一、引言:微服务架构的背景与优势
随着互联网应用的复杂度不断提升,传统的单体架构(Monolithic Architecture)在可维护性、可扩展性、部署灵活性等方面逐渐暴露出瓶颈。微服务架构(Microservices Architecture)应运而生,它将一个大型应用拆分为多个小型、独立、松耦合的服务,每个服务运行在独立的进程中,通过轻量级通信机制(如HTTP/REST、gRPC)进行交互。
Java作为企业级开发的主流语言,拥有Spring Boot、Spring Cloud等成熟的生态体系,是构建微服务的理想选择。
本文将深入探讨Java微服务架构中的常见设计模式,结合代码示例、Mermaid流程图、图表、Prompt设计示例,全面解析微服务的设计与实现。
二、微服务核心设计模式
1. 服务发现模式(Service Discovery)
在微服务架构中,服务实例动态变化,客户端无法通过硬编码地址访问服务。服务发现模式通过注册中心(如Eureka、Consul、Nacos)实现服务的自动注册与发现。
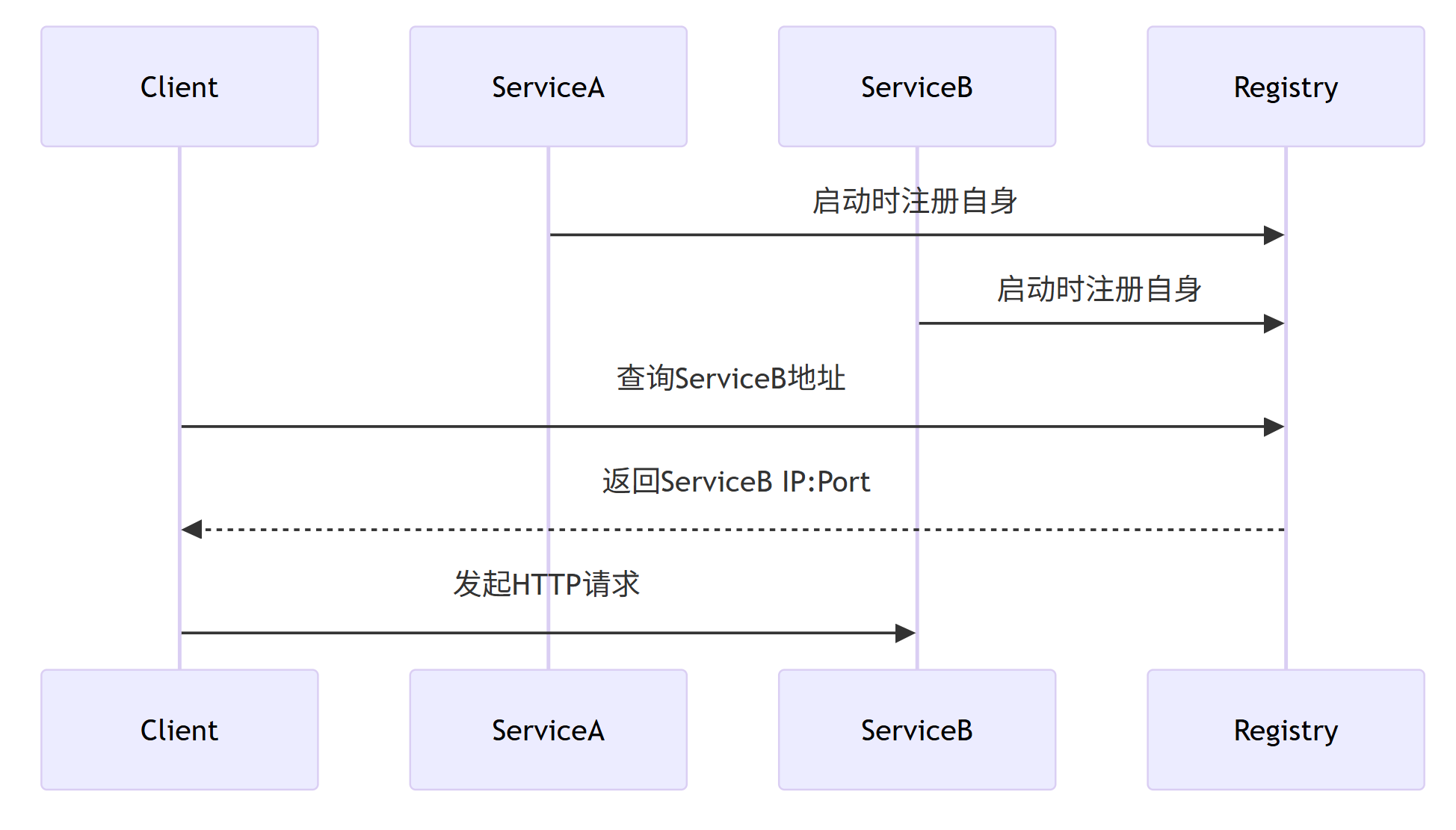
Mermaid 流程图:服务注册与发现流程
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant ServiceA
participant ServiceB
participant Registry
ServiceA->>Registry: 启动时注册自身
ServiceB->>Registry: 启动时注册自身
Client->>Registry: 查询ServiceB地址
Registry-->>Client: 返回ServiceB IP:Port
Client->>ServiceB: 发起HTTP请求
Java代码示例(Spring Cloud + Eureka)
// 服务提供者(ServiceB)
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RestController
public class ServiceBApplication {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello from Service B!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceBApplication.class, args);
}
}
application.yml
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: service-b
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
// 服务消费者(ServiceA)调用ServiceB
@RestController
public class ServiceAController {
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
@GetMapping("/call-b")
public String callServiceB() {
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.choose("service-b");
String url = "http://" + instance.getHost() + ":" + instance.getPort() + "/hello";
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
}
}
说明 :
LoadBalancerClient从Eureka获取服务实例,实现负载均衡调用。
2. API网关模式(API Gateway)
API网关是微服务架构的入口,负责请求路由、认证、限流、日志等横切关注点。
Mermaid 架构图:API网关结构
graph TD
A[客户端] --> B[API 网关]
B --> C[服务A]
B --> D[服务B]
B --> E[服务C]
B --> F[认证服务]
B --> G[限流组件]
B --> H[日志组件]
Java代码示例(Spring Cloud Gateway)
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("service_a_route", r -> r.path("/api/service-a/**")
.uri("http://localhost:8080"))
.route("service_b_route", r -> r.path("/api/service-b/**")
.uri("http://localhost:8081"))
.build();
}
}
gateway配置
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: service_a
predicates:
- Path=/api/service-a/**
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=Authorization, Bearer token123
优势:统一入口、安全控制、简化客户端调用。
3. 断路器模式(Circuit Breaker)
当服务调用失败率过高时,断路器会"熔断"请求,防止雪崩效应。常用实现:Hystrix (已停更)或 Resilience4j。
Mermaid 状态图:断路器状态转换
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> Closed
Closed --> Open : 失败次数 > 阈值
Open --> Half-Open : 超时后尝试恢复
Half-Open --> Closed : 调用成功
Half-Open --> Open : 调用失败Java代码示例(Resilience4j)
@Service
public class ExternalServiceClient {
private final CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker;
public ExternalServiceClient() {
CircuitBreakerConfig config = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofMillis(1000))
.slidingWindowSize(5)
.build();
circuitBreaker = CircuitBreaker.of("externalService", config);
}
public String callExternalService() {
Supplier<String> decoratedSupplier = CircuitBreaker
.decorateSupplier(circuitBreaker, () -> {
// 模拟远程调用
if (Math.random() < 0.6) {
throw new RuntimeException("Service unavailable");
}
return "Success";
});
Try<String> result = Try.ofSupplier(decoratedSupplier);
return result.isSuccess() ? result.get() : "Fallback Response";
}
}
4. 配置中心模式(Configuration Management)
微服务数量多,配置分散。配置中心(如Nacos、Spring Cloud Config)实现配置的集中管理与动态刷新。
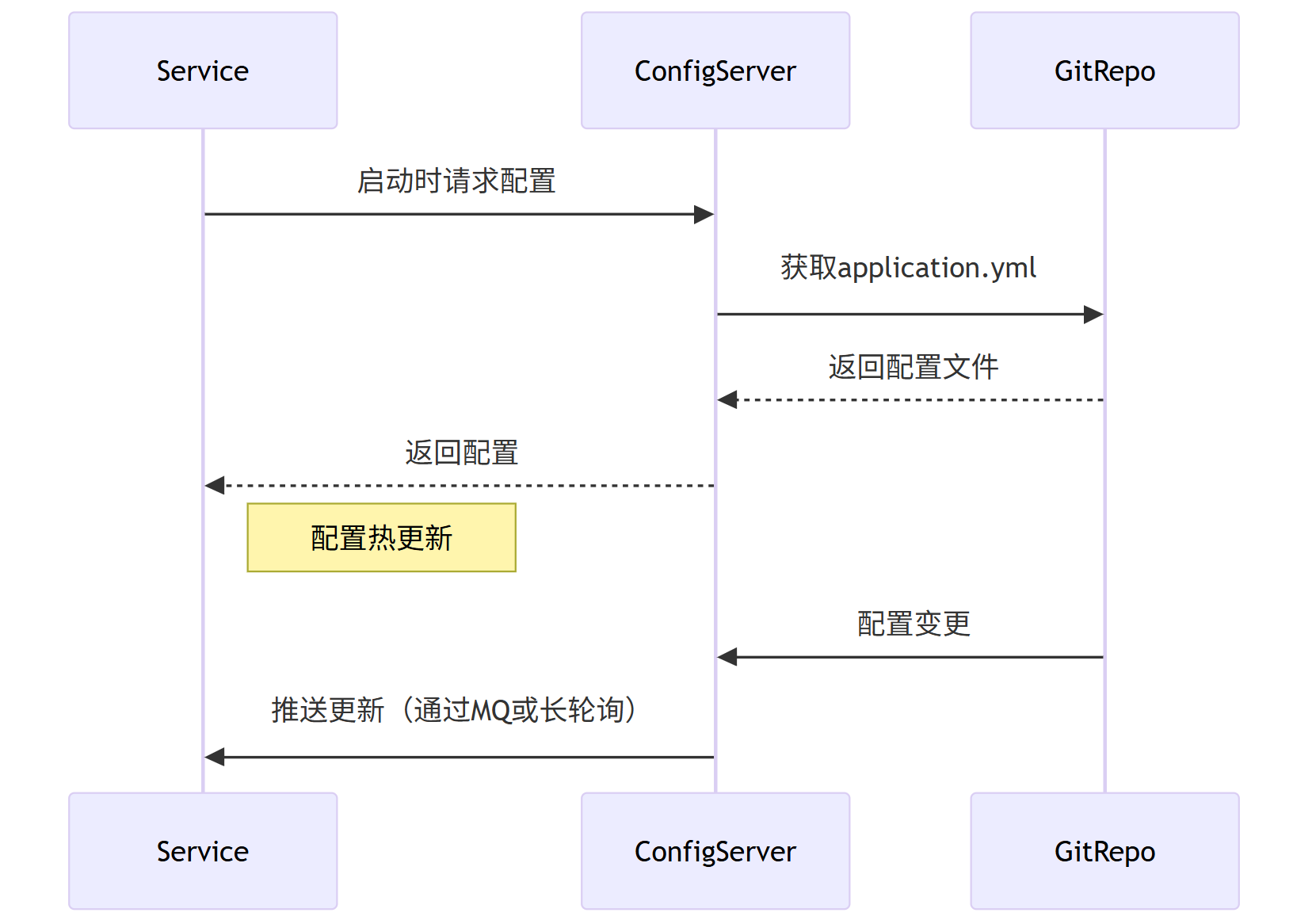
Mermaid 流程图:配置中心工作流程
sequenceDiagram
participant Service
participant ConfigServer
participant GitRepo
Service->>ConfigServer: 启动时请求配置
ConfigServer->>GitRepo: 获取application.yml
GitRepo-->>ConfigServer: 返回配置文件
ConfigServer-->>Service: 返回配置
Note right of Service: 配置热更新
GitRepo->>ConfigServer: 配置变更
ConfigServer->>Service: 推送更新(通过MQ或长轮询)
Java代码示例(Spring Cloud Config + Nacos)
@RestController
@RefreshScope // 支持配置热更新
public class ConfigController {
@Value("${app.message:Default}")
private String message;
@GetMapping("/config")
public String getConfig() {
return message;
}
}
bootstrap.yml
spring:
application:
name: my-service
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
file-extension: yaml
优势:配置统一管理、支持灰度发布、环境隔离。
5. 分布式追踪(Distributed Tracing)
微服务调用链复杂,难以定位问题。Sleuth + Zipkin 实现请求链路追踪。
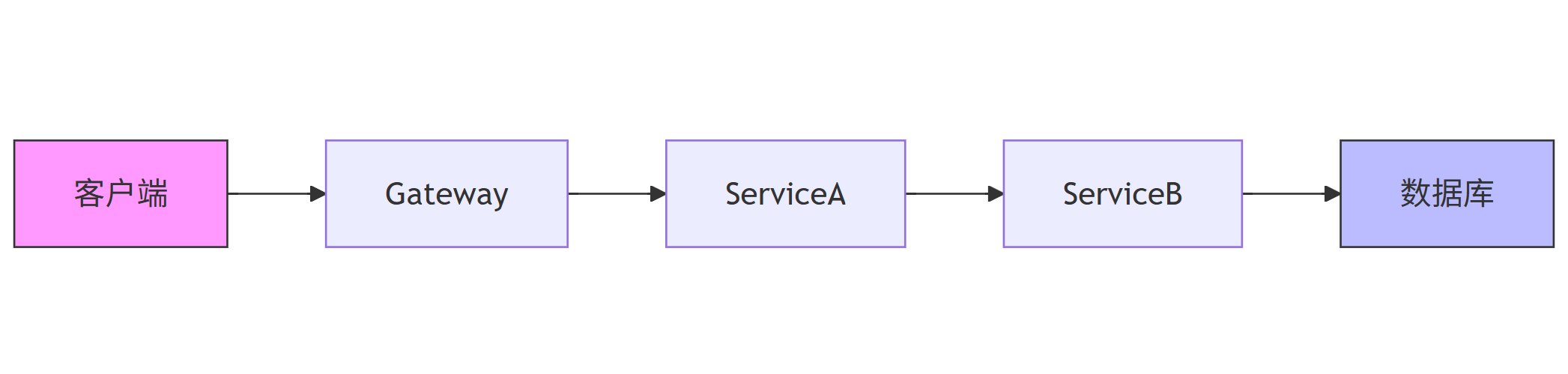
Mermaid 调用链图
graph LR
A[客户端] --> B[Gateway]
B --> C[ServiceA]
C --> D[ServiceB]
D --> E[数据库]
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333
style E fill:#bbf,stroke:#333
Java代码示例(Sleuth集成)
<!-- pom.xml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml
spring:
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9411
sleuth:
sampler:
probability: 1.0 # 100%采样
效果:每个请求生成唯一Trace ID,Zipkin可视化调用链。
6. 事件驱动架构(Event-Driven Architecture)
通过消息队列(如Kafka、RabbitMQ)实现服务间异步通信,提升系统响应性与解耦。
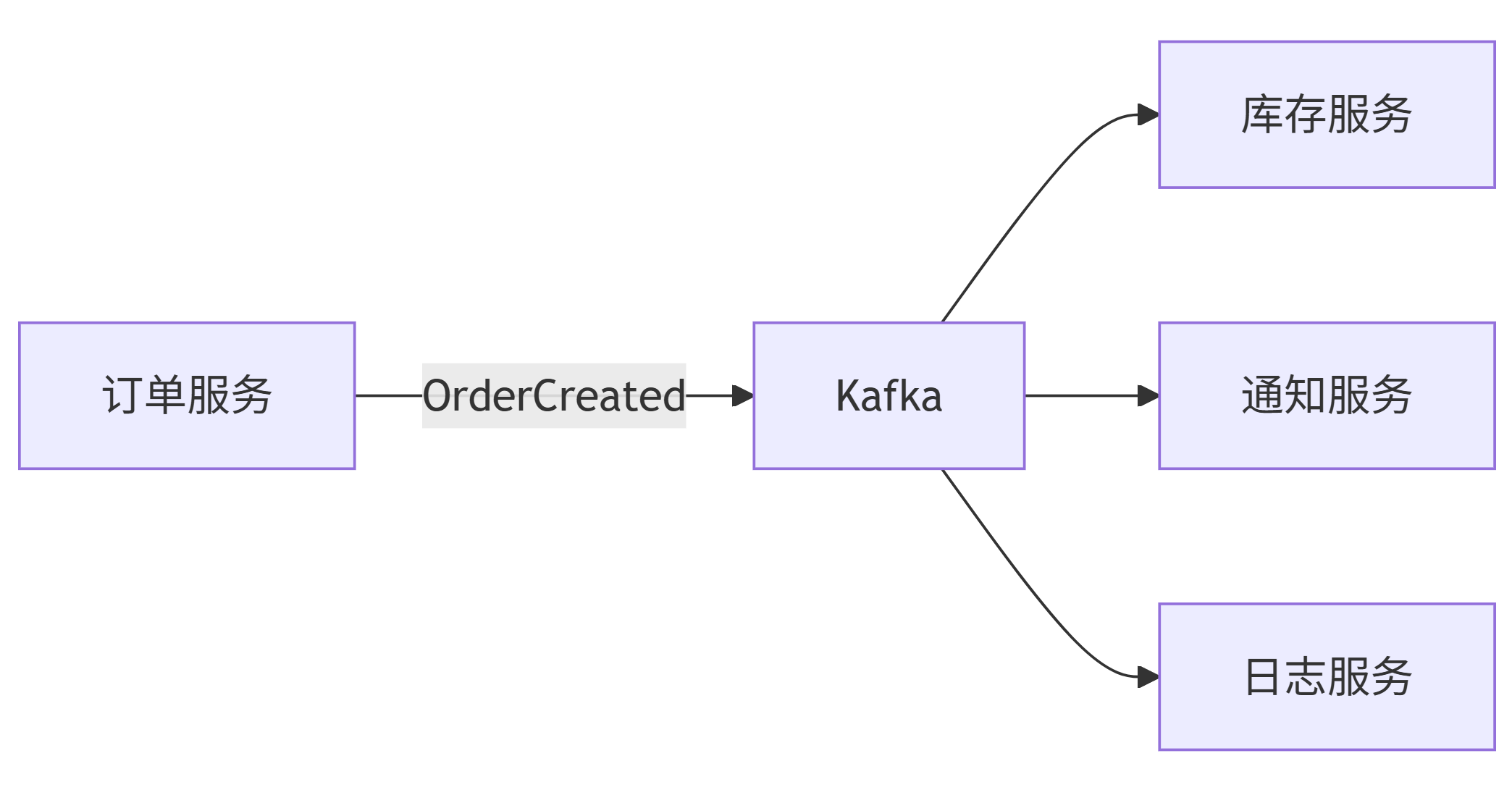
Mermaid 消息流图
graph LR
A[订单服务] -- "OrderCreated" --> B[Kafka]
B --> C[库存服务]
B --> D[通知服务]
B --> E[日志服务]
Java代码示例(Spring Kafka)
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public void createOrder(String orderId) {
// 创建订单逻辑
System.out.println("订单创建: " + orderId);
// 发送事件
kafkaTemplate.send("order-events", orderId, "CREATED");
}
}
@Component
public class InventoryConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = "order-events", groupId = "inventory-group")
public void consume(String orderId, String status) {
if ("CREATED".equals(status)) {
System.out.println("库存服务处理订单: " + orderId);
// 扣减库存
}
}
}
优势:削峰填谷、最终一致性、高可用。
三、微服务通信模式
1. 同步通信(REST + Feign)
@FeignClient(name = "user-service", url = "http://localhost:8082")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
2. 异步通信(gRPC)
// user.proto
syntax = "proto3";
package com.example;
service UserService {
rpc GetUser (UserRequest) returns (UserResponse);
}
message UserRequest {
int64 id = 1;
}
message UserResponse {
string name = 1;
string email = 2;
}
Java生成代码后可直接调用,性能高于HTTP。
四、数据库设计模式
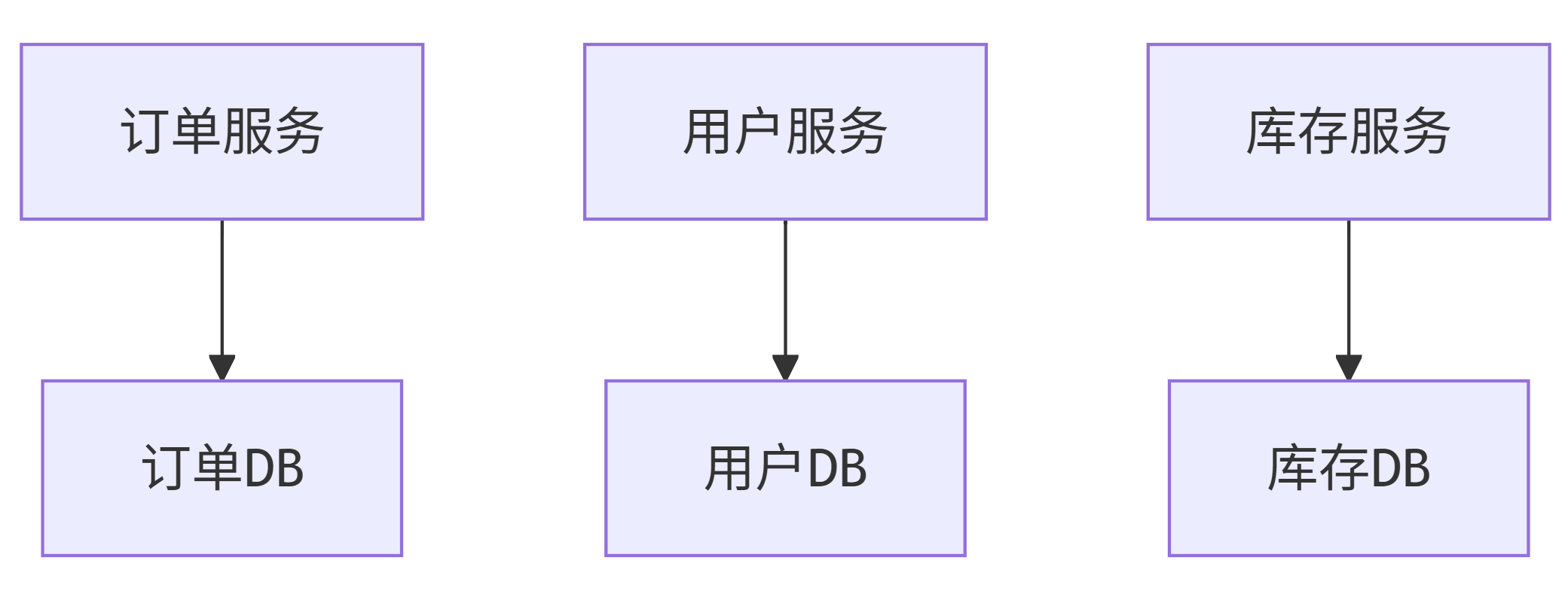
1. 每个服务独立数据库(Database per Service)
避免服务间数据库耦合。
Mermaid 架构图
graph TD
A[订单服务] --> B[订单DB]
C[用户服务] --> D[用户DB]
E[库存服务] --> F[库存DB]
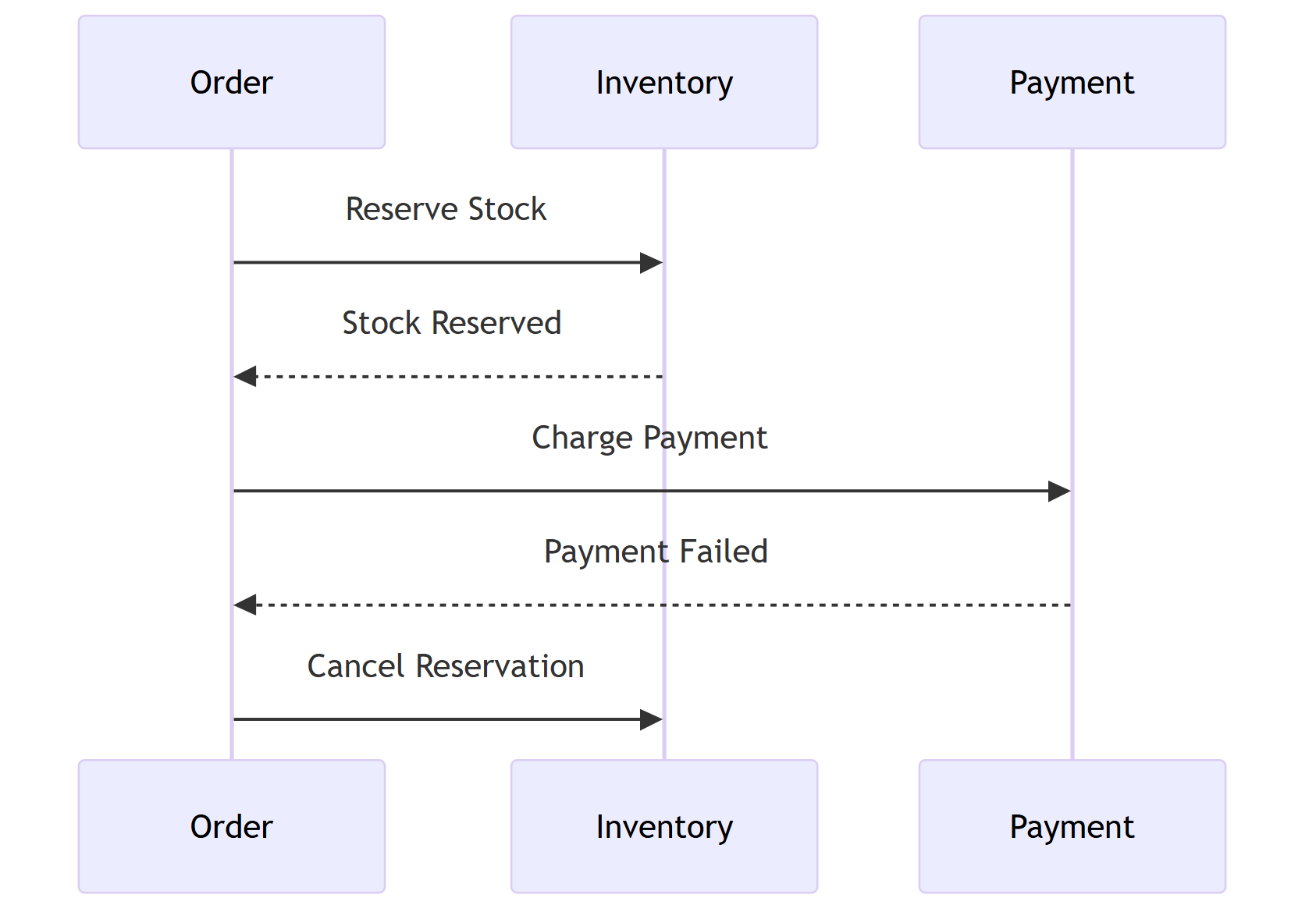
2. Saga模式(分布式事务)
使用事件或补偿机制实现跨服务事务。
Mermaid Saga流程图
sequenceDiagram
participant Order
participant Inventory
participant Payment
Order->>Inventory: Reserve Stock
Inventory-->>Order: Stock Reserved
Order->>Payment: Charge Payment
Payment-->>Order: Payment Failed
Order->>Inventory: Cancel Reservation
Java代码示例(基于事件的Saga)
@Service
public class OrderSaga {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafka;
public void createOrder(Order order) {
// 步骤1:预留库存
kafka.send("inventory-topic", "RESERVE:" + order.getId());
// 步骤2:扣款
try {
boolean success = paymentService.charge(order.getAmount());
if (success) {
kafka.send("order-topic", "CONFIRM:" + order.getId());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("支付失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 补偿:取消库存预留
kafka.send("inventory-topic", "CANCEL:" + order.getId());
}
}
}
五、安全设计模式
1. JWT认证
public String generateToken(String username) {
return Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(username)
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 86400000))
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, "secretKey")
.compact();
}
2. OAuth2 + Spring Security
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/api/public/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer(OAuth2ResourceServerConfigurer::jwt);
return http.build();
}
}
六、监控与日志
1. Prometheus + Grafana
application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: prometheus,health,info
metrics:
export:
prometheus:
enabled: true
暴露 /actuator/prometheus 接口供Prometheus抓取。
2. ELK日志系统
- Elasticsearch:存储日志
- Logstash:日志收集
- Kibana:可视化
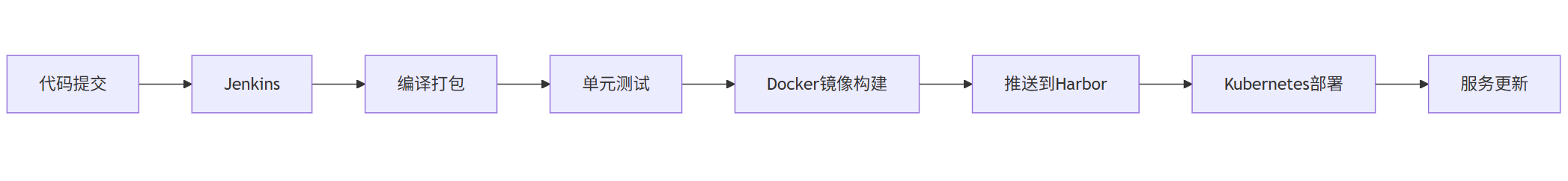
七、部署与CI/CD
Mermaid 部署流程图
graph LR
A[代码提交] --> B[Jenkins]
B --> C[编译打包]
C --> D[单元测试]
D --> E[Docker镜像构建]
E --> F[推送到Harbor]
F --> G[Kubernetes部署]
G --> H[服务更新]
示例:Dockerfile
FROM openjdk:11-jre-slim
COPY target/myapp.jar /app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/app.jar"]
八、Prompt设计示例(用于AI辅助开发)
在实际开发中,可使用大模型辅助生成代码、文档或架构设计。以下是几个典型Prompt示例:
Prompt 1:生成Spring Boot微服务启动类
Prompt: 请生成一个使用Spring Boot和Eureka客户端的Java微服务启动类,包含@RestController,提供一个GET接口返回"Hello World",端口8080,服务名为user-service。
预期输出:@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RestController
public class UserServiceApplication {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
Prompt 2:设计API网关路由
Prompt : 使用Spring Cloud Gateway为三个微服务(user-service:8080, order-service:8081, product-service:8082)配置路由,路径分别为/api/user/, /api/order/, /api/product/**,并为所有请求添加请求头X-Request-Id。
预期输出:spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user_route
predicates:
- Path=/api/user/**
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Id, {uuid}
Prompt 3:生成Resilience4j断路器配置
Prompt: 请用Java代码创建一个Resilience4j断路器,失败率阈值60%,滑动窗口大小10秒,打开状态持续5秒,记录调用结果日志。
预期输出:CircuitBreakerConfig config = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(60)
.slidingWindowSize(10)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.build();
CircuitBreaker cb = CircuitBreaker.of("myService", config);
cb.getEventPublisher().onStateTransition(event ->
System.out.println("State changed: " + event.getStateTransition()));
九、微服务架构对比图
| 服务发现 | 动态伸缩、高可用 | 增加网络开销 | 服务实例频繁变化 |
| API网关 | 统一入口、安全控制 | 单点故障风险 | 多服务对外暴露 |
| 断路器 | 防止雪崩 | 增加复杂度 | 依赖不稳定服务 |
| 配置中心 | 配置统一管理 | 依赖外部系统 | 多环境、多实例 |
| 事件驱动 | 异步、解耦 | 最终一致性 | 高并发、异步处理 |
十、总结
Java微服务架构通过一系列设计模式解决了分布式系统的复杂性问题:
- 服务发现 实现动态寻址
- API网关 统一入口与治理
- 断路器 提升容错能力
- 配置中心 实现集中管理
- 事件驱动 实现异步解耦
- 分布式追踪 增强可观测性
结合Spring Boot + Spring Cloud生态,开发者可以快速构建高可用、可扩展的微服务系统。
建议:微服务不是银弹,应根据业务规模、团队能力合理选择。小项目建议从单体起步,逐步演进。
附录:完整项目结构示例
microservices-demo/
├── api-gateway/
├── user-service/
├── order-service/
├── inventory-service/
├── config-server/
├── eureka-server/
└── docker-compose.yml
推荐使用Docker Compose统一编排,实现本地一键启动。