SSE 技术选型(原生 SSE vs fetch-event-source)
在ai对话聊天中,一般采用sse通信方式,但是原生 SSE 的有一些问题,在实际使用中并不好用
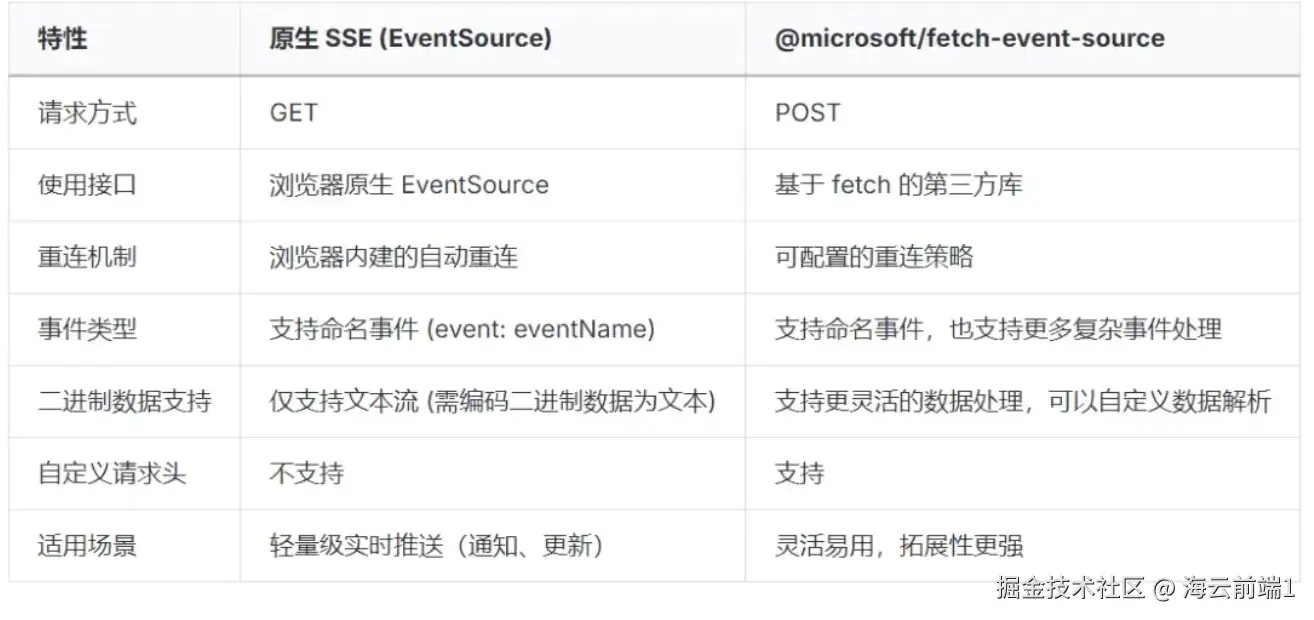
1)仅支持 Get 请求:对需要传递一些复杂请求体的场景不友好。
2)不支持自定义 http header:无法支持自定义 header 透传,鉴权等场景,目前市面大部分解决方案是使用 Cookie 来携带自定义参数。
但是有一个微软开源的 SSE 网络库 @microsoft/fetch-event-source(以下简称 fes)能够很好的解决。fes 是基于 Fetch 和 ReadableStream 来实现的 SSE 功能,旨在提供更加灵活便利的调用方式。
原生 SSE 和 fes 的对比
fetch-event-source 详解
fes 的核心原理是通过 Fetch 发送请求,ReadableStream 读取响应流,在 JS 侧实现字节流数据的解析。通过对比原生 SSE(chromium 内核中 EventSource)和 fes 的代码,发现整体流程与实现方案大致相同,关键区别在于流的解析,原生 SSE 在浏览器内核由 C++实现,fes 在 JS 侧实现。
fes 的流解析
核心方法:getBytes、getLines 和 getMessages
getBytes:通过 ReadableStream 读取响应字节流,获取每个字节块。
getLines :将 getBytes 获取到的字节块解析为 EventSource 行缓冲区,处理这些字节块并解析为行,然后调用 onLine 回调函数处理每一行。
getMessages:创建 EventSourceMessage 对象,将行缓冲区数据解析并进行组装,处理完成后回调给调用方。
javascript
export async function getBytes(stream: ReadableStream<Uint8Array>, onChunk: (arr: Uint8Array) => void) {
const reader = stream.getReader();
let result: ReadableStreamDefaultReadResult<Uint8Array>;
while (!(result = await reader.read()).done) {
onChunk(result.value);
}
}
typescript
export function getMessages(
onId: (id: string) => void,
onRetry: (retry: number) => void,
onMessage?: (msg: EventSourceMessage) => void
) {
let message = newMessage();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
// return a function that can process each incoming line buffer:
return function onLine(line: Uint8Array, fieldLength: number) {
if (line.length === 0) {
// empty line denotes end of message. Trigger the callback and start a new message:
onMessage?.(message);
message = newMessage();
} else if (fieldLength > 0) { // exclude comments and lines with no values
// line is of format "<field>:<value>" or "<field>: <value>"
// https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/server-sent-events.html#event-stream-interpretation
const field = decoder.decode(line.subarray(0, fieldLength));
const valueOffset = fieldLength + (line[fieldLength + 1] === ControlChars.Space ? 2 : 1);
const value = decoder.decode(line.subarray(valueOffset));
switch (field) {
case 'data':
// if this message already has data, append the new value to the old.
// otherwise, just set to the new value:
message.data = message.data
? message.data + '\n' + value
: value;
break;
case 'event':
message.event = value;
break;
case 'id':
onId(message.id = value);
break;
case 'retry':
const retry = parseInt(value, 10);
if (!isNaN(retry)) {
onRetry(message.retry = retry);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
ini
export function getLines(onLine: (line: Uint8Array, fieldLength: number) => void) {
let buffer: Uint8Array | undefined;
let position: number; // current read position
let fieldLength: number; // length of the `field` portion of the line
let discardTrailingNewline = false;
return function onChunk(arr: Uint8Array) {
if (buffer === undefined) {
buffer = arr;
position = 0;
fieldLength = -1;
} else {
buffer = concat(buffer, arr);
}
const bufLength = buffer.length;
let lineStart = 0; // index where the current line starts
while (position < bufLength) {
if (discardTrailingNewline) {
if (buffer[position] === ControlChars.NewLine) {
lineStart = ++position; // skip to next char
}
discardTrailingNewline = false;
}
let lineEnd = -1; // index of the \r or \n char
for (; position < bufLength && lineEnd === -1; ++position) {
switch (buffer[position]) {
case ControlChars.Colon:
if (fieldLength === -1) { // first colon in line
fieldLength = position - lineStart;
}
break;
case ControlChars.CarriageReturn:
discardTrailingNewline = true;
case ControlChars.NewLine:
lineEnd = position;
break;
}
}
if (lineEnd === -1) {
break;
}
onLine(buffer.subarray(lineStart, lineEnd), fieldLength);
lineStart = position; // we're now on the next line
fieldLength = -1;
}
if (lineStart === bufLength) {
buffer = undefined; // we've finished reading it
} else if (lineStart !== 0) {
buffer = buffer.subarray(lineStart);
position -= lineStart;
}
}
}fes 在使用上更适用于现代 Web 应用和 Node.js 环境,解决了原生 EventSource 的局限性,提供了更丰富的功能和更细粒度的控制。
海云前端丨前端开发丨简历面试辅导丨求职陪跑