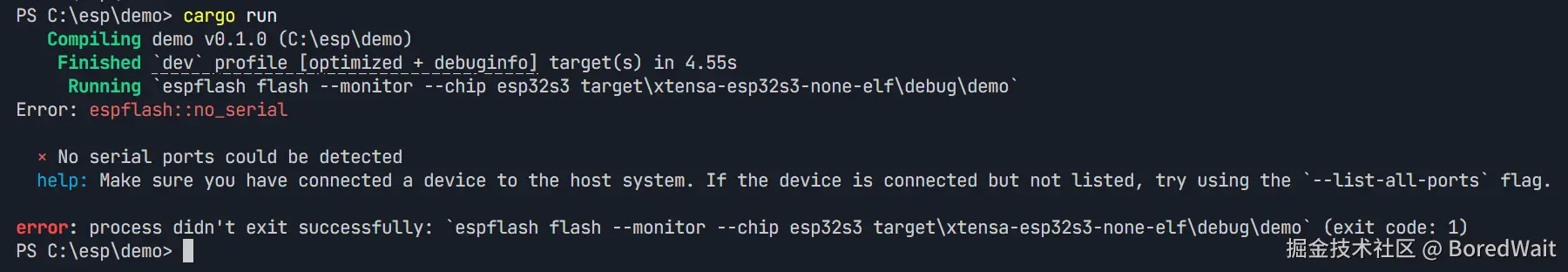
学习rust嵌入式之esp32单片机,从打印hello word开发。 rust 嵌入式 ESP23
学习rust嵌入式之esp32单片机,从打印hello word开发。 rust 嵌入式 ESP23
搭建环境:
相关连接:docs.espressif.com/projects/ru...
安装rust www.rust-lang.org/zh-CN/tools... 验证是否安装成功:
shell
cargo -V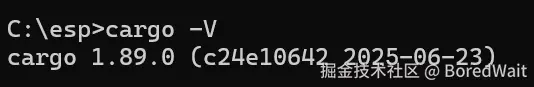
安装espup
shell
cargo install espup --lockedespup 安装相关依赖
shell
espup install安装ldproxy 相关配置
shell
cargo install ldproxy安装esp-generate项目生成工具:
shell
cargo install esp-generate运行项目:
构建项目代码 (your-project)自定义项目名称
js
esp-generate --chip=esp32c6 your-project项目结构
file
├── build.rs
├── .cargo
│ └── config.toml
├── Cargo.toml
├── .gitignore
├── rust-toolchain.toml
├── src
│ ├── bin
│ │ └── main.rs
│ └── lib.rs
└── .vscode
└── settings.json修改src/bin/main.rs的代码
rs
#![no_std]
#![no_main]
#![deny(
clippy::mem_forget,
reason = "mem::forget is generally not safe to do with esp_hal types, especially those \
holding buffers for the duration of a data transfer."
)]
use esp_hal::{
clock::CpuClock,
main,
time::{Duration, Instant},
};
use esp_println::println;
#[panic_handler]
fn panic(_: &core::panic::PanicInfo) -> ! {
loop {
println!("111 world!");
println!("Panic!");
}
}
// This creates a default app-descriptor required by the esp-idf bootloader.
// For more information see: <https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/stable/esp32/api-reference/system/app_image_format.html#application-description>
esp_bootloader_esp_idf::esp_app_desc!();
#[main]
fn main() -> ! {
// generator version: 0.5.0
let config = esp_hal::Config::default().with_cpu_clock(CpuClock::max());
let _peripherals = esp_hal::init(config);
loop {
println!("hello world!");
let delay_start = Instant::now();
while delay_start.elapsed() < Duration::from_millis(500) {}
}
// for inspiration have a look at the examples at https://github.com/esp-rs/esp-hal/tree/esp-hal-v1.0.0-rc.0/examples/src/bin
}插入esp32设备连接电脑usb
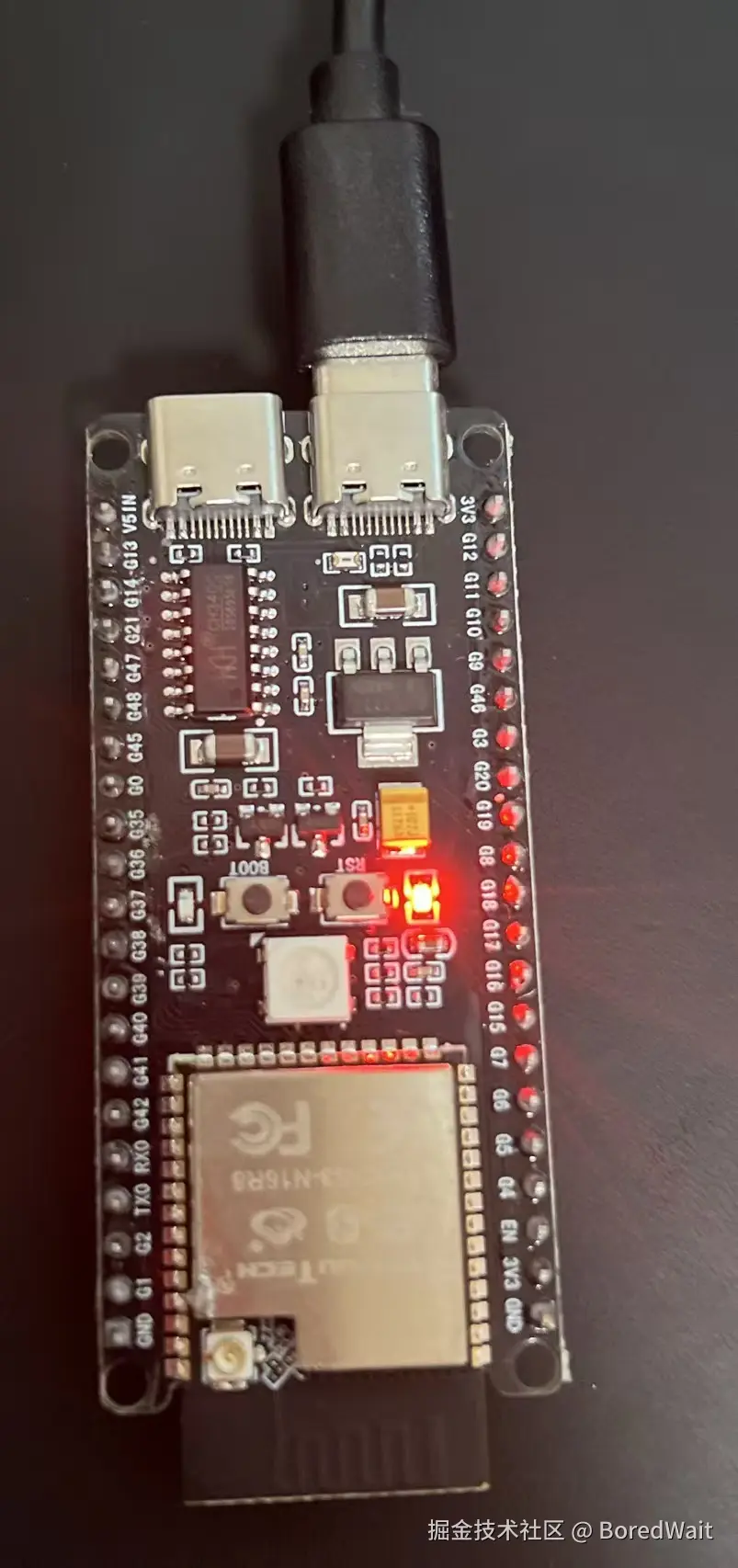 运行项目
运行项目
shell
cargo run结果成功 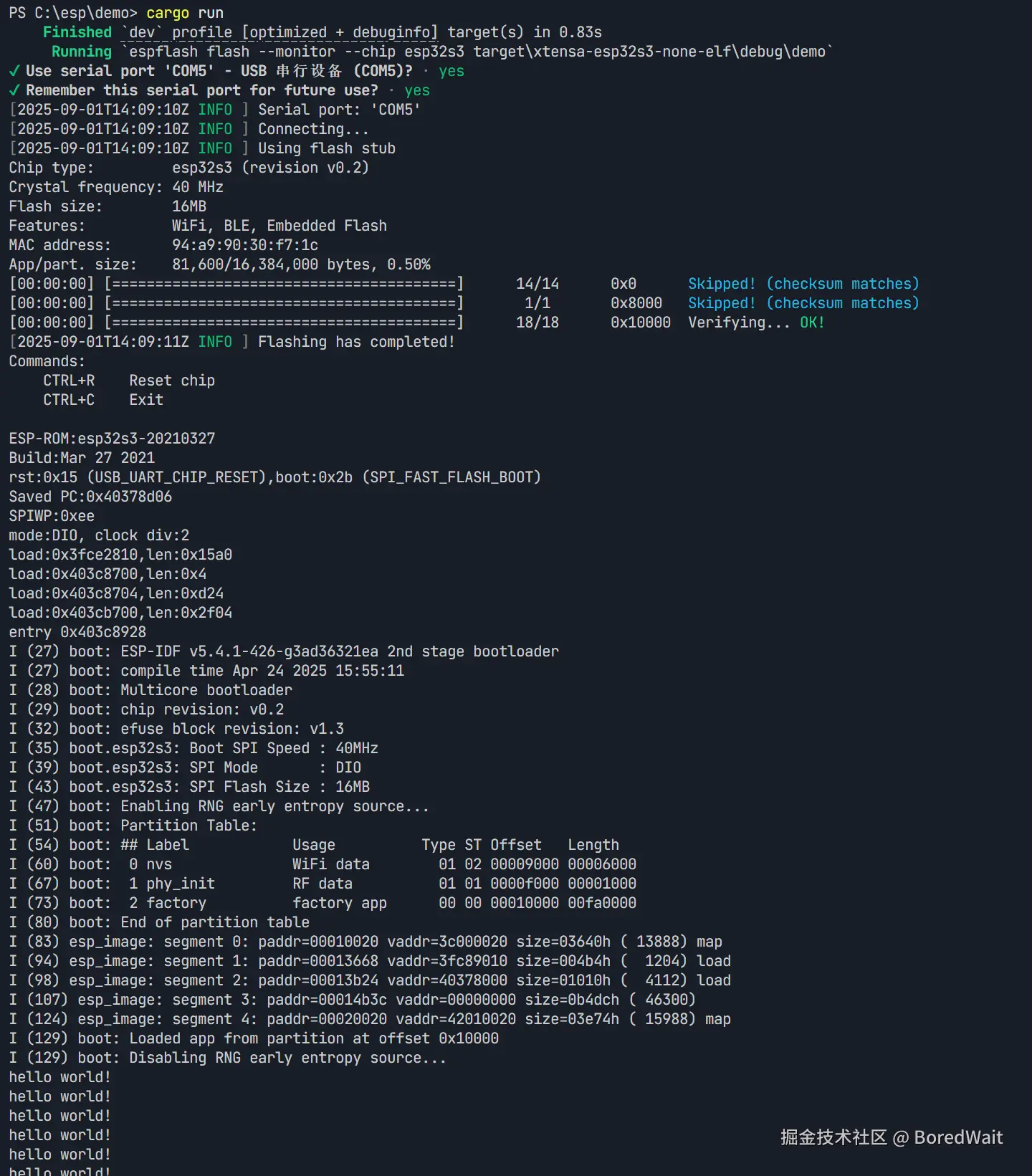
!如果未插入设备标识运行成功但是没有烧录