目录
[4、给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL](#4、给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL)
续接上一话
一、常见的链表题目练习(续)
1、链表的回文结构。
和前面一样,先使用快慢指针找到中间结点,再用第2题的方法将整个链表进行反转,再依次进行比较,看是否完全相同
java
public boolean chkPalindrome() {
// write code here
if(head == null) return true;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//slow 指向的位置 就是中间节点
//2.进行翻转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curN;
}
//3.判断回文
while (head != slow) {
if(head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
if(head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}2、输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
这里首先要清楚,两个链表如果有着公共结点,那么一定是Y字型的关系
小技巧:如果两个链表相交,那么同时出发,依次向后走一步,若是为空下一步走到另一个链表的头结点上,他们相遇时一定是在公共结点位置。(不相交则同时为null)
java
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = ((pA == null) ? headB : pA.next);
pB = ((pB == null) ? headA : pB.next);
}
return pA;
}
}3、给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
这里依旧采用快慢指针,如果有环,那么一定会相遇,若是没有环,则快指针一定会先null
java
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}那么,为什么我们要让fast和slow分别走2步和1步呢?能不能一个走3步,一个走2步呢?
首先要明确,若是一个走3步一个走1步,快指针可能刚好将慢指针进行套圈,永远无法相遇(如环的长度只有2,一个走3步一个走1步刚好永远无法相遇!!!)
而若是一个走3步,一个走2步,那么就会存在不确定性,如不确定什么时候可以相遇等。
4、给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
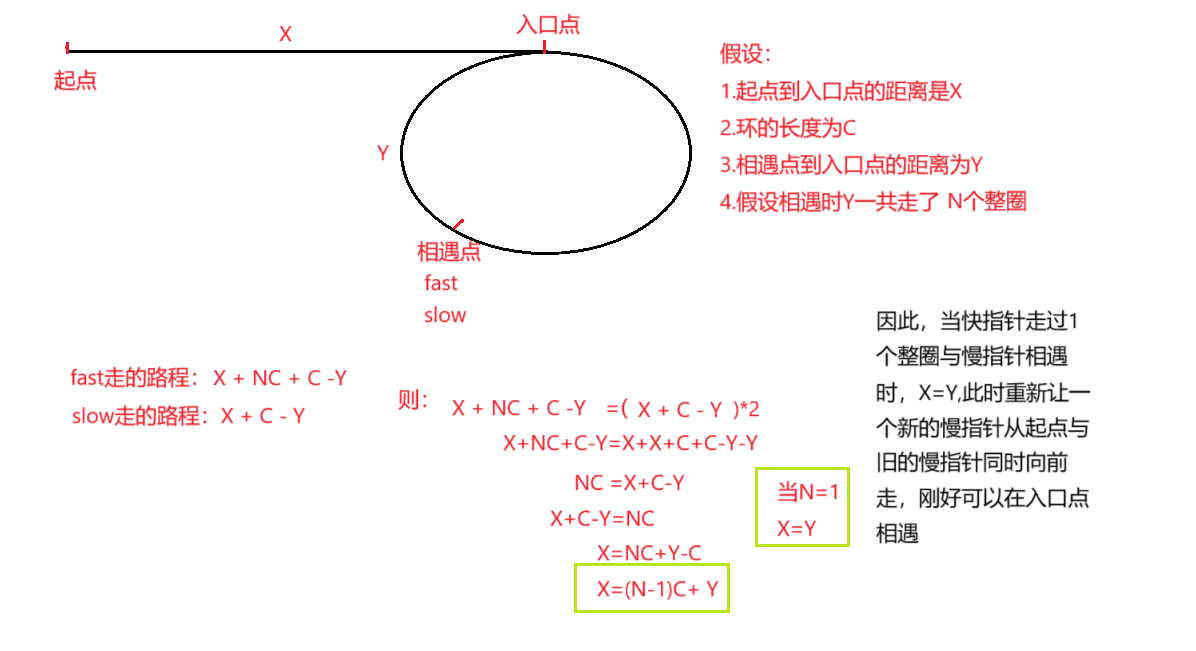
依旧使用快慢指针操作,当两个指针相遇时,快指针走的距离是a+n(b+c)+b=a+(n+1)b+nc
快指针的速度是慢指针的一倍,所以a+(n+1)b+nc=2(a+b) ==> a=c+(n−1)(b+c),我们会发现:从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n−1 圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离。
因此,当发现 slow 与 fast 相遇时,我们再额外使用一个指针 ptr。起始,它指向链表头部;随后,它和 slow 每次向后移动一个位置。最终,它们会在入环点相遇。
java
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode ptr = head;
while (ptr != slow) {
ptr = ptr.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return null;
}
}二、LinkedList
1、LinkedList的模拟实现
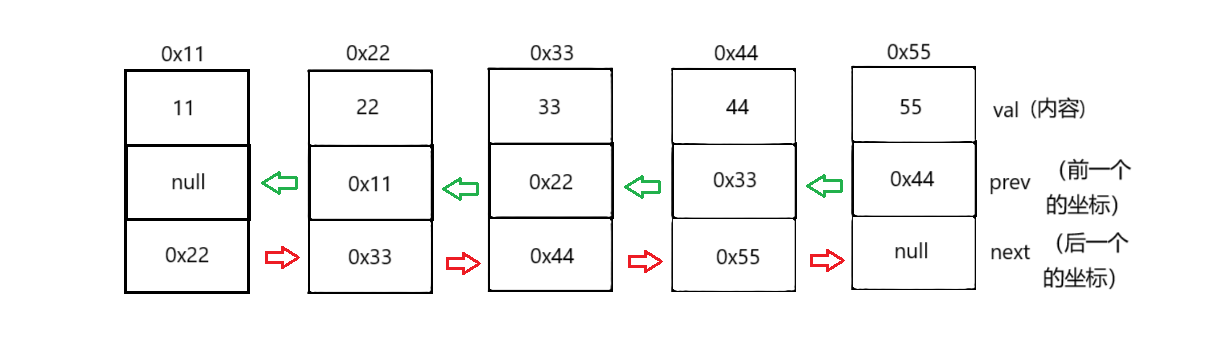
java
// 无头双向链表实现
public class MyLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = last = node;
}else {
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = last = node;
}else {
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = last.next;
}
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
int len = size();
if(index < 0 || index > len) {
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == len) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if(cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next == null) {
last = last.prev;
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if(cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next == null) {
last = last.prev;
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curN;
}
head = last = null;
}
}2、LinkedList的使用
2.1什么是LinkedList
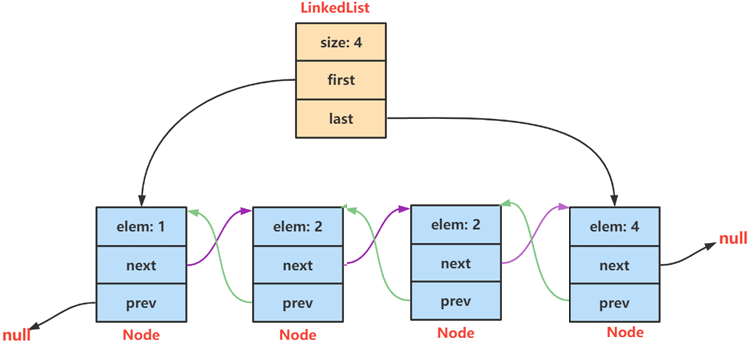
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的结点中,然后通过引用将结点连接起来了,因此在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高。
#注:
(1)LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持随机访问
(2)LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为O(1)
(3)LinkedList比较适合任意位置插入的场景
2.2LinkedList的使用
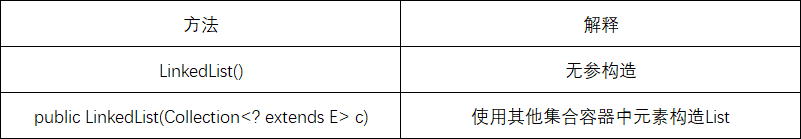
2.2.1LinkedList的构造
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个空的LinkedList
List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> list2 = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
list2.add("JavaSE");
list2.add("JavaWeb");
list2.add("JavaEE");
// 使用ArrayList构造LinkedList
List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
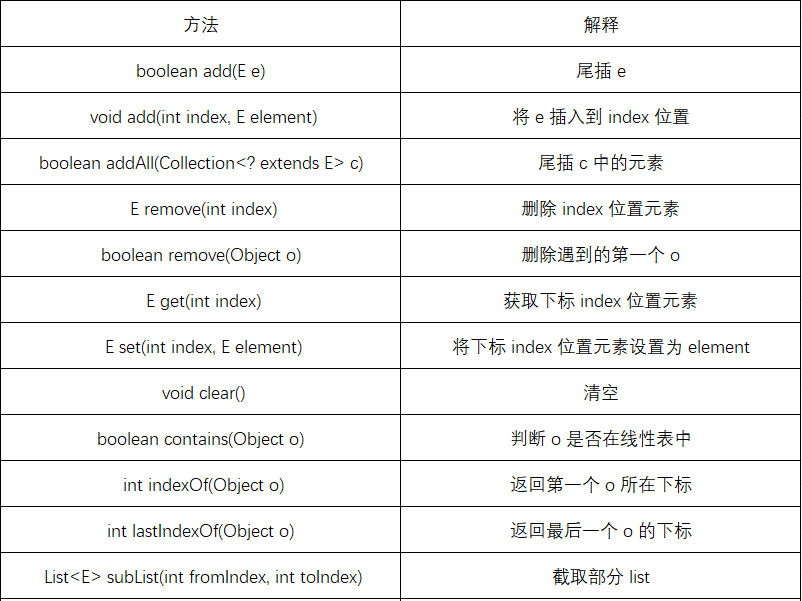
}2.2.2LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
// 在起始位置插入0
list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
System.out.println(list);
// contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
if(!list.contains(1)){
list.add(0, 1);
}
list.add(1);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
System.out.println(list);
// subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(copy);
list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
System.out.println(list.size());
}2.2.3LinkedList的遍历
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
// foreach遍历
for (int e:list) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
}
System.out.println();
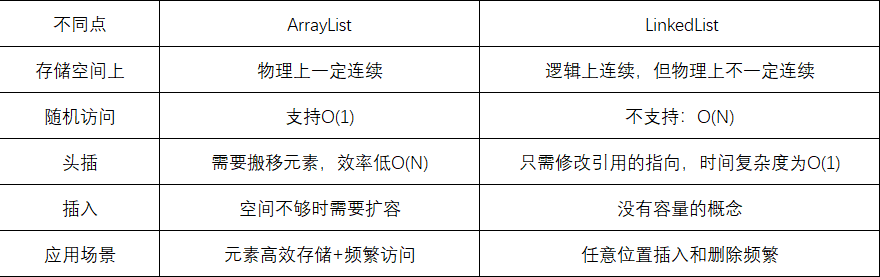
}3、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别