三三要成为安卓糕手
一:安卓中文件存储位置
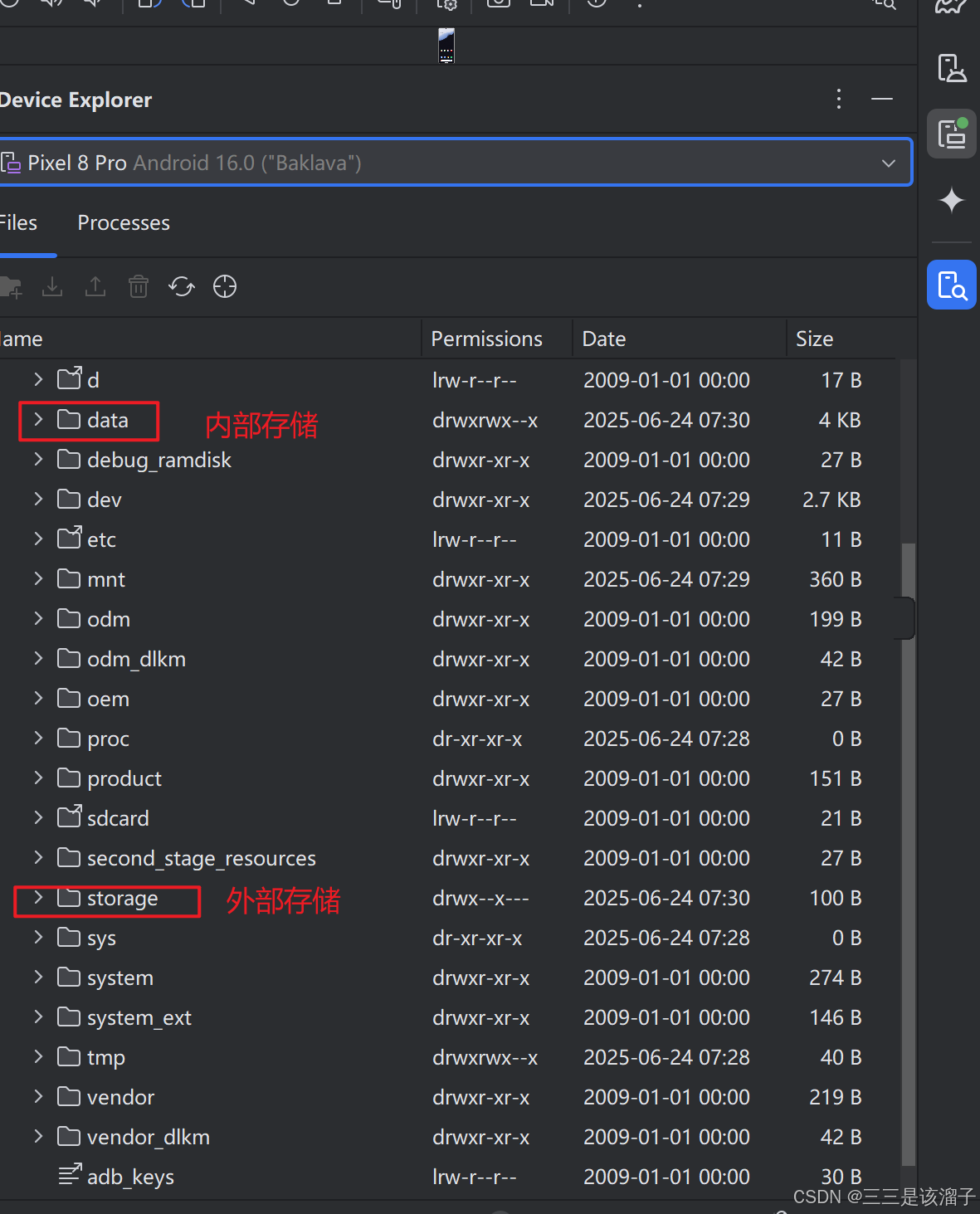
- 应用内部存储空间目录:这些目录既包括用于存储持久性文件的专属位置,也包括用于存储缓存数据的其他位置。系统会阻止其他应用访问这些位置,并且在 Android 10(API 级别 29)及更高版本中,系统会对这些位置进行加密。这些特征使得这些位置非常适合存储只有应用本身才能访问的敏感数据。
- 应用专属外部存储:这些目录既包括用于存储持久性文件的专属位置,也包括用于存储缓存数据的其他位置。其他应用可以在具有适当权限的情况下访问这些目录,更多的还是自己使用。当应用被卸载时,存储在这里的文件会被删除。
- 公共存储空间:如果明确打算创建其他应用能够访问的文件,可以将文件存储在外部存储空间的共享存储空间部分。所有应用均可访问,适合存储对所有应用可见的数据,如图片、音乐、视频等
二:应用内部私有存储数据的写入
internal 内部的
external 外部的
1:客户端布局
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".file.PrivateFileActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="应用内部私有存储相关操作"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_internal_save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="保存文件" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_internal_read"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="读取文件" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:text="应用外部私有存储相关操作"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_external_save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="保存文件" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_external_read"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="读取文件" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="=============我是分割线==========="
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我想把这段内容保存到文件当中"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="读取到了如下信息:\n" />
</LinearLayout>2:数据写入文件代码
java
findViewById(R.id.btn_internal_save).setOnClickListener(view -> {
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
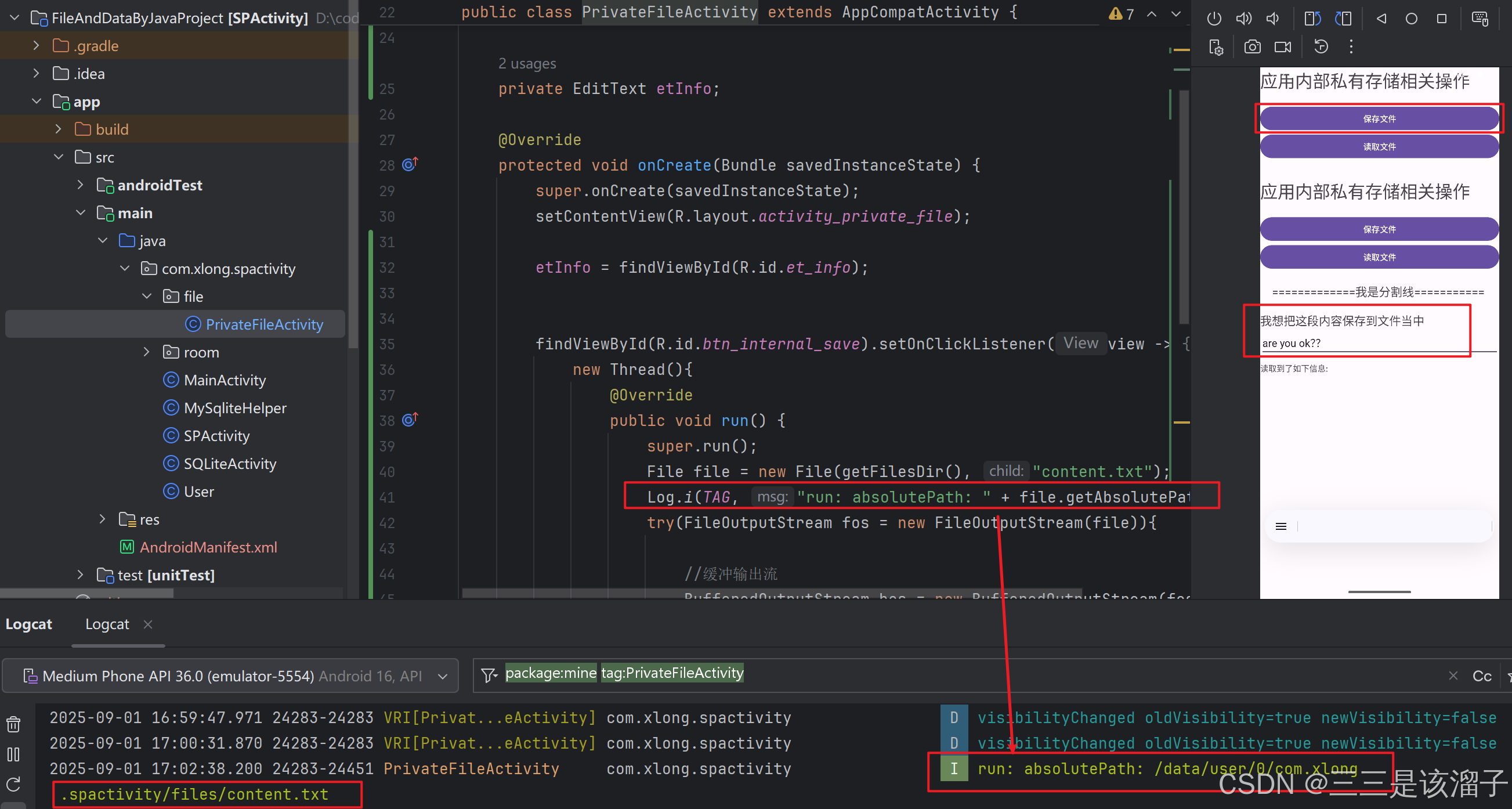
File file = new File(getFilesDir(), "content.txt");
Log.i(TAG, "run: absolutePath: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos)) {
//获取框中的数据
String content = etInfo.getText().toString().trim();
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
bos.write(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}.start();
});- getFilesDir():返回内部存储位置的目录 ; "context.txt"给即将创建的文件取得名字
- 资源自动关闭:传统方式在
try块中创建流,需要在finally块中显式调用close()手动释放资源;这里直接放到try()括号中,操作完毕会自动关闭资源;(流操作实现了AutoCloseable接口) - 缓冲输出流:遇到大文件,不会很吃力;攒一波数据一次性写入,减少读写次数,提高效率;内部本身自带一个字节数组,这里我们自己申请了一个;资源自动
close()前内部会先调用flush(),保证缓冲区中剩余的所有数据(可能缓冲区没攒满一波也能)写入到底层输出流 - bos.write():传入有数据的数组,从offset到末尾所有的数据写入到文件中
- 读文件是一个耗时的操作,放在子线程中
3:如何理解输入和输出流
理清楚程序(也就是代码)和文件之间的流向就能区分开
- "从文件里读取内容,放到程序里",数据流向是:文件 → 程序 那就是输入流 (
InputStream相关类) - "把代码中的数据(比如说输入框EditText中的内容),存储到文件里" 数据的流向:程序 → 文件 那就是输出流 (
OutputStream相关类)
4:如何理解字节和字符
程序这边就是字符,存储一方就是字节;所以输出流操作时,往往先要把字符数据转换为字节格式,在写入保存到文件中
上面代码中的流程:字符串(字符)→ 字节数组 → 字节流写入文件
- 程序里操作的是输入框中的字符内容(
String类型)。 - 当要写入文件时,通过
content.getBytes()把字符转换为字节,然后用字节流(FileOutputStream、BufferedOutputStream)将字节写入文件存储。
5:如何理解缓冲流
BufferedOutputStream 是缓冲流: 是先将数据暂存在内存缓冲区中,当缓冲区满了自动或手动调用 flush()/close() 时,才会将数据真正写入底层的 FileOutputStream(即磁盘文件)
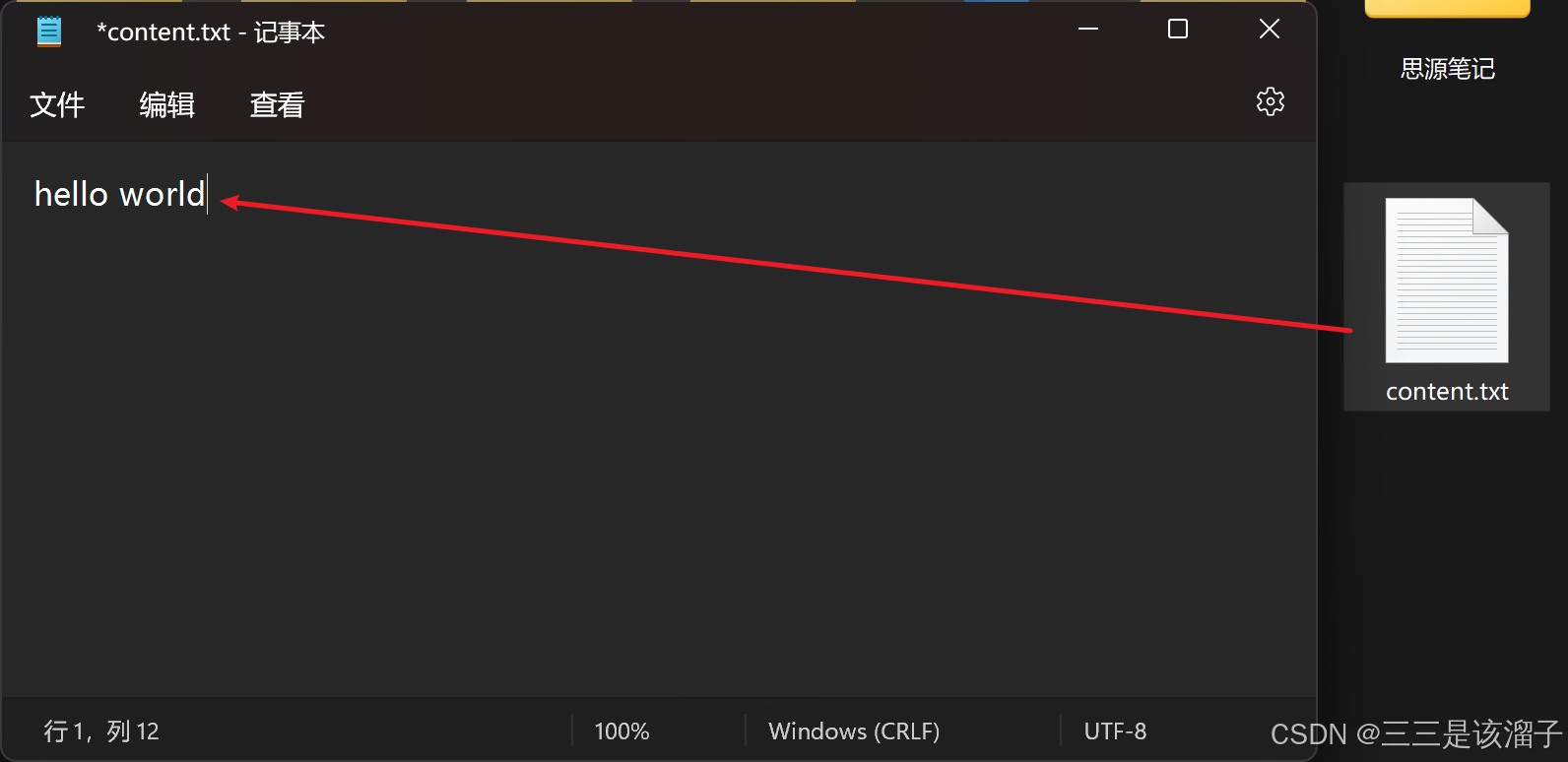
6:效果
三:应用内部私有存储数据的读取
java
findViewById(R.id.btn_internal_read).setOnClickListener(view -> {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//拿到这个文件对象
File file = new File(getFilesDir(), "content.txt");
//FileInputStream本身读取的是字节,转化成读字符
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//字节流转化为字符流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr)//缓冲读取
) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
String line;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
buffer.append(line);
}
String result = buffer.toString().trim();
tvInfo.setText(tvInfo.getText() + result);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}).start();
});1:字节转换字符
通过 InputStreamReader 把字节流转为字符流,再用 BufferedReader 包装,readLine读取

2:效果

四:应用外部私有存储数据的写入
java
findViewById(R.id.btn_external_save).setOnClickListener(view -> {
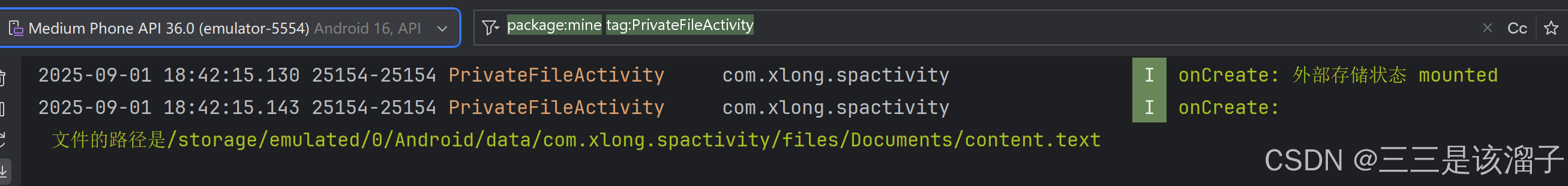
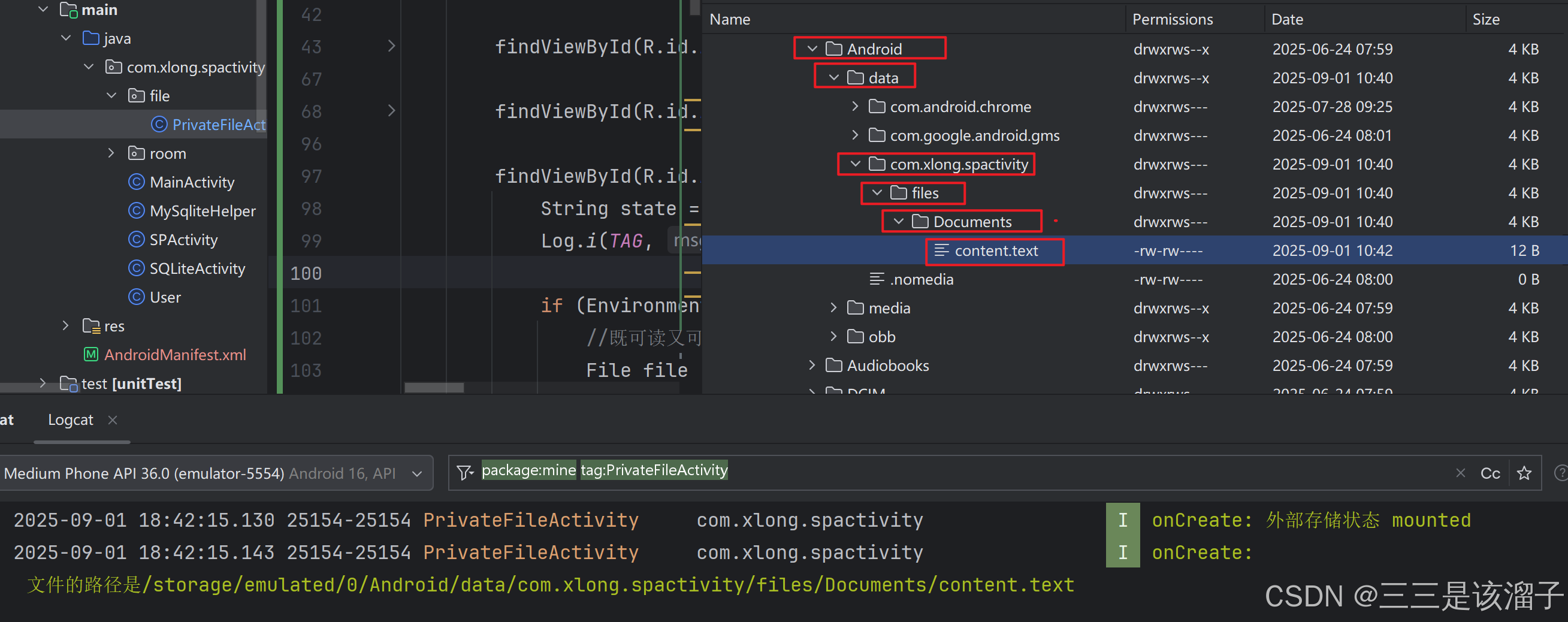
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate: 外部存储状态"+" "+ state);
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)){
//既可读又可写
File file = new File(getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOCUMENTS), "content.txt");
String path = file.getAbsolutePath();
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate: 文件的路径是" + path);
//把字符流转化为字节流,从程序写到硬盘中
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos)){
String text = etInfo.getText().toString().trim();
byte[] bytes = text.getBytes();
bos.write(bytes,0,bytes.length);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED_READ_ONLY.equals(state)) {
//只读
}else{
//外部存储不可用
}
});1:获取外部文件路径
- getExternalFilesDir():返回外部私有目录
- Environment.DIRECTORY_DOCUMENTS:DOCUMENTS指的就是下图中的文件夹,可能还会有Picture文件夹对应的就是PICTURE;这是内部封装好的常量值,当然也可以直接传入字符串
2:外部文件读写权限
- Environment.getExternalStorageState(); 获取外部存储状态
- Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED 既可读又可写
- Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED_READ_ONLY 只能读取
- Environment.MEDIA_UNMOUNTED 未挂载
3:挂载的概念
media媒体 mounted已挂载
简单说,"挂载" 就是给存储设备(比如 U 盘、SD 卡)在系统里 "办个接入手续",让系统能找到它、用它。
比如插 U 盘到电脑,系统弹出 U 盘图标,就是完成了挂载;安卓手机识别到 SD 卡能存照片,也是 SD 卡挂载成功了。
4:效果

五:应用外部私有存储数据的读取
java
findViewById(R.id.btn_external_read).setOnClickListener(view -> {
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)){
File file = new File(getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_DOCUMENTS), "content.txt");
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(isr)){
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
String line;
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){
buffer.append(line);
}
String result = buffer.toString();
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate: result " + result);
tvInfo.setText(tvInfo.getText() + result);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});4.0~6.0低版本的安卓,都可以用上述方法对内部存储文件进行处理;高版本的安卓,对处理文件的权限要求越发的严格,就要使用一些更新的方式去访问外部存储权限,