Linux scheduling Linux 调度
- 调度域
- 调度类(调度器)
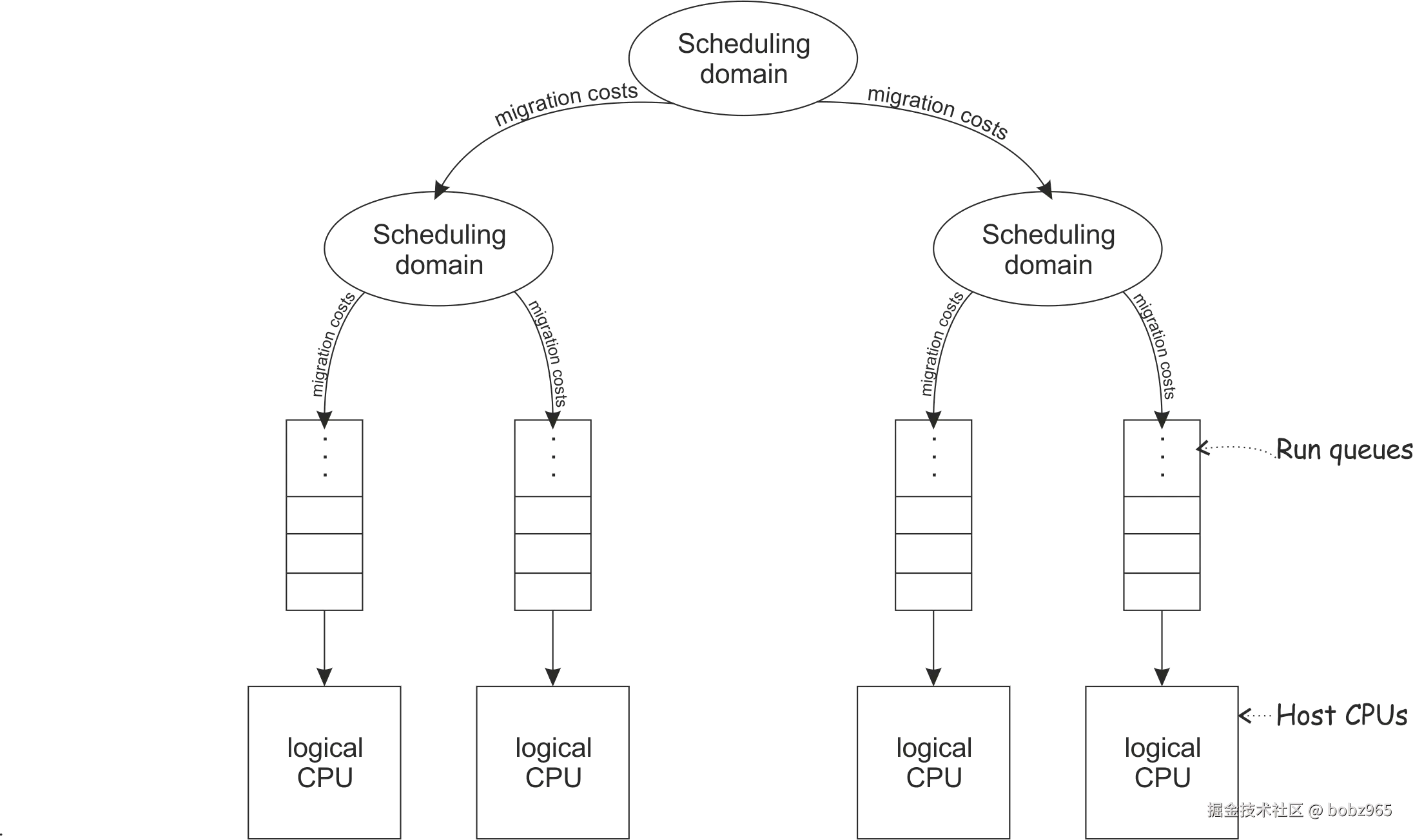
Based on the hardware layout of the physical cores, the Linux® scheduler maintains hierarchically ordered scheduling domains.
根据物理核的硬件布局,Linux® 调度程序采用"分层有序"的方式维护调度域 。
Basic scheduling domains consist of those processes that are run on physically adjacent cores, such as the cores on the same chip. Higher level scheduling domains group physically adjacent scheduling domains, such as the chips on the same book.
基本调度域 由在物理相邻内核(例如同一芯片上的核心)上运行的进程组成。更高级别的调度域 将物理上相邻的调度域分组,例如同一主板上的两个物理芯片。
The Linux scheduler is a multi-queue scheduler, which means that for each of the logical host CPUs, there is a run queue of processes waiting for this CPU. Each virtual CPU waits for its execution in one of these run queues.
Linux 调度程序是一个多队列调度程序 ,这意味着对于每个逻辑主机 CPU,都有一个等待此 CPU 的进程运行队列 。每个虚拟 CPU 在其中一个运行队列中等待其执行。
Moving a virtual CPU from one run queue to another is called a (CPU) migration. Be sure not to confuse the term ""CPU migration"" with a ""live migration"", which is the migration of a virtual server from one host to another. The Linux scheduler might decide to migrate a virtual CPU when the estimated wait time until the virtual CPU will be executed is too long, the run queue where it is supposed to be waiting is full, or another run queue is empty and needs to be filled up.
将虚拟 CPU 从一个运行队列移动到另一个运行队列称为 (CPU) 迁移 。请务必不要将"术语"CPU 迁移 "" 与 "" 实时迁移 "" 混淆,"实时迁移"是将虚拟服务器从一台主机迁移到另一台主机 。当执行虚拟 CPU 之前的估计等待时间过长 、应该等待的运行队列已满或另一个运行队列为空且需要填充时,Linux 调度程序可能会决定迁移虚拟 CPU。
Migrating a virtual CPU within the same scheduling domain is less cost intensive than to a different scheduling domain because of the caches being moved from one core to another. The Linux scheduler has detailed information about the migration costs between different scheduling domains or CPUs. Migration costs are an important factor for the decision if the migration of a virtual CPU to another host CPU is valuable.
将同一调度域中 的虚拟 CPU 迁移到不同的调度域的成本更低,因为缓存从一个内核移动到另一个内核。Linux 调度程序具有有关不同调度域或 CPU 之间的迁移成本的详细信息。迁移成本是决定将虚拟 CPU 迁移到另一个主机 CPU 是否有意义的重要因素。
- (root)调度域:可以实现跨物理核心调度:开销最大,跨 numa,内存访问延迟变长
- (子|numa0|1)调度域:可以实现 numa 内从 vcpuA 到 vcpuB 的调度:开销很小
- linux 调度器:将调度队列绑定到 vcpu
小结:
Linux CPU调度器在内核中有不同的层级结构和调度类别,主要可以按以下几个层面理解:
调度域(Scheduling Domains)层级
Linux内核为每个CPU构建一个调度域(sched_domain),调度域表示一组CPU,按照系统硬件拓扑层级构建,如同一核心的逻辑CPU、同一物理CPU的多个核心、多个物理CPU等。调度域之间通过父子层级组织,实现不同粒度的负载均衡和调度决策。kernel+1
调度类(Scheduling Classes)
Linux支持多种调度策略,并将其按调度类分类。主要调度类包括:
- CFS(Completely Fair Scheduler) :Linux默认的公平调度器,基于虚拟运行时间平衡各进程的CPU使用。
- RT(Real-Time 实时调度类) :包括FIFO和轮转调度,用于实时任务。
- Deadline调度,如SCHED_DEADLINE,实现基于任务截止时间的调度。
- 一些能量感知调度(EAS)、容量感知调度(CAS)等特殊调度类。man7+2
运行队列(Runqueue)
每个逻辑CPU拥有独立的运行队列,存储可以运行的任务。调度器从这些队列中选择下一个执行的任务。多核系统中,多个调度器并行管理各自的运行队列,结合调度域实现系统-wide负载均衡。ibm+1
总结:Linux CPU调度器体系呈现分层结构,从物理硬件拓扑(调度域)到各种调度策略(调度类),再到每个逻辑CPU的任务运行队列,协同工作以实现高效公平的进程调度。kernel+2