继承
在 Kotlin 中,所有的类都有个共同的超类 Any,即使不显示继承,也会默认继承:
kotlin
class Example // Implicitly inherits from AnyAny 有三个方法:equals()、hashCode()和 toString()。因此,所有的Kotlin类都有这三个方法。
Kotlin 类默认是 final 的,所以默认是不可以被继承的。如果想要一个类变的可被继承,就需要使用open 标记:
kotlin
open class Base // Class is open for inheritance在类头使用冒号来显示的指定超类:
kotlin
open class Base(p: Int)
class Derived(p: Int) : Base(p)假如派生类有主构造函数,那么基类必须根据其参数在该主构造函数中进行初始化。
如果派生类没有主构造函数,那么每个次构造函数都必须使用 super 关键字来初始化基类类型,或者必须委托给另一个能完成该初始化操作的构造函数。
在这种情况下,不同的次构造函数可以调用基类的不同构造函数。
kotlin
class MyView : View {
constructor(ctx: Context) : super(ctx)
constructor(ctx: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : super(ctx, attrs)
}方法重写
Kotlin 要求对可重写成员和重写操作使用显式修饰符:
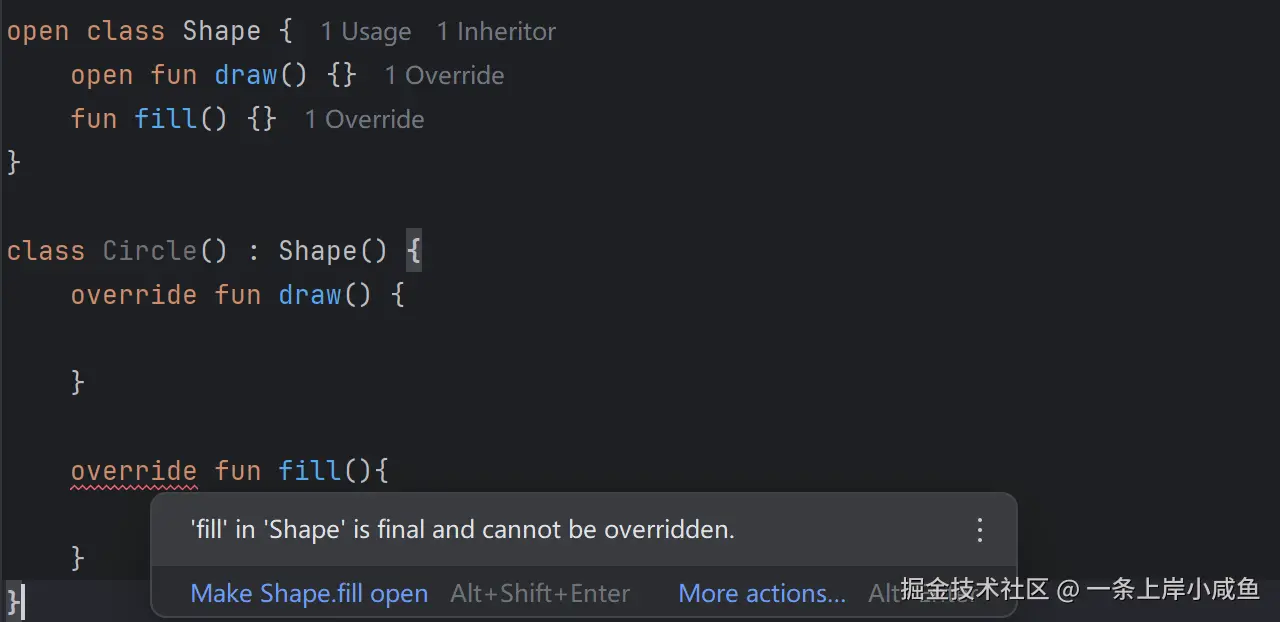
对于重写的 draw 来说,override 标识符是必须的。如果没有的话,编译器会报错。Shape 的fill方法没有 open 标识符,所以编译器报了错。当 open 修饰符被添加到 final 类(的成员上时,它不会产生任何效果。
被标记为 override 的成员本身是可重写的(open),因此它可以在子类中被再次重写。如果希望禁止再次重写,可使用 final 修饰符:
kotlin
open class Rectangle() : Shape() {
final override fun draw() { /*...*/ }
}属性重写
属性的重写机制与方法的重写机制相同。在超类中声明的属性若要在派生类中重新声明,必须以 override 开头,且它们必须具有兼容的类型。
每个已声明的属性都可以被带有初始化器的属性或带有 get 方法的属性重写:
kotlin
open class Shape {
open val vertexCount: Int = 0
}
class Rectangle : Shape() {
override val vertexCount = 4
}开发者可以使用 var 来重写 val,但是反过来不行。这是因为 val 属性本身声明了一个 get 方法,如果使用 var 来重写的的话,相当于子类在父类的基础上扩展了 set 方法。如果父类是 var ,var 是带有get 和 set 方法的,如果子类是 val 的话,相当于只有 get,这就违反了继承的规则。
开发者可以在主构造函数中使用 override 关键字:
kotlin
interface Shape {
val vertexCount: Int
}
class Rectangle(override val vertexCount: Int = 4) : Shape // Always has 4 vertices
class Polygon : Shape {
override var vertexCount: Int = 0 // Can be set to any number later
}子类初始化顺序
构造子类的对象时,基类的初始化会在子类的初始化之前执行。
kotlin
open class Base(val name: String) {
init { println("Initializing a base class") }
open val size: Int =
name.length.also { println("Initializing size in the base class: $it") }
}
class Derived(
name: String,
val lastName: String,
) : Base(name.replaceFirstChar { it.uppercase() }.also { println("Argument for the base class: $it") }) {
init { println("Initializing a derived class") }
override val size: Int =
(super.size + lastName.length).also { println("Initializing size in the derived class: $it") }
}
// Argument for the base class: Java
// Initializing a base class
// Initializing size in the base class: 4
// Initializing a derived class
// Initializing size in the derived class: 101.首先执行 Derived 的构造中传递给 Base 的表达式
name.replaceFirstChar { it.uppercase() }.also { ... }
此时会打印:Argument for the base class: Java
2.执行基类的初始化 执行基类的 init 块:Initializing a base class
初始化基类的 size 属性:计算 name 长度("Java" 长度为 4),打印:Initializing size in the base class: 4
3.执行子类的初始化 执行派生类的 init 块:Initializing a derived class
初始化派生类的 size 属性:计算 super.size (4) + lastName.length (6) 得到 10,打印:Initializing size in the derived class: 10
调用父类的实现
通过 super 关键字就可以在子类中访问父类的方法和属性:
kotlin
open class Rectangle {
open fun draw() { println("Drawing a rectangle") }
val borderColor: String get() = "black"
}
class FilledRectangle : Rectangle() {
override fun draw() {
super.draw()
println("Filling the rectangle")
}
val fillColor: String get() = super.borderColor
}在内部类中,若要访问外部类的超类(即外部类的父类),需使用 super 关键字并结合外部类类名进行限定,语法形式为:super@Outer(其中 Outer 需替换为实际的外部类类名):
kotlin
class FilledRectangle: Rectangle() {
override fun draw() {
val filler = Filler()
filler.drawAndFill()
}
inner class Filler {
fun fill() { println("Filling") }
fun drawAndFill() {
super@FilledRectangle.draw() // Calls Rectangle's implementation of draw()
fill()
println("Drawn a filled rectangle with color ${super@FilledRectangle.borderColor}") // Uses Rectangle's implementation of borderColor's get()
}
}
}
Drawing rectangle // 来自 Rectangle 的 draw()
Filling // 来自 Filler 的 fill()
Drawn a filled rectangle with color black // 使用 Rectangle 的 borderColor重写规则
在 Kotlin 中,实现继承受以下规则约束
- 若一个类从其直接超类( immediate superclasses )中继承了同一成员的多个实现,该类必须重写这个成员并提供自己的实现。
- 若要指明新实现中复用的是哪个超类的继承实现,需使用 super 关键字并结合尖括号中的超类名进行限定,例如 super(其中 Base 需替换为实际的超类类名)。
kotlin
open class Rectangle {
open fun draw() { /* ... */ }
}
interface Polygon {
fun draw() { /* ... */ } // interface members are 'open' by default
}
class Square() : Rectangle(), Polygon {
// The compiler requires draw() to be overridden:
override fun draw() {
super<Rectangle>.draw() // call to Rectangle.draw()
super<Polygon>.draw() // call to Polygon.draw()
}
}