1. 函数的概念与用途
std::map::insert 是 C++ 标准模板库(STL)中 map 容器的一个核心成员函数。它的核心任务很明确:向 map 中插入一个新的键值对(key-value pair)。
核心用途:
- 数据构建 :初始化一个
map或动态地向其中添加数据。 - 避免重复 :在插入前,
map会检查键(key)是否已存在。如果键已存在,则插入操作通常不会覆盖原有的值(这与[]操作符的行为不同)。这个特性使得insert非常适合用于"如果不存在则添加"的场景,例如词频统计时初始化一个词的计数器为1。
简单来说,insert 是一个"安全"的插入方式,它不会意外地覆盖你已经存在的数据。
2. 函数的声明与出处
std::map 及其 insert 函数定义在 <map> 头文件中,属于 C++ 标准库,因此不需要额外链接库,只需包含头文件即可。
它有多个重载版本,最常用的一种声明如下:
cpp
#include <map>
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& value);- 这里的
value_type对于std::map<int, std::string>来说,就是std::pair<const int, std::string>。你需要构造一个这样的键值对对象传给它。
3. 返回值的含义与取值范围
这是 insert 函数非常关键的一部分。它的返回值是一个 std::pair,包含两个成员:
-
first:一个迭代器(iterator)。- 如果插入成功 (即原先不存在该键),它指向新插入的那个元素。
- 如果插入失败 (即该键已存在),它指向
map中已经存在的那个同名键的元素。
-
second:一个布尔值(bool)。- 如果插入成功 ,值为
true。 - 如果插入失败 (键已存在),值为
false。
- 如果插入成功 ,值为
通过检查 second 成员,你可以立即知道插入操作是否成功。
4. 参数的含义与取值范围
最常用的重载版本参数是 const value_type& value。
- 参数
value:- 含义 :要插入的键值对。其类型必须是
std::pair<const Key, T>,其中Key是键的类型,T是值的类型。 - 取值范围 :任何有效的该类型的对象。键(
first)必须是唯一的,如果键重复,则插入操作无效。
- 含义 :要插入的键值对。其类型必须是
其他常见重载:
insert(iterator hint, const value_type& value);:提供一个"提示"(hint)迭代器,提示新元素可能会插入在这个迭代器指向的元素之后。如果提示准确,可以加快插入速度;如果不准确,也没关系,插入操作会正常进行。insert(InputIt first, InputIt last);:允许插入一个范围内的多个元素,例如从另一个map插入。
5. 函数使用案例
下面是一个典型的代码示例,演示了如何插入、如何检查返回值以及如何避免重复插入。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::map<int, std::string> studentMap;
// 方式一:直接用 pair 插入
auto ret1 = studentMap.insert(std::pair<const int, std::string>(1, "Alice"));
if (ret1.second) {
std::cout << "Inserted student: (" << ret1.first->first << ", " << ret1.first->second << ")\n";
}
// 方式二:更现代的方法,使用 make_pair 或 {}
auto ret2 = studentMap.insert({2, "Bob"});
if (ret2.second) {
std::cout << "Inserted student: (" << ret2.first->first << ", " << ret2.first->second << ")\n";
}
// 尝试插入一个重复的键
auto ret3 = studentMap.insert({1, "Charlie"}); // 键 1 已存在
if (!ret3.second) {
std::cout << "Insertion failed. Key " << 1 << " already exists with value: " << ret3.first->second << "\n";
}
// 使用 C++17 的结构化绑定 (Structured Binding) 来简化返回值处理
auto [iterator, success] = studentMap.insert({3, "David"});
if (success) {
std::cout << "Inserted student: (" << iterator->first << ", " << iterator->second << ")\n";
}
// 打印整个 map
std::cout << "\nFinal map contents:\n";
for (const auto& [id, name] : studentMap) {
std::cout << id << " => " << name << '\n';
}
return 0;
}6. 编译方式与注意事项
编译命令(使用 GCC):
bash
g++ -std=c++17 -o map_insert_demo map_insert_demo.cpp-std=c++17:本例中使用了 C++17 的结构化绑定特性,所以需要指定标准。如果使用更早的 C++ 标准(如 C++11),可以将结构化绑定部分改为传统的std::pair访问方式(ret.second)。
注意事项:
- 键的唯一性 :
map的键是唯一的。insert不会覆盖已存在的键对应的值。如果你想要覆盖,应该使用map[key] = value;。 - 性能 :插入操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n) ,因为
map底层通常是红黑树实现。 - 返回值务必检查 :如果你需要知道插入是否成功,一定要检查返回值的
second成员。忽略返回值可能会导致你误以为插入成功了。 - C++11 及以上 :推荐使用花括号
{}来创建pair对象,代码更简洁(如{key, value})。
7. 执行结果说明
运行上面的示例代码,你会得到如下输出:
Inserted student: (1, Alice)
Inserted student: (2, Bob)
Insertion failed. Key 1 already exists with value: Alice
Inserted student: (3, David)
Final map contents:
1 => Alice
2 => Bob
3 => David结果解释:
- 前两次插入(键1和键2)都成功了,所以打印了插入的信息。
- 第三次尝试插入键1(值为"Charlie")时失败了,因为键1已存在(其值为"Alice")。程序打印出了失败信息和已存在的值。
- 第四次插入(键3)使用 C++17 语法,成功插入。
- 最后遍历整个
map,可以看到只有三个元素,重复插入的 "Charlie" 并没有出现,证明了insert的保护性。
8. 图文总结 (Mermaid流程图)
下面这个流程图总结了 std::map::insert 函数的执行逻辑和返回值处理过程:
flowchart TD
A["Start insert(std::pair value)"] --> B{"Does the key\nalready exist in the map?"}
B -- Yes (Key exists) --> C[Insertion fails]
C --> D["Return a pair:
iterator (points to existing element)
bool (false)"] D --> E["End (No change to map)"] B -- No (Key is new) --> F[Insertion succeeds] F --> G["Return a pair:
iterator (points to new element)
bool (true)"] G --> H["End (New element added)"]
iterator (points to existing element)
bool (false)"] D --> E["End (No change to map)"] B -- No (Key is new) --> F[Insertion succeeds] F --> G["Return a pair:
iterator (points to new element)
bool (true)"] G --> H["End (New element added)"]
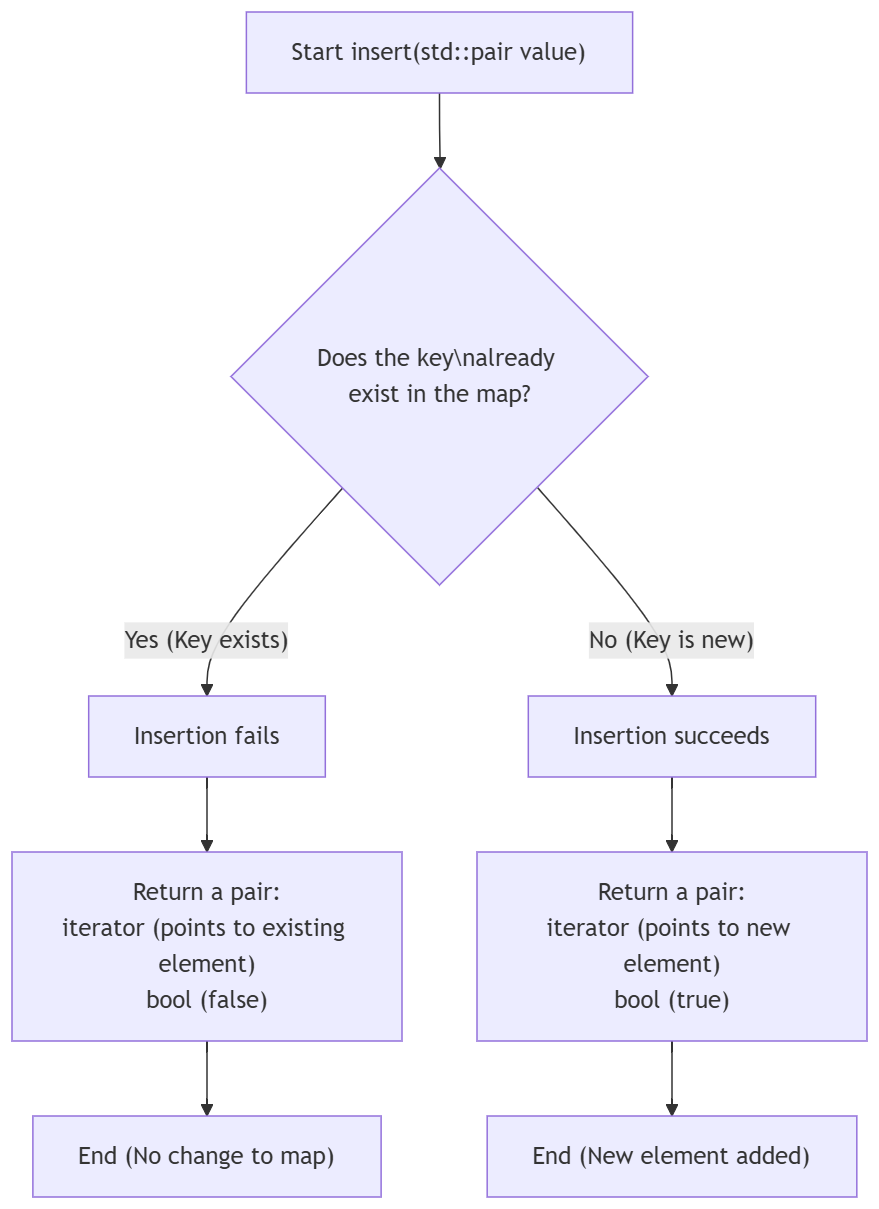
流程图解读:
该流程图清晰地展示了 insert 函数的决策过程:
- 函数开始后,首先检查待插入的键(Key)是否在
map中已存在。 - 如果存在 :插入失败,函数返回一个
pair,其中迭代器指向已存在的元素,bool值为false。map内容不发生任何变化。 - 如果不存在 :插入成功,新键值对被添加到
map中,函数返回一个pair,其中迭代器指向新插入的元素,bool值为true。
这个"检查-决策-返回"的过程完美地体现了 insert 函数安全、不覆盖的特性。