验证 HashMap 的扩容时机
背景
读者朋友在日常的工作或学习中,应该听到过这类的描述 ⬇️
HashMap的size超过阈值时,会进行扩容
上述说法是正确的,本文会先找到对应的源码,然后用一段代码来验证 HashMap 的扩容时机。
正文
在 HashMap.java 中可以看到 HashMap 的源码。
当我们调用 put(K key, V value) 方法时,HashMap 会尝试添加一个 key-value pair。 HashMap 的所有 key-value pair 都会保存在 table 字段中。
查看源码
table 字段
java
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;可见 table 字段是一个数组。
put(K key, V value) 方法
java
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}这个方法做了两件事 ⬇️
- 调用
hash(Object key)这个静态方法获取hashCode(),然后在hashCode()的基础上,算出一个调整后的值。 - 调用
putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict)方法尝试保存这个key-value pair。
我们再去看 hash(Object key) 方法。
hash(Object key) 方法
java
/**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}这里有两种情况
- 如果
key为null,则返回 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 - 否则返回
h ^ (h>>>16)(这里用h表示hashCode()方法的返回值)
第 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 2 </math>2 种情况为什么会有特殊的处理呢?参考它的 javadoc 可知, 有些类的 hashCode() 会出现低位全都相同的场景,这样就会导致大量实例被分配到 table 的同一个位置,从而导致 HashMap 性能变差。
这里以 java.util.Float 为例,来进行说明。当我们用 java.lang.Float 来表示比较小的正整数时,就会出现这种情况。下方列举了用 java.lang.Float 来表示 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 到 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 5 5 </math>5 的情况 ⬇️
float 的值 |
十六进制的 hashCode |
二进制的 hashCode |
|---|---|---|
1.0f |
0x3f800000 |
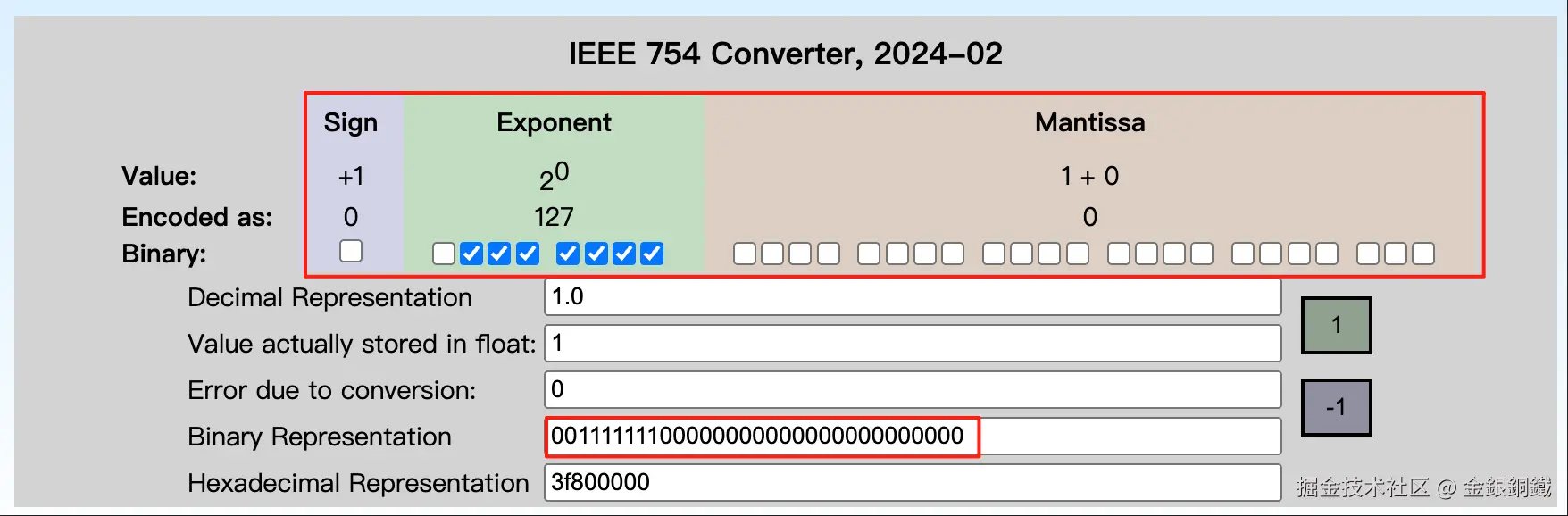 |
2.0f |
0x40000000 |
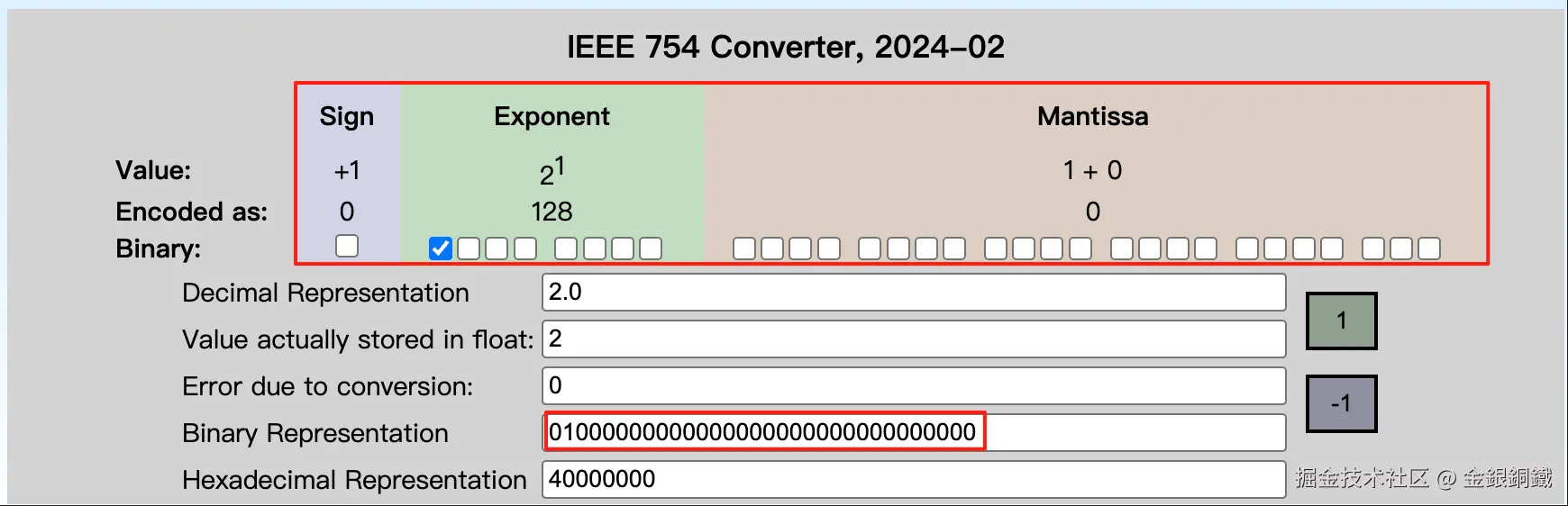 |
3.0f |
0x40400000 |
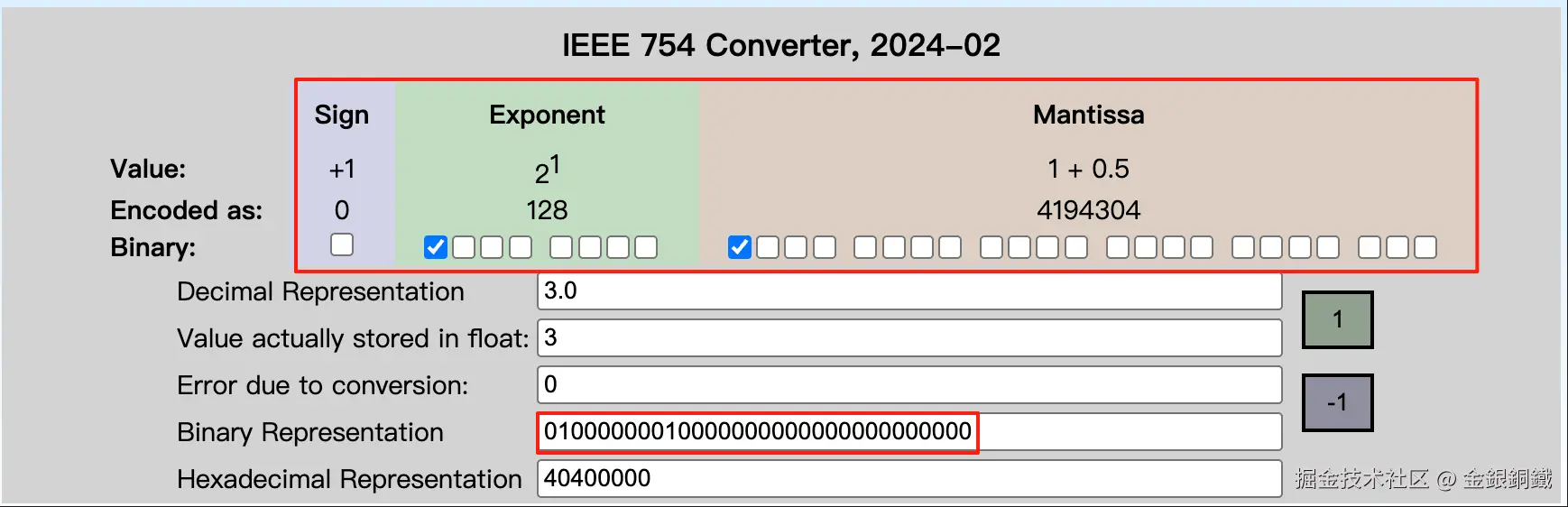 |
4.0f |
0x40800000 |
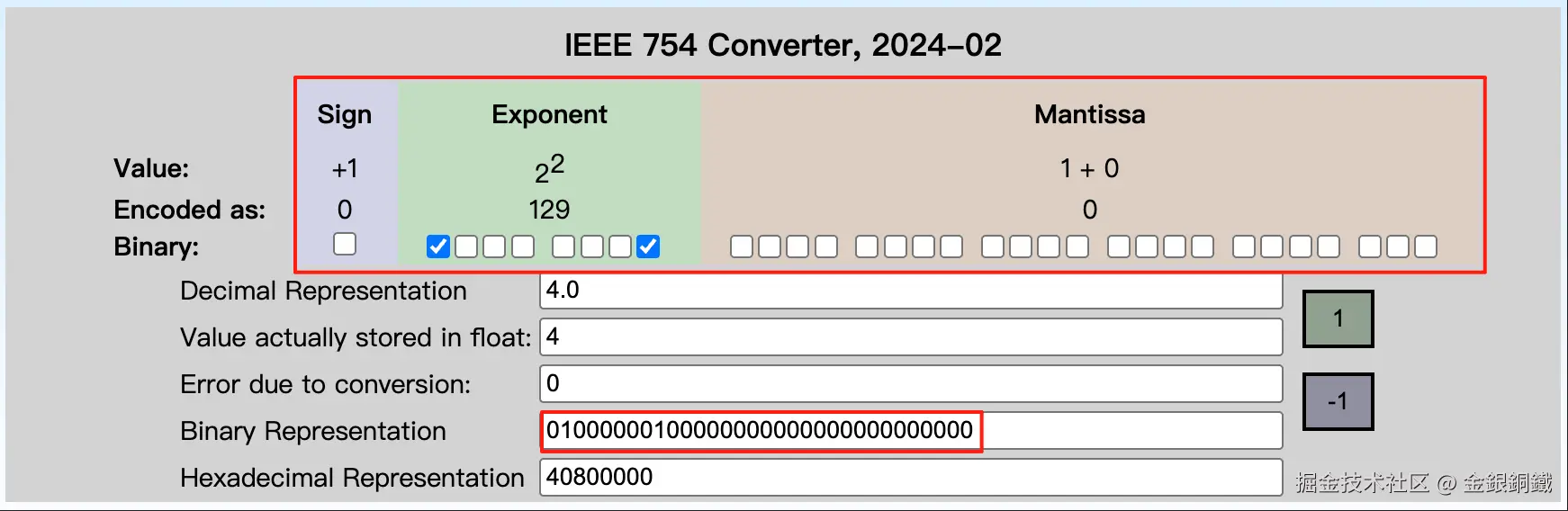 |
5.0f |
0x40a00000 |
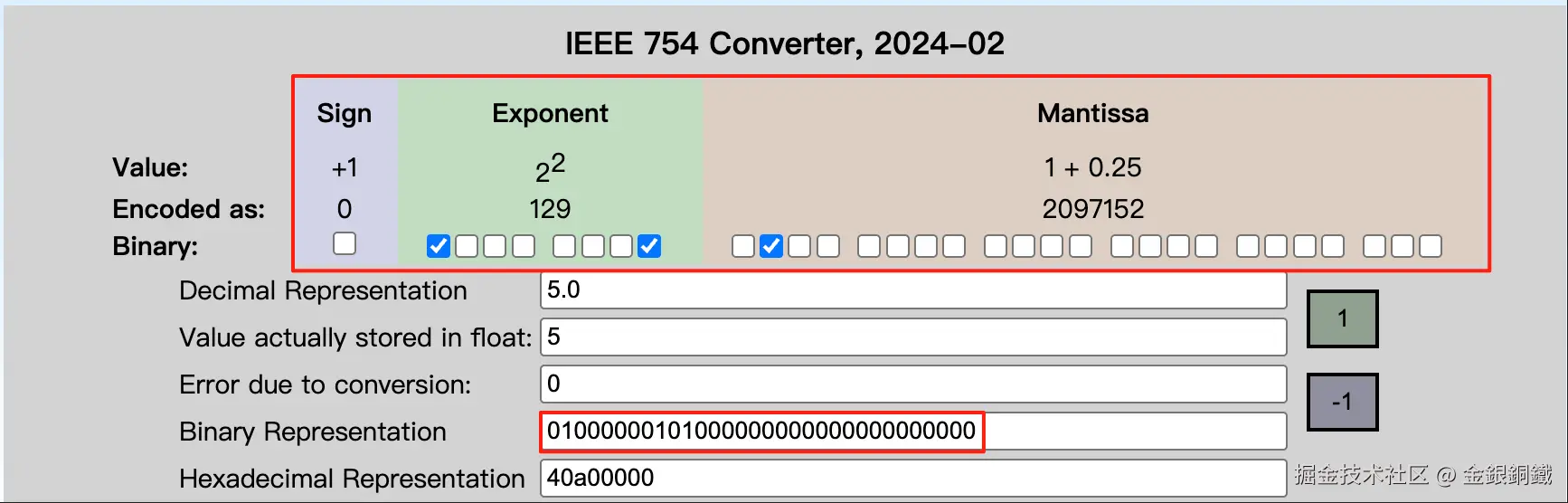 |
其中最后一列是在 IEEE-754 Floating Point Converter 的帮助下画出来的。
假设现在 HashMap 中的 table 字段的 length 是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 256 256 </math>256(即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 8 2^{8} </math>28),如果我们直接用java.lang.Float 的 hashCode() 的话,那么 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1.0 f , 2.0 f , 3.0 f , 4.0 f , 5.0 f . . . 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f, 4.0f, 5.0f ... </math>1.0f,2.0f,3.0f,4.0f,5.0f... 都会分配到 table 的下标为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 的位置(因为它们的最低的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 8 8 </math>8 bit 都是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0)。
然后再去看 putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) 方法。
putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) 方法
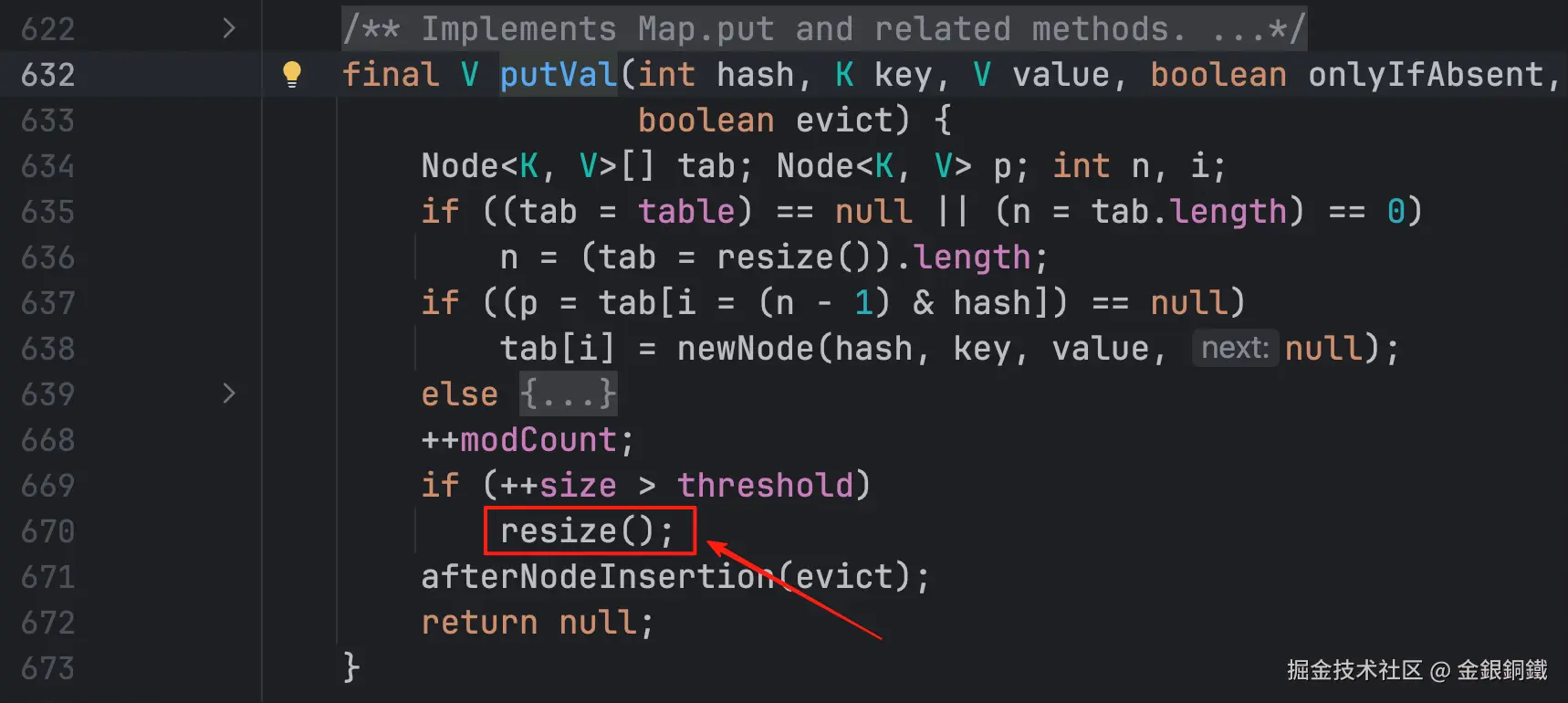
由于本文的主题是 HashMap 的扩容时机,我们只看上图中 resize() 的条件。resize() 的前提是 if (++size > threshold) 成立,从这里可以看出,是先变更 size,然后再比较 size 和 threshold 的大小。
既然已经找到 HashMap 扩容所对应的代码,我们就可以写点代码来进行验证了。
写代码验证扩容时机
请将以下代码保存为 FindResizeTime.java ⬇️
java
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.OptionalInt;
public class FindResizeTime {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
FindResizeTime findResizeTime = new FindResizeTime();
// use default value for both initial capacity (16) and loadFactor (0.75f)
findResizeTime.showHowLengthChanges(new HashMap<>(), 100);
// use default value for loadFactor (0.75f), initial capacity will be 8 here
findResizeTime.showHowLengthChanges(new HashMap<>(5), 100);
// use explicit loadFactor=1.0f, initial capacity will be 8 here
findResizeTime.showHowLengthChanges(new HashMap<>(5, 1.0f), 100);
}
private void showHowLengthChanges(Map<Integer, Integer> map, int n) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field loadFactorField = map.getClass().getDeclaredField("loadFactor");
loadFactorField.setAccessible(true);
float loadFactor = (float) loadFactorField.get(map);
System.out.println("loadFactor 是: " + loadFactor);
Field tableField = map.getClass().getDeclaredField("table");
tableField.setAccessible(true);
int prevSize = 0;
OptionalInt prevLength = OptionalInt.empty();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
map.put(i, i);
Object[] table = (Object[]) tableField.get(map);
int currSize = map.size();
int currLength = table.length;
if (prevLength.isPresent() && currLength != prevLength.getAsInt()) {
String message = String.format("当 map 的 size 从 %s 变为 %s 时, table 字段的 length 从 %s 变为 %s (因为 %s * %s < %s)",
prevSize, currSize, prevLength.getAsInt(), currLength,
prevLength.getAsInt(), loadFactor, currSize);
System.out.println(message);
}
prevSize = currSize;
prevLength = OptionalInt.of(currLength);
}
System.out.println();
}
}用下方的命令可以编译 FindResizeTime.java 以及运行 FindResizeTime 中的 main(...) 方法 ⬇️
bash
javac FindResizeTime.java
java --add-opens=java.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED FindResizeTime运行结果如下 ⬇️
text
loadFactor 是: 0.75
当 map 的 size 从 12 变为 13 时, table 字段的 length 从 16 变为 32 (因为 16 * 0.75 < 13)
当 map 的 size 从 24 变为 25 时, table 字段的 length 从 32 变为 64 (因为 32 * 0.75 < 25)
当 map 的 size 从 48 变为 49 时, table 字段的 length 从 64 变为 128 (因为 64 * 0.75 < 49)
当 map 的 size 从 96 变为 97 时, table 字段的 length 从 128 变为 256 (因为 128 * 0.75 < 97)
loadFactor 是: 0.75
当 map 的 size 从 6 变为 7 时, table 字段的 length 从 8 变为 16 (因为 8 * 0.75 < 7)
当 map 的 size 从 12 变为 13 时, table 字段的 length 从 16 变为 32 (因为 16 * 0.75 < 13)
当 map 的 size 从 24 变为 25 时, table 字段的 length 从 32 变为 64 (因为 32 * 0.75 < 25)
当 map 的 size 从 48 变为 49 时, table 字段的 length 从 64 变为 128 (因为 64 * 0.75 < 49)
当 map 的 size 从 96 变为 97 时, table 字段的 length 从 128 变为 256 (因为 128 * 0.75 < 97)
loadFactor 是: 1.0
当 map 的 size 从 8 变为 9 时, table 字段的 length 从 8 变为 16 (因为 8 * 1.0 < 9)
当 map 的 size 从 16 变为 17 时, table 字段的 length 从 16 变为 32 (因为 16 * 1.0 < 17)
当 map 的 size 从 32 变为 33 时, table 字段的 length 从 32 变为 64 (因为 32 * 1.0 < 33)
当 map 的 size 从 64 变为 65 时, table 字段的 length 从 64 变为 128 (因为 64 * 1.0 < 65)main(...) 方法里有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 3 3 </math>3 种情形 ⬇️
- 情形 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1:
initial capacity和loadFactor都使用默认值(两者的默认值分别为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 16 16 </math>16 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0.75 f 0.75f </math>0.75f - 情形 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 2 </math>2:
- 指定
initial capacity为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 5 5 </math>5(实际上会被调整为大于等于它的最小的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 2 </math>2 的幂次,即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 3 → 8 2^3\rightarrow8 </math>23→8) loadFactor使用默认值(即, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0.75 f 0.75f </math>0.75f)
- 指定
- 情形 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 3 3 </math>3:
- 指定
initial capacity为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 5 5 </math>5(实际上会被调整为大于等于它的最小的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 2 </math>2 的幂次,即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 3 → 8 2^3\rightarrow8 </math>23→8) - 指定
loadFactor为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1.0 f 1.0f </math>1.0f
- 指定