本文介绍了Langgraph服务的四种调用方式:
-
通过LangGraph Studio UI界面手动测试;
-
使用Python SDK进行同步/异步调用;
-
通过REST API测试;
-
使用JavaScript SDK接入。
Langgraph 服务端代码 graph.py
python
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model='qwq-32b',
temperature=0.8,
api_key='sk-****',
streaming=True,
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
# extra_body={'chat_template_kwargs': {'enable_thinking': False}},
)
#
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""Get weather for a given city."""
return f"在 {city},今天天气不错!"
graph = create_react_agent(
llm,
tools=[get_weather],
prompt="你是一个智能助手"
)通过命令langgraph dev 启动服务,可以看到控制台返回的API地址
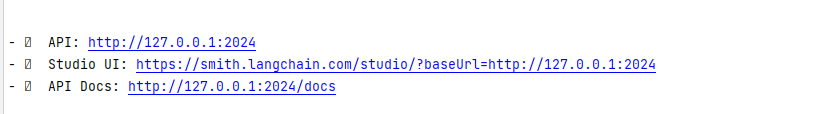
1.第一种访问方式:LangGraph Studio
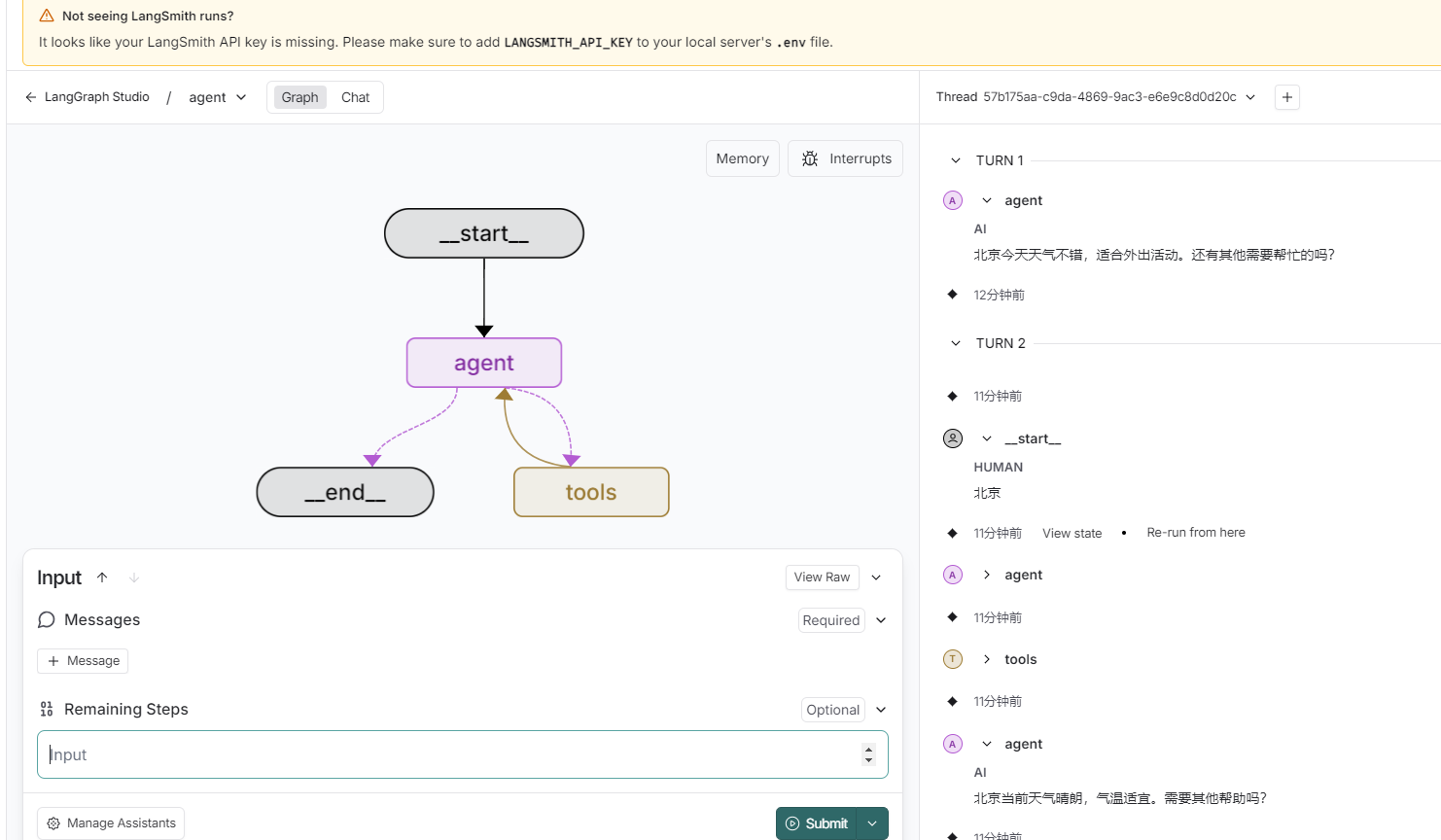
当启动服务后,浏览器中会自动打开 Studio UI的地址,页面如下
可手动输入message,完成调用
2.第二种访问方式:PythonSDK测试
先安装依赖:pip install langgraph-sdk
1)异步测试
langgraph_async_test.py文件内容:
python
from langgraph_sdk import get_client
import asyncio
client = get_client(url="http://localhost:2024")
async def main():
async for chunk in client.runs.stream(
None, # Threadless run
"agent", # Name of assistant. Defined in langgraph.json.
input={
"messages": [{
"role": "human",
"content": "上海今天的天气",
}],
},
stream_mode="messages-tuple",
):
# print(f"Receiving new event of type: {chunk.event}...")
# print(chunk.data)
if isinstance(chunk.data,list) and 'type' in chunk.data[0] and chunk.data[0]['type'] == 'AIMessageChunk':
print(chunk.data[0]['content'], end='', flush=True)
asyncio.run(main())运行结果:
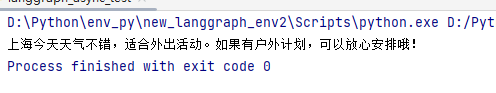
2)同步测试
langgraph_sync_test.py文件内容:
python
from langgraph_sdk import get_sync_client
client = get_sync_client(url="http://localhost:2024")
for chunk in client.runs.stream(
None, # Threadless run
"agent", # Name of assistant. Defined in langgraph.json.
input={
"messages": [{
"role": "human",
"content": "上海今天的天气",
}],
},
stream_mode="messages-tuple",
):
# print(f"Receiving new event of type: {chunk.event}...")
# print(chunk.data)
if isinstance(chunk.data,list) and 'type' in chunk.data[0] and chunk.data[0]['type'] == 'AIMessageChunk':
print(chunk.data[0]['content'], end='', flush=True)运行结果:
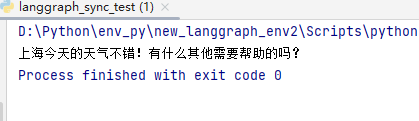
后面2种方式,可自动测试,参考如下
3.第三种访问方式:REST API测试
Haskell
curl -s --request POST \
--url "http://localhost:2024/runs/stream" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data "{
\"assistant_id\": \"agent\",
\"input\": {
\"messages\": [
{
\"role\": \"human\",
\"content\": \"上海的天气?\"
}
]
},
\"stream_mode\": \"messages-tuple\"
}"4.第四种访问方式:JavaScript SDK测试
安装 LangGraph JS SDK:npm install @langchain/langgraph-sdk
向LangGraph服务区发送消息:
javascript
const { Client } = await import("@langchain/langgraph-sdk");
// only set the apiUrl if you changed the default port when calling langgraph dev
const client = new Client({ apiUrl: "http://localhost:2024"});
const streamResponse = client.runs.stream(
null, // Threadless run
"agent", // Assistant ID
{
input: {
"messages": [
{ "role": "user", "content": "上海的天气?"}
]
},
streamMode: "messages-tuple",
}
);
for await (const chunk of streamResponse) {
console.log(`Receiving new event of type: ${chunk.event}...`);
console.log(JSON.stringify(chunk.data));
console.log("\n\n");
}graph.py中的get_weather方法可替找成工具
python
TAVILY_API_KEY='tvly-dev-***'
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""Get real-time weather for a given city using Tavily search."""
from langchain_community.tools import TavilySearchResults
import re
# 创建 Tavily 搜索工具实例
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(
max_results=1,
search_depth="advanced",
include_answer=True,
api_key=TAVILY_API_KEY
)
# 构造搜索查询
query = f"{city} 当前天气 温度 湿度 风力 风向 天气状况"
try:
# 执行搜索
results = search_tool.invoke({"query": query})
# 解析结果
if isinstance(results, list) and len(results) > 0:
result = results[0]
content = result.get('content', '暂无详细信息')
# 修复编码问题的函数
def fix_encoding(text):
if not isinstance(text, str):
return text
# 尝试多种编码修复方法
encodings_to_try = [
('latin1', 'utf-8'),
('cp1252', 'utf-8'),
]
for from_enc, to_enc in encodings_to_try:
try:
# 将字符串以from_enc编码方式重新编码,再以to_enc解码
return text.encode(from_enc).decode(to_enc)
except (UnicodeEncodeError, UnicodeDecodeError):
continue
# 如果上面的方法都不行,尝试直接使用raw_unicode_escape
try:
return text.encode('raw_unicode_escape').decode('utf-8')
except (UnicodeEncodeError, UnicodeDecodeError):
pass
# 如果所有方法都失败,返回原始内容
return text
# 修复编码
fixed_content = fix_encoding(content)
print(f"处理后内容: {fixed_content}")
# 从修复后的内容中提取天气信息
def extract_weather_info(text):
info = {}
# 提取天气状况(如晴、多云、阴等)
weather_conditions = ['晴', '多云', '阴', '雨', '雪', '雾', '霾', '雷阵雨', '小雨', '中雨', '大雨', '暴雨']
for condition in weather_conditions:
if condition in text:
info['condition'] = condition
break
# 如果没找到中文天气状况,尝试用正则表达式
if 'condition' not in info:
condition_match = re.search(r'天气[:\s]*([^\s,,。\.]+)', text)
if condition_match:
info['condition'] = condition_match.group(1)
# 提取温度 (寻找数字+度/℃)
temp_match = re.search(r'(\d+\.?\d*)[度℃]', text)
if temp_match:
info['temperature'] = temp_match.group(1) + "℃"
# 提取湿度
humidity_match = re.search(r'湿度[:\s]*([0-9]+\.?[0-9]*)[%%]', text)
if humidity_match:
info['humidity'] = humidity_match.group(1) + "%"
# 提取风向
wind_dir_match = re.search(r'风向[:\s]*([东南西北风]+)', text)
if wind_dir_match:
info['wind_direction'] = wind_dir_match.group(1)
# 提取风力
wind_speed_match = re.search(r'风力[:\s]*([0-9]+\.?[0-9]*[级m/s])', text)
if wind_speed_match:
info['wind_speed'] = wind_speed_match.group(1)
return info
# 提取天气信息
weather_info = extract_weather_info(fixed_content)
# 构建最终输出格式
if weather_info:
output_parts = [f"{city} 天气"]
if 'condition' in weather_info:
output_parts.append(f"{weather_info['condition']}")
output_parts.append("实时天气情况")
if 'temperature' in weather_info:
output_parts.append(f"温度{weather_info['temperature']}")
if 'humidity' in weather_info:
output_parts.append(f"湿度{weather_info['humidity']}")
if 'wind_direction' in weather_info:
output_parts.append(f"风向{weather_info['wind_direction']}")
if 'wind_speed' in weather_info:
output_parts.append(f"风力{weather_info['wind_speed']}")
return " ".join(output_parts)
else:
# 如果无法提取结构化信息,则返回修复后的内容
return f"{city}天气信息: {fixed_content}"
else:
return f"无法获取{city}的天气信息"
except Exception as e:
# 异常处理
return f"查询{city}天气时出现错误: {str(e)}"替换后再次测试,结果如下:
