概述
Fused QKV Projection 是一个在大语言模型推理中广泛使用的高效算子,它将输入特征通过共享权重矩阵同时投影到 Query、Key、Value 三个空间。本文深入分析其 native 实现,揭示其核心算法和优化策略。
算子定义
python
def fused_qkv_proj(q: Tensor, kv: Tensor, x: Tensor, weight: Tensor,
x_scale: Tensor, weight_scale: Tensor, group_size: int) -> None输入参数:
q: Query 输出张量,形状为[M, N_0]kv: Key-Value 输出张量,形状为[M, N_1]x: 输入特征张量,形状为[M, K]weight: 权重矩阵,形状为[N, K],其中N = N_0 + N_1x_scale: 输入缩放因子,用于量化反量化weight_scale: 权重缩放因子,用于量化反量化group_size: 分组量化的大小
输出:
- 直接修改
q和kv张量,无返回值
核心算法流程
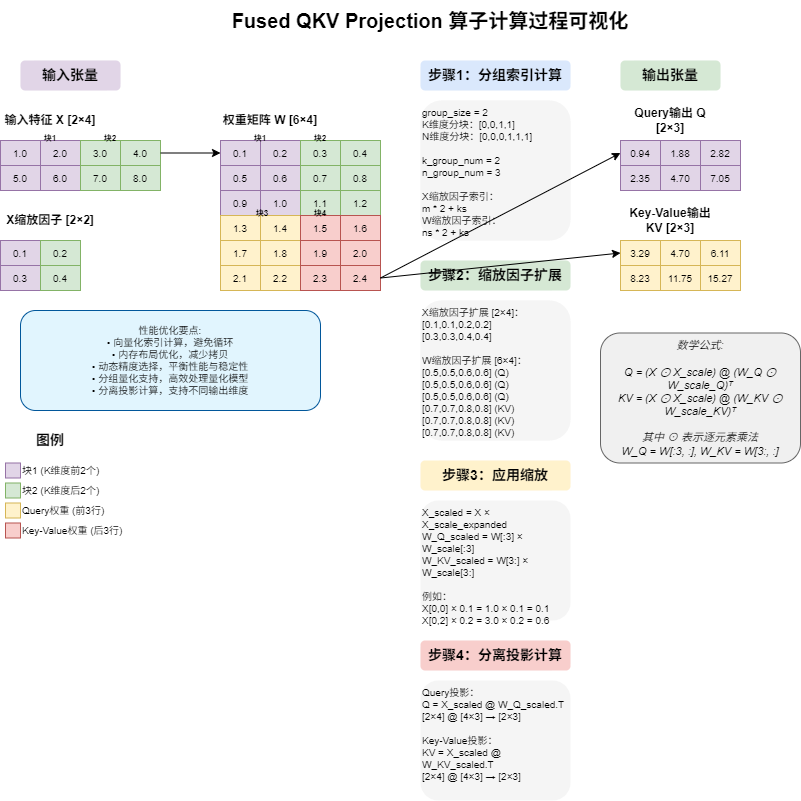
- native 实现
python
class FusedQKVProjImpl:
def native_impl(self, q: torch.Tensor, kv: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor, weight: torch.Tensor, x_scale: torch.Tensor, weight_scale: torch.Tensor, group_size: int) -> None:
"""
CPU实现,使用torch.matmul进行矩阵乘法和缩放,与native实现完全一致
"""
# return torch.ops._VLLM_C.fused_qkv_proj(q, kv, x, weight, x_scale, weight_scale, group_size)
# 获取输入张量的维度信息
# x: [M, K], weight: [N, K], q: [M, N_0], kv: [M, N_1]
x_sizes = x.shape
M = 1
for i in range(len(x_sizes) - 1):
M *= x_sizes[i]
K = x_sizes[-1]
# 获取输出张量的维度
N_0 = q.shape[-1] # q的最后一维
N_1 = kv.shape[-1] # kv的最后一维
N = N_0 + N_1 # 总的输出特征维度
# 验证weight的维度
if weight.shape != (N, K):
raise ValueError(f"Expected weight shape ({N}, {K}), but got {weight.shape}")
# 将输入张量转换为2D视图用于矩阵乘法
x_2d = x.view(M, K)
# 根据设备类型选择计算精度
if x.device.type == 'cpu':
# CPU设备使用fp16计算
compute_dtype = torch.float64
else:
# 其他设备使用fp32计算
compute_dtype = torch.float32
# 转换为选择的计算精度
x_compute = x_2d.to(compute_dtype)
weight_compute = weight.to(compute_dtype)
x_scale_compute = x_scale.to(compute_dtype)
weight_scale_compute = weight_scale.to(compute_dtype)
# 计算group数量,与native实现一致
k_group_num = (K + group_size - 1) // group_size
n_group_num = (N + group_size - 1) // group_size
# 向量化创建与native实现完全一致的scale张量
# 创建索引张量
k_indices = torch.arange(K, dtype=torch.long)
n_indices = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long)
m_indices = torch.arange(M, dtype=torch.long)
# 计算group索引
ks_indices = k_indices // group_size # [K]
ns_indices = n_indices // group_size # [N]
# 计算x_scale索引: m * k_group_num + ks_idx
# 使用广播: [M, 1] + [K] -> [M, K]
x_scale_indices = m_indices.unsqueeze(1) * k_group_num + ks_indices.unsqueeze(0) # [M, K]
# 计算weight_scale索引: ns_idx * k_group_num + ks_idx
# 使用广播: [N, 1] + [K] -> [N, K]
weight_scale_indices = ns_indices.unsqueeze(1) * k_group_num + ks_indices.unsqueeze(0) # [N, K]
# 展平scale张量并索引
x_scale_flat = x_scale_compute.view(-1)
weight_scale_flat = weight_scale_compute.view(-1)
# 使用高级索引获取scale值
x_scale_expanded = x_scale_flat[x_scale_indices] # [M, K]
weight_scale_expanded = weight_scale_flat[weight_scale_indices] # [N, K]
# 应用scale: x * x_scale_expanded
x_scaled = x_compute * x_scale_expanded # [M, K] * [M, K] -> [M, K]
# 计算 q = x_scaled @ weight[:N_0, :].T,应用weight_scale
weight_q = weight_compute[:N_0, :] # [N_0, K]
weight_scale_q = weight_scale_expanded[:N_0, :] # [N_0, K]
# 应用weight_scale到weight: weight_q * weight_scale_q
weight_q_scaled = weight_q * weight_scale_q # [N_0, K] * [N_0, K] -> [N_0, K]
q_out = torch.matmul(x_scaled, weight_q_scaled.T) # [M, K] @ [K, N_0] -> [M, N_0]
# 计算 kv = x_scaled @ weight[N_0:, :].T,应用weight_scale
weight_kv = weight_compute[N_0:, :] # [N_1, K]
weight_scale_kv = weight_scale_expanded[N_0:, :] # [N_1, K]
# 应用weight_scale到weight: weight_kv * weight_scale_kv
weight_kv_scaled = weight_kv * weight_scale_kv # [N_1, K] * [N_1, K] -> [N_1, K]
kv_out = torch.matmul(x_scaled, weight_kv_scaled.T) # [M, K] @ [K, N_1] -> [M, N_1]
# 将结果转换为原始数据类型并复制到输出张量
q.copy_(q_out.to(q.dtype).view(q.shape))
kv.copy_(kv_out.to(kv.dtype).view(kv.shape))
return1. 张量维度解析与验证
python
# 解析输入张量维度
M = prod(x.shape[:-1]) # 批次大小
K = x.shape[-1] # 输入特征维度
N_0 = q.shape[-1] # Query 输出维度
N_1 = kv.shape[-1] # Key-Value 输出维度
N = N_0 + N_1 # 总输出维度
# 验证权重矩阵维度
assert weight.shape == (N, K)2. 动态精度选择
根据设备类型自动选择计算精度,确保数值稳定性:
python
if x.device.type == 'cpu':
compute_dtype = torch.float64 # CPU 使用双精度
else:
compute_dtype = torch.float32 # GPU 使用单精度3. 分组量化索引计算
这是算法的核心部分,通过向量化操作高效计算每个元素的缩放因子索引:
python
# 计算分组数量
k_group_num = (K + group_size - 1) // group_size
n_group_num = (N + group_size - 1) // group_size
# 创建索引张量
k_indices = torch.arange(K, dtype=torch.long)
n_indices = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long)
m_indices = torch.arange(M, dtype=torch.long)
# 计算分组索引
ks_indices = k_indices // group_size # [K]
ns_indices = n_indices // group_size # [N]
# 计算 x_scale 索引: m * k_group_num + ks_idx
x_scale_indices = m_indices.unsqueeze(1) * k_group_num + ks_indices.unsqueeze(0) # [M, K]
# 计算 weight_scale 索引: ns_idx * k_group_num + ks_idx
weight_scale_indices = ns_indices.unsqueeze(1) * k_group_num + ks_indices.unsqueeze(0) # [N, K]4. 缩放因子应用
通过高级索引高效获取和应用缩放因子:
python
# 展平并索引缩放因子
x_scale_expanded = x_scale_flat[x_scale_indices] # [M, K]
weight_scale_expanded = weight_scale_flat[weight_scale_indices] # [N, K]
# 应用输入缩放
x_scaled = x_compute * x_scale_expanded # [M, K]5. 分离投影计算
将权重矩阵分割为两部分,分别计算 Query 和 Key-Value 投影:
python
# Query 投影: q = x_scaled @ weight[:N_0, :].T
weight_q = weight_compute[:N_0, :] # [N_0, K]
weight_scale_q = weight_scale_expanded[:N_0, :] # [N_0, K]
weight_q_scaled = weight_q * weight_scale_q # [N_0, K]
q_out = torch.matmul(x_scaled, weight_q_scaled.T) # [M, N_0]
# Key-Value 投影: kv = x_scaled @ weight[N_0:, :].T
weight_kv = weight_compute[N_0:, :] # [N_1, K]
weight_scale_kv = weight_scale_expanded[N_0:, :] # [N_1, K]
weight_kv_scaled = weight_kv * weight_scale_kv # [N_1, K]
kv_out = torch.matmul(x_scaled, weight_q_scaled.T) # [M, N_1]性能优化策略
1. 向量化索引计算
使用 PyTorch 的广播机制和高级索引,避免循环操作:
python
# 高效的广播索引计算
x_scale_indices = m_indices.unsqueeze(1) * k_group_num + ks_indices.unsqueeze(0)2. 内存布局优化
- 使用
view()操作避免内存拷贝 - 通过
copy_()直接修改输出张量,减少内存分配 - 保持张量连续性,优化矩阵乘法性能
3. 计算精度自适应
根据设备类型自动选择最优计算精度,平衡性能和数值稳定性。
数学公式
基础投影公式
对于输入特征 x∈RM×Kx \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times K}x∈RM×K 和权重矩阵 W∈RN×KW \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times K}W∈RN×K:
Query:Q=x⋅WQTwhereWQ=W[:N0,:]\text{Query}: Q = x \cdot W_Q^T \quad \text{where} \quad W_Q = W[:N_0, :]Query:Q=x⋅WQTwhereWQ=W[:N0,:]
Key-Value:KV=x⋅WKVTwhereWKV=W[N0:,:]\text{Key-Value}: KV = x \cdot W_{KV}^T \quad \text{where} \quad W_{KV} = W[N_0:, :]Key-Value:KV=x⋅WKVTwhereWKV=W[N0:,:]
分组量化缩放
对于每个元素 (m,k)(m, k)(m,k) 和 (n,k)(n, k)(n,k):
x_scale[m,k]=x_scale_flat[m⋅k_group_num+⌊k/group_size⌋]\text{x\_scale}[m, k] = \text{x\_scale\_flat}[m \cdot \text{k\_group\_num} + \lfloor k / \text{group\_size} \rfloor]x_scale[m,k]=x_scale_flat[m⋅k_group_num+⌊k/group_size⌋]
weight_scale[n,k]=weight_scale_flat[⌊n/group_size⌋⋅k_group_num+⌊k/group_size⌋]\text{weight\_scale}[n, k] = \text{weight\_scale\_flat}[\lfloor n / \text{group\_size} \rfloor \cdot \text{k\_group\_num} + \lfloor k / \text{group\_size} \rfloor]weight_scale[n,k]=weight_scale_flat[⌊n/group_size⌋⋅k_group_num+⌊k/group_size⌋]
最终计算
q_out=(x⊙x_scale)⋅(WQ⊙weight_scaleQ)T\text{q\_out} = (x \odot \text{x\_scale}) \cdot (W_Q \odot \text{weight\_scale}_Q)^Tq_out=(x⊙x_scale)⋅(WQ⊙weight_scaleQ)T
kv_out=(x⊙x_scale)⋅(WKV⊙weight_scaleKV)T\text{kv\_out} = (x \odot \text{x\scale}) \cdot (W{KV} \odot \text{weight\scale}{KV})^Tkv_out=(x⊙x_scale)⋅(WKV⊙weight_scaleKV)T
其中 ⊙\odot⊙ 表示逐元素乘法。
应用场景
- Transformer 模型推理: 在注意力机制中同时计算 Q、K、V 投影
- 大语言模型: 支持长序列推理,减少内存访问
- 量化推理: 通过分组量化减少模型大小,保持精度
- 多设备支持: 兼容 CPU、GPU、GCU 等多种计算设备
总结
Fused QKV Projection 算子的 native 实现通过以下关键技术实现了高效计算:
- 向量化索引计算: 避免循环,充分利用硬件并行能力
- 内存优化: 最小化内存拷贝和分配
- 精度自适应: 根据设备特性选择最优计算精度
- 分组量化支持: 高效处理量化模型的缩放因子
triton 实现
python
from vllm.triton_utils import tl, triton
from vllm.platforms import current_platform
from vllm.logger import init_logger
import torch
import os
import functools
from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, Union
logger = init_logger(__name__)
@functools.lru_cache
def get_w8a8_block_fp8_configs(N: int, K: int, block_n: int,
block_k: int) -> Optional[dict[int, Any]]:
"""
Return optimized configurations for the w8a8 block fp8 kernel.
The return value will be a dictionary that maps an irregular grid of
batch sizes to configurations of the w8a8 block fp8 kernel. To evaluate the
kernel on a given batch size bs, the closest batch size in the grid should
be picked and the associated configuration chosen to invoke the kernel.
"""
# First look up if an optimized configuration is available in the configs
# directory
device_name = current_platform.get_device_name().replace(" ", "_")
json_file_name = f"N={N},K={K},device_name={device_name},dtype=fp8_w8a8,block_shape=[{block_n},{block_k}].json" # noqa: E501
config_file_path = os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)), "configs", json_file_name)
if os.path.exists(config_file_path):
with open(config_file_path) as f:
logger.info(
"Using configuration from %s for W8A8 Block FP8 kernel.",
config_file_path,
)
# If a configuration has been found, return it
return {int(key): val for key, val in json.load(f).items()}
# If no optimized configuration is available, we will use the default
# configuration
logger.warning(
"Using default W8A8 Block FP8 kernel config. Performance might "
"be sub-optimal! Config file not found at %s",
config_file_path,
)
return None
def w8a8_block_fp8_matmul(
A: torch.Tensor,
B: torch.Tensor,
As: torch.Tensor,
Bs: torch.Tensor,
dot_dtype = None,
block_size: list[int] = [128, 128],
output_dtype: torch.dtype = torch.bfloat16,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""This function performs matrix multiplication with block-wise
quantization.
It takes two input tensors `A` and `B` with scales `As` and `Bs`.
The output is returned in the specified `output_dtype`.
Args:
A: The input tensor, e.g., activation.
B: The input tensor, e.g., weight.
As: The per-token-group quantization scale for `A`.
Bs: The per-block quantization scale for `B`.
block_size: The block size for per-block quantization. It should
be 2-dim, e.g., [128, 128].
output_dytpe: The dtype of the returned tensor.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: The result of matmul.
"""
if isinstance(dot_dtype, int) and dot_dtype == 1:
dot_dtype = tl.bfloat16
assert len(block_size) == 2
block_n, block_k = block_size[0], block_size[1]
assert A.shape[-1] == B.shape[-1]
assert A.shape[:-1] == As.shape[:-1] and A.is_contiguous()
assert triton.cdiv(A.shape[-1], block_k) == As.shape[-1]
M = A.numel() // A.shape[-1]
assert B.ndim == 2 and Bs.ndim == 2
N, K = B.shape
assert triton.cdiv(N, block_n) == Bs.shape[0]
assert triton.cdiv(K, block_k) == Bs.shape[1]
C_shape = A.shape[:-1] + (N, )
C = A.new_empty(C_shape, dtype=output_dtype)
configs = get_w8a8_block_fp8_configs(N, K, block_size[0], block_size[1])
if configs:
# Get the optimal config if there is one
config = configs[min(configs.keys(), key=lambda x: abs(x - M))]
else:
# Default config
# Block-wise quant: BLOCK_SIZE_N must be divisible by block_size[0]
# BLOCK_SIZE_K must be divisible by block_size[1]
config = {
"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 64,
"BLOCK_SIZE_N": block_size[0],
"BLOCK_SIZE_K": block_size[1],
"GROUP_SIZE_M": 32,
"num_warps": 4,
"num_stages": 2,
}
def grid(META):
return (triton.cdiv(M, META["BLOCK_SIZE_M"]) *
triton.cdiv(N, META["BLOCK_SIZE_N"]), )
_w8a8_block_fp8_matmul[grid](
A,
B,
C,
As,
Bs,
M,
N,
K,
block_n,
block_k,
# dot_dtype,
A.stride(-2),
A.stride(-1),
B.stride(1),
B.stride(0),
C.stride(-2),
C.stride(-1),
As.stride(-2),
As.stride(-1),
Bs.stride(1),
Bs.stride(0),
**config,
)
return C
def get_default_config(
M: int,
E: int,
N: int,
K: int,
topk: int,
dtype: Optional[str],
is_marlin: bool,
block_shape: Optional[list[int]] = None,
) -> dict[str, int]:
if dtype == "fp8_w8a8" and block_shape is not None:
# Block-wise quant: BLOCK_SIZE_N must be divisible by block_shape[0]
# BLOCK_SIZE_K must be divisible by block_shape[1]
# num_stages=3 can cause triton.runtime.errors.OutOfResources
# on ROCm, set it to 2 instead.
config = {
"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 64,
"BLOCK_SIZE_N": block_shape[0],
"BLOCK_SIZE_K": block_shape[1],
"GROUP_SIZE_M": 32,
"num_warps": 4,
# "num_stages": 3 if not current_platform.is_rocm() else 2,
"num_stages": 2
}
elif dtype in ["int4_w4a16", "int8_w8a16"] and block_shape is not None:
# moe wna16 kernels
# only set BLOCK_SIZE_M
# BLOCK_SIZE_N and BLOCK_SIZE_K would be set later
bit = 4 if dtype == "int4_w4a16" else 8
use_moe_wna16_cuda = should_moe_wna16_use_cuda(M * topk,
block_shape[1], E, bit)
if use_moe_wna16_cuda:
config = {"BLOCK_SIZE_M": min(16, M)}
elif M <= 20:
config = {"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 16, "GROUP_SIZE_M": 1}
elif M <= 40:
config = {"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 32, "GROUP_SIZE_M": 1}
else:
config = {"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 64, "GROUP_SIZE_M": 1}
elif is_marlin:
for block_size_m in [8, 16, 32, 48, 64]:
if M * topk / E / block_size_m < 0.9:
break
return {"BLOCK_SIZE_M": block_size_m}
elif M <= E:
config = {
"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 16,
"BLOCK_SIZE_N": 32,
"BLOCK_SIZE_K": 64,
"GROUP_SIZE_M": 1,
}
else:
config = {
"BLOCK_SIZE_M": 64,
"BLOCK_SIZE_N": 64,
"BLOCK_SIZE_K": 32,
"GROUP_SIZE_M": 8,
}
return config
def try_get_optimal_moe_config(
w1_shape: tuple[int, ...],
w2_shape: tuple[int, ...],
top_k: int,
dtype: Optional[str],
M: int,
is_marlin: bool = False,
block_shape: Optional[list[int]] = None,
) -> dict[str, int]:
from vllm.model_executor.layers.fused_moe import get_config
override_config = get_config()
if override_config:
config = override_config
else:
# First try to load optimal config from the file
E, _, N = w2_shape
if dtype == "int4_w4a16":
N = N * 2
block_n = block_shape[0] if block_shape else 0
block_k = block_shape[1] if block_shape else 0
# Else use the default config
config = get_default_config(M, E, N, w1_shape[2], top_k, dtype,
is_marlin, block_shape)
return config
@triton.jit
def _w8a8_block_fp8_matmul(
# Pointers to inputs and output
A,
B,
C,
As,
Bs,
# Shape for matmul
M,
N,
K,
# Block size for block-wise quantization
group_n,
group_k,
# dot_dtype,
# Stride for inputs and output
stride_am,
stride_ak,
stride_bk,
stride_bn,
stride_cm,
stride_cn,
stride_As_m,
stride_As_k,
stride_Bs_k,
stride_Bs_n,
# Meta-parameters
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr,
BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr,
GROUP_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
):
"""Triton-accelerated function used to perform linear operations (dot
product) on input tensors `A` and `B` with block-wise quantization, and
store the result in output tensor `C`.
"""
# dot_dtype = tl.bfloat16
dot_dtype = None
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(M, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
pid_m = first_pid_m + (pid % group_size_m)
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m
offs_am = (pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)) % M
offs_bn = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
a_ptrs = A + (offs_am[:, None] * stride_am + offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak)
b_ptrs = B + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk + offs_bn[None, :] * stride_bn)
As_ptrs = As + offs_am * stride_As_m
offs_bsn = offs_bn // group_n
Bs_ptrs = Bs + offs_bsn * stride_Bs_n
accumulator = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
a = tl.load(a_ptrs,
mask=offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K,
other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptrs,
mask=offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K,
other=0.0)
k_start = k * BLOCK_SIZE_K
offs_ks = k_start // group_k
a_s = tl.load(As_ptrs + offs_ks * stride_As_k)
b_s = tl.load(Bs_ptrs + offs_ks * stride_Bs_k)
if dot_dtype is not None:
a = a.to(dot_dtype)
b = b.to(dot_dtype)
accumulator += tl.dot(a, b) * a_s[:, None] * b_s[None, :]
a_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
b_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
if C.dtype.element_ty == tl.bfloat16:
c = accumulator.to(tl.bfloat16)
elif C.dtype.element_ty == tl.float16:
c = accumulator.to(tl.float16)
else:
c = accumulator.to(tl.float32)
offs_cm = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = C + stride_cm * offs_cm[:, None] + stride_cn * offs_cn[None, :]
c_mask = (offs_cm[:, None] < M) & (offs_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, c, mask=c_mask)
def get_config_dtype_str(
dtype: torch.dtype,
use_int4_w4a16: Optional[bool] = False,
use_int8_w8a16: Optional[bool] = False,
use_fp8_w8a8: Optional[bool] = False,
use_mxfp4_w4a4: Optional[bool] = False) -> Optional[str]:
if use_fp8_w8a8:
return "fp8_w8a8"
elif use_int8_w8a16:
return "int8_w8a16"
elif use_int4_w4a16:
return "int4_w4a16"
elif use_mxfp4_w4a4:
return "mxfp4_w4a4"
elif dtype == torch.float:
# avoiding cases where kernel fails when float32 MoE
# use fp16/bfloat16 configs
return "float32"
return None
def invoke_fused_moe_kernel(A: torch.Tensor,
B: torch.Tensor,
C: torch.Tensor,
A_scale: Optional[torch.Tensor],
B_scale: Optional[torch.Tensor],
B_zp: Optional[torch.Tensor],
topk_weights: Optional[torch.Tensor],
sorted_token_ids: torch.Tensor,
expert_ids: torch.Tensor,
num_tokens_post_padded: torch.Tensor,
mul_routed_weight: bool,
top_k: int,
config: dict[str, Any] = None,
compute_type: tl.dtype = tl.bfloat16,
use_fp8_w8a8: bool = True,
use_int8_w8a8: bool = False,
use_int8_w8a16: bool = False,
use_int4_w4a16: bool = False,
per_channel_quant: bool = False,
block_shape: Optional[list[int]] = [128, 128],
dot_dtype = None) -> None:
if isinstance(dot_dtype, int) and dot_dtype == 1:
dot_dtype = tl.bfloat16
assert topk_weights is not None or not mul_routed_weight
assert topk_weights is None or topk_weights.stride(1) == 1
assert sorted_token_ids.stride(0) == 1
if config is None:
M = A.size(0)
config_dtype = get_config_dtype_str(use_fp8_w8a8=use_fp8_w8a8,
use_int8_w8a16=use_int8_w8a16,
use_int4_w4a16=use_int4_w4a16,
use_mxfp4_w4a4=False,
dtype=A.dtype)
get_config_func = functools.partial(
try_get_optimal_moe_config,
B.size(),
B.size(),
top_k,
config_dtype,
block_shape=block_shape,
)
config = get_config_func(M)
# config = {
# 'BLOCK_SIZE_K': 128,
# 'BLOCK_SIZE_M': 64,
# 'BLOCK_SIZE_N': 128,
# 'GROUP_SIZE_M': 32,
# 'num_warps': 4,
# 'num_stages': 2
# }
if use_fp8_w8a8 or use_int8_w8a8:
assert B_scale is not None
assert (block_shape is None
or triton.cdiv(B.size(-2), block_shape[0]) == B_scale.size(-2))
assert (block_shape is None
or triton.cdiv(B.size(-1), block_shape[1]) == B_scale.size(-1))
elif use_int8_w8a16 or use_int4_w4a16:
assert B_scale is not None
assert block_shape is None or block_shape[0] == 0
else:
assert A_scale is None
assert B_scale is None
M = A.size(0)
num_tokens = M * top_k
EM = sorted_token_ids.size(0)
if A.size(0) < config["BLOCK_SIZE_M"]:
# optimize for small batch_size.
# We assume that top_ids of each token is unique, so
# so num_valid_experts <= batch_size <= BLOCK_SIZE_M,
# and we can skip some invalid blocks.
EM = min(sorted_token_ids.size(0),
A.size(0) * top_k * config['BLOCK_SIZE_M'])
grid = lambda META: (triton.cdiv(EM, META['BLOCK_SIZE_M']) * triton.cdiv(
B.size(1), META['BLOCK_SIZE_N']), )
config = config.copy()
BLOCK_SIZE_K = config.pop("BLOCK_SIZE_K")
if block_shape is not None:
BLOCK_SIZE_K = min(BLOCK_SIZE_K, min(block_shape[0],
block_shape[1]))
fused_moe_kernel[grid](
A,
B,
C,
A_scale,
B_scale,
topk_weights,
sorted_token_ids,
expert_ids,
num_tokens_post_padded,
B.size(1),
B.size(2),
EM,
num_tokens,
A.stride(0),
A.stride(1),
B.stride(0),
B.stride(2),
B.stride(1),
C.stride(1),
C.stride(2),
A_scale.stride(0)
if A_scale is not None and A_scale.ndim == 2 else 0,
A_scale.stride(1)
if A_scale is not None and A_scale.ndim == 2 else 0,
B_scale.stride(0)
if B_scale is not None and B_scale.ndim >= 2 else 0,
B_scale.stride(2)
if B_scale is not None and B_scale.ndim == 3 else 0,
B_scale.stride(1)
if B_scale is not None and B_scale.ndim >= 2 else 0,
0 if block_shape is None else block_shape[0],
0 if block_shape is None else block_shape[1],
MUL_ROUTED_WEIGHT=mul_routed_weight,
top_k=top_k,
compute_type=compute_type,
use_fp8_w8a8=use_fp8_w8a8,
use_int8_w8a8=use_int8_w8a8,
use_int8_w8a16=use_int8_w8a16,
per_channel_quant=per_channel_quant,
BLOCK_SIZE_K=BLOCK_SIZE_K,
**config,
)
@triton.jit
def write_zeros_to_output(c_ptr, stride_cm, stride_cn, pid_n, N, offs_token,
token_mask, BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N,
compute_type):
accumulator = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=compute_type)
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = c_ptr + stride_cm * offs_token[:, None] + stride_cn * offs_cn[
None, :]
c_mask = token_mask[:, None] & (offs_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, accumulator, mask=c_mask)
@triton.jit
def fused_moe_kernel(
# Pointers to matrices
a_ptr,
b_ptr,
c_ptr,
a_scale_ptr,
b_scale_ptr,
topk_weights_ptr,
sorted_token_ids_ptr,
expert_ids_ptr,
num_tokens_post_padded_ptr,
# Matrix dimensions
N,
K,
EM,
num_valid_tokens,
# The stride variables represent how much to increase the ptr by when
# moving by 1 element in a particular dimension. E.g. `stride_am` is
# how much to increase `a_ptr` by to get the element one row down
# (A has M rows).
stride_am,
stride_ak,
stride_be,
stride_bk,
stride_bn,
stride_cm,
stride_cn,
stride_asm,
stride_ask,
stride_bse,
stride_bsk,
stride_bsn,
# Block size for block-wise quantization
group_n: tl.constexpr,
group_k: tl.constexpr,
# Meta-parameters
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr,
BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr,
GROUP_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
MUL_ROUTED_WEIGHT: tl.constexpr,
top_k: tl.constexpr,
compute_type: tl.constexpr,
use_fp8_w8a8: tl.constexpr,
use_int8_w8a8: tl.constexpr,
use_int8_w8a16: tl.constexpr,
per_channel_quant: tl.constexpr,
):
"""
Implements the fused computation for a Mixture of Experts (MOE) using
token and expert matrices.
Key Parameters:
- A: The input tensor representing tokens with shape (*, K), where '*' can
be any shape representing batches and K is the feature dimension of
each token.
- B: The stacked MOE weight tensor with shape (E, N, K), where E is
the number of experts, K is the input feature dimension, and N is
the output feature dimension.
- C: The output cache tensor with shape (M, topk, N), where M is the
total number of tokens post padding, topk is the number of times
each token is repeated, and N is the output feature dimension.
- sorted_token_ids: A tensor containing the sorted indices of tokens,
repeated topk times and arranged by the expert index they are
assigned to.
- expert_ids: A tensor containing the indices of the expert for each
block. It determines which expert matrix from B should be used for
each block in A.
This kernel performs the multiplication of a token by its corresponding
expert matrix as determined by `expert_ids`. The sorting of
`sorted_token_ids` by expert index and padding ensures divisibility by
BLOCK_SIZE_M, which is necessary to maintain consistency in block matrix
multiplication across different blocks processed by the same expert.
"""
dot_dtype = tl.bfloat16
# dot_dtype = None
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Map program ids `pid` to the block of C it should compute.
# This is done in a grouped ordering to promote L2 data reuse.
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(EM, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
pid_m = first_pid_m + ((pid % num_pid_in_group) % group_size_m)
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m
# ----------------------------------------------------------
# Create pointers for the first blocks of A and B.
# We will advance this pointer as we move in the K direction
# and accumulate
# `a_ptrs` is a block of [BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_K] pointers
# `b_ptrs` is a block of [BLOCK_SIZE_K, BLOCK_SIZE_N] pointers
num_tokens_post_padded = tl.load(num_tokens_post_padded_ptr)
if pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M >= num_tokens_post_padded:
return
offs_token_id = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M).to(
tl.int64)
offs_token = tl.load(sorted_token_ids_ptr + offs_token_id)
token_mask = offs_token < num_valid_tokens
off_experts = tl.load(expert_ids_ptr + pid_m).to(tl.int64)
if off_experts == -1:
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Write back zeros to the output when the expert is not
# in the current expert parallel rank.
write_zeros_to_output(c_ptr, stride_cm, stride_cn, pid_n, N,
offs_token, token_mask, BLOCK_SIZE_M,
BLOCK_SIZE_N, compute_type)
return
offs_bn = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N +
tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N).to(tl.int64)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
a_ptrs = a_ptr + (offs_token[:, None] // top_k * stride_am +
offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak)
b_ptrs = b_ptr + off_experts * stride_be + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk +
offs_bn[None, :] * stride_bn)
if use_int8_w8a16:
b_scale_ptrs = b_scale_ptr + off_experts * stride_bse + offs_bn[
None, :] * stride_bsn
b_scale = tl.load(b_scale_ptrs)
if use_fp8_w8a8 or use_int8_w8a8:
# block-wise
if group_k > 0 and group_n > 0:
a_scale_ptrs = a_scale_ptr + (offs_token // top_k) * stride_asm
offs_bsn = offs_bn // group_n
b_scale_ptrs = (b_scale_ptr + off_experts * stride_bse +
offs_bsn * stride_bsn)
# channel-wise
elif per_channel_quant:
b_scale_ptrs = b_scale_ptr + off_experts * stride_bse + offs_bn[
None, :] * stride_bsn
b_scale = tl.load(b_scale_ptrs)
# Load per-token scale for activations
a_scale_ptrs = a_scale_ptr + (offs_token // top_k) * stride_asm
a_scale = tl.load(a_scale_ptrs, mask=token_mask, other=0.0)[:,
None]
# tensor-wise
else:
a_scale = tl.load(a_scale_ptr)
b_scale = tl.load(b_scale_ptr + off_experts)
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Iterate to compute a block of the C matrix.
# We accumulate into a `[BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N]` block
# of fp32 values for higher accuracy.
# `accumulator` will be converted back to fp16 after the loop.
accumulator = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
# Load the next block of A and B, generate a mask by checking the
# K dimension.
a = tl.load(a_ptrs,
mask=token_mask[:, None] &
(offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K),
other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptrs,
mask=offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K,
other=0.0)
if dot_dtype is not None:
a = a.to(dot_dtype)
b = b.to(dot_dtype)
# We accumulate along the K dimension.
if use_int8_w8a16:
accumulator = tl.dot(a, b.to(compute_type), acc=accumulator)
elif use_fp8_w8a8 or use_int8_w8a8:
if group_k > 0 and group_n > 0:
k_start = k * BLOCK_SIZE_K
offs_ks = k_start // group_k
a_scale = tl.load(a_scale_ptrs + offs_ks * stride_ask,
mask=token_mask,
other=0.0)
b_scale = tl.load(b_scale_ptrs + offs_ks * stride_bsk)
accumulator += tl.dot(a, b) * a_scale[:,
None] * b_scale[None, :]
else:
if use_fp8_w8a8:
# acc used to enable fp8_fast_accum
accumulator = tl.dot(a, b, acc=accumulator)
else:
accumulator += tl.dot(a, b)
else:
accumulator += tl.dot(a, b)
# Advance the ptrs to the next K block.
a_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
b_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
if MUL_ROUTED_WEIGHT:
moe_weight = tl.load(topk_weights_ptr + offs_token,
mask=token_mask,
other=0)
accumulator = accumulator * moe_weight[:, None]
if use_int8_w8a16:
accumulator = (accumulator * b_scale).to(compute_type)
elif use_fp8_w8a8 or use_int8_w8a8:
if group_k > 0 and group_n > 0:
accumulator = accumulator.to(compute_type)
else:
accumulator = (accumulator * a_scale * b_scale).to(compute_type)
else:
accumulator = accumulator.to(compute_type)
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Write back the block of the output
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = c_ptr + stride_cm * offs_token[:, None] + stride_cn * offs_cn[
None, :]
c_mask = token_mask[:, None] & (offs_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, accumulator, mask=c_mask)
def w8a8_block_fp8_matmul_triton(q: torch.Tensor, kv: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor, weight: torch.Tensor, x_scale: torch.Tensor, weight_scale: torch.Tensor, group_size: int) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Triton实现
"""
from ._triton import w8a8_block_fp8_matmul
out = w8a8_block_fp8_matmul(x, weight, x_scale, weight_scale)
# 参考cpu实现,将output_sizes、q、kv抽取出来
M = x.shape[0]
N = weight.shape[0]
N_0 = q.shape[-1]
N_1 = kv.shape[-1]
output_sizes = [N_0, N_1]
q_out, kv_out = tuple(i.contiguous() for i in out.split(output_sizes, dim=-1))
q.copy_(q_out)
kv.copy_(kv_out)
return