1.概念
策略(Strategy)模式定义了一系列算法,并将每个算法封装起来,使它们可以相互替换,且算法的变化不会影响使用算法的客户。策略模式属于行为型设计模式,它通过对算法进行封装,把使用算法的责任和算法的实现分割开来,并委派给不同的对象对这些算法进行管理。
策略模式可以简单理解为:"一件事有多种做法,你可以随时换着来,不用改其他地方"。
打个生活比方:
比如你要去上班(这是 "目标"),可以有多种方式(这些方式就是 "策略"):
- 晴天骑共享单车
- 下雨打出租车
- 赶时间就坐地铁
这些方式都是去上班的办法,互不影响。你可以根据天气、时间随时换,而 "上班" 这个目标本身不用变,换方式时也不用改其他安排。
核心就是:把做一件事的不同方法单独拎出来,想用哪个就用哪个,切换起来很方便,还不影响其他部分。
2.策略模式结构
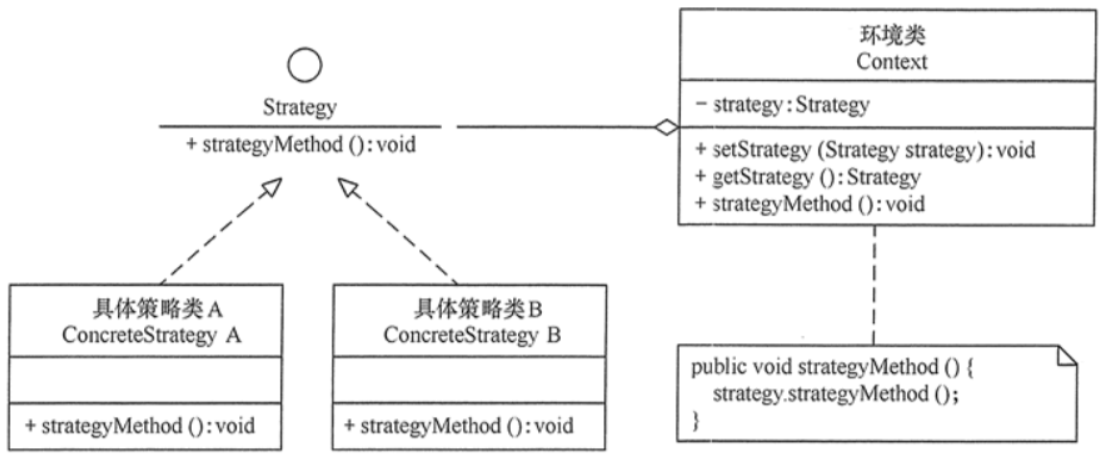
策略模式包含 3 个核心角色:
- 策略接口(Strategy):定义所有支持的算法的公共接口(或抽象类),声明算法的核心方法。
- 具体策略(ConcreteStrategy):实现策略接口,包含具体的算法逻辑(如不同的排序算法、支付方式等)。
- 上下文(Context):持有一个策略接口的引用,负责调用策略的算法。客户端通过上下文间接使用策略,且上下文可动态切换策略(通过 setter 方法)。
3.优点
- 灵活性高:算法可动态切换,客户端无需修改代码即可更换策略。
- 符合开闭原则:新增算法只需新增具体策略类,无需修改上下文或其他策略。
- 避免多重条件判断 :用多态代替
if-else或switch语句,代码更清晰。 - 算法复用:策略类可在不同场景中复用。
4.适用场景
- 当一个问题有多种解决方案(算法),且需要动态选择其中一种时(如支付系统的多种支付方式、排序算法的选择)。
- 当代码中存在大量与算法相关的
if-else判断,且这些算法可能频繁变化时。 - 当需要隐藏算法的具体实现细节,只暴露其接口时。
5.策略模式示例
说明:设计一个 "折扣计算" 模块,支持 3 种折扣策略:
- 新用户折扣(满 100 减 20)
- 会员折扣(9 折)
- 促销折扣(满 200 减 50)
java
// 1. 策略接口:定义折扣计算方法
public interface DiscountStrategy {
// 计算折扣后金额:参数为原价,返回折后价
double calculate(double originalPrice);
}
// 2. 具体策略:新用户折扣
public class NewUserDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
// 满100减20
return originalPrice >= 100 ? originalPrice - 20 : originalPrice;
}
}
// 具体策略:会员折扣(9折)
public class MemberDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * 0.9;
}
}
// 具体策略:促销折扣(满200减50)
public class PromotionDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice >= 200 ? originalPrice - 50 : originalPrice;
}
}
// 3. 上下文:折扣计算器(使用策略的类)
public class DiscountContext {
// 持有策略接口的引用
private DiscountStrategy strategy;
// 构造方法:初始化时指定策略
public DiscountContext(DiscountStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 动态切换策略
public void setStrategy(DiscountStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 调用策略计算折扣
public double getFinalPrice(double originalPrice) {
return strategy.calculate(originalPrice);
}
}
// 1. 策略接口:定义折扣计算方法
public interface DiscountStrategy {
// 计算折扣后金额:参数为原价,返回折后价
double calculate(double originalPrice);
}
// 2. 具体策略:新用户折扣
public class NewUserDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
// 满100减20
return originalPrice >= 100 ? originalPrice - 20 : originalPrice;
}
}
// 具体策略:会员折扣(9折)
public class MemberDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * 0.9;
}
}
// 具体策略:促销折扣(满200减50)
public class PromotionDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice >= 200 ? originalPrice - 50 : originalPrice;
}
}
// 3. 上下文:折扣计算器(使用策略的类)
public class DiscountContext {
// 持有策略接口的引用
private DiscountStrategy strategy;
// 构造方法:初始化时指定策略
public DiscountContext(DiscountStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 动态切换策略
public void setStrategy(DiscountStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 调用策略计算折扣
public double getFinalPrice(double originalPrice) {
return strategy.calculate(originalPrice);
}
}客户端:
java
public DiscountStrategy strategy(String role) {
switch (role) {
case "new":
return new NewUserDiscount();
case "member":
return new MemberDiscount();
case "promotion":
return new PromotionDiscount();
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知用户类型");
}
}可见虽然我们采用策略模式进行算法封装,但是在逻辑分配时还是使用到了if-else式硬编码格式,到后续我们想要新增新的策略也需要修改客户端的代码!
6.策略模式优化
策略模式的核心是封装算法变化,让客户端可以灵活切换不同实现,避免冗余的条件判断。它与工厂方法模式都通过抽象接口实现解耦,但策略模式聚焦 "行为 / 算法的使用",工厂方法聚焦 "对象的创建"。实际开发中,两者常结合使用:用工厂方法创建策略对象,用策略模式使用这些对象,既简化了对象创建,又实现了算法的灵活切换。
说明:使用工厂方法+Map集合+策略模式优化
使用工厂方法可将对象的创建解耦,使用Map集合可消除if-else,使用策略模式可将算法的使用解耦。
java
/**
* 角色处理器接口
* 策略模式的核心接口,定义不同角色的处理行为
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface RoleHandler {
/**
* 处理用户角色相关业务逻辑
* @param userDTO 用户数据传输对象
*/
void handle(UserDTO userDTO);
}
/**
* 管理员角色处理器
* 处理管理员角色相关的业务逻辑
*/
@Component
public class ManagerRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {
@Resource
private ManagerMapper managerMapper;
@Override
public void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {
managerMapper.insertManager(userDTO);
}
}
/**
* 学生角色处理器
* 处理学生角色相关的业务逻辑
*/
@Component
public class StudentRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {
@Resource
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {
studentMapper.insertStudent(userDTO);
}
}
/**
* 教师角色处理器
* 处理教师角色相关的业务逻辑
*/
@Component
public class TeacherRoleHandler implements RoleHandler {
@Resource
private TeacherMapper teacherMapper;
@Override
public void handle(UserDTO userDTO) {
teacherMapper.insertTeacher(userDTO);
}
}
/**
* 角色处理器工厂
* 用于获取不同角色的处理器实例
*/
@Component
public class RoleHandlerFactory {
private final Map<String, RoleHandler> roleHandlerMap = new HashMap<>();
public RoleHandlerFactory(StudentRoleHandler studentRoleHandler, TeacherRoleHandler teacherRoleHandler, ManagerRoleHandler managerRoleHandler) {
roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.STUDENT, studentRoleHandler);
roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.TEACHER, teacherRoleHandler);
roleHandlerMap.put(RedisConstant.MANAGER, managerRoleHandler);
}
/**
* 根据角色名称获取对应的处理器
* @param roleName 角色名称
* @return 角色处理器
* @throws TypeException 当角色不支持时抛出异常
*/
public RoleHandler getRoleHandler(String roleName) {
RoleHandler handler = roleHandlerMap.get(roleName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new TypeException("不支持的用户角色: " + roleName);
}
return handler;
}
}客户端使用:
java
RoleHandler handler = roleHandlerFactory.getRoleHandler(role);
handler.handle(userDTO);