey(c, record.id);WiredTiger引擎游标设置索引record.id值;
WiredTigerItem value(record.data.data(), record.data.size());生成文档WiredTigerItem
c->set_value(c, value.Get());WiredTiger引擎游标设置文档WiredTigerItem
int ret = WT_OP_CHECK(c->insert(c));;WiredTiger引擎游标插入。
WiredTiger引擎游标WiredTigerCursor是第三方WiredTiger引擎核心mongo-r4.0.7\src\third_party\wiredtiger,后续文档会继续分析的,B+树怎么存储索引,对应文档的。
mongo插入单条文档insert()主要分4个阶段:
(1)分割文档,分批次插入
(2)将文档传递给集合类插入
(3)将文档传递给记录record插入
(4)传递给引擎游标WiredTigerCursor插入