题⽬描述
输⼊⼀棵⼆叉搜索树,将该⼆叉搜索树转换成⼀个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向
思路及解答
递归中序遍历(推荐)
根据二叉搜索树的特点:左结点的值<根结点的值<右结点的值,我们不难发现,使用二叉树的中序遍历出来的数据的数序,就是排序的顺序。因此,首先,确定了二叉搜索树的遍历方法。
我们看下图,我们可以把树分成三个部分:值为10的结点、根结点为6的左子树、根结点为14的右子树。根据排序双向链表的定义,值为10的结点将和它的左子树的最大一个结点链接起来,同时它还将和右子树最小的结点链接起来。
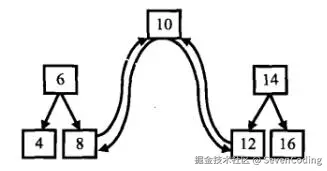
按照中序遍历的顺序,当我们遍历到根结点时,它的左子树已经转换成一个排序好的双向链表了,并且处在链表中最后一个的结点是当前值最大的结点。
具体思路如下,可以利用BST中序遍历的有序性,在遍历过程中调整指针:
- 中序遍历:按照左子树→根节点→右子树的顺序遍历
- 指针调整 :维护一个
pre指针记录前驱节点,将当前节点与前驱节点双向连接 - 头节点处理:第一个被访问的节点(最左节点)作为链表头节点
java
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
private TreeNode pre = null; // 记录前驱节点
private TreeNode head = null; // 链表头节点
public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
// 中序遍历左子树
convert(root.left);
// 处理当前节点
if (pre == null) {
head = root; // 第一个节点作为头节点
} else {
pre.right = root; // 前驱节点的next指向当前节点
root.left = pre; // 当前节点的prev指向前驱节点
}
pre = root; // 更新前驱节点为当前节点
// 中序遍历右子树
convert(root.right);
return head;
}
}- 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点被访问一次
- 空间复杂度:O(n),递归调用栈的空间(最坏情况下树退化为链表)
迭代中序遍历(栈辅助)
使用栈模拟递归过程,避免递归带来的栈溢出风险:
- 栈辅助遍历:利用栈实现中序遍历的非递归版本
- 指针调整 :同样维护
pre指针记录前驱节点 - 头节点标记:使用布尔变量标记第一个节点作为链表头
java
public class Solution {
public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode head = null;
boolean isFirst = true; // 标记第一个节点
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 走到最左节点
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (isFirst) {
head = root; // 第一个节点作为头节点
pre = head;
isFirst = false;
} else {
pre.right = root; // 连接前驱和当前节点
root.left = pre;
pre = root;
}
root = root.right; // 处理右子树
}
return head;
}
}- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n),栈的空间消耗
Morris遍历
利用Morris遍历实现O(1)空间复杂度的中序遍历:
- 线索化:利用叶子节点的空指针指向中序前驱或后继
- 指针调整:在遍历过程中实时调整指针关系
- 无栈递归:不需要额外栈空间或递归调用
java
public class Solution {
public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.left == null) {
// 处理当前节点
if (pre == null) {
head = current;
} else {
pre.right = current;
current.left = pre;
}
pre = current;
current = current.right;
} else {
// 找到当前节点的中序前驱
TreeNode predecessor = current.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != current) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = current; // 建立线索
current = current.left;
} else {
// 处理当前节点
predecessor.right = null;
if (pre == null) {
head = current;
} else {
pre.right = current;
current.left = pre;
}
pre = current;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
return head;
}
}- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1),只使用固定数量的指针变量