一、栈(Stack)
01 栈的概念
栈的概念:
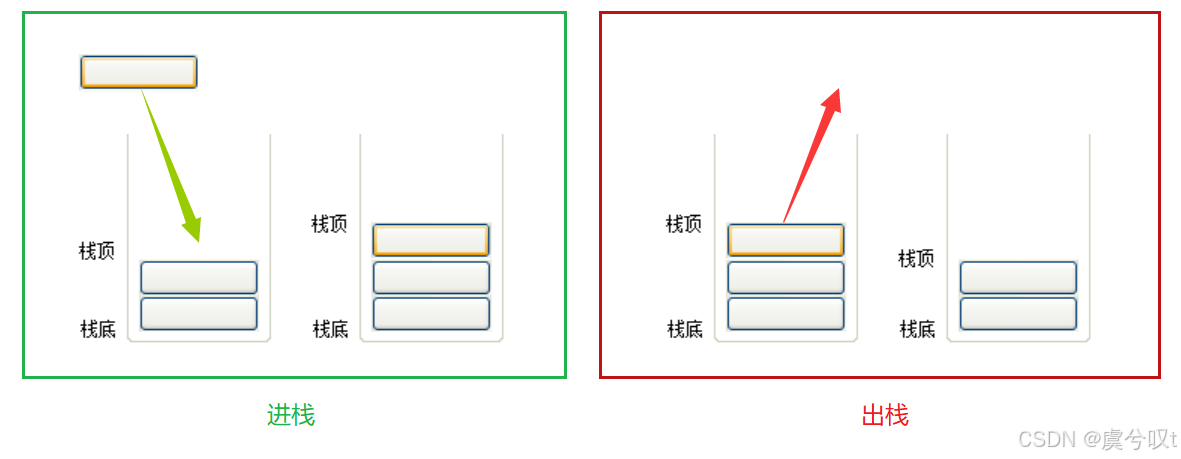
① 栈是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素的操作。
② 进行数据插入的删除和操作的一端,称为 栈顶 。另一端则称为 栈底。
③ 栈中的元素遵守后进先出的原则,即 LIFO原则(Last In First Out)。
**压栈:**栈的插入操作叫做 进栈 / 压栈 / 入栈 ,入数据在栈顶。
**出栈:**栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
02 栈的结构
栈的结构:
03 数组栈和链式栈
实现栈无非就两种结构:数组结构 和 链式结构,两种结构都可以实现。
数组栈和链式栈哪种结构更好?
相对而言数组的结构实现更优,尾插尾删的效率高,缓存利用率高,它的唯一缺点只是增容,但是增容 1 次扩 2 倍对栈来说本身就比较合理,是无伤大雅的。而链式栈虽然不会空间浪费,用一个 malloc 申请一个,但是链式栈存在一个致命的缺点:单链表不好出数据,必须要实现双向链表,否则尾删数据将会异常麻烦。
如果硬要使用链式栈:
① 如果用尾做栈顶,尾插尾删,要设计成双向链表,否则删数据效率低。
② 如果用头做栈顶,头插头删,就可以设计成单链表。
二、栈的定义
01 动态栈
本章将采用动态栈实现!
cpp
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType* array;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;解读:顺序表相信大家已经很熟了,这里和顺序表没啥两样。创建结构体,结构体有三个变量,array 是用来存放数据的数组。top 用来表示栈顶,这里相当于顺序表中的size 变量。capacity 表示栈的容量。
02 静态栈
cpp
typedef char StackDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType _array[N];
int _top;
} Stack;解读:N 给多了浪费给少了又不够用,所以静态栈在实际中是不实用的。静态栈满了就不能扩大了,而动态栈是 malloc 出来的,不够了可以 realloc 扩容。
03 接口函数
cpp
// 初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
// 销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool StackIsEmpty(Stack* pst);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
// 返回栈顶
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
// 计算栈的大小
int StackSize(Stack* pst);三、栈的实现
01 初始化(StackInit)
Stack.h:
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType* array;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
// 初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst);解读:大家学到这里想必已然轻车熟路,应该知道需要引入哪些头文件了,动态内存开辟需要引入 stdlib.h,断言需要引入 assert,使用布尔值需要引入 stdbool.h 。
Stack.c:
cpp
/* 初始化 */
void StackInit(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
pst->array = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}解析:初始化和顺序表几乎没有区别。首先通过结构体指针(我们定义的Stack)pst 指向array,将数组为空。因为是初始化,所以将有效数据个数和数组实际能存数据的空间容量一并置为0。
02 销毁(StackDestory)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 销毁 */
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
free(pst->array);
pst->array = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}03 判断栈是否为空(StackIsEmpty)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 判断栈是否为空
bool StackIsEmpty(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 判断栈是否为空 */
bool StackIsEmpty(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}04 入栈(StackPush)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 入栈 */
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x) {
assert(pst);
// 检查是否需要增容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity) {
int new_capacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(pst->array, sizeof(StackDataType) * new_capacity);
if (tmp == NULL) {
printf("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
pst->array = tmp;
pst->capacity = new_capacity;
}
pst->array[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}解读:这里和顺序表尾插的实现没有任何区别。首先防止 pst为空,随后检查是否要增容,如果要增容就进行增容操作。最后再填入数据即可。
05 出栈(StackPop)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 出栈 */
void StackPop(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(!StackIsEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}解读:
① 首先防止 pst为空。这里要注意的是,不能让栈内没有数据,必须要有东西能 "出栈" 才行。
② 出栈是非常简单的,就是把数据吐出来。直接将 top-- ,就能直接达到目的。
06 返回栈顶数据(StackTop)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 返回栈顶
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 返回栈顶 */
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(!StackIsEmpty(pst));
return pst->array[pst->top--];
}解读:
① 首先防止 pst为空。同样地,不能让栈内没有数据。
② 我们直接返回栈顶数据就可以了,pst->array[pst->top--] 。
为什么这里要 -1?
这里 -1 的原因是我们初始化栈的时候定义 top 时给的值是 0,意味着 top 指向的是栈顶数据的下一个位置(无数据),所以这里既然要返回的是栈顶数据,自然需要 -1。这里的代码到底要不要 -1,主要看我们初始化 top 的时候给的是什么值,如果我们当时给的是 -1,那么 top 将指向栈顶数据,自然这里就不需要 -1,就应该是 pst->array[pst->top] 了。
Test.c:
cpp
void TestStack1() {
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackDestroy(&st);
}07 计算栈的大小(StackSize)
Stack.h:
cpp
// 计算栈的大小
int StackSize(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
/* 计算栈的大小 */
int StackSize(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}解读:首先防止 pst 为空。因为我们之前初始化时top 给的是0,指向栈顶的下一个。所以 top 就是栈的大小,直接 return top 即可。
08 完整代码
Stack.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
StackDataType* array;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
// 初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
// 销毁
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool StackIsEmpty(Stack* pst);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
// 返回栈顶
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
// 计算栈的大小
int StackSize(Stack* pst);Stack.c:
cpp
#include "Stack.h"
/* 初始化 */
void StackInit(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
pst->array = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
/* 销毁 */
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
free(pst->array);
pst->array = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
/* 判断栈是否为空 */
bool StackIsEmpty(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
/* 入栈 */
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x) {
assert(pst);
// 检查是否需要增容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity) {
int new_capacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(pst->array, sizeof(StackDataType) * new_capacity);
if (tmp == NULL) {
printf("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
pst->array = tmp;
pst->capacity = new_capacity;
}
pst->array[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
/* 出栈 */
void StackPop(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(!StackIsEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
/* 返回栈顶 */
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(!StackIsEmpty(pst));
return pst->array[pst->top--];
}
/* 计算栈的大小 */
int StackSize(Stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}