CAD图纸上的表格信息承载着大量关键数据,生产过程中会导出表格数据到excel,本文将介绍如何通过自定义 MxCAD 插件,在web端实现对CAD图纸中表格的智能识别、自动合并与高效导出,大幅提升数据提取效率与准确性,效果如下:
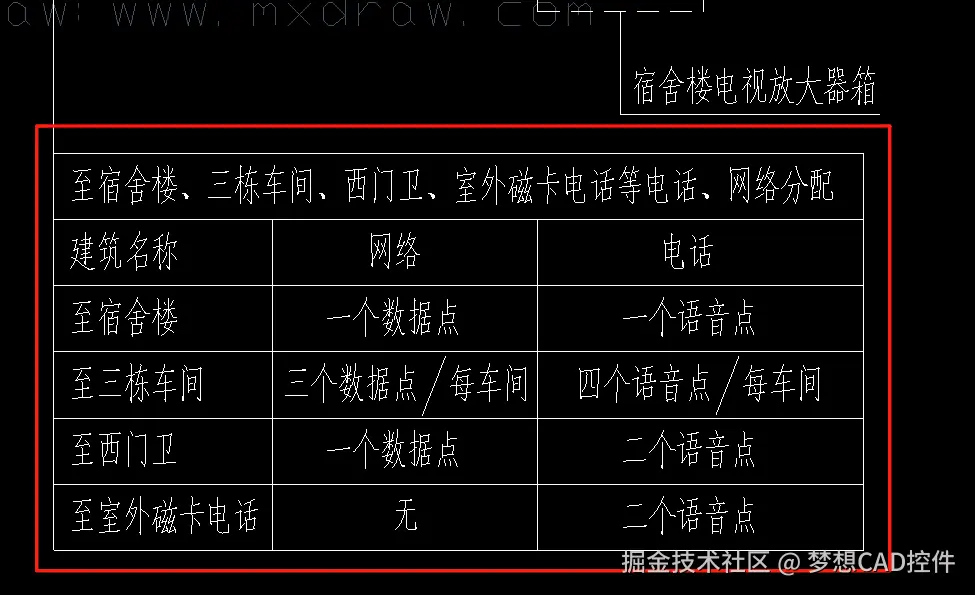
一、功能概述
本次图纸表格提取主要实现以下核心功能:
- 交互式区域选择:用户通过鼠标框选目标表格区域。
- 图形元素识别:自动识别范围内的直线、文字、多段线等实体。
- 表格结构重建:基于交点分析重建表格网格。
- 智能单元格合并:支持横向与纵向跨单元格合并识别。
- 内容提取与导出:提取单元格文本内容并导出为 Excel 文件。
二、技术实现原理
2.1 实体获取与预处理
首先让用户指定一个提取范围(矩形框),然后利用 mxcad 中的 MxCADSelectionSet 选择集跨区域选择所有相关实体:
ts
const ss = new MxCADSelectionSet();
await ss.crossingSelect(corner1.x, corner1.y, corner2.x, corner2.y);为确保嵌套块(BlockReference)中的实体也能被识别,程序递归遍历块定义,并应用变换矩阵(blockTransform)还原其真实坐标位置。
ts
const needTransformEntity: { handle: string, mart: McGeMatrix3d }[] = [];
const Mx_getBlokEntity = (blkRec: McDbBlockTableRecord, mart: McGeMatrix3d) => {
blkRec.getAllEntityId().forEach(id => {
let ent = id.getMcDbEntity();
if (ent instanceof McDbBlockReference) {
let blkref = ent as McDbBlockReference;
let mat = blkref.blockTransform.clone();
mat.preMultBy(mart);
Mx_getBlokEntity(blkref.blockTableRecordId.getMcDbBlockTableRecord(), mat);
} else {
needTransformEntity.push({ handle: ent.getHandle(), mart });
...
}
})
}此外,多段线(Polyline)会被打散为独立的直线或圆弧段,便于后续交点计算。
ts
const explodePl = (ent: McDbPolyline, mart?: McGeMatrix3d): McDbEntity[] => {
// 如果是多段线,需要打散成线段
const numVert = ent.numVerts();
const entsArr: McDbEntity[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < numVert; i++) {
if (i < numVert - 1) {
const convexity = ent.getBulgeAt(i);
const pt1 = ent.getPointAt(i).val;
const pt2 = ent.getPointAt(i + 1).val;
if (mart) {
pt1.transformBy(mart);
pt2.transformBy(mart);
}
if (!convexity) {
const line = new McDbLine(pt1, pt2);
entsArr.push(line)
} else {
const d = (ent.getDistAtPoint(pt1).val + ent.getDistAtPoint(pt2).val) / 2;
const midPt = ent.getPointAtDist(d).val;
const arc = new McDbArc();
arc.computeArc(pt1.x, pt1.y, midPt.x, midPt.y, pt2.x, pt2.y);
entsArr.push(arc)
}
} else {
if (ent.isClosed) entsArr.push(new McDbLine(ent.getPointAt(0).val, ent.getPointAt(numVert - 1).val))
}
}
return entsArr;
}2.2 表格线段分类
在上述步骤中,我们提取到了图纸框选范围内的所有实体并对部分实体做了初步处理,接下来我们需要通过提取出框选范围内的所有直线,并将这些直线分为两类:
- 水平线:方向接近 X 轴
- 垂直线:方向接近 Y 轴 直线的分类通过线向量与X轴、Y轴的单位向量之间的夹角来判断:
ts
const horizontalLineArr: McDbLine[] = [];//横向
const verticalLineArr: McDbLine[] = [];//纵向
lineArr.forEach(item => {
const vec_x = McGeVector3d.kXAxis;
const vec_y = McGeVector3d.kYAxis;
const line = item.clone() as McDbLine;
//判断直线是块内实体,如果是则需要使用变换矩阵还原真是坐标位置
const res = needTransformEntity.find(i => i.handle === item.getHandle());
if (res) {
line.startPoint = line.startPoint.clone().transformBy(res.mart);
line.endPoint = line.endPoint.transformBy(res.mart);
}
const _vec = line.startPoint.sub(line.endPoint).normalize().mult(precision);
if (vec_x.angleTo1(_vec) < precision || Math.abs((vec_x.angleTo1(_vec) - Math.PI)) < precision) {
horizontalLineArr.push(new McDbLine(line.startPoint.addvec(_vec), line.endPoint.subvec(_vec)))
}
if (vec_y.angleTo1(_vec) < precision || Math.abs((vec_y.angleTo1(_vec) - Math.PI)) < precision) {
verticalLineArr.push(new McDbLine(line.startPoint.addvec(_vec), line.endPoint.subvec(_vec)))
};
});2.3 表格交点提取与去重
在上一步中,我们以及获取到了所有的横纵直线。接下来,我们将利用水平线与垂直线之间的交点构建表格节点矩阵。所有交点经过坐标四舍五入(精度控制)和去重处理,形成唯一的网格点集合。
ts
// 点数组去重
const deduplicatePoints = (points: McGePoint3d[]): McGePoint3d[]=> {
const allPoints: McGePoint3d[] = [];
points.forEach((item, index) => {
const res = points.filter((j, ind) => {
return ind > index && item.distanceTo(j) < 0.00001
});
if (!res.length) allPoints.push(item)
});
return allPoints;
}
// 根据线拿到所有的点
const roundToPrecision = (num, precision = 0.0001): number => {
const decimals = Math.abs(Math.floor(Math.log10(precision))); // 计算精度对应的小数位数
const factor = Math.pow(10, decimals);
return Math.round(num * factor) / factor;
}
let allPoints: McGePoint3d[] = [];
horizontalLineArr.forEach(line1 => {
verticalLineArr.forEach(line2 => {
const res = line1.IntersectWith(line2, McDb.Intersect.kOnBothOperands);
if (res.length()) res.forEach(pt => {
pt.x = roundToPrecision(pt.x, precision);
pt.y = roundToPrecision(pt.y, precision);
if (arePointsInRectangle([new_corner1, new McGePoint3d(new_corner1.x, new_corner2.y), new_corner2, new McGePoint3d(new_corner2.x, new_corner1.y)], [pt])) {
allPoints.push(pt)
}
})
})
});
allPoints = deduplicatePoints(allPoints);//点数组去重;2.4 构建初始单元格矩阵
根据交点的 X 和 Y 坐标排序,生成二维网格结构 cellPointsArr,每个元素为交点或 null(表示缺失的角点),例如:
csharp
[
[A1, B1, null, D1],
[A2, B2, C2, D2],
[null, B3, C3, D3]
]
ts
const _x = Array.from(new Set(allPoints.map(item => item.x))).sort((a, b) => a - b);
const _y = Array.from(new Set(allPoints.map(item => item.y))).sort((a, b) => b - a);
const cellPointsArr: (McGePoint3d | null)[][] = [];
_y.forEach((y, row) => {
const arr: (McGePoint3d | null)[] = [];
const pts = allPoints.filter(item => item.y === y);
if (pts.length) {
_x.forEach((x, col) => {
const index = pts.findIndex(item => item.x === x);
// 若表格四个角点缺失,则手动补充数据使表格完整
if (index === -1) {
if ((row === 0 || row === _y.length - 1) && (col === 0 || row === _x.length - 1)) {
arr.push(new McGePoint3d(x, y));
} else {
arr.push(null)
}
} else {
arr.push(pts[index])
}
});
cellPointsArr.push(arr)
} else {
cellPointsArr.push(null);
}
});三、智能单元格合并机制
3.1 合并策略总览
接下来我们将采用两阶段合并策略:
- 横向合并优先
- 纵向合并补充
纵向合并仅在横向合并后形成的 2×2 子矩阵仍包含 null 元素 时触发。
3.2 横向合并逻辑
系统将整个表格划分为多个 2×2 子矩阵块 ,每个块以左上角单元格命名(如 B2 表示第2行第2列开始的块)。 对于每一个 2×2 块,若其四个角点中有 null,则判定为"不完整",需要参与合并。
合并规则(横向扩展)
| 条件 | 查找方向 | 判断依据 |
| ------------------- |-------- | ---------------------------------------------- |
| 第一个元素为 null | 左侧块 | 当前块的左邻块(如 A2)第二个元素是否为 null |
| 第二个元素为 null | 右侧块 | 当前块的右邻块(如 C2)第一个元素是否为 null |
| 第三个元素为 null | 左侧块 | 当前块的左邻块第四个元素是否为 null |
| 第四个元素为 null | 右侧块 | 当前块的右邻块第三个元素是否为 null |
示例:
B2:[[null,a],[c,b]]→ 检查A2的第二个元素是否为null
通过广度优先搜索(BFS),收集所有可横向连接的"不完整"块,形成一个合并组。
3.3 纵向合并触发条件
当横向合并完成后,若新生成的 2×2 外围矩阵仍含有 null,则启动纵向合并流程。
纵向合并规则
| 条件 | 查找方向 | 判断依据 |
| ------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------- |
| 第一个元素为 null | 上方块 | 上方块(如 B1)第三个元素是否为 null |
| 第二个元素为 null | 上方块 | 上方块第四个元素是否为 null |
| 第三个元素为 null | 下方块 | 下方块(如 B3)第一个元素是否为 null |
| 第四个元素为 null | 下方块 | 下方块第二个元素是否为 null |
示例:
B2:[[a,null],[c,b]]→ 检查B1的第四个元素是否为null
程序继续扩展合并组,直到包围盒内所有 2×2 块都被纳入,最终形成一个完整的矩形区域。
3.4 合并结果生成
合并完成后,系统计算最小行/列与最大行/列,生成新的 2×2 矩阵代表合并区域的四个角点,并记录其原始单元格范围(如 "A1+B1+A2+B2")。
ts
// 合并表格
function solveWithMerging(input: MatrixValue[][]): MergeResult[] {
const rows = input.length;
const cols = input[0].length;
if (rows < 2 || cols < 2) {
return;
}
// 1. 提取所有 2x2 子矩阵
const blocks: Record<string, MatrixValue[][]> = {};
const positions: Record<string, Position> = {};
for (let r = 0; r <= rows - 2; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c <= cols - 2; c++) {
const key = `${String.fromCharCode(65 + c)}${r + 1}`;
blocks[key] = [
[input[r][c], input[r][c + 1]],
[input[r + 1][c], input[r + 1][c + 1]]
];
positions[key] = { row: r, col: c };
}
}
// 工具:判断是否含 null
const hasNull = (mat: MatrixValue[][]): boolean =>
mat.some(row => row.some(cell => cell === null));
const processed = new Set<string>(); // 已参与合并的块
const results: MergeResult[] = [];
// 筛选出所有块
const getAllBlockNames = (visited: Set<string>): { fullRangeKeys: string[], newMatrix: MatrixValue[][] } => {
// 获取包围盒(原始合并区域)
let minRow = Infinity, maxRow = -Infinity;
let minCol = Infinity, maxCol = -Infinity;
Array.from(visited).forEach(key => {
const { row, col } = positions[key];
minRow = Math.min(minRow, row);
maxRow = Math.max(maxRow, row);
minCol = Math.min(minCol, col);
maxCol = Math.max(maxCol, col);
});
// ===== 拓展:生成包围盒内所有 2×2 块名(完整矩形区域)=====
const fullRangeKeys: string[] = [];
for (let r = minRow; r <= maxRow; r++) {
for (let c = minCol; c <= maxCol; c++) {
const key = `${String.fromCharCode(65 + c)}${r + 1}`;
fullRangeKeys.push(key);
// 标记这些块为已处理(防止在独立块中重复)
processed.add(key);
}
};
// 提取新 2x2 矩阵(四个角)
const safeGet = (r: number, c: number): MatrixValue =>
r < rows && c < cols ? input[r][c] : null;
const newMatrix: MatrixValue[][] = [
[safeGet(minRow, minCol), safeGet(minRow, maxCol + 1)],
[safeGet(maxRow + 1, minCol), safeGet(maxRow + 1, maxCol + 1)]
];
return { fullRangeKeys, newMatrix }
}
// ===== 第一阶段:处理含 null 的合并组 =====
for (const startKey in blocks) {
if (processed.has(startKey) || !hasNull(blocks[startKey])) continue;
const visited = new Set<string>();
const queue: string[] = [startKey];
visited.add(startKey);
processed.add(startKey);
while (queue.length > 0) {
const key = queue.shift()!;
const { row, col } = positions[key];
const block = blocks[key];
const [a, b] = block[0];
const [c, d] = block[1];
const leftKey = col > 0 ? `${String.fromCharCode(64 + col)}${row + 1}` : null;
const rightKey = col < cols - 2 ? `${String.fromCharCode(66 + col)}${row + 1}` : null;
// 先横向合并,如果符合要求就跳出循环
// 规则1: 第一个元素 null → 上方第三个 或 左边第二个
if (a === null) {
if (leftKey && blocks[leftKey] && !visited.has(leftKey) && blocks[leftKey][0][1] === null) {
visited.add(leftKey);
queue.push(leftKey);
processed.add(leftKey);
}
}
// 规则2: 第二个元素 null → 上方第四个 或 右边第一个
if (b === null) {
if (rightKey && blocks[rightKey] && !visited.has(rightKey) && blocks[rightKey][0][0] === null) {
visited.add(rightKey);
queue.push(rightKey);
processed.add(rightKey);
}
}
// 规则3: 第三个元素 null → 下方第一个 或 左边第四个
if (c === null) {
if (leftKey && blocks[leftKey] && !visited.has(leftKey) && blocks[leftKey][1][1] === null) {
visited.add(leftKey);
queue.push(leftKey);
processed.add(leftKey);
}
}
// 规则4: 第四个元素 null → 下方第二个 或 右边第三个
if (d === null) {
if (rightKey && blocks[rightKey] && !visited.has(rightKey) && blocks[rightKey][1][0] === null) {
visited.add(rightKey);
queue.push(rightKey);
processed.add(rightKey);
}
};
}
if (visited.size === 1) queue.push(startKey);
if (!getAllBlockNames(visited).newMatrix.flat().every(item => item !== null)) {
while (queue.length > 0) {
const key = queue.shift()!;
const { row, col } = positions[key];
const block = blocks[key];
const [a, b] = block[0];
const [c, d] = block[1];
const upKey = row > 0 ? `${String.fromCharCode(65 + col)}${row}` : null;
const downKey = row < rows - 2 ? `${String.fromCharCode(65 + col)}${row + 2}` : null;
// 规则1: 第一个元素 null → 上方第三个 或 左边第二个
if (a === null) {
if (upKey && blocks[upKey] && !visited.has(upKey) && blocks[upKey][1][0] === null) {
visited.add(upKey);
queue.push(upKey);
processed.add(upKey);
}
}
// 规则2: 第二个元素 null → 上方第四个 或 右边第一个
if (b === null) {
if (upKey && blocks[upKey] && !visited.has(upKey) && blocks[upKey][1][1] === null) {
visited.add(upKey);
queue.push(upKey);
processed.add(upKey);
}
}
// 规则3: 第三个元素 null → 下方第一个 或 左边第四个
if (c === null) {
if (downKey && blocks[downKey] && !visited.has(downKey) && blocks[downKey][0][0] === null) {
visited.add(downKey);
queue.push(downKey);
processed.add(downKey);
}
}
// 规则4: 第四个元素 null → 下方第二个 或 右边第三个
if (d === null) {
if (downKey && blocks[downKey] && !visited.has(downKey) && blocks[downKey][0][1] === null) {
visited.add(downKey);
queue.push(downKey);
processed.add(downKey);
}
};
}
}
const { fullRangeKeys, newMatrix } = getAllBlockNames(visited);
const isOnlyCol = (cells: string[]): Boolean => {
const prefixes = new Set<string>();
for (const cell of cells) {
// 提取开头的字母部分(连续的大写A-Z)
const match = cell.match(/^[A-Z]+/);
if (match) {
prefixes.add(match[0]);
}
}
return prefixes.size === 1;
}
if (isOnlyCol(fullRangeKeys)) {
results.push({
merged: {
fullRangeKeys: fullRangeKeys, // 重命名后的完整范围
matrix: newMatrix
}
});
} else {
// 拿到所有合并元素后再重新组合
const res = combineSubMatrices(input, fullRangeKeys);
res.forEach(item => {
results.push({
merged: {
fullRangeKeys: getAllBlockNames(new Set(item.name.split('+'))).fullRangeKeys, // 重命名后的完整范围
matrix: item.data
}
});
})
}
}
// ===== 第二阶段:处理独立块(未被合并且未被覆盖)=====
for (const key in blocks) {
if (!processed.has(key)) {
results.push({
standalone: {
key,
matrix: blocks[key]
}
});
}
}
return results
}
type Matrix = any[][];
type SubMatrix2x2 = MatrixValue[][];
interface CombineResult<T> {
name: string;
data: SubMatrix2x2;
}
/**
* 生成所有左块 + 右块组合,只保留左块行号 ≤ 右块行号的组合
* 规则:
* - 左块:最左列的子矩阵 (A列)
* - 右块:最右列的子矩阵 (C列)
* - 组合:Xr + Ys,其中 r <= s
* - 输出:所有满足条件的组合
*/
// 改为支持任意类型 T
function combineSubMatrices<T>(matrix: Matrix, inputNames: string[]): CombineResult<T>[] {
if (!matrix || matrix.length === 0 || matrix[0].length < 2) {
throw new Error("Matrix must be at least 1x2");
}
const nameToPosition = new Map<string, { row: number; col: number }>();
// 解析输入名称
for (const rawName of inputNames) {
const name = rawName.trim().toUpperCase();
const match = name.match(/^([A-Z])(\d+)$/);
if (!match) continue;
const colIndex = match[1].charCodeAt(0) - 65;
const rowIndex = parseInt(match[2], 10) - 1;
if (rowIndex >= 0 && colIndex >= 0 &&
rowIndex <= matrix.length - 2 && colIndex <= matrix[0].length - 2) {
nameToPosition.set(name, { row: rowIndex, col: colIndex });
}
}
if (nameToPosition.size === 0) {
console.log("No valid submatrices found in input.");
return [];
}
// 按列分组
const colGroups = new Map<number, Map<number, string>>(); // col -> row -> name
nameToPosition.forEach((pos, name) => {
if (!colGroups.has(pos.col)) {
colGroups.set(pos.col, new Map());
}
colGroups.get(pos.col)!.set(pos.row, name);
})
// 找出最左列(左块)和最右列(右块)
const cols = Array.from(colGroups.keys()).sort((a, b) => a - b);
if (cols.length < 2) {
console.log("Need at least two columns for combination.");
return [];
}
const leftCol = cols[0];
const rightCol = cols[cols.length - 1];
const leftColMap = colGroups.get(leftCol)!;
const rightColMap = colGroups.get(rightCol)!;
// 获取所有行号
const leftRows = Array.from(leftColMap.keys()).sort((a, b) => a - b);
const rightRows = Array.from(rightColMap.keys()).sort((a, b) => a - b);
const results: CombineResult<T>[] = [];
// 生成所有左块 + 右块组合,只保留左块行号 ≤ 右块行号
for (const leftRow of leftRows) {
const leftName = leftColMap.get(leftRow)!;
const leftRowNum = leftRow + 1; // 0-based to 1-based
for (const rightRow of rightRows) {
const rightName = rightColMap.get(rightRow)!;
const rightRowNum = rightRow + 1;
// 只保留左块行号 ≤ 右块行号的组合
if (leftRowNum > rightRowNum) continue;
const combinedName = `${leftName}+${rightName}`;
try {
// 统一规则:对于 Xr + Ys
// - [0][0]: Xr 的左上角
// - [0][1]: Yr 的右上角 (同左块行号)
// - [1][0]: Xs 的左下角 (同右块行号)
// - [1][1]: Ys 的右下角
const yRowName = `${String.fromCharCode(65 + rightCol)}${leftRowNum}`;
const xSRowName = `${String.fromCharCode(65 + leftCol)}${rightRowNum}`;
if (!nameToPosition.has(yRowName) || !nameToPosition.has(xSRowName)) {
console.warn(`Required blocks not found for ${combinedName}: ${yRowName}, ${xSRowName}`);
continue;
}
const yRowPos = nameToPosition.get(yRowName)!;
const xSRowPos = nameToPosition.get(xSRowName)!;
const topLeft = matrix[leftRow][leftCol];
const topRight = matrix[yRowPos.row][yRowPos.col + 1];
const bottomLeft = matrix[xSRowPos.row + 1][xSRowPos.col];
const bottomRight = matrix[rightRow + 1][rightCol + 1];
const data: SubMatrix2x2 = [
[topLeft, topRight],
[bottomLeft, bottomRight]
];
if (!data.flat().filter(item => !item).length) {
results.push({ name: combinedName, data });
break;
}
} catch (error) {
console.warn(`Error processing ${combinedName}:`, error);
continue;
}
}
}
return results;
}四、文字内容提取与Excel导出
4.1 文本匹配
遍历所有文本实体(McDbText / McDbMText),判断其几何中心是否落在某个单元格范围内,若匹配成功,则将其内容附加到对应单元格。
ts
/**
* 判断点是否都在矩形范围内(含边界)
* @param rectPoints - 矩形的四个顶点(顺序无关,要求为轴对齐矩形)
* @param points - 点数组
* @returns 两个点都在矩形内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
function arePointsInRectangle(
rectPoints: McGePoint3d[],
points: McGePoint3d[],
): boolean {
// 提取所有 x 和 y 坐标
const xs = rectPoints.map(p => p.x);
const ys = rectPoints.map(p => p.y);
const minX = Math.min(...xs);
const maxX = Math.max(...xs);
const minY = Math.min(...ys);
const maxY = Math.max(...ys);
/**
* 检查单个点是否在矩形边界内(含边界)
*/
const isPointInRect = (p: McGePoint3d): boolean => {
return p.x >= minX && p.x <= maxX && p.y >= minY && p.y <= maxY;
};
// 两个点都必须在矩形内
return points.every(pt => isPointInRect(pt));
}
// 筛选出所有表格数据
const tableDataArr: CellInput[] = []
const results = solveWithMerging(cellPointsArr);
const getTextContent = (matrix: McGePoint3d[][]): string => {
let str: string = '';
const textArr = scopeAllEntity.filter(item => {
const ent = item.clone() as McDbEntity;
let _minPt: McGePoint3d, _maxPt: McGePoint3d
if (ent instanceof McDbText) {
const { minPt, maxPt } = ent.getBoundingBox();
_minPt = minPt;
_maxPt = maxPt;
} else if (item instanceof McDbMText) {
const textStyleId = MxCpp.getCurrentMxCAD().getDatabase().getCurrentlyTextStyleId();
ent.textStyleId = textStyleId;
(ent as McDbMText).reCompute();
const { minPt, maxPt } = MxCADUtility.getTextEntityBox(ent, false);
_minPt = minPt;
_maxPt = maxPt;
}
if (_maxPt && _minPt) {
// matrix扁平化
const res = needTransformEntity.find(i => i.handle === item.getHandle())
if (res) {
_minPt.transformBy(res.mart);
_maxPt.transformBy(res.mart);
}
return arePointsInRectangle(matrix.flat(), [_minPt.clone().addvec(_maxPt.sub(_minPt).mult(1 / 2))])
} else {
return false
}
})
if (textArr.length) {
textArr.forEach(text => {
if (text instanceof McDbText) {
str += `${text.textString}\n`
} else if (text instanceof McDbMText) {
str += `${text.contents}\n`
}
})
};
return str
}
results.forEach(async res => {
if (res.merged) {
const { fullRangeKeys, matrix } = res.merged;
const str = getTextContent(matrix);
tableDataArr.push({ type: DataType.merged, content: str, name: fullRangeKeys.join('+') })
} else if (res.standalone) {
const { key, matrix } = res.standalone;
const str = getTextContent(matrix);
tableDataArr.push({ type: DataType.standalone, content: str, name: key });
}
});4.2 Excel输出
使用 ExcelJS 库创建工作簿,执行以下操作:
- 合并单元格 :根据
fullRangeKeys设置跨行跨列 - 填充内容:写入提取的文本
- 样式美化:添加边框、居中对齐、自动换行
- 文件导出 :浏览器端生成 Blob 下载,Node.js 端保存为
.xlsx文件
ts
/**
* 将单元格数据导出为 Excel
*/
async function exportExcelFromCells(
data: CellInput[],
filename: string = 'tableData.xlsx'
) {
const workbook = new ExcelJS.Workbook();
const worksheet = workbook.addWorksheet('Sheet1');
const cellRegex = /^([A-Z]+)(\d+)$/;
const parsedMerges: { start: { row: number; col: number }; end: { row: number; col: number } }[] = [];
const cellsToSet: { row: number; col: number; value: string }[] = [];
/**
* 解析 A1 格式为 {row, col}
*/
function parseCellRef(cellName: string): { row: number; col: number } {
const match = cellName.match(cellRegex);
if (!match) throw new Error(`无效的单元格名: ${cellName}`);
const [, colStr, rowStr] = match;
let col = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < colStr.length; i++) {
col = col * 26 + (colStr.charCodeAt(i) - 64);
}
return { row: parseInt(rowStr), col };
}
// 第一步:处理所有数据
for (const item of data) {
if (item.type === DataType.merged) {
const cellNames = item.name.split('+').map(s => s.trim());
const positions = cellNames.map(parseCellRef);
const startRow = Math.min(...positions.map(p => p.row));
const endRow = Math.max(...positions.map(p => p.row));
const startCol = Math.min(...positions.map(p => p.col));
const endCol = Math.max(...positions.map(p => p.col));
parsedMerges.push({
start: { row: startRow, col: startCol },
end: { row: endRow, col: endCol }
});
worksheet.mergeCells(startRow, startCol, endRow, endCol);
const masterCell = worksheet.getCell(startRow, startCol);
masterCell.value = item.content;
masterCell.alignment = { horizontal: 'center', vertical: 'middle' };
} else if (item.type === DataType.standalone) {
const pos = parseCellRef(item.name);
cellsToSet.push({ row: pos.row, col: pos.col, value: item.content });
}
}
// 第二步:设置独立单元格(跳过合并区域)
for (const cell of cellsToSet) {
const isOverlapped = parsedMerges.some(merge =>
cell.row >= merge.start.row &&
cell.row <= merge.end.row &&
cell.col >= merge.start.col &&
cell.col <= merge.end.col
);
if (!isOverlapped) {
const wsCell = worksheet.getCell(cell.row, cell.col);
wsCell.value = cell.value;
}
}
// 第三步:添加边框样式到所有已使用的单元格
// 正确写法:TypeScript 兼容
const borderStyle = {
top: { style: 'thin' as const, color: { argb: 'FF000000' } },
left: { style: 'thin' as const, color: { argb: 'FF000000' } },
bottom: { style: 'thin' as const, color: { argb: 'FF000000' } },
right: { style: 'thin' as const, color: { argb: 'FF000000' } }
};
// 获取最大行列范围
let maxRow = 1;
let maxCol = 1;
[...cellsToSet, ...parsedMerges.flatMap(merge => [
merge.start, { row: merge.end.row, col: merge.end.col }
])].forEach(pos => {
maxRow = Math.max(maxRow, pos.row);
maxCol = Math.max(maxCol, pos.col);
});
// 为所有可能用到的单元格加边框
for (let row = 1; row <= maxRow; row++) {
for (let col = 1; col <= maxCol; col++) {
const cell = worksheet.getCell(row, col);
if (cell.value !== null && cell.value !== undefined) {
cell.border = borderStyle;
// 可选:默认居中对齐
if (!cell.alignment) {
cell.alignment = { horizontal: 'center', vertical: 'middle', wrapText: true };
}
}
}
}
// 浏览器环境
const buffer = await workbook.xlsx.writeBuffer();
const blob = new Blob([buffer], {
type: 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet',
});
// @ts-ignore
saveAs(blob, filename);
}
worksheet.mergeCells(startRow, startCol, endRow, endCol);
masterCell.value = item.content;
masterCell.alignment = { horizontal: 'center', vertical: 'middle' };五、实践结果
根据上述步骤实践,我们能得到一个图纸表格提取的初步demo,如果遇到其他表格情况可以参考上述实现思路在此基础上二开更多识别表格的功能。
我们编写的提取表格的demo的实践效果如下: 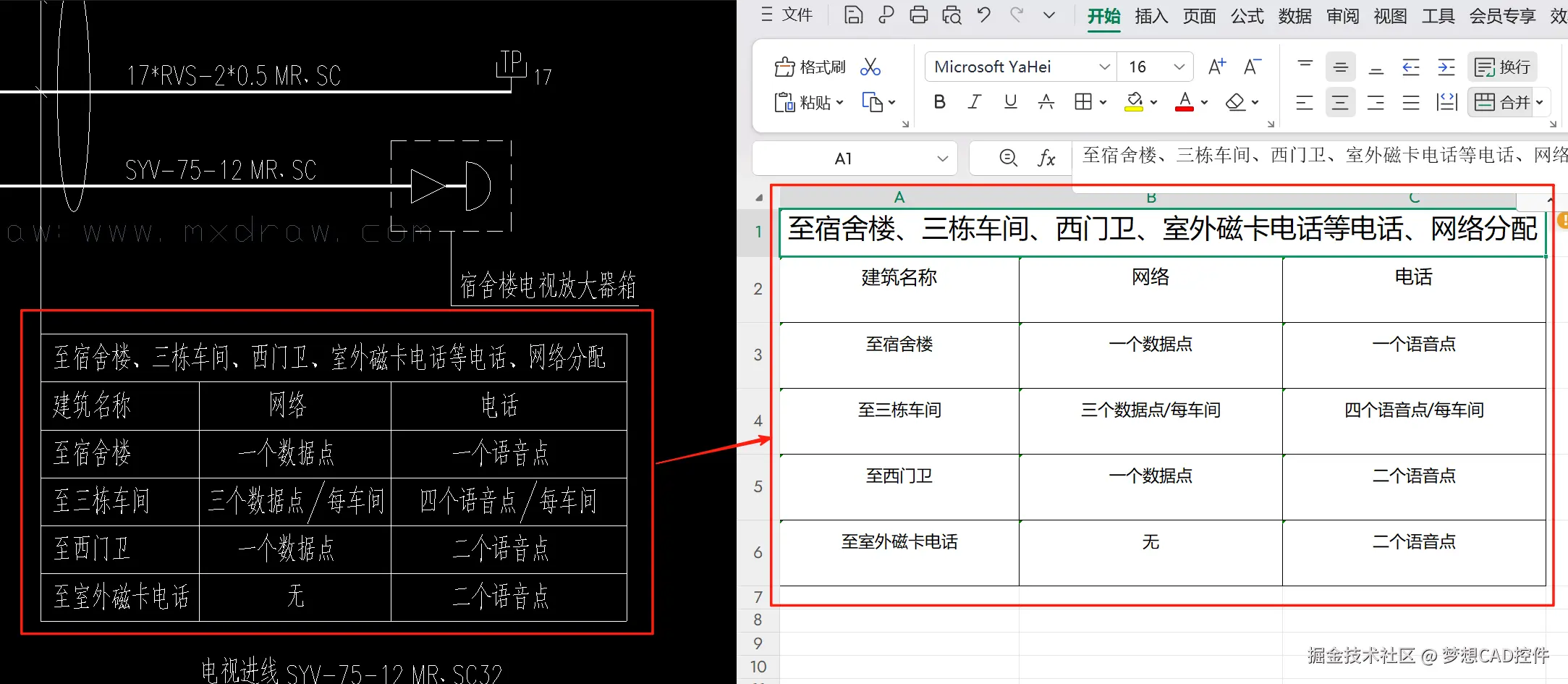
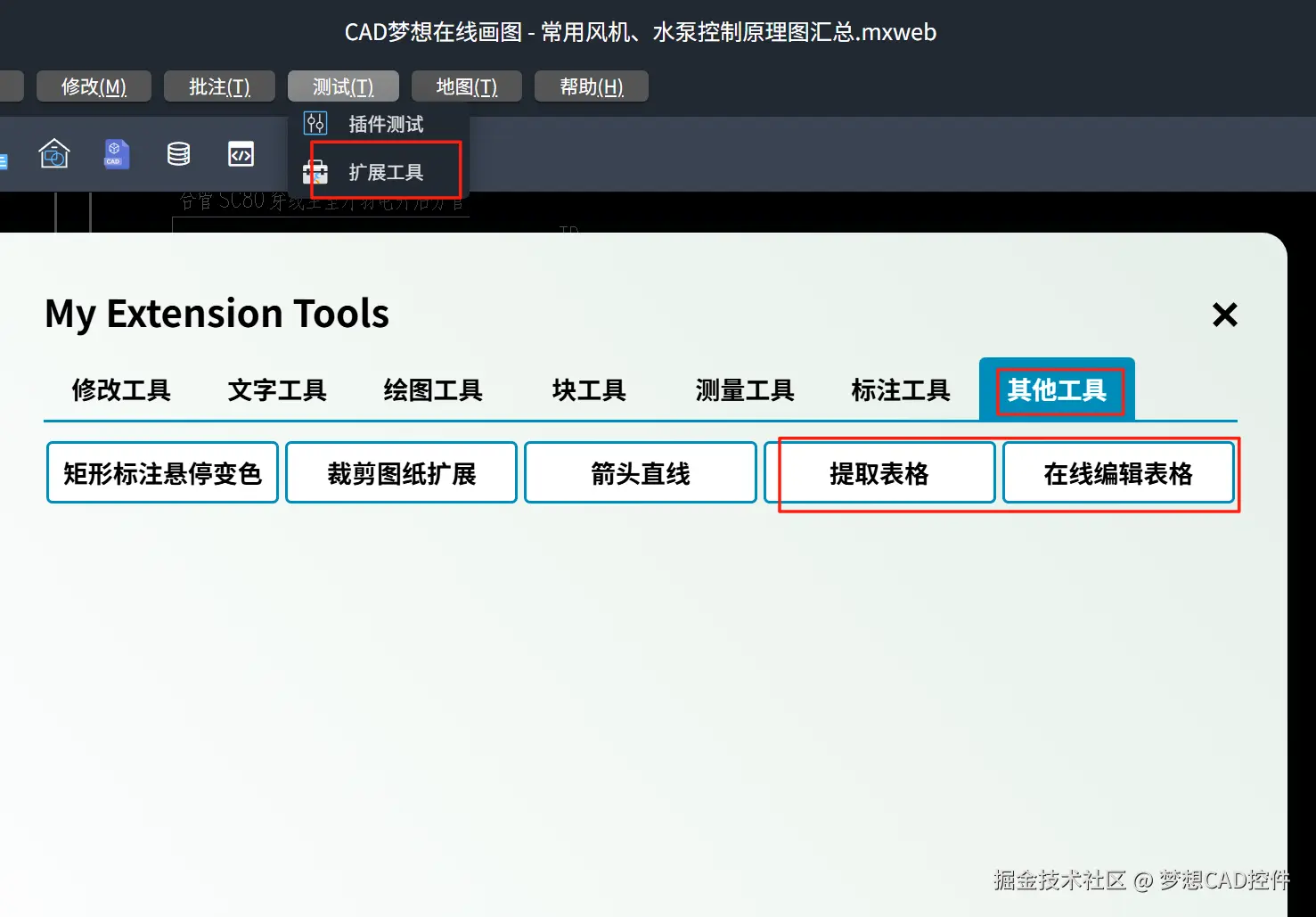
如果想要更多提取表格相关的功能实践,可以在demo2.mxdraw3d.com:3000/mxcad/ mxcad在线demo的扩展工具中查看:
若想要查看表格提取的源码,可直接下载我们的云图在线开发包。