一、背景
需要了解RN的新架构原理,看看它主要增加了什么,解决了什么问题,主要文章为:reactnative.dev/architectur...
备注:涉及到大量源码分析想要看完耗时较久,可以先点赞和收藏再看^_^,文章里的图片,流程图,代码看着不清晰可以直接访问我的语雀文档React Native新架构原理分析
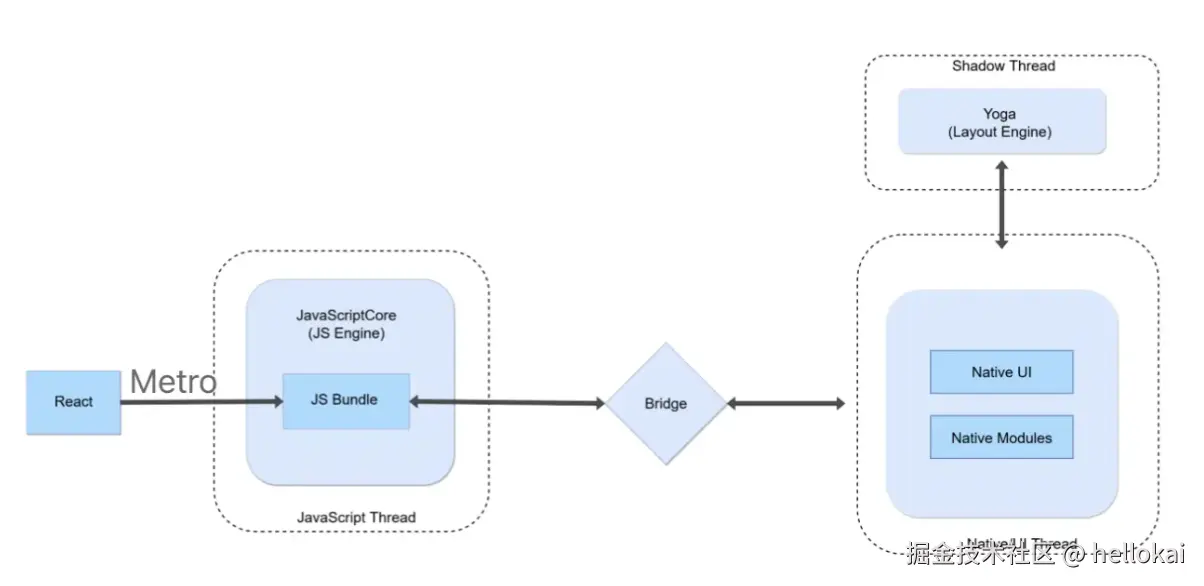
1.1 旧架构的问题
从以上图我们就可以看出来它的问题:
- js和native的通信都是通过桥来做的,如果频繁通信大量的序列化操作会影响其性能和内存占用;在通过消息队列机制来处理会让js和native的操作都是异步化的
- 旧架构的渲染,shadow树是分不同端实现的,例如Android,主要的逻辑在Java侧,这样渲染逻辑不仅多了一层JNI调用,而且还导致双端不统一,要分端维护。
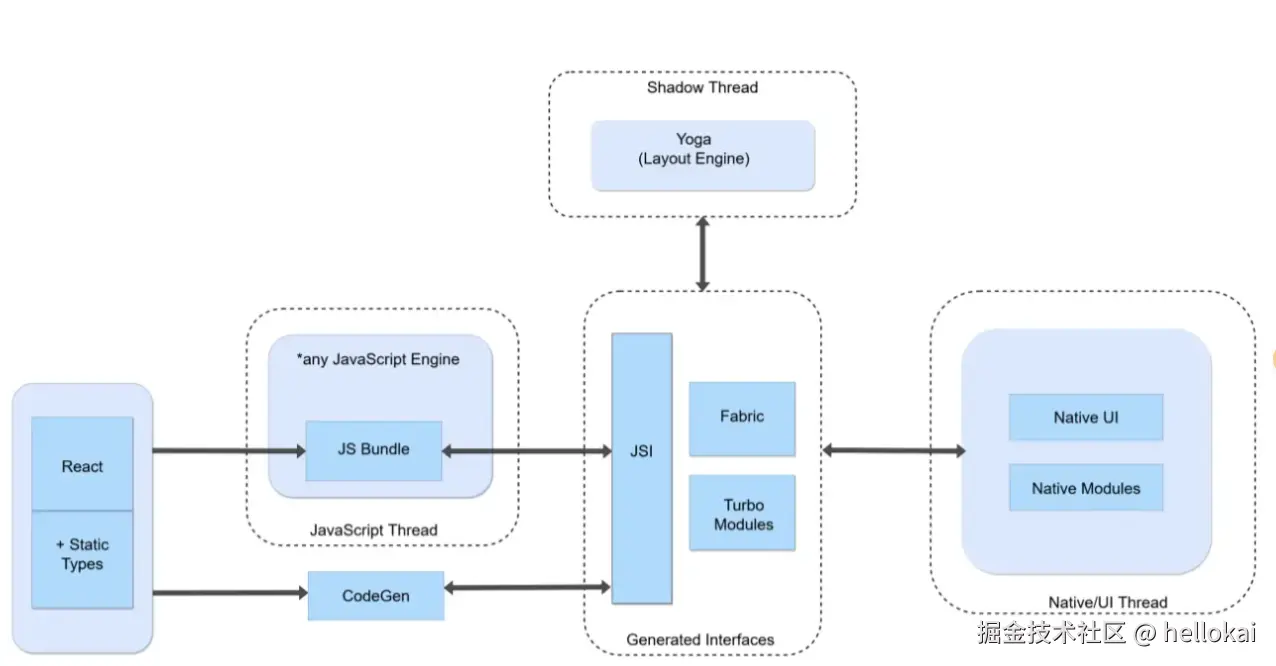
1.2 新架构的解决方法
我们再来看看新架构是如何做的呢:
- 原来的操作是通过桥通信,大量不必要的序列化,那就移除序列化,直接使用JSI,让JS有可以直接操作C++的能力
- 原来是异步操作,直接通过JSI改成同步操作
- 原来渲染Shadow树是在双端各自维护的渲染逻辑,改到C++层,统一渲染层Fabric
- 桥通信和定义要大量的心智负担,例如类型怕定义错误,它是否为null等,直接引入codegen,只需要定义一次接口,自动生成多端代码
二、新架构介绍
自 2018 年以来,React Native 团队一直在重新设计其核心内部结构,以帮助开发者创造更高质量的体验。截至 2024 年,此版本的 React Native 已得到大规模验证,并由 Meta 提供支持生产环境的应用。
新架构自 React Native 0.68 版本起已开放实验性选择,并在后续每个版本中持续改进。团队目前正致力于使其成为 React Native 开源生态系统的默认体验。
新架构的渲染基准测试:
三、新旧架构对比
我们用同一个FlatList渲染列表,分别跑在旧架构和新架构中看下性能如何
cpp
import React, { useState, useCallback, useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
import {
SafeAreaView,
StyleSheet,
Text,
View,
FlatList,
Image,
ActivityIndicator,
Platform,
Dimensions,
Animated,
Easing,
UIManager,
findNodeHandle,
ScrollView,
NativeModules,
} from 'react-native';
// 强制启用LayoutAnimation(Android需要)
if (Platform.OS === 'android') {
if (UIManager.setLayoutAnimationEnabledExperimental) {
UIManager.setLayoutAnimationEnabledExperimental(true);
}
}
// 判断当前是否使用新架构的更可靠方法
const checkArchitecture = () => {
const isNewArch =
// 检查TurboModule是否存在
global.__turboModuleProxy !== undefined ||
// 检查Fabric组件是否存在
global.nativeFabricUIManager !== undefined ||
// 检查其他新架构标识
(global.RN$Bridgeless !== undefined && global.RN$Bridgeless === true);
return isNewArch ? '新架构 (Fabric)' : '旧架构 (Paper)';
};
// 用于创建随机颜色
const generateRandomColor = () => {
const r = Math.floor(Math.random() * 200 + 55);
const g = Math.floor(Math.random() * 200 + 55);
const b = Math.floor(Math.random() * 200 + 55);
return `rgb(${r}, ${g}, ${b})`;
};
// 简化数据生成函数,增加用于动画的数据
const generateSimpleItems = (count: number) => {
return Array(count)
.fill(0)
.map((_, index) => ({
id: `item-${index}`,
title: `Item ${index}`,
description: `This is a simple description for item ${index}. We're testing the performance of React Native with a large list of ${count} items.`,
imageUrl: `https://picsum.photos/id/${(index % 100) + 1}/200/200`,
color: generateRandomColor(),
animationBaseValue: Math.random(), // 用于动画的随机初始值
tags: Array(5).fill(0).map((_, i) => `Tag ${i+1}`),
}));
};
// 一个频繁更新的子组件
const AnimatedProgressBar = ({ value, color }) => {
const [animatedValue] = useState(new Animated.Value(0));
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
// 创建平滑动画
useEffect(() => {
Animated.timing(animatedValue, {
toValue: value,
duration: 500,
useNativeDriver: true,
easing: Easing.inOut(Easing.quad),
}).start();
// 持续更新一个计数器来制造额外的渲染负担
const interval = setInterval(() => {
setCounter(prev => (prev + 1) % 1000);
}, 100);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [value]);
return (
<View style={{ height: 6, width: '100%', backgroundColor: '#e0e0e0', borderRadius: 3, overflow: 'hidden', marginTop: 4 }}>
<Animated.View
style={{
height: '100%',
width: '100%',
backgroundColor: color,
transform: [{
scaleX: animatedValue
}],
opacity: 0.7 + ((counter % 30) / 100), // 轻微改变不透明度
transformOrigin: 'left',
}}
/>
</View>
);
};
// 计算密集型组件 - 模拟复杂计算并频繁更新
const ComplexCalculation = ({ seed }) => {
const [result, setResult] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
const interval = setInterval(() => {
// 计算密集型操作,模拟密集JS计算
let value = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
value += Math.sin(i * seed * Date.now() % 10) * Math.cos(i);
}
setResult(value);
}, 300);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [seed]);
return (
<Text style={styles.calculationResult}>
计算结果: {result.toFixed(2)}
</Text>
);
};
// 频繁更新的标签列表,具有横向滚动
const TagsList = ({ tags, baseColor }) => {
const [selectedIndex, setSelectedIndex] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
const interval = setInterval(() => {
setSelectedIndex(prev => (prev + 1) % tags.length);
}, 1000);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [tags.length]);
// 计算标签颜色
const getTagColor = (index) => {
if (index === selectedIndex) {
return baseColor;
}
// 降低亮度的颜色
const color = baseColor.replace('rgb', 'rgba').replace(')', ', 0.5)');
return color;
};
return (
<ScrollView
horizontal
showsHorizontalScrollIndicator={false}
style={styles.tagsContainer}
contentContainerStyle={{ paddingVertical: 4 }}
>
{tags.map((tag, index) => (
<View
key={index}
style={[
styles.tag,
{ backgroundColor: getTagColor(index) }
]}
>
<Text style={styles.tagText}>{tag}</Text>
</View>
))}
</ScrollView>
);
};
// 复杂的列表项组件,包含多个子组件和动画
const ComplexListItem = React.memo(({ item, index }: any) => {
const [imageLoaded, setImageLoaded] = useState(false);
// 模拟与本地代码的频繁交互
useEffect(() => {
const interval = setInterval(() => {
// 在真实场景中这会触发原生模块调用
NativeModules.DeviceInfo?.getConstants();
}, 500);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, []);
// 计算动画进度值
const progressValue = (index % 10) / 10 + item.animationBaseValue / 2;
return (
<View
style={[
styles.item,
{
borderLeftColor: item.color,
borderLeftWidth: 4,
},
]}
>
<View style={styles.imageContainer}>
{!imageLoaded && <ActivityIndicator style={styles.loader} />}
<Image
source={{ uri: item.imageUrl }}
style={styles.image}
onLoad={() => setImageLoaded(true)}
/>
<View style={[styles.imageOverlay, { backgroundColor: `${item.color}88` }]}>
<Text style={styles.overlayText}>{index}</Text>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.content}>
<Text style={styles.title}>{item.title}</Text>
<Text style={styles.description} numberOfLines={2}>{item.description}</Text>
{/* 添加动画进度条 */}
<AnimatedProgressBar value={progressValue} color={item.color} />
{/* 添加复杂计算组件 */}
<ComplexCalculation seed={item.animationBaseValue} />
{/* 添加动态标签列表 */}
<TagsList tags={item.tags} baseColor={item.color} />
</View>
</View>
);
});
// 主组件
export default function ListPerformanceTest() {
// 使用1000条数据即可看到差异
const [data] = useState(() => generateSimpleItems(100));
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>架构性能测试列表3 (1000条)</Text>
<Text style={styles.architecture}>
架构: {checkArchitecture()}
</Text>
</View>
<FlatList
style={styles.list}
data={data}
renderItem={({ item, index }) => (
<ComplexListItem item={item} index={index} />
)}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
windowSize={21}
initialNumToRender={10}
maxToRenderPerBatch={5}
updateCellsBatchingPeriod={50}
removeClippedSubviews={true}
getItemLayout={(data, index) => (
{length: 160, offset: 160 * index, index}
)}
showsVerticalScrollIndicator={true}
persistentScrollbar={Platform.OS === 'android'}
indicatorStyle={Platform.OS === 'ios' ? 'black' : undefined}
fadingEdgeLength={Platform.OS === 'android' ? 50 : undefined}
/>
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
// 样式
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#f5f5f5',
},
header: {
padding: 12,
backgroundColor: 'white',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#e0e0e0',
elevation: 4,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.1,
shadowRadius: 2,
},
headerTitle: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 4,
},
architecture: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
},
list: {
flex: 1,
},
item: {
backgroundColor: 'white',
flexDirection: 'row',
padding: 10,
marginVertical: 4,
marginHorizontal: 8,
borderRadius: 8,
elevation: 2,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 1 },
shadowOpacity: 0.2,
shadowRadius: 2,
height: 150,
},
imageContainer: {
width: 120,
height: 120,
borderRadius: 6,
overflow: 'hidden',
backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0',
position: 'relative',
},
loader: {
position: 'absolute',
left: 0,
top: 0,
right: 0,
bottom: 0,
},
image: {
width: '100%',
height: '100%',
resizeMode: 'cover',
},
imageOverlay: {
position: 'absolute',
bottom: 0,
left: 0,
right: 0,
height: 30,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
overlayText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 16,
},
content: {
flex: 1,
marginLeft: 12,
justifyContent: 'space-between',
},
title: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 4,
},
description: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#666',
marginBottom: 4,
},
calculationResult: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#555',
fontStyle: 'italic',
},
tagsContainer: {
marginTop: 4,
maxHeight: 30,
},
tag: {
paddingHorizontal: 8,
paddingVertical: 2,
borderRadius: 12,
marginRight: 6,
},
tagText: {
fontSize: 10,
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
performanceContainer: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-around',
paddingVertical: 6,
backgroundColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05)',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#ddd',
},
performanceText: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#333',
},
performanceValue: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 12,
},
}); 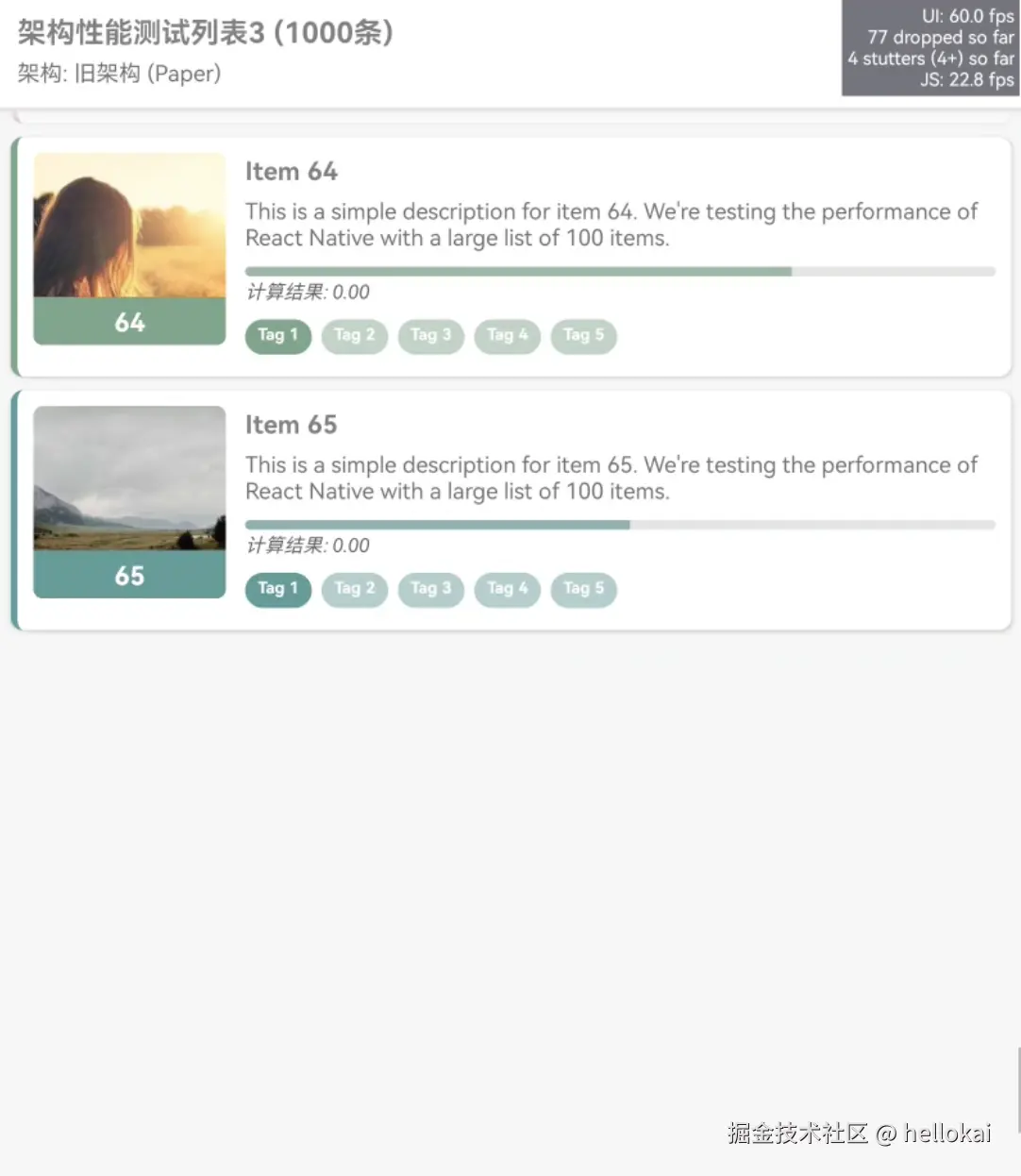
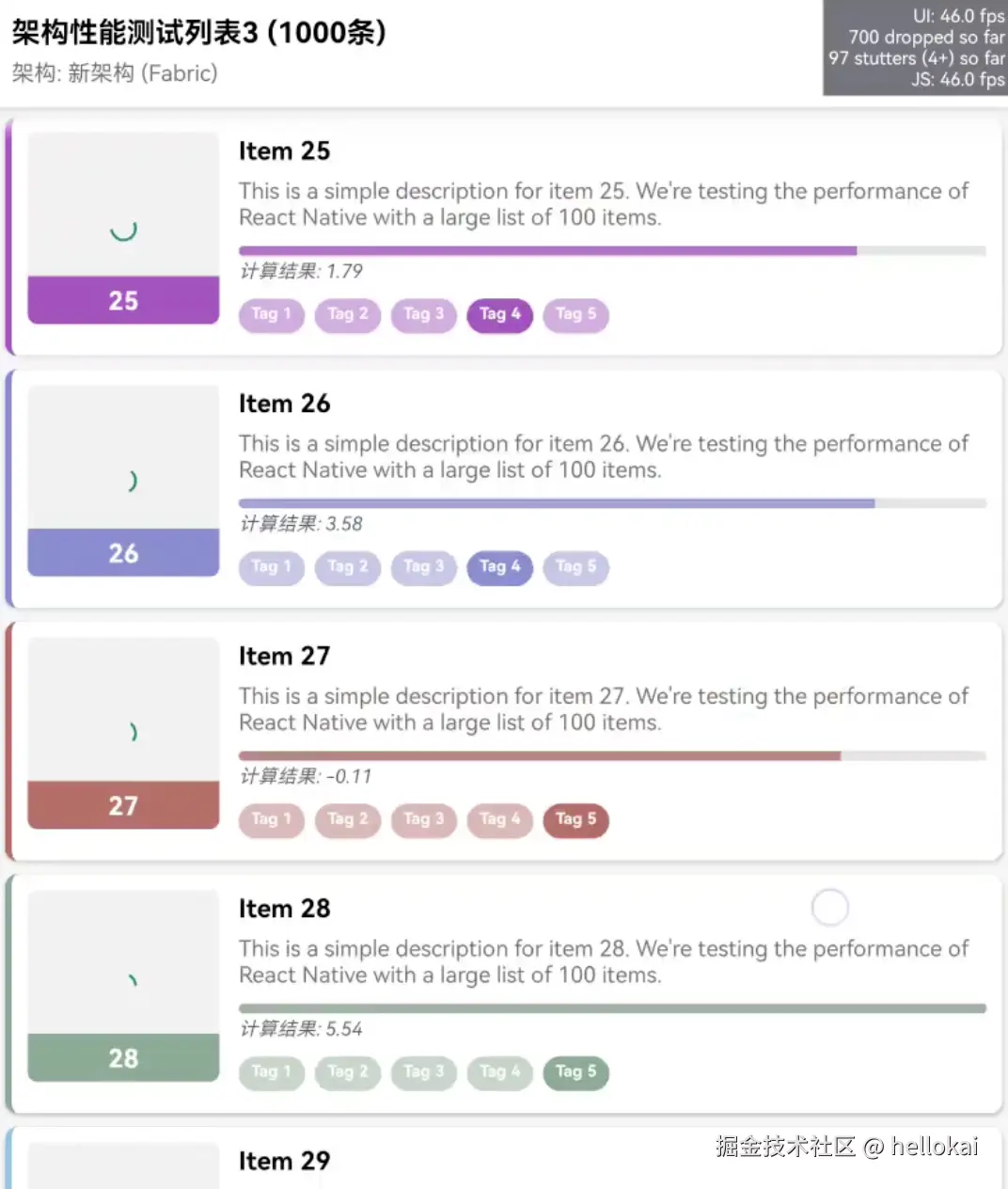
从图中可以看到新老架构,新架构JS和UI的帧率一致,老架构JS帧率快速滑动很低,并且会有白屏现象,主要原因:
- 老架构是异步通信,JS和UI线程分离,快速滑动UI线程会占用大量CPU资源,导致JS无法获得足够资源来处理
- 新架构使用的是同步通信,可以直接调用原生方法,一帧内完成数据通信,更好的协同
三、JSI
JSI能够实现同步调用的核心原理在于它创建了一个允许JavaScript和C++代码直接交互的机制:
- 统一运行时访问:JSI提供了一个抽象层,可以直接访问JavaScript引擎的运行时
- 宿主对象(HostObject)机制:C++对象可以作为"宿主对象"直接暴露给JavaScript
- 宿主函数(HostFunction)机制:C++函数可以直接注册为JavaScript可调用的函数
- 直接内存访问:JSI允许在不序列化的情况下直接访问和操作JavaScript值
具体实现上,JSI通过以下方式实现同步调用:
cpp
// C++端定义一个宿主对象
class MyHostObject : public jsi::HostObject {
public:
jsi::Value get(jsi::Runtime& runtime, const jsi::PropNameID& name) override {
if (name.utf8(runtime) == "syncMethod") {
// 返回一个可以从JS同步调用的函数
return jsi::Function::createFromHostFunction(
runtime,
jsi::PropNameID::forAscii(runtime, "syncMethod"),
1, // 参数个数
[](jsi::Runtime& runtime, const jsi::Value& thisVal, const jsi::Value* args, size_t count) {
// 直接在C++中执行逻辑并返回结果
return jsi::String::createFromUtf8(runtime, "Result from C++");
}
);
}
return jsi::Value::undefined();
}
};
// 将宿主对象安装到JavaScript全局对象
auto myObject = std::make_shared<MyHostObject>();
runtime.global().setProperty(runtime, "nativeModule", jsi::Object::createFromHostObject(runtime, myObject));在JavaScript中,可以直接同步调用这个方法:
javascript
// 直接同步调用C++方法,并立即获得返回值
const result = global.nativeModule.syncMethod();
console.log(result); // "Result from C++"3.1 为什么JSI能实现同步而Bridge不能
JSI能够实现同步调用而Bridge不能的根本原因有:
- 直接内存共享 :
- JSI:JavaScript引擎和C++代码共享内存空间,可以直接传递引用
- Bridge:两边完全隔离,必须通过序列化/反序列化传递数据
- 运行时集成级别 :
- JSI:在JavaScript引擎的运行时级别集成,可以直接操作JavaScript对象
- Bridge:在应用层级集成,无法直接操作JavaScript引擎内部对象
- 执行模型 :
- JSI:可以在同一个线程上执行JavaScript和C++代码
- Bridge:JavaScript和原生代码在不同线程上执行
- 对象生命周期管理 :
- JSI:提供了引用计数和垃圾回收机制,使C++对象可以安全地暴露给JavaScript
- Bridge:没有统一的对象生命周期管理机制
3.2 技术实现示例
以下是JSI如何在底层实现同步调用的简化示例:
- 对象引用传递 :
当JavaScript调用C++方法时,JSI不会复制或序列化参数,而是直接传递对象的引用:
cpp
// JSI实现中的函数调用
jsi::Value callHostFunction(const jsi::Function& func, const jsi::Value& thisVal, const jsi::Value* args, size_t count) {
// 直接调用宿主函数,传递参数引用
return hostFunctionImpl(func, thisVal, args, count);
}- 线程模型 :
JSI允许在JavaScript线程上直接执行C++代码,避免了线程切换开销:
cpp
// 在JavaScript线程上执行C++代码
jsi::Value executeSync(jsi::Runtime& runtime, const std::function<jsi::Value(jsi::Runtime&)>& func) {
// 直接在当前线程执行,无需切换线程
return func(runtime);
}- 值的直接访问 :
JSI提供了API直接访问JavaScript值,无需序列化:
cpp
// 直接访问JavaScript对象的属性
jsi::Value getProperty(jsi::Runtime& runtime, const jsi::Object& obj, const char* name) {
// 直接从JavaScript对象中获取属性,无需序列化
return obj.getProperty(runtime, name);
}总结
JSI能够实现JavaScript和C++之间的同步调用,是因为它从根本上改变了JavaScript引擎与原生代码的集成方式,从应用层的消息传递提升到了运行时级别的直接集成。这种深度集成使得两个环境可以直接共享内存和对象引用,从而实现同步调用。
新架构jsi可以直接引用而老架构只能序列化的真正原因是,老架构的js引擎也支持c++ binding,但是老架构没有用,而是只开放了nativemodule来序列化传递数据,但是新架构通过jsi抽象,把js引擎原有的能力都暴漏给开发者了,所以可以使用同步的方式,
思考:为什么不直接使用JSI而是用的桥通信序列话的方式?
结合AI和自己的思考,我想有以下几个原因:
- 序列化实现简单,不需要对JS引擎有深入理解
- Android缺少好的JSRuntime来做,并且还要考虑C++中内存问题,RN项目初期的目标是让跨平台整体架构是否能够跑通,正确性,稳定性和开发效率是关键,而非性能优化
- 这里引用Donald Knuth来说明下:
- We should forget about small efficiencies, say about 97% of the time: premature optimization is the root of all evil. Yet we should not pass up our opportunities in that critical 3%.
- 我们应该忽略小的效率问题,大约97%的时间都是如此:过早优化是万恶之源。但我们不应该错过那关键的3%的优化机会。
- 我们在做整体系统设计时,重点是先让他跑起来,先完成再完美。
四、TurboModule模块系统
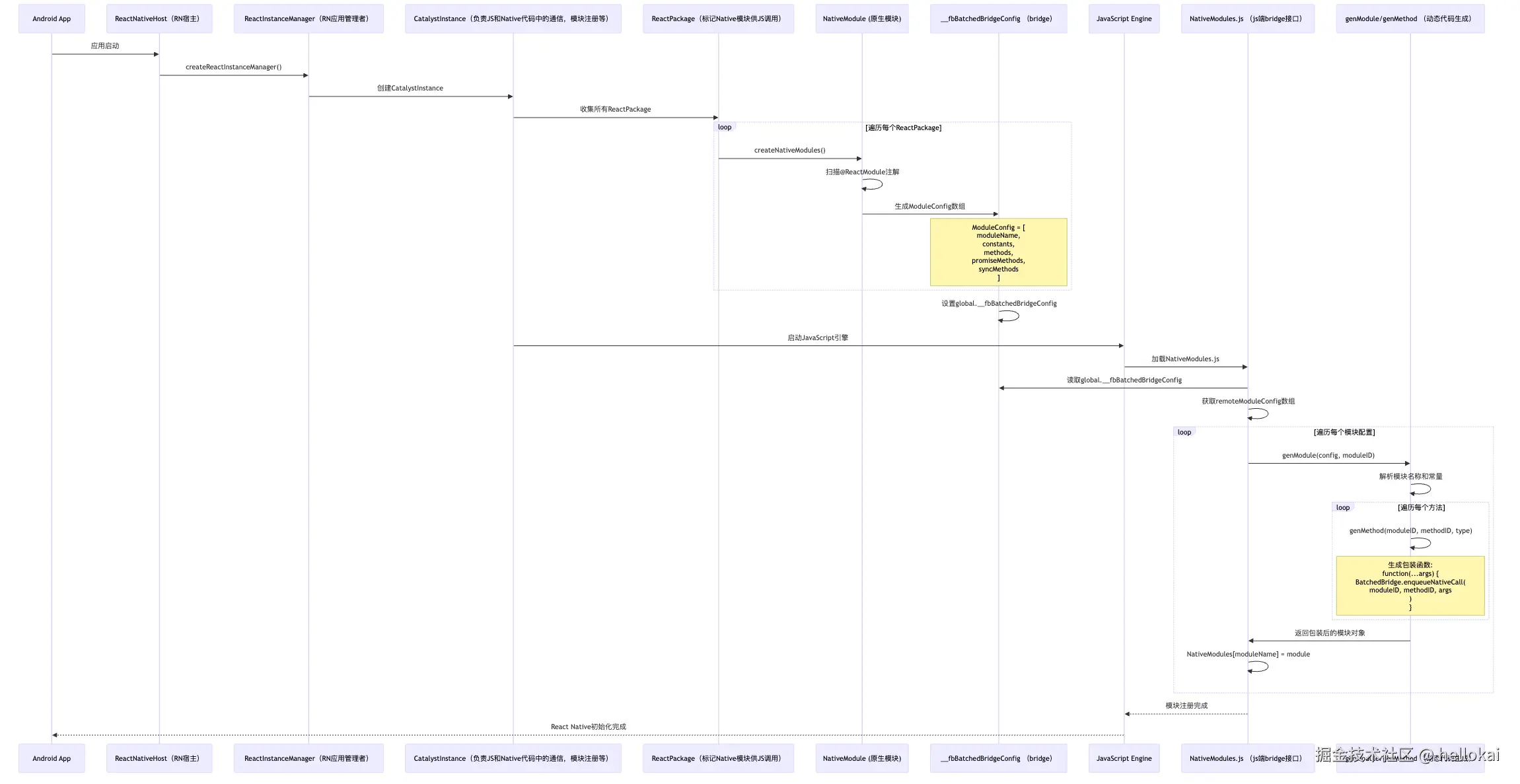
之前我们介绍过,RN旧架构是通过桥来通信的,那官方写的各种桥和我们写的各种桥,就要做Leagy Module,它是基于序列化方式通信的,那我们一起来看下整体module模块是如何工作的以及新老架构的源码吧!
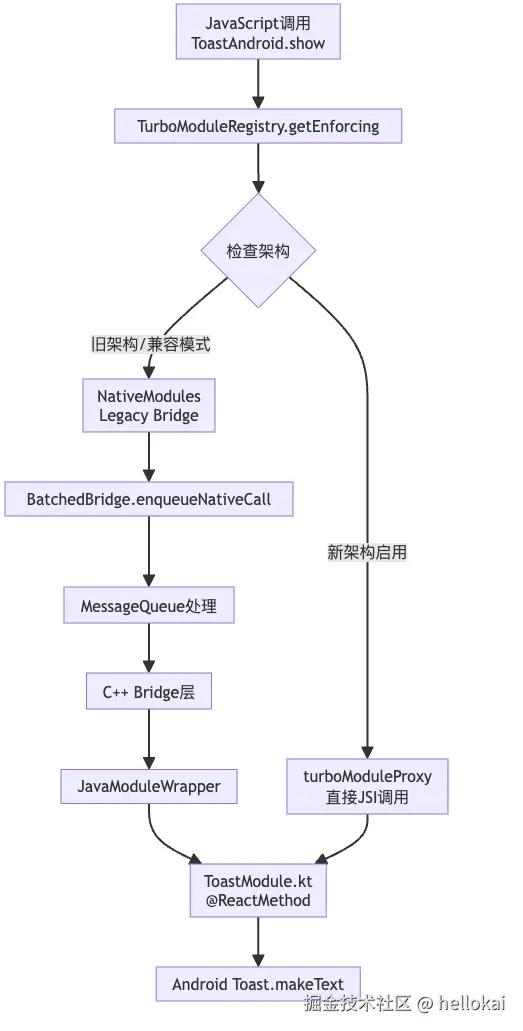
整体调用流程图
4.1 Legacy Module调用源码
shell
/**
* Copyright (c) Meta Platforms, Inc. and affiliates.
*
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
*
* @flow strict
* @format
*/
import type {TurboModule} from '../../../../Libraries/TurboModule/RCTExport';
import * as TurboModuleRegistry from '../../../../Libraries/TurboModule/TurboModuleRegistry';
// 这里是一个手写的规范定义文件
export interface Spec extends TurboModule {
+getConstants: () => {
SHORT: number,
LONG: number,
TOP: number,
BOTTOM: number,
CENTER: number,
};
+show: (message: string, duration: number) => void;
+showWithGravity: (
message: string,
duration: number,
gravity: number,
) => void;
+showWithGravityAndOffset: (
message: string,
duration: number,
gravity: number,
xOffset: number,
yOffset: number,
) => void;
}
// 1.TurboModuleRegistry
export default (TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing<Spec>('ToastAndroid'): Spec);
shell
function requireModule<T: TurboModule>(name: string): ?T {
if (turboModuleProxy != null) {
// 新架构
const module: ?T = turboModuleProxy(name);
if (module != null) {
return module;
}
}
if (
global.RN$Bridgeless !== true ||
global.RN$TurboInterop === true ||
global.RN$UnifiedNativeModuleProxy === true
) {
// 2.老架构
const legacyModule: ?T = NativeModules[name];
if (legacyModule != null) {
return legacyModule;
}
}
return null;
}
shell
let NativeModules: {[moduleName: string]: any, ...} = {};
if (global.nativeModuleProxy) { // 新架构
NativeModules = global.nativeModuleProxy;
} else { // 3.老架构
const bridgeConfig = global.__fbBatchedBridgeConfig;
invariant(
bridgeConfig,
'__fbBatchedBridgeConfig is not set, cannot invoke native modules',
);
const defineLazyObjectProperty =
require('../Utilities/defineLazyObjectProperty').default;
(bridgeConfig.remoteModuleConfig || []).forEach(
(config: ModuleConfig, moduleID: number) => {
// Initially this config will only contain the module name when running in JSC. The actual
// configuration of the module will be lazily loaded.
// 4.定义老架构的module对象
const info = genModule(config, moduleID);
if (!info) {
return;
}
if (info.module) {
NativeModules[info.name] = info.module;
}
// If there's no module config, define a lazy getter
else {
defineLazyObjectProperty(NativeModules, info.name, {
get: () => loadModule(info.name, moduleID),
});
}
},
);
}
shell
// 5.这个是生成JSModule对象的具体方法
function genMethod(moduleID: number, methodID: number, type: MethodType) {
let fn = null;
if (type === 'promise') {
fn = function promiseMethodWrapper(...args: Array<mixed>) {
// In case we reject, capture a useful stack trace here.
/* $FlowFixMe[class-object-subtyping] added when improving typing for
* this parameters */
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-type]
const enqueueingFrameError: ExtendedError = new Error();
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 如果是Promise方法,则使用这个发送
BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall(
moduleID,
methodID,
args,
data => resolve(data),
errorData =>
reject(
updateErrorWithErrorData(
(errorData: $FlowFixMe),
enqueueingFrameError,
),
),
);
});
};
} else {
fn = function nonPromiseMethodWrapper(...args: Array<mixed>) {
const lastArg = args.length > 0 ? args[args.length - 1] : null;
const secondLastArg = args.length > 1 ? args[args.length - 2] : null;
const hasSuccessCallback = typeof lastArg === 'function';
const hasErrorCallback = typeof secondLastArg === 'function';
hasErrorCallback &&
invariant(
hasSuccessCallback,
'Cannot have a non-function arg after a function arg.',
);
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-type]
const onSuccess: ?(mixed) => void = hasSuccessCallback ? lastArg : null;
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-type]
const onFail: ?(mixed) => void = hasErrorCallback ? secondLastArg : null;
// $FlowFixMe[unsafe-addition]
const callbackCount = hasSuccessCallback + hasErrorCallback;
const newArgs = args.slice(0, args.length - callbackCount);
if (type === 'sync') {
// 6.如果是同步方法调用这个函数
return BatchedBridge.callNativeSyncHook(
moduleID,
methodID,
newArgs,
onFail,
onSuccess,
);
} else {
// 非同步方法调用这个函数
BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall(
moduleID,
methodID,
newArgs,
onFail,
onSuccess,
);
}
};
}
// $FlowFixMe[prop-missing]
fn.type = type;
return fn;
}
shell
// 7.来看异步方法
cruntime_->global().setProperty(
*runtime_,
"nativeFlushQueueImmediate",
Function::createFromHostFunction(
*runtime_,
PropNameID::forAscii(*runtime_, "nativeFlushQueueImmediate"),
1,
[this](
jsi::Runtime&,
const jsi::Value&,
const jsi::Value* args,
size_t count) {
if (count != 1) {
throw std::invalid_argument(
"nativeFlushQueueImmediate arg count must be 1");
}
// 8.真正调用地方
callNativeModules(args[0], false);
return Value::undefined();
}));
cpp
void JSIExecutor::callNativeModules(const Value& queue, bool isEndOfBatch) {
TraceSection s("JSIExecutor::callNativeModules");
// If this fails, you need to pass a fully functional delegate with a
// module registry to the factory/ctor.
CHECK(delegate_) << "Attempting to use native modules without a delegate";
#if 0 // maybe useful for debugging
std::string json = runtime_->global().getPropertyAsObject(*runtime_, "JSON")
.getPropertyAsFunction(*runtime_, "stringify").call(*runtime_, queue)
.getString(*runtime_).utf8(*runtime_);
#endif
BridgeNativeModulePerfLogger::asyncMethodCallBatchPreprocessStart();
//9.
delegate_->callNativeModules(
*this, dynamicFromValue(*runtime_, queue), isEndOfBatch);
}
cpp
void callNativeModules(
[[maybe_unused]] JSExecutor& executor,
folly::dynamic&& calls,
bool isEndOfBatch) override {
CHECK(m_registry || calls.empty())
<< "native module calls cannot be completed with no native modules";
m_batchHadNativeModuleOrTurboModuleCalls =
m_batchHadNativeModuleOrTurboModuleCalls || !calls.empty();
std::vector<MethodCall> methodCalls = parseMethodCalls(std::move(calls));
BridgeNativeModulePerfLogger::asyncMethodCallBatchPreprocessEnd(
(int)methodCalls.size());
// An exception anywhere in here stops processing of the batch. This
// was the behavior of the Android bridge, and since exception handling
// terminates the whole bridge, there's not much point in continuing.
for (auto& call : methodCalls) {
// 10
m_registry->callNativeMethod(
call.moduleId, call.methodId, std::move(call.arguments), call.callId);
}
if (isEndOfBatch) {
// onBatchComplete will be called on the native (module) queue, but
// decrementPendingJSCalls will be called sync. Be aware that the bridge
// may still be processing native calls when the bridge idle signaler
// fires.
if (m_batchHadNativeModuleOrTurboModuleCalls) {
m_callback->onBatchComplete();
m_batchHadNativeModuleOrTurboModuleCalls = false;
}
m_callback->decrementPendingJSCalls();
}
}
void ModuleRegistry::callNativeMethod(
unsigned int moduleId,
unsigned int methodId,
folly::dynamic&& params,
int callId) {
if (moduleId >= modules_.size()) {
throw std::runtime_error(folly::to<std::string>(
"moduleId ", moduleId, " out of range [0..", modules_.size(), ")"));
}
//11
modules_[moduleId]->invoke(methodId, std::move(params), callId);
}
// JavaMethodWrapper.cpp
void JavaNativeModule::invoke(
unsigned int reactMethodId,
folly::dynamic&& params,
int callId) {
// 12. 发送消息
messageQueueThread_->runOnQueue(
[this, reactMethodId, params = std::move(params), callId] {
static auto invokeMethod =
wrapper_->getClass()
->getMethod<void(jint, ReadableNativeArray::javaobject)>(
"invoke");
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
if (callId != -1) {
fbsystrace_end_async_flow(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS, "native", callId);
}
#endif
invokeMethod(
wrapper_,
static_cast<jint>(reactMethodId),
ReadableNativeArray::newObjectCxxArgs(std::move(params)).get());
});
}
// JavaMethodWrapper.java
@DoNotStrip
public void invoke(int methodId, ReadableNativeArray parameters) {
if (methodId >= mMethods.size()) {
return;
}
//13.
mMethods.get(methodId).invoke(mJSInstance, parameters);
}
// NativeModuleREgistryBuilder.kt
public fun processPackage(reactPackage: ReactPackage) {
// We use an iterable instead of an iterator here to ensure thread safety, and that this list
// cannot be modified
val moduleHolders =
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
if (reactPackage is LazyReactPackage) {
reactPackage.getNativeModuleIterator(reactApplicationContext)
} else if (reactPackage is BaseReactPackage) {
reactPackage.getNativeModuleIterator(reactApplicationContext)
} else {
ReactPackageHelper.getNativeModuleIterator(reactPackage, reactApplicationContext)
}
for (moduleHolder in moduleHolders) {
val name = moduleHolder.name
val existingNativeModule = modules[name]
if (existingNativeModule != null) {
}
}
// NativeToJsBridge.cpp,最后Java侧调用Promise会执行到这里,
void NativeToJsBridge::invokeCallback(
double callbackId,
folly::dynamic&& arguments) {
int systraceCookie = -1;
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
systraceCookie = m_systraceCookie++;
FbSystraceAsyncFlow::begin(
TRACE_TAG_REACT_CXX_BRIDGE, "<callback>", systraceCookie);
#endif
runOnExecutorQueue(
[this, callbackId, arguments = std::move(arguments), systraceCookie](
JSExecutor* executor) {
if (m_applicationScriptHasFailure) {
LOG(ERROR)
<< "Attempting to call JS callback on a bad application bundle: "
<< callbackId;
throw std::runtime_error(
"Attempting to invoke JS callback on a bad application bundle.");
}这上面就是整体JS到Native的调用过程,整体流程还是很长的。
4.2 Turbo Module调用源码
shell
runtime.global().setProperty(
runtime,
"__turboModuleProxy", // 1.挂载到js的global对象上
jsi::Function::createFromHostFunction(
runtime,
jsi::PropNameID::forAscii(runtime, "__turboModuleProxy"),
1,
[binding = TurboModuleBinding(
runtime,
std::move(moduleProvider),
longLivedObjectCollection)](
jsi::Runtime& rt,
const jsi::Value& /*thisVal*/,
const jsi::Value* args,
size_t count) {
if (count < 1) {
throw std::invalid_argument(
"__turboModuleProxy must be called with at least 1 argument");
}
std::string moduleName = args[0].getString(rt).utf8(rt);
return binding.getModule(rt, moduleName);
}));
return;
shell
jsi::Value TurboModuleBinding::getModule(
jsi::Runtime& runtime,
const std::string& moduleName) const {
std::shared_ptr<TurboModule> module;
{
TraceSection s("TurboModuleBinding::moduleProvider", "module", moduleName);
module = moduleProvider_(moduleName);
}
if (module) {
// What is jsRepresentation? A cache for the TurboModule's properties
// Henceforth, always return the cache (i.e: jsRepresentation) to JavaScript
//
// If a jsRepresentation is found on the TurboModule, return it.
//
// Note: TurboModules are cached by name in TurboModuleManagers. Hence,
// jsRepresentation is also cached by by name by the TurboModuleManager
auto& weakJsRepresentation = module->jsRepresentation_;
if (weakJsRepresentation) {
auto jsRepresentation = weakJsRepresentation->lock(runtime);
if (!jsRepresentation.isUndefined()) {
return jsRepresentation;
}
}
// Status: No jsRepresentation found on TurboModule
// Create a brand new jsRepresentation, and attach it to TurboModule
jsi::Object jsRepresentation(runtime);
weakJsRepresentation =
std::make_unique<jsi::WeakObject>(runtime, jsRepresentation);
// Lazily populate the jsRepresentation, on property access.
//
// How does this work?
// 1. Initially jsRepresentation is empty: {}
// 2. If property lookup on jsRepresentation fails, the JS runtime will
// search jsRepresentation's prototype: jsi::Object(TurboModule).
// 3. TurboModule::get(runtime, propKey) executes. This creates the
// property, caches it on jsRepresentation, then returns it to
// JavaScript.
// 2. 直接看这里,它是通过jsi创建了一个hostObject,这个就像当于把native端的module注入到了这个js对象上
// 3. 翻译一下这里的逻辑是如何做的,jsRepresentation是作为native侧的js对象,它使用的是懒加载的方式,只有第一次用到了这个module的方法才会创建
// 创建的代码在TurboModule::get(runtime, propKey)这里面
auto hostObject =
jsi::Object::createFromHostObject(runtime, std::move(module));
jsRepresentation.setProperty(runtime, "__proto__", std::move(hostObject));
return jsRepresentation;
} else {
return jsi::Value::null();
}
}
shell
class JSI_EXPORT TurboModule : public jsi::HostObject {
public:
TurboModule(std::string name, std::shared_ptr<CallInvoker> jsInvoker);
// DO NOT OVERRIDE - it will become final in a future release.
// This method provides automatic caching of properties on the TurboModule's
// JS representation. To customize lookup of properties, override `create`.
// Note: keep this method declared inline to avoid conflicts
// between RTTI and non-RTTI compilation units
//
// 4.那就看下这里面的懒加载逻辑
jsi::Value get(jsi::Runtime& runtime, const jsi::PropNameID& propName)
override {
auto prop = create(runtime, propName);
// If we have a JS wrapper, cache the result of this lookup
// We don't cache misses, to allow for methodMap_ to dynamically be
// extended
if (jsRepresentation_ && !prop.isUndefined()) {
// 5.直接将native的module绑定到这个jsRepresentation_对象上
jsRepresentation_->lock(runtime).asObject(runtime).setProperty(
runtime, propName, prop);
}
return prop;
}可以看出来它是利用了jsi的机制,直接在引擎层面建立了module的对应关系,这样js侧直接调用即可,他就是引擎层给js的对象了。
主要基于的就是JS的原型链逻辑,当前属性没有就去找__proto__,这个就是就会走到get方法里,此时会创建一个新的属性到jsRepresentation_对象上,这样下次js再方法就可以直接返回了。
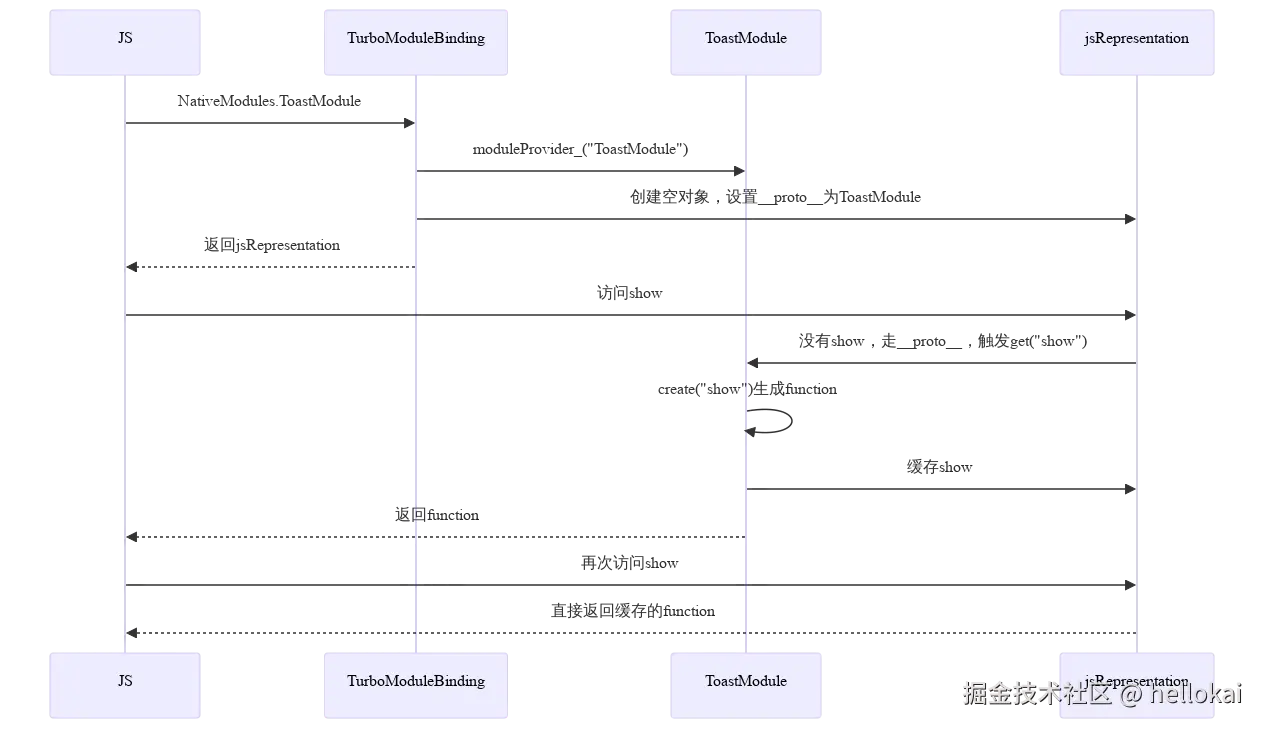
以上TurboModule就分析完了,接下来再看下渲染器吧!
五、Fabric渲染
刚才所说的,同步,优先级,并发渲染都是渲染器来实现的,RN中的渲染器叫做Fabric。
老架构中的渲染系统,渲染那树的逻辑及优化都是针对单个平台实现的,而当前的渲染器则是通过共享一个核心C++实现的。
那说到渲染,我们都知道类似于这种响应式的UI开发,都是通过虚拟DOM的形式来渲染的,那我们直接来看看它的三个树都有啥吧。
5.1 Element Tree
纯JS逻辑,我们所有写的RN标签就是Element,最后会变成一个视图树
shell
// Element Tree的结构
const elementTree = {
type: 'View',
props: {
style: { backgroundColor: 'red', width: 100, height: 100 },
onPress: () => console.log('clicked')
},
children: [
{
type: 'Text',
props: { children: 'Hello World' },
children: []
}
]
};Diff算法在这里:
- 同级比较:只比较同一层级的节点
- key优化:使用key属性优化列表diff
- 类型判断:type不同直接替换整个子树
shell
// React的reconciliation算法
function reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren) {
if (current === null) {
// 首次渲染,直接创建
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(workInProgress, null, nextChildren);
} else {
// 更新渲染,执行diff
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren
);
}
}感兴趣的可以推荐看这个pomb.us/build-your-...,实现自己的React。
5.2 Shadow Tree
C++层逻辑,使用Yoga库来计算视图树的逻辑,Yoga负责样式计算和布局算法(flex布局),同步测量
原来是使用的是JNI的方式,有Java到C++的数据转换,现在新架构直接使用c++在c++层操作yoga
Java侧无需再维护YogaNode视图树对象
老架构是使用的Java来维护的ShadowTree,现在统一到Fabric,c++侧维护
整体新老架构shadow tree对比图
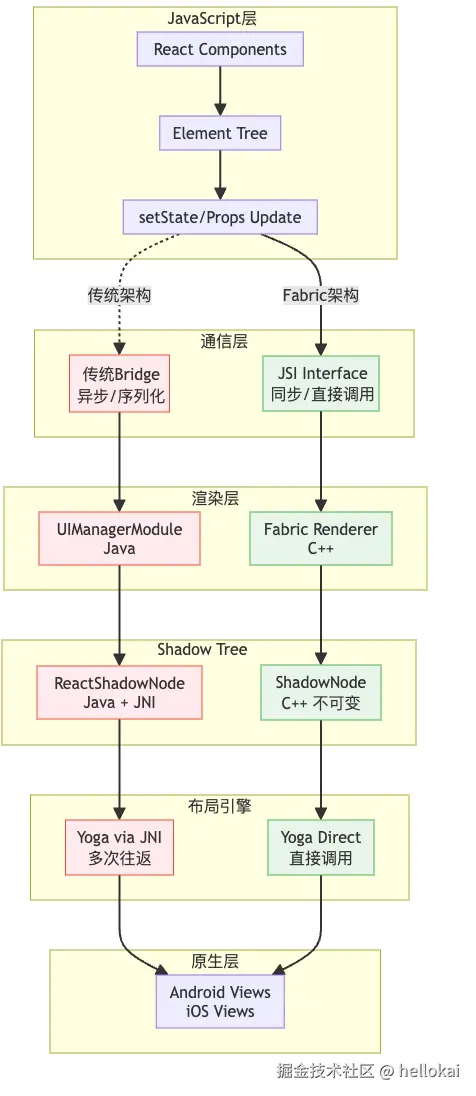
我们以创建一个View为例子看下具体如何实现的吧
shell
//1.js侧会调用到此,创建一个view
@ReactMethod
public void createView(int tag, String className, int rootViewTag, ReadableMap props) {
if (DEBUG) {
String message =
"(UIManager.createView) tag: " + tag + ", class: " + className + ", props: " + props;
FLog.d(ReactConstants.TAG, message);
PrinterHolder.getPrinter().logMessage(ReactDebugOverlayTags.UI_MANAGER, message);
}
mUIImplementation.createView(tag, className, rootViewTag, props);
}
shell
public void createView(int tag, String className, int rootViewTag, ReadableMap props) {
if (!mViewOperationsEnabled) {
return;
}
synchronized (uiImplementationThreadLock) {
ReactShadowNode cssNode = createShadowNode(className);
ReactShadowNode rootNode = mShadowNodeRegistry.getNode(rootViewTag);
Assertions.assertNotNull(rootNode, "Root node with tag " + rootViewTag + " doesn't exist");
cssNode.setReactTag(tag); // Thread safety needed here
cssNode.setViewClassName(className);
cssNode.setRootTag(rootNode.getReactTag());
cssNode.setThemedContext(rootNode.getThemedContext());
mShadowNodeRegistry.addNode(cssNode);
ReactStylesDiffMap styles = null;
if (props != null) {
styles = new ReactStylesDiffMap(props);
cssNode.updateProperties(styles);
}
// 2. 实际处理
handleCreateView(cssNode, rootViewTag, styles);
}
}
}
shell
protected void handleCreateView(
ReactShadowNode cssNode, int rootViewTag, @Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap styles) {
if (!cssNode.isVirtual()) {
// 3. mNativeViewHierarchyOptimizer处理
mNativeViewHierarchyOptimizer.handleCreateView(cssNode, cssNode.getThemedContext(), styles);
}
}
shell
public void handleCreateView(
ReactShadowNode node,
ThemedReactContext themedContext,
@Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap initialProps) {
if (!ENABLED) {
assertNodeSupportedWithoutOptimizer(node);
int tag = node.getReactTag();
mUIViewOperationQueue.enqueueCreateView(
themedContext, tag, node.getViewClass(), initialProps);
return;
}
boolean isLayoutOnly =
node.getViewClass().equals(ViewProps.VIEW_CLASS_NAME)
&& isLayoutOnlyAndCollapsable(initialProps);
node.setIsLayoutOnly(isLayoutOnly);
if (node.getNativeKind() != NativeKind.NONE) {
// 4. 将创建作为命令添加到队列中去
mUIViewOperationQueue.enqueueCreateView(
themedContext, node.getReactTag(), node.getViewClass(), initialProps);
}
}
shell
// 5. commit 提交更新
public void dispatchViewUpdates(int batchId) {
SystraceMessage.beginSection(
Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE, "UIImplementation.dispatchViewUpdates")
.arg("batchId", batchId)
.flush();
final long commitStartTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
try {
updateViewHierarchy();
mNativeViewHierarchyOptimizer.onBatchComplete();
// 6. 分发view更新
mOperationsQueue.dispatchViewUpdates(batchId, commitStartTime, mLastCalculateLayoutTime);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
}
shell
public void dispatchViewUpdates(
final int batchId, final long commitStartTime, final long layoutTime) {
//....
synchronized (mDispatchRunnablesLock) {
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
// 7. 所有更新加到mDispatchUIRunnables中
mDispatchUIRunnables.add(runOperations);
}
//....
}
shell
@Override
public void doFrameGuarded(long frameTimeNanos) {
if (mIsInIllegalUIState) {
FLog.w(
ReactConstants.TAG,
"Not flushing pending UI operations because of previously thrown Exception");
return;
}
Systrace.beginSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE, "dispatchNonBatchedUIOperations");
try {
// 8.1 分发操作
dispatchPendingNonBatchedOperations(frameTimeNanos);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
// 8.2 一样的分发操作
flushPendingBatches();
ReactChoreographer.getInstance()
.postFrameCallback(ReactChoreographer.CallbackType.DISPATCH_UI, this);
}从这里我们就可以看出来了,它是通过js序列化消息传递到客户端的UIManager,然后也通过队列的方式进行UI相关命令缓存,等到vsync信号后开始渲染
shell
public synchronized void createView(
ThemedReactContext themedContext,
int tag,
String className,
@Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap initialProps) {
if (DEBUG_MODE) {
FLog.d(
TAG,
"createView[%d]: %s %s",
tag,
className,
(initialProps != null ? initialProps.toString() : "<null>"));
}
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
SystraceMessage.beginSection(
Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_VIEW, "NativeViewHierarchyManager_createView")
.arg("tag", tag)
.arg("className", className)
.flush();
try {
// 9 通过viewmanger找到对应的真实view,然后创建绑定
ViewManager viewManager = mViewManagers.get(className);
View view =
viewManager.createView(tag, themedContext, initialProps, null, mJSResponderHandler);
mTagsToViews.put(tag, view);
mTagsToViewManagers.put(tag, viewManager);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_VIEW);
}
}从这里我们就可以看出来它主题逻辑还是由Java侧计算渲染的。
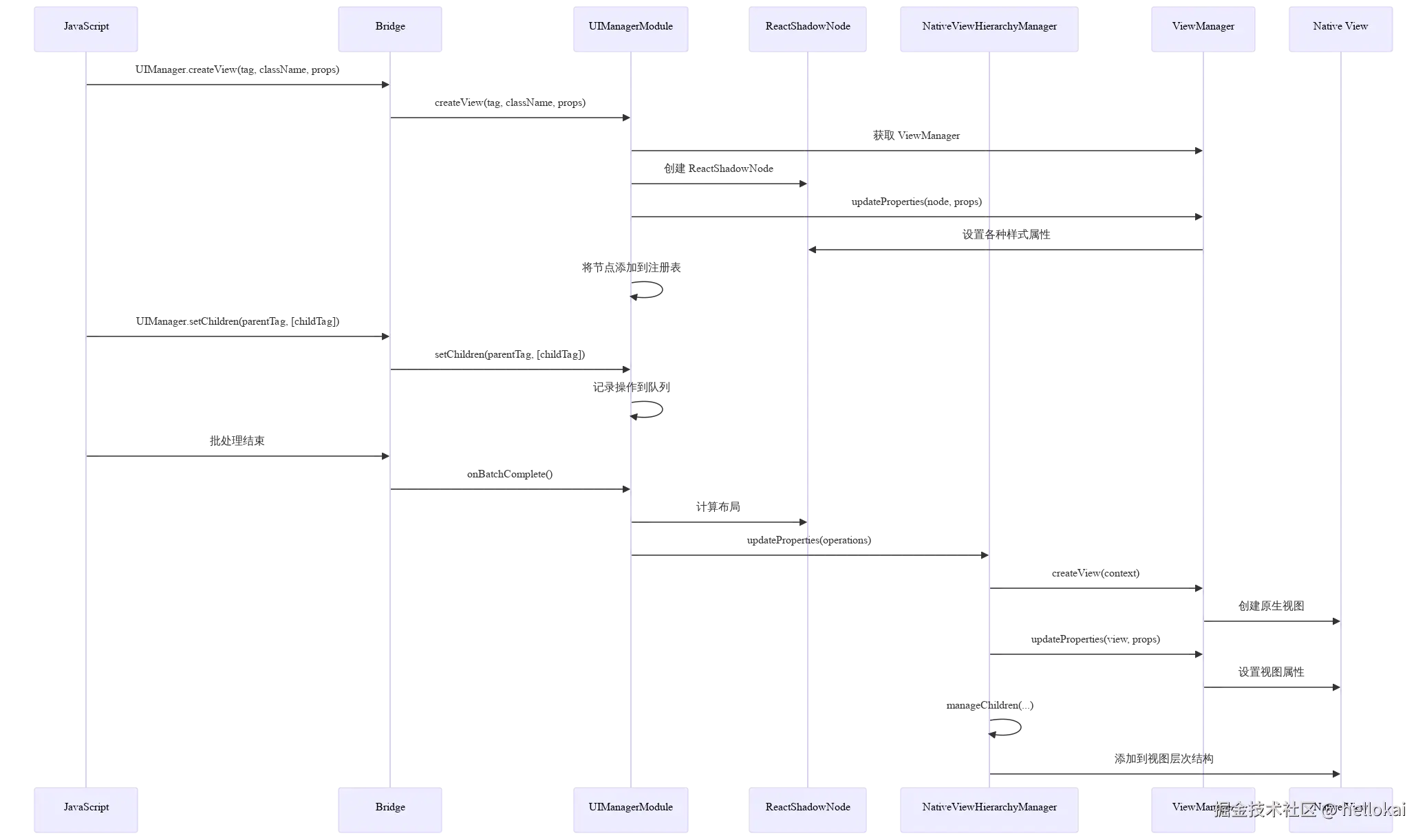
5.3 新架构Fabric渲染
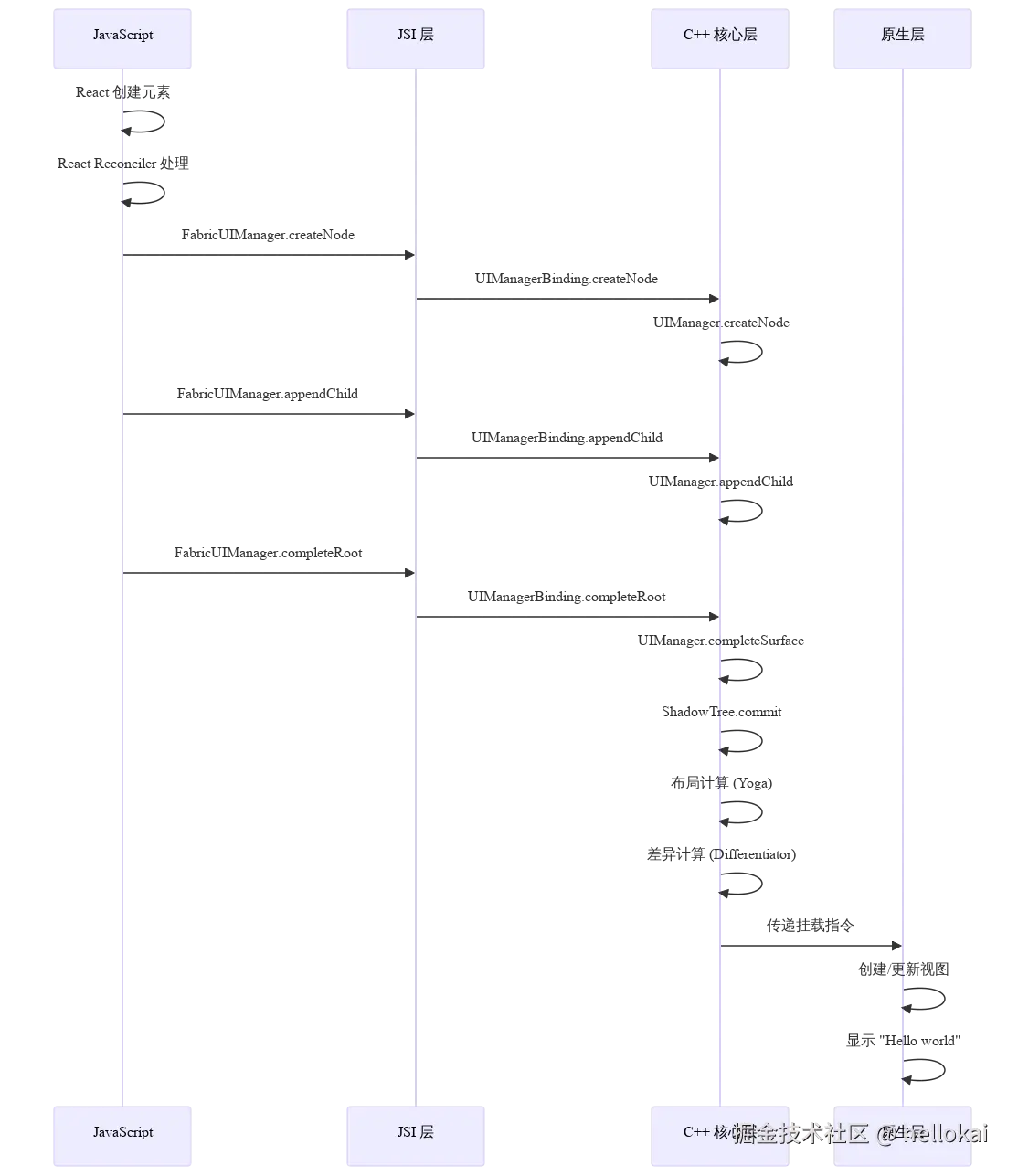
如果从渲染的角度来看,结合Vysnc来看:
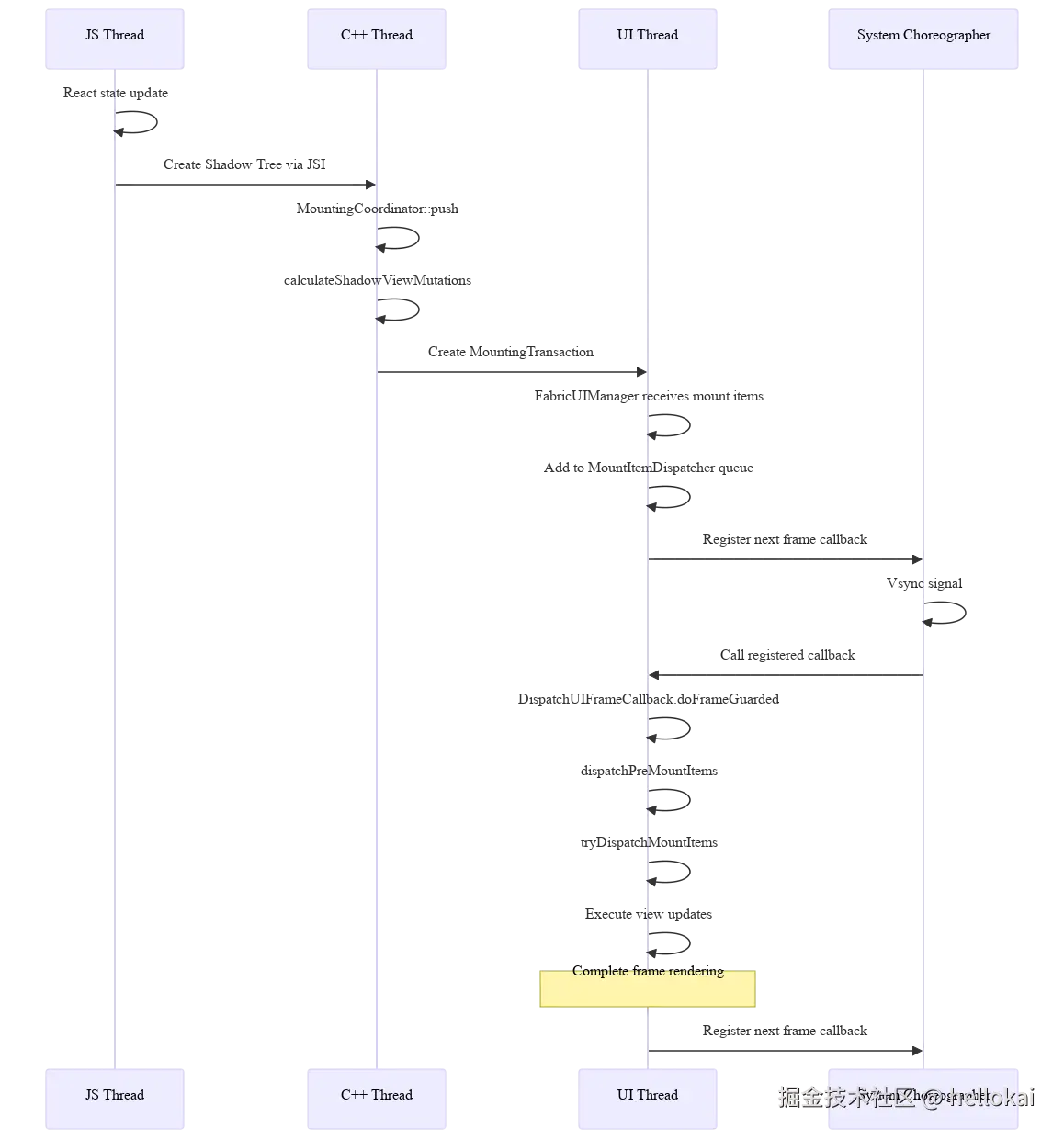
Fabric架构也是通过的JSI来做的,它在JS侧的定义为
shell
/**
* Copyright (c) Meta Platforms, Inc. and affiliates.
*
* This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
*
* @flow strict-local
* @format
*/
'use strict';
import type {
MeasureInWindowOnSuccessCallback,
MeasureLayoutOnSuccessCallback,
MeasureOnSuccessCallback,
} from '../../src/private/types/HostInstance';
import type {NativeElementReference} from '../../src/private/webapis/dom/nodes/specs/NativeDOM';
import type {
InternalInstanceHandle,
LayoutAnimationConfig,
Node,
} from '../Renderer/shims/ReactNativeTypes';
import type {RootTag} from '../Types/RootTagTypes';
import defineLazyObjectProperty from '../Utilities/defineLazyObjectProperty';
export type NodeSet = Array<Node>;
export type NodeProps = {...};
export interface Spec {
+createNode: (
reactTag: number,
viewName: string,
rootTag: RootTag,
props: NodeProps,
instanceHandle: InternalInstanceHandle,
) => Node;
+cloneNode: (node: Node) => Node;
+cloneNodeWithNewChildren: (node: Node) => Node;
+cloneNodeWithNewProps: (node: Node, newProps: NodeProps) => Node;
+cloneNodeWithNewChildrenAndProps: (node: Node, newProps: NodeProps) => Node;
+createChildSet: (rootTag: RootTag) => NodeSet;
+appendChild: (parentNode: Node, child: Node) => Node;
+appendChildToSet: (childSet: NodeSet, child: Node) => void;
+completeRoot: (rootTag: RootTag, childSet: NodeSet) => void;
+measure: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
callback: MeasureOnSuccessCallback,
) => void;
+measureInWindow: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
callback: MeasureInWindowOnSuccessCallback,
) => void;
+measureLayout: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
relativeNode: Node | NativeElementReference,
onFail: () => void,
onSuccess: MeasureLayoutOnSuccessCallback,
) => void;
+configureNextLayoutAnimation: (
config: LayoutAnimationConfig,
callback: () => void, // check what is returned here
errorCallback: () => void,
) => void;
+sendAccessibilityEvent: (node: Node, eventType: string) => void;
+findShadowNodeByTag_DEPRECATED: (reactTag: number) => ?Node;
+setNativeProps: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
newProps: NodeProps,
) => void;
+dispatchCommand: (
node: Node,
commandName: string,
args: Array<mixed>,
) => void;
+findNodeAtPoint: (
node: Node,
locationX: number,
locationY: number,
callback: (instanceHandle: ?InternalInstanceHandle) => void,
) => void;
+compareDocumentPosition: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
otherNode: Node | NativeElementReference,
) => number;
+getBoundingClientRect: (
node: Node | NativeElementReference,
includeTransform: boolean,
) => ?[
/* x: */ number,
/* y: */ number,
/* width: */ number,
/* height: */ number,
];
}
let nativeFabricUIManagerProxy: ?Spec;
// This is a list of all the methods in global.nativeFabricUIManager that we'll
// cache in JavaScript, as the current implementation of the binding
// creates a new host function every time methods are accessed.
const CACHED_PROPERTIES = [
'createNode', // 1. 创建node
'cloneNode',
'cloneNodeWithNewChildren',
'cloneNodeWithNewProps',
'cloneNodeWithNewChildrenAndProps',
'createChildSet',
'appendChild',
'appendChildToSet',
'completeRoot',
'measure',
'measureInWindow',
'measureLayout',
'configureNextLayoutAnimation',
'sendAccessibilityEvent',
'findShadowNodeByTag_DEPRECATED',
'setNativeProps',
'dispatchCommand',
'compareDocumentPosition',
'getBoundingClientRect',
];
// This is exposed as a getter because apps using the legacy renderer AND
// Fabric can define the binding lazily. If we evaluated the global and cached
// it in the module we might be caching an `undefined` value before it is set.
export function getFabricUIManager(): ?Spec {
if (
nativeFabricUIManagerProxy == null &&
global.nativeFabricUIManager != null
) {
nativeFabricUIManagerProxy = createProxyWithCachedProperties(
global.nativeFabricUIManager,
CACHED_PROPERTIES,
);
}
return nativeFabricUIManagerProxy;
}
/**
*
* Returns an object that caches the specified properties the first time they
* are accessed, and falls back to the original object for other properties.
*/
function createProxyWithCachedProperties(
implementation: Spec,
propertiesToCache: $ReadOnlyArray<string>,
): Spec {
const proxy = Object.create(implementation);
for (const propertyName of propertiesToCache) {
defineLazyObjectProperty(proxy, propertyName, {
// $FlowExpectedError[prop-missing]
get: () => implementation[propertyName],
});
}
return proxy;
}
cpp
if (methodName == "createNode") {
auto paramCount = 5;
return jsi::Function::createFromHostFunction(
runtime,
name,
paramCount,
[uiManager, methodName, paramCount](
jsi::Runtime& runtime,
const jsi::Value& /*thisValue*/,
const jsi::Value* arguments,
size_t count) -> jsi::Value {
try {
validateArgumentCount(runtime, methodName, paramCount, count);
auto instanceHandle =
instanceHandleFromValue(runtime, arguments[4], arguments[0]);
if (!instanceHandle) {
react_native_assert(false);
return jsi::Value::undefined();
}
return valueFromShadowNode(
runtime,
uiManager->createNode( //2.创建node
tagFromValue(arguments[0]),
stringFromValue(runtime, arguments[1]),
surfaceIdFromValue(runtime, arguments[2]),
RawProps(runtime, arguments[3]),
std::move(instanceHandle)),
true);
} catch (const std::logic_error& ex) {
LOG(FATAL) << "logic_error in createNode: " << ex.what();
}
});
}
cpp
std::shared_ptr<ShadowNode> UIManager::createNode(
Tag tag,
const std::string& name,
SurfaceId surfaceId,
RawProps rawProps,
InstanceHandle::Shared instanceHandle) const {
TraceSection s("UIManager::createNode", "componentName", name);
auto& componentDescriptor = componentDescriptorRegistry_->at(name);
auto fallbackDescriptor =
componentDescriptorRegistry_->getFallbackComponentDescriptor();
PropsParserContext propsParserContext{surfaceId, *contextContainer_.get()};
auto family = componentDescriptor.createFamily(
{tag, surfaceId, std::move(instanceHandle)});
const auto props = componentDescriptor.cloneProps(
propsParserContext, nullptr, std::move(rawProps));
const auto state = componentDescriptor.createInitialState(props, family);
//3. 创建ShadowNode
auto shadowNode = componentDescriptor.createShadowNode(
ShadowNodeFragment{
.props = fallbackDescriptor != nullptr &&
fallbackDescriptor->getComponentHandle() ==
componentDescriptor.getComponentHandle()
? componentDescriptor.cloneProps(
propsParserContext,
props,
RawProps(folly::dynamic::object("name", name)))
: props,
.children = ShadowNodeFragment::childrenPlaceholder(),
.state = state,
},
family);
if (delegate_ != nullptr) {
delegate_->uiManagerDidCreateShadowNode(*shadowNode);
}
if (leakChecker_) {
leakChecker_->uiManagerDidCreateShadowNodeFamily(family);
}
return shadowNode;
}
cpp
if (methodName == "completeRoot") {// 4. 一次渲染周期完成,通知Fabric渲染完成
auto paramCount = 2;
return jsi::Function::createFromHostFunction(
runtime,
name,
paramCount,
[uiManager, methodName, paramCount](
jsi::Runtime& runtime,
const jsi::Value& /*thisValue*/,
const jsi::Value* arguments,
size_t count) -> jsi::Value {
validateArgumentCount(runtime, methodName, paramCount, count);
auto runtimeSchedulerBinding =
RuntimeSchedulerBinding::getBinding(runtime);
auto surfaceId = surfaceIdFromValue(runtime, arguments[0]);
auto shadowNodeList = shadowNodeListFromValue(runtime, arguments[1]);
//5. 实际触发渲染
uiManager->completeSurface(
surfaceId,
shadowNodeList,
{.enableStateReconciliation = true, .mountSynchronously = false});
return jsi::Value::undefined();
});
}
cpp
void UIManager::completeSurface(
SurfaceId surfaceId,
const ShadowNode::UnsharedListOfShared& rootChildren,
ShadowTree::CommitOptions commitOptions) {
TraceSection s("UIManager::completeSurface", "surfaceId", surfaceId);
shadowTreeRegistry_.visit(surfaceId, [&](const ShadowTree& shadowTree) {
// 6.提交commit
auto result = shadowTree.commit(
[&](const RootShadowNode& oldRootShadowNode) {
return std::make_shared<RootShadowNode>(
oldRootShadowNode,
ShadowNodeFragment{
.props = ShadowNodeFragment::propsPlaceholder(),
.children = rootChildren,
});
},
commitOptions);
if (result == ShadowTree::CommitStatus::Succeeded &&
lazyShadowTreeRevisionConsistencyManager_ != nullptr) {
// It's safe to update the visible revision of the shadow tree immediately
// after we commit a specific one.
lazyShadowTreeRevisionConsistencyManager_->updateCurrentRevision(
surfaceId, shadowTree.getCurrentRevision().rootShadowNode);
}
});
}
cpp
//7.针对于shadowtree的新老版本进行对比
CommitStatus ShadowTree::tryCommit(
const ShadowTreeCommitTransaction& transaction,
const CommitOptions& commitOptions) const {
TraceSection s("ShadowTree::commit");
auto telemetry = TransactionTelemetry{};
telemetry.willCommit();
CommitMode commitMode;
auto oldRevision = ShadowTreeRevision{};
auto newRevision = ShadowTreeRevision{};
{
// Reading `currentRevision_` in shared manner.
std::shared_lock lock(commitMutex_);
commitMode = commitMode_;
oldRevision = currentRevision_;
}
const auto& oldRootShadowNode = oldRevision.rootShadowNode;
auto newRootShadowNode = transaction(*oldRevision.rootShadowNode);
if (!newRootShadowNode) {
return CommitStatus::Cancelled;
}
if (commitOptions.enableStateReconciliation) {
//8.真正的shadowtree的diff算法在ProgressState
auto updatedNewRootShadowNode =
progressState(*newRootShadowNode, *oldRootShadowNode);
if (updatedNewRootShadowNode) {
newRootShadowNode =
std::static_pointer_cast<RootShadowNode>(updatedNewRootShadowNode);
}
}
// Run commit hooks.
newRootShadowNode = delegate_.shadowTreeWillCommit(
*this, oldRootShadowNode, newRootShadowNode);
if (!newRootShadowNode) {
return CommitStatus::Cancelled;
}
// Layout nodes.
std::vector<const LayoutableShadowNode*> affectedLayoutableNodes{};
affectedLayoutableNodes.reserve(1024);
telemetry.willLayout();
telemetry.setAsThreadLocal();
//9.进行layout
newRootShadowNode->layoutIfNeeded(&affectedLayoutableNodes);
telemetry.unsetAsThreadLocal();
telemetry.didLayout(static_cast<int>(affectedLayoutableNodes.size()));
{
// Updating `currentRevision_` in unique manner if it hasn't changed.
std::unique_lock lock(commitMutex_);
if (currentRevision_.number != oldRevision.number) {
return CommitStatus::Failed;
}
auto newRevisionNumber = currentRevision_.number + 1;
{
std::scoped_lock dispatchLock(EventEmitter::DispatchMutex());
updateMountedFlag(
currentRevision_.rootShadowNode->getChildren(),
newRootShadowNode->getChildren());
}
telemetry.didCommit();
telemetry.setRevisionNumber(static_cast<int>(newRevisionNumber));
// Seal the shadow node so it can no longer be mutated
// Does nothing in release.
newRootShadowNode->sealRecursive();
newRevision = ShadowTreeRevision{
std::move(newRootShadowNode), newRevisionNumber, telemetry};
currentRevision_ = newRevision;
}
emitLayoutEvents(affectedLayoutableNodes);
if (commitMode == CommitMode::Normal) {
//10.shadow tree处理完成进行mount处理
mount(std::move(newRevision), commitOptions.mountSynchronously);
}
return CommitStatus::Succeeded;
}
cpp
void ShadowTree::mount(ShadowTreeRevision revision, bool mountSynchronously)
const {
mountingCoordinator_->push(std::move(revision));
//11.处理mount
delegate_.shadowTreeDidFinishTransaction(
mountingCoordinator_, mountSynchronously);
}
cpp
void UIManager::shadowTreeDidFinishTransaction(
std::shared_ptr<const MountingCoordinator> mountingCoordinator,
bool mountSynchronously) const {
TraceSection s("UIManager::shadowTreeDidFinishTransaction");
if (delegate_ != nullptr) {
//13.
delegate_->uiManagerDidFinishTransaction(
std::move(mountingCoordinator), mountSynchronously);
}
}
cpp
//14.是在Scheduler来进行的调度
void Scheduler::uiManagerDidFinishTransaction(
std::shared_ptr<const MountingCoordinator> mountingCoordinator,
bool mountSynchronously) {
TraceSection s("Scheduler::uiManagerDidFinishTransaction");
if (delegate_ != nullptr) {
// This is no-op on all platforms except for Android where we need to
// observe each transaction to be able to mount correctly.
delegate_->schedulerDidFinishTransaction(mountingCoordinator);
if (!mountSynchronously) {
auto surfaceId = mountingCoordinator->getSurfaceId();
runtimeScheduler_->scheduleRenderingUpdate(
surfaceId,
[delegate = delegate_,
mountingCoordinator = std::move(mountingCoordinator)]() {
delegate->schedulerShouldRenderTransactions(mountingCoordinator);
});
} else {
delegate_->schedulerShouldRenderTransactions(mountingCoordinator);
}
}
}
cpp
void FabricUIManagerBinding::schedulerShouldRenderTransactions(
const std::shared_ptr<const MountingCoordinator>& mountingCoordinator) {
auto mountingManager =
getMountingManager("schedulerShouldRenderTransactions");
if (!mountingManager) {
return;
}
if (ReactNativeFeatureFlags::enableAccumulatedUpdatesInRawPropsAndroid()) {
//15.调度
auto mountingTransaction = mountingCoordinator->pullTransaction();
if (mountingTransaction.has_value()) {
auto transaction = std::move(*mountingTransaction);
//17.执行真正的指令
mountingManager->executeMount(transaction);
}
} else {
std::vector<MountingTransaction> pendingTransactions;
{
// Retain the lock to access the pending transactions but not to execute
// the mount operations because that method can call into this method
// again.
//
// This can be re-entrant when mounting manager triggers state updates
// synchronously (this can happen when committing from the UI thread).
// This is safe because we're already combining all the transactions for
// the same surface ID in a single transaction in the pending transactions
// list, so operations won't run out of order.
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(pendingTransactionsMutex_);
pendingTransactions_.swap(pendingTransactions);
}
for (auto& transaction : pendingTransactions) {
mountingManager->executeMount(transaction);
}
}
}
cpp
std::optional<MountingTransaction> MountingCoordinator::pullTransaction(
bool willPerformAsynchronously) const {
TraceSection section("MountingCoordinator::pullTransaction");
std::scoped_lock lock(mutex_);
auto transaction = std::optional<MountingTransaction>{};
// Base case
if (lastRevision_.has_value()) {
number_++;
auto telemetry = lastRevision_->telemetry;
telemetry.willDiff();
//16.这里是进行diff的地方,将shadowtree变成nativeview对应的实际指令
auto mutations = calculateShadowViewMutations(
*baseRevision_.rootShadowNode, *lastRevision_->rootShadowNode);
telemetry.didDiff();
transaction = MountingTransaction{
surfaceId_, number_, std::move(mutations), telemetry};
}
cpp
void FabricMountingManager::executeMount(
const MountingTransaction& transaction) {
TraceSection section("FabricMountingManager::executeMount");
std::scoped_lock lock(commitMutex_);
auto finishTransactionStartTime = telemetryTimePointNow();
auto env = jni::Environment::current();
auto telemetry = transaction.getTelemetry();
auto surfaceId = transaction.getSurfaceId();
auto& mutations = transaction.getMutations();
bool maintainMutationOrder =
ReactNativeFeatureFlags::disableMountItemReorderingAndroid();
auto revisionNumber = telemetry.getRevisionNumber();
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppCommonMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppDeleteMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdatePropsMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdateStateMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdatePaddingMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdateLayoutMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems;
std::vector<CppMountItem> cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems;
{
std::lock_guard allocatedViewsLock(allocatedViewsMutex_);
auto allocatedViewsIterator = allocatedViewRegistry_.find(surfaceId);
auto defaultAllocatedViews = std::unordered_set<Tag>{};
// Do not remove `defaultAllocatedViews` or initialize
// `std::unordered_set<Tag>{}` inline in below ternary expression - if falsy
// operand is a value type, the compiler will decide the expression to be a
// value type, an unnecessary (sometimes expensive) copy will happen as a
// result.
auto& allocatedViewTags =
allocatedViewsIterator != allocatedViewRegistry_.end()
? allocatedViewsIterator->second
: defaultAllocatedViews;
if (allocatedViewsIterator == allocatedViewRegistry_.end()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Executing commit after surface " << surfaceId
<< " was stopped!";
}
for (const auto& mutation : mutations) {
auto parentTag = mutation.parentTag;
const auto& oldChildShadowView = mutation.oldChildShadowView;
const auto& newChildShadowView = mutation.newChildShadowView;
auto& mutationType = mutation.type;
auto& index = mutation.index;
bool isVirtual = mutation.mutatedViewIsVirtual();
switch (mutationType) {
case ShadowViewMutation::Create: {
bool shouldCreateView =
!allocatedViewTags.contains(newChildShadowView.tag);
if (shouldCreateView) {
cppCommonMountItems.push_back(
CppMountItem::CreateMountItem(newChildShadowView));
allocatedViewTags.insert(newChildShadowView.tag);
}
break;
}
case ShadowViewMutation::Remove: {
if (!isVirtual) {
cppCommonMountItems.push_back(CppMountItem::RemoveMountItem(
parentTag, oldChildShadowView, index));
}
break;
}
case ShadowViewMutation::Delete: {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems : cppDeleteMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::DeleteMountItem(oldChildShadowView));
if (allocatedViewTags.erase(oldChildShadowView.tag) != 1) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Emitting delete for unallocated view "
<< oldChildShadowView.tag;
}
break;
}
case ShadowViewMutation::Update: {
if (!isVirtual) {
if (!allocatedViewTags.contains(newChildShadowView.tag)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Emitting update for unallocated view "
<< newChildShadowView.tag;
}
if (oldChildShadowView.props != newChildShadowView.props) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePropsMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdatePropsMountItem(
oldChildShadowView, newChildShadowView));
}
if (oldChildShadowView.state != newChildShadowView.state) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateStateMountItems)
.push_back(
CppMountItem::UpdateStateMountItem(newChildShadowView));
}
// Padding: padding mountItems must be executed before layout props
// are updated in the view. This is necessary to ensure that events
// (resulting from layout changes) are dispatched with the correct
// padding information.
if (oldChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.contentInsets !=
newChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.contentInsets) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePaddingMountItems)
.push_back(
CppMountItem::UpdatePaddingMountItem(newChildShadowView));
}
if (oldChildShadowView.layoutMetrics !=
newChildShadowView.layoutMetrics) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateLayoutMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateLayoutMountItem(
mutation.newChildShadowView, parentTag));
}
// OverflowInset: This is the values indicating boundaries including
// children of the current view. The layout of current view may not
// change, and we separate this part from layout mount items to not
// pack too much data there.
if ((oldChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.overflowInset !=
newChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.overflowInset)) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateOverflowInsetMountItem(
newChildShadowView));
}
}
if (oldChildShadowView.eventEmitter !=
newChildShadowView.eventEmitter) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePropsMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateEventEmitterMountItem(
mutation.newChildShadowView));
}
break;
}
case ShadowViewMutation::Insert: {
if (!isVirtual) {
// Insert item
cppCommonMountItems.push_back(CppMountItem::InsertMountItem(
parentTag, newChildShadowView, index));
bool shouldCreateView =
!allocatedViewTags.contains(newChildShadowView.tag);
if (ReactNativeFeatureFlags::
enableAccumulatedUpdatesInRawPropsAndroid()) {
if (shouldCreateView) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Emitting insert for unallocated view "
<< newChildShadowView.tag;
}
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePropsMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdatePropsMountItem(
{}, newChildShadowView));
} else {
if (shouldCreateView) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Emitting insert for unallocated view "
<< newChildShadowView.tag;
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePropsMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdatePropsMountItem(
{}, newChildShadowView));
}
}
// State
if (newChildShadowView.state) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateStateMountItems)
.push_back(
CppMountItem::UpdateStateMountItem(newChildShadowView));
}
// Padding: padding mountItems must be executed before layout props
// are updated in the view. This is necessary to ensure that events
// (resulting from layout changes) are dispatched with the correct
// padding information.
if (newChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.contentInsets !=
EdgeInsets::ZERO) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdatePaddingMountItems)
.push_back(
CppMountItem::UpdatePaddingMountItem(newChildShadowView));
}
// Layout
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateLayoutMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateLayoutMountItem(
newChildShadowView, parentTag));
// OverflowInset: This is the values indicating boundaries including
// children of the current view. The layout of current view may not
// change, and we separate this part from layout mount items to not
// pack too much data there.
if (newChildShadowView.layoutMetrics.overflowInset !=
EdgeInsets::ZERO) {
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateOverflowInsetMountItem(
newChildShadowView));
}
}
// EventEmitter
// On insert we always update the event emitter, as we do not pass
// it in when preallocating views
(maintainMutationOrder ? cppCommonMountItems
: cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems)
.push_back(CppMountItem::UpdateEventEmitterMountItem(
mutation.newChildShadowView));
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
}
}
// We now have all the information we need, including ordering of mount items,
// to know exactly how much space must be allocated
auto [batchMountItemIntsSize, batchMountItemObjectsSize] = computeBufferSizes(
cppCommonMountItems,
cppDeleteMountItems,
cppUpdatePropsMountItems,
cppUpdateStateMountItems,
cppUpdatePaddingMountItems,
cppUpdateLayoutMountItems,
cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems,
cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems);
//19.拿到Java层的FabricUIManager.java中的scheduleMountItem方法进行调度
static auto scheduleMountItem = JFabricUIManager::javaClassStatic()
->getMethod<void(
JMountItem::javaobject,
jint,
jlong,
jlong,
jlong,
jlong,
jlong,
jlong,
jlong,
jint)>("scheduleMountItem");
if (batchMountItemIntsSize == 0) {
auto finishTransactionEndTime = telemetryTimePointNow();
scheduleMountItem(
javaUIManager_,
nullptr,
telemetry.getRevisionNumber(),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getCommitStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getDiffStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getDiffEndTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getLayoutStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getLayoutEndTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(finishTransactionStartTime),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(finishTransactionEndTime),
telemetry.getAffectedLayoutNodesCount());
return;
}
// Allocate the intBuffer and object array, now that we know exact sizes
// necessary
InstructionBuffer buffer = {
env,
env->NewIntArray(batchMountItemIntsSize),
jni::JArrayClass<jobject>::newArray(batchMountItemObjectsSize),
};
// Fill in arrays
int prevMountItemType = -1;
// Fill in CREATE instructions.
for (int i = 0; i < cppCommonMountItems.size(); i++) {
const auto& mountItem = cppCommonMountItems[i];
const auto& mountItemType = mountItem.type;
// Get type here, and count forward how many items of this type are in a
// row. Write preamble to any common type here.
if (prevMountItemType != mountItemType) {
int numSameItemTypes = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < cppCommonMountItems.size() &&
cppCommonMountItems[j].type == mountItemType;
j++) {
numSameItemTypes++;
}
writeMountItemPreamble(buffer, mountItemType, numSameItemTypes);
prevMountItemType = mountItemType;
}
switch (mountItemType) {
case CppMountItem::Type::Create:
writeCreateMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::Delete:
writeDeleteMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::Insert:
writeInsertMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::Remove:
writeRemoveMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdateProps:
writeUpdatePropsMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdateState:
writeUpdateStateMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdateLayout:
writeUpdateLayoutMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdateEventEmitter:
writeUpdateEventEmitterMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdatePadding:
writeUpdatePaddingMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
case CppMountItem::Type::UpdateOverflowInset:
writeUpdateOverflowInsetMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unexpected CppMountItem type: " << mountItemType;
}
}
if (!cppUpdatePropsMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdateProps,
cppUpdatePropsMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdatePropsMountItems) {
writeUpdatePropsMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
if (!cppUpdateStateMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdateState,
cppUpdateStateMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdateStateMountItems) {
writeUpdateStateMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
if (!cppUpdatePaddingMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdatePadding,
cppUpdatePaddingMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdatePaddingMountItems) {
writeUpdatePaddingMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
if (!cppUpdateLayoutMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdateLayout,
cppUpdateLayoutMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdateLayoutMountItems) {
writeUpdateLayoutMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
if (!cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdateOverflowInset,
cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdateOverflowInsetMountItems) {
writeUpdateOverflowInsetMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
if (!cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer,
CppMountItem::Type::UpdateEventEmitter,
cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppUpdateEventEmitterMountItems) {
writeUpdateEventEmitterMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
// Write deletes last - so that all prop updates, etc, for the tag in the same
// batch don't fail. Without additional machinery, moving deletes here
// requires that the differ never produces "DELETE...CREATE" in that order for
// the same tag. It's nice to be able to batch all similar operations together
// for space efficiency.
// FIXME: this optimization is incorrect when multiple transactions are
// merged together
if (!cppDeleteMountItems.empty()) {
writeMountItemPreamble(
buffer, CppMountItem::Type::Delete, cppDeleteMountItems.size());
for (const auto& mountItem : cppDeleteMountItems) {
writeDeleteMountItem(buffer, mountItem);
}
}
static auto createMountItemsIntBufferBatchContainer =
JFabricUIManager::javaClassStatic()
->getMethod<jni::alias_ref<JMountItem>(
jint, jintArray, jni::jtypeArray<jobject>, jint)>(
"createIntBufferBatchMountItem");
auto batch = createMountItemsIntBufferBatchContainer(
javaUIManager_,
surfaceId,
// If there are no items, we pass a nullptr instead of passing the
// object through the JNI
batchMountItemIntsSize > 0 ? buffer.ints : nullptr,
batchMountItemObjectsSize > 0 ? buffer.objects.get() : nullptr,
revisionNumber);
auto finishTransactionEndTime = telemetryTimePointNow();
scheduleMountItem(
javaUIManager_,
batch.get(),
telemetry.getRevisionNumber(),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getCommitStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getDiffStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getDiffEndTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getLayoutStartTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(telemetry.getLayoutEndTime()),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(finishTransactionStartTime),
telemetryTimePointToMilliseconds(finishTransactionEndTime),
telemetry.getAffectedLayoutNodesCount());
env->DeleteLocalRef(buffer.ints);
}
cpp
@Override
public void execute(MountingManager mountingManager) {
SurfaceMountingManager surfaceMountingManager = mountingManager.getSurfaceManager(mSurfaceId);
if (surfaceMountingManager == null) {
FLog.e(
TAG,
"Skipping batch of MountItems; no SurfaceMountingManager found for [%d].",
mSurfaceId);
return;
}
if (surfaceMountingManager.isStopped()) {
FLog.e(TAG, "Skipping batch of MountItems; was stopped [%d].", mSurfaceId);
return;
}
if (ReactNativeFeatureFlags.enableFabricLogs()) {
FLog.d(TAG, "Executing IntBufferBatchMountItem on surface [%d]", mSurfaceId);
}
beginMarkers("mountViews");
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < mIntBufferLen) {
int rawType = mIntBuffer[i++];
int type = rawType & ~INSTRUCTION_FLAG_MULTIPLE;
int numInstructions = ((rawType & INSTRUCTION_FLAG_MULTIPLE) != 0 ? mIntBuffer[i++] : 1);
String[] args = {"numInstructions", String.valueOf(numInstructions)};
Systrace.beginSection(
Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE,
"IntBufferBatchMountItem::mountInstructions::" + nameForInstructionString(type),
args,
args.length);
for (int k = 0; k < numInstructions; k++) {
if (type == INSTRUCTION_CREATE) {
String componentName = getFabricComponentName((String) mObjBuffer[j++]);
//20.这里也就是创建指令真正执行的地方了
surfaceMountingManager.createView(
componentName,
mIntBuffer[i++],
(ReadableMap) mObjBuffer[j++],
(StateWrapper) mObjBuffer[j++],
(EventEmitterWrapper) mObjBuffer[j++],
mIntBuffer[i++] == 1);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_DELETE) {
surfaceMountingManager.deleteView(mIntBuffer[i++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_INSERT) {
int tag = mIntBuffer[i++];
int parentTag = mIntBuffer[i++];
surfaceMountingManager.addViewAt(parentTag, tag, mIntBuffer[i++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_REMOVE) {
surfaceMountingManager.removeViewAt(mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_PROPS) {
surfaceMountingManager.updateProps(mIntBuffer[i++], (ReadableMap) mObjBuffer[j++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_STATE) {
surfaceMountingManager.updateState(mIntBuffer[i++], (StateWrapper) mObjBuffer[j++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_LAYOUT) {
int reactTag = mIntBuffer[i++];
int parentTag = mIntBuffer[i++];
int x = mIntBuffer[i++];
int y = mIntBuffer[i++];
int width = mIntBuffer[i++];
int height = mIntBuffer[i++];
int displayType = mIntBuffer[i++];
int layoutDirection = mIntBuffer[i++];
surfaceMountingManager.updateLayout(
reactTag, parentTag, x, y, width, height, displayType, layoutDirection);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_PADDING) {
surfaceMountingManager.updatePadding(
mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++], mIntBuffer[i++]);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_OVERFLOW_INSET) {
int reactTag = mIntBuffer[i++];
int overflowInsetLeft = mIntBuffer[i++];
int overflowInsetTop = mIntBuffer[i++];
int overflowInsetRight = mIntBuffer[i++];
int overflowInsetBottom = mIntBuffer[i++];
surfaceMountingManager.updateOverflowInset(
reactTag,
overflowInsetLeft,
overflowInsetTop,
overflowInsetRight,
overflowInsetBottom);
} else if (type == INSTRUCTION_UPDATE_EVENT_EMITTER) {
surfaceMountingManager.updateEventEmitter(
mIntBuffer[i++], (EventEmitterWrapper) mObjBuffer[j++]);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid type argument to IntBufferBatchMountItem: " + type + " at index: " + i);
}
}
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
endMarkers();
}六、总结
以上就是整体新老架构的不同,新架构提供了TurboModule,Fabric渲染,Codegen代码生成来解决旧架构中的不同问题,再来回顾下吧:
| 对比项 | 新架构 | 旧架构 |
|---|---|---|
| TurboModule | 提供TurboModule,将异步调用变为同步调用,提升性能和开发效率。 | 旧架构无TurboModule,依赖传统模块系统。 |
| Fabric渲染 | 使用Fabric c++统一渲染逻辑,不在端侧渲染处理,优化渲染性能和内存占用。 | 旧架构依赖React Native原生渲染。 |
| Codegen代码生成 | 引入Codegen工具,自动化代码生成,减少冗余。 | 旧架构依赖手动编写或传统代码生成工具。 |