概念
线性回归是通过属性的线性组合进行预测的线性模型,核心目标是找到一条直线、平面或更高维的超平面,使预测值与真实值之间的误差最小化。例如在房屋价格预测场景中,通过拟合 "价格 = 房屋大小" 这样的直线来实现预测
一般形式
基本表达式:对于由d个属性描述的样本x=(x1;x2;⋅⋅⋅;xd),线性模型的预测函数为f(x)=w1x1+w2x2+...+wdxd+b,向量形式可简写为f(x)=wTx+b,其中w为权重向量,b为偏置项。
简化形式:对于单属性样本,可表示为f(xi)=wxi+b,目标是使f(xi)尽可能接近真实值yi。
最小二乘法
原理:均方误差对应欧氏距离,最小二乘法通过最小化均方误差来求解模型参数,即找到使所有样本到直线的欧氏距离之和最小的直线。
参数估计:求w和b使误差函数E(w,b)=∑i=1m(yi−wxi−b)2最小化的过程称为参数估计。通过对E(w,b)分别对w和b求导,并令导数为 0,可得到w和b的最优解。
多元线性回归
当样本包含多个属性时,多元线性回归模型表达式为y=w0+w1x1+w2x2+...+wnxn,通过多属性的线性组合实现预测,其模型形式可通过矩阵等方式进一步简化和求解。
评估指标
误差平方和 / 残差平方和(SSE/RSS):计算公式为SSE=∑i=1m(yi−y^i)2,用于衡量预测值与真实值之间的总误差。
均方误差(MSE):计算公式为MSE=n1∑i=1n(yi−y^i)2,是 SSE 的平均值,反映误差的平均水平。
R 方(R2):计算公式为R2=1−SSTSSE=1−VarMSE(其中 SST 为总平方和,Var 为真实值的方差),R2越接近 1,说明模型对数据的拟合效果越好。
from sklearn import linear_model
linear_model.LinearRegression():线性回归算法
案例
波士顿房价预测
python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
# 加载数据集(适配新版sklearn)
boston = fetch_openml(name='boston', version=1, as_frame=True)
X = pd.DataFrame(boston.data, columns=boston.feature_names)
y = pd.Series(boston.target, name='MEDV') # 目标变量:房价中位数(千美元)
python
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 使用黑体显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制特征相关性热力图
corr_matrix = X.join(y).corr()
sns.heatmap(corr_matrix, annot=True, fmt=".2f", cmap='coolwarm')# annot在单元格内显示数值
plt.title("特征与房价相关性")
plt.show()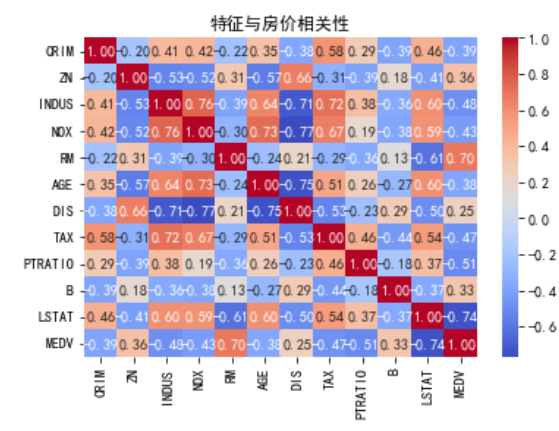
python
# 将数据转换为均值为 0、标准差为 1的标准正态分布
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# 划分训练集/测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练与评估
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = lr.predict(X_test)
print(f"线性回归性能:")
print(f"RMSE: {np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)):.2f}")#反映预测值与真实值的绝对偏差
print(f"R²: {r2_score(y_test, y_pred):.4f}") # 衡量模型拟合优度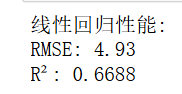
python
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
# 构建流水线(标准化+模型)
pipeline = Pipeline([
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('regressor', RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42))
])
# 训练与评估
pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_rf = pipeline.predict(X_test)
print(f"随机森林初始性能:")
print(f"RMSE: {np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_rf)):.2f}")
print(f"R²: {r2_score(y_test, y_pred_rf):.4f}")
python
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, alpha=0.6, color='blue')
plt.plot([y.min(), y.max()], [y.min(), y.max()], 'r--', lw=2)#X轴与Y轴范围
plt.xlabel('真实价格(千美元)')
plt.ylabel('预测价格(千美元)')
plt.title('真实值 vs 预测值')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()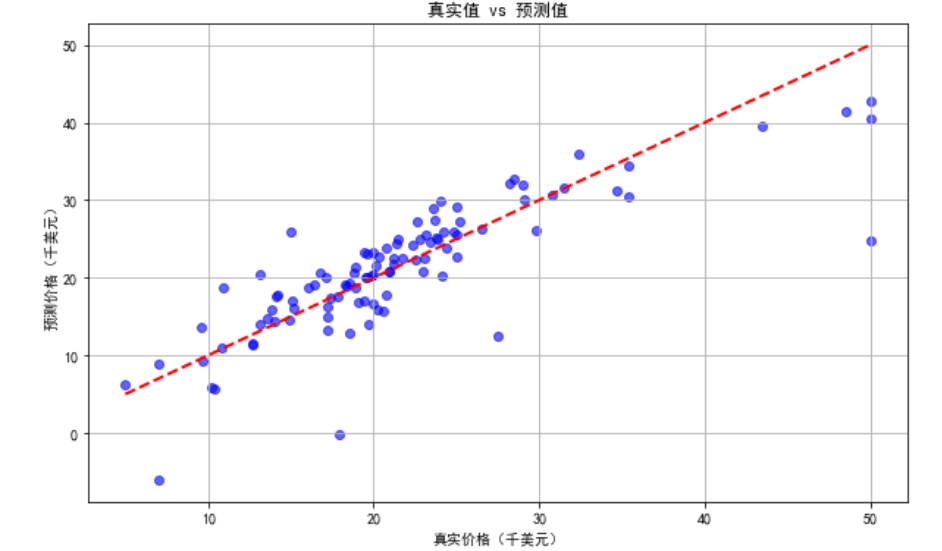
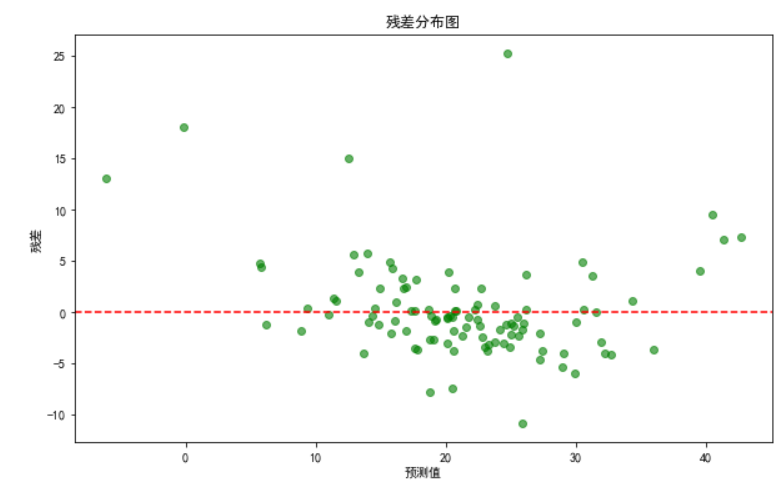
python
residuals = y_test - y_pred
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.scatter(y_pred, residuals, alpha=0.6, color='green')
plt.axhline(y=0, color='r', linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('预测值')
plt.ylabel('残差')
plt.title('残差分布图')
plt.show()